Unit 7- The Growth and Suppression of Democracy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
The Crimean War
A conflict from 1853 to 1856 between Russia and an alliance of Britain, France, the Ottoman Empire, and Sardinia, primarily over territorial disputes and the decline of the Ottoman Empire.
big Russian lose bc they were fighting alone
What is significant about the Crimean War?
it broke up the Concert of Europe
50 years of peace after the Napoleonic Wars
marked a shift in the balance of power in Europe, leading to increased nationalism and military reforms.
Italian Unification background?
Italy was all fragmented states controlled by foreign powers and local rulers
Count Cavour, minister of Piedmont, wanted unification
However, there was a problem
Austria and France were in the way of unification
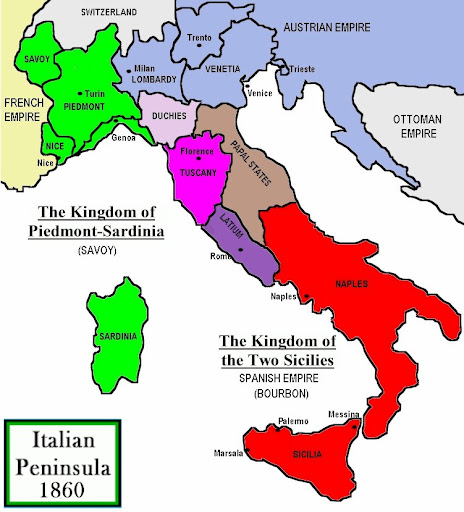
First Phase of Italian Unification?
Count Cavour promised Napoleon III (France) land if he helped Cavour drive out Austria from Northern Italy, leading to key victories and paving the way for the unification of Italy
Cavour didnt have a great military so he needed French helpto drive out Austrian forces effectively.
How did Southern Italy unify?
Southern Italy was unified through the efforts of Giuseppe Garibaldi, who led the Expedition of the Thousand, successfully conquering Sicily and the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, and subsequently handing over control to Cavour and the Kingdom of Piedmont.
When did Italy Unify?
1861
Background of German Unification?
Germany was a mix of fragmented states
They question arose, who would unify and lead Germany, Austria or Prussia?
Who was Otto Von Bismark?
He was the and the architect of German unification, using diplomacy and war tactics to consolidate German states under Prussian leadership.
Known for his strong military training and success
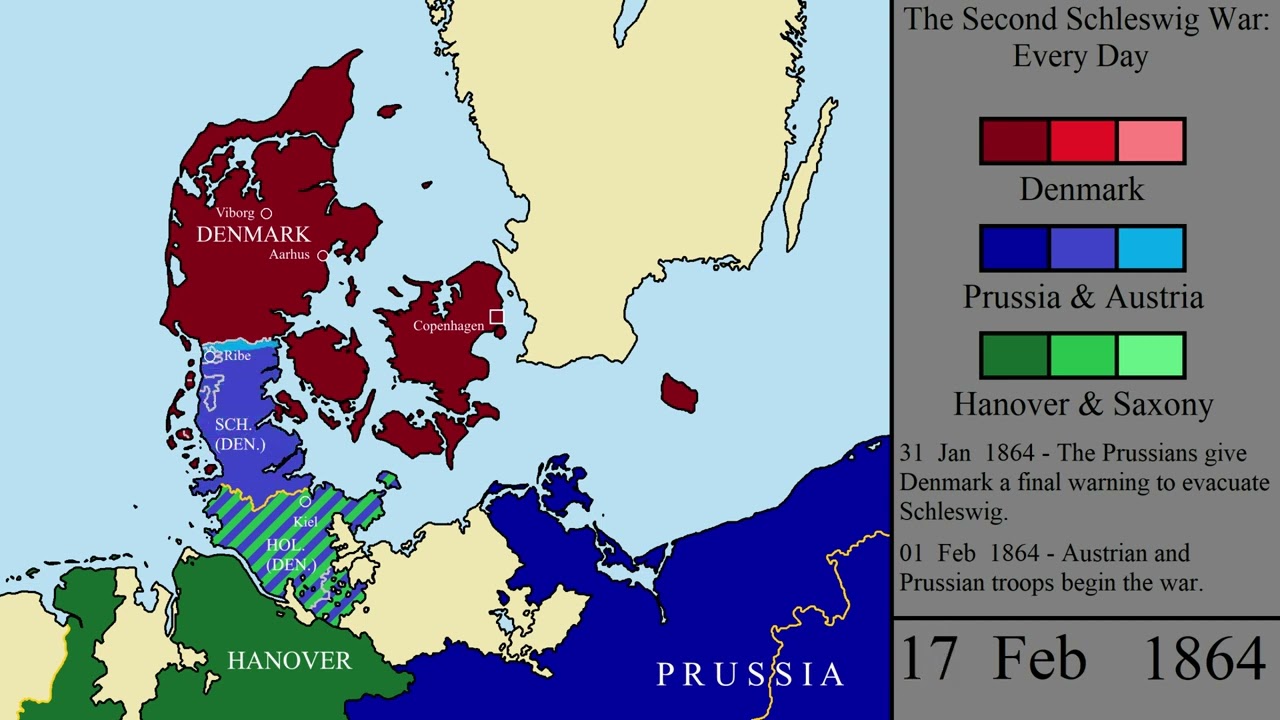
Prussia-Danish War (1864)
first war of german unification
there where two danish provinces and germany sought to acquire them, resulting in a conflict between Prussia and Denmark
Bismark got help from Austria to win the provinces and he agreed to split them between the two to of them
Austo- Prussian War (1866)
Bismarck caused fighting between the two provinces, where they ultimately sided with Prussia and not Austria.
Bismarck also made non-aggression treaties with Britain and Russia so they don’t mess him u.p
This is continuationin of how Hitler made a non-aggression pact with Russia in WW2 before invading poland
Franco- Prussian War (1870)
Bismark belived the onlt way to unification was through nationalism and he thought what better way to being people together than through war
So he falsified a Prussian document crap taokung France and the France went to war with them
It worked, Prussia defeated France and they unified in the process
Bismark and Cavour similarities
both leaders in unification
both used diplomatic skills
Cavour got help from Napoleon III in France to drive out Austria
Bismark used Austria to help him win Danish provinces
Bismark and Cavour differences
Bismark stronger militray
defeated France in the Franco Prussian War
Cavour relied on diplomatic alliances and negotiation and diplomacy
had to get help to rid Austria from Italy
Bismark’s alliances
Triple Alliance and the Reinsurance Treaty with Russia, aimed at isolating France and maintaining peace in Europe.
What was happening in the Baltkans
The Balkans were experiencing nationalist movements and conflicts among diverse ethnic groups, contributing to instability in Europe leading up to World War I.
20th Centruy Frame of Mind?
more people being educated
Darwin gets famous/hate for his ideas about evolution
Natural selection
Social Darwinism stemmed from this
beilef that one race is superior to another
Fredrich Nietzsche
attacked reason, democracy, and christianity
famous for “God is Dead”
Realism- accepting somthing for what it is
What is changing about imperialism
used to be focused on New World Trade
now focus on expanding into Africa and Asia
What are some Imperialism motivations?
economic (raw materials and markets around the worls)
political (scramble for Africa)
Racial Supperiority(belief in the superiority of one's race)
Opium Wars (1839-1842)
an example of an economic imperial motivation
British vs China
A series of conflicts over trade imbalances and British smuggling Opium into China, which led to significant territorial and economic concessions by China.
China loss
European advantages in imperalism
Advanced Weapons
thanks to industrialization
Better Communication
telegraph
Advancment in Medicine
and sanitation such as quinine to combat malaria, enabling deeper penetration into Africa.
Romanticism
an artistic and intellectual movement that emphasized emotion, individualism, and nature over reason and civilization, often reacting against the industrial revolution and rationalism.
Why did romanticism become popular
rebirth after a huge spike in nationalism
Imperialism Global Effects
Berlin Conference
Moroccan Crisis
Sepoy Rebellion
the expansion of empires and influence across the world, leading to political, economic, and social changes in both colonizing and colonized nations, often resulting in conflicts and resistance movements.
Berlin Conference
European Nations made boundaries for Africa (done by Bismark)
Soon tensions emerged
Moroccan Crisis
demonstrated the increasing bond between France and Britain over Morocco and tested German claims.
Sepoy Rebelion
British East India Company in India and not being considerate about Muslim/Hindu beliefs
make them fight in Indian military and bite off cartridges that had pig fat in them which went against their religion
There was a violent uprising which the British won and then transferred power for the East India company directly to the crown