Patho Exam 1 (copy)
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
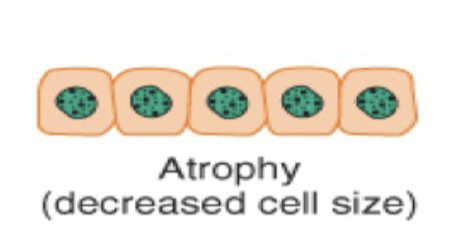
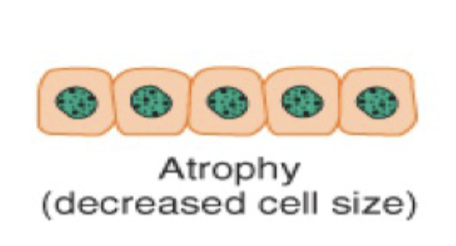
Atrophy is a type of cellular adaptation where there is a _____ in cell size due to ____ synthesis or increased _____ _____, or both.
a decrease in cell due to protein synthesis or increased protein catabolism or both.
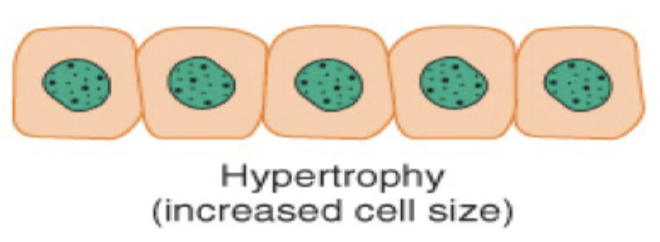
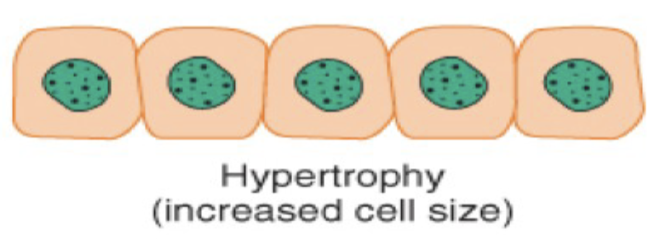
Hypertrophy is cellular adaption where there is an _____ in _____ of cell due to _____ work demands or _____ _____.
increase in size of cell due to increased work demands or hormonal stimulation.
Example of physiologic cellular adaption (normal stressors)
enlargement of skeletal muscles with exercise.
Example of pathologic cellular adaption (abnormal stressors)
enlargement of the heart due to CHF (congenital heart failure)
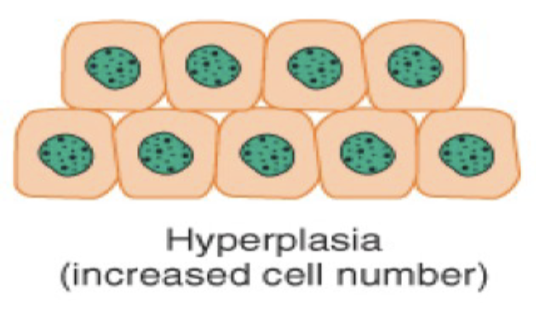
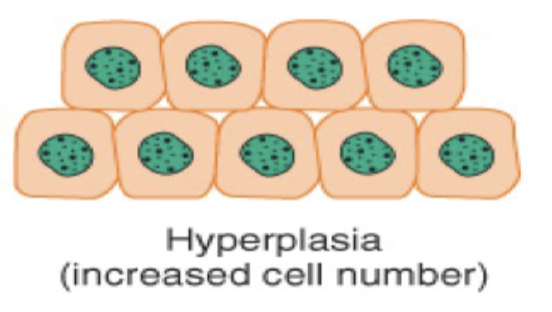
Hyperplasia is a cellular adaptation where the ___ of cells ___.
amount of cells increases.
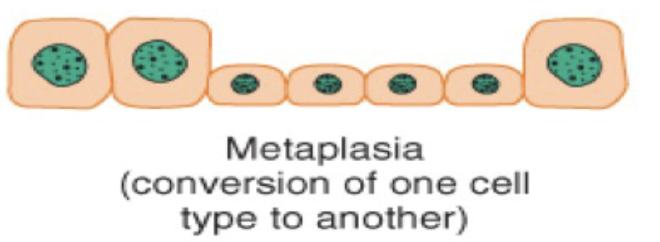
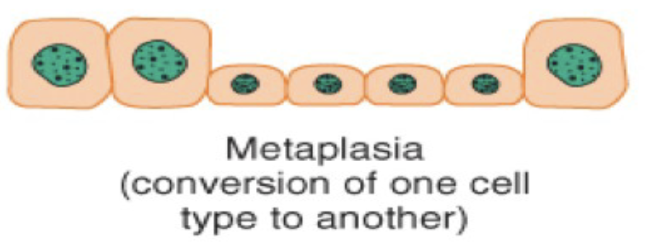
Metaplasia is a cellular adaption with the ____ of one ____ ____ to another.
the conversion of one cell type to another.
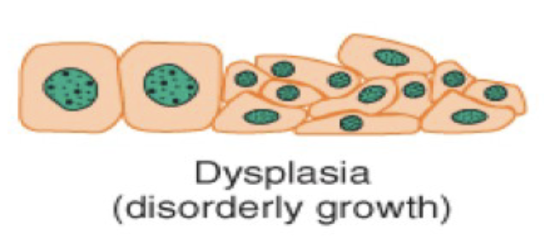
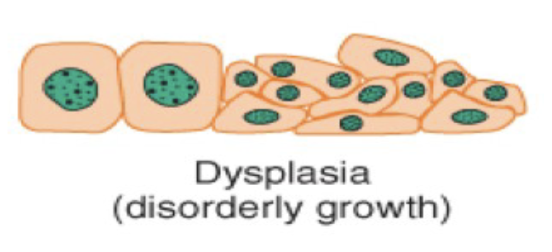
Dysplasia (cellular adaptation) is ____ cell ____.
disorderly cell growth.
What term describes varying degrees of a disease?
expressivity
This term describes how to define a child’s parents who are siblings.
consanguinity
Another name for Down Syndrome is
Trisomy 21
What is the genetic term for an allele with observable effects?
dominance
What is the most important risk factor for Down Syndrome?
increased maternal age
What aneuploidy (cell containing abnormal # of chromosomes) occurs in females only?
Turner’s syndrome
In Klinefelter’s disease, this a variant:
abnormal # of X chromosomes with at least one Y chromosome.
What can you conclude if a couple has 2 children and only 1 has CF (cystic fibrosis) and the other does not?
both parents of the children are carriers.
What autosomal recessive disorder is characterized by defective chloride and thick mucous?
cystic fibrosis
What is the most common genetic disorder that is not a X-linked disorder?
Down syndrome
What is the definition of metaplasia?
the conversion of one cell type to another
What is the type of cellular change expected with a lung cancer diagnosis?
dysplasia
To confirm somatic death, you should look for
cessation of respiratory and circulatory function.
What is the term is used to describe cellular destruction through programmed death?
apoptosis
What is the cause of warmth and swelling during inflammation?
increased vascular permeability
A provider notes that a group of institutionalized people develop similar respiratory symptoms due to what type of necrosis?
caseous necrosis
What type of tissue includes skeletal and smooth?
muscular tissue
What term describes a steady decline in body temperature to match ambient temperature?
algomortus (when you die your body temperature matches the temperature of the room)
Liquefactive necrosis occurs in the brain, why?
the cells are digested by self hydrolase because the brain is rich in hydrolytic enzymes and lipids.
Irreversible cell injury involves an increase in intracellular what?
massive calcium influx
What term describes the outward manifestation of a disease?
phenotype
What type of pathologic atrophy occurs with prolonged bedrest?
decreased muscle size atrophy
If the skin is breached, the second line of defense is activated, known as:
inflammatory response
The bacteria that make up normal flora prevents two things:
colonization and multiplication
What type of cells responds to parasitic infection?
eosinophils
____ is a protein synthesized by the liver, as are all ___ ____ except for immunoglobulins, and is catabolized by all ____ active tissues.
albumin, liver, plasma proteins except for immunoglobulins, and catabolized by all metabolically active tissues.
Oncotic/ osmotic pressure in induced by ____, notably ____.
proteins, albumin
_____ fluid is the fluid that lies within tissues, outside of and in between the ____.
interstitial fluid, the cell
Intracellular fluid is ____ the cell while extracellular fluid lies ____ of the cell.
within, outside
____ is a process by which molecules of a ____ (water) tend to pass through a ____ membrane from a ____ concentrated solution into a ____ concentrated one, thus ____ the concentrations on each side of the ____.
osmosis, solvent, semipermeable, less, more, equalizing, membrane
Osmosis equalizes ____ and happens only in a ____ medium.
concentration, liquid
____ is the tendency of the ____ of a ____ (gas/ liquid/ solid) to move from a region of ____ to ____ concentration.
diffusion, molecules, substance, high, low
Diffusion moves molecules from
a high to low concentration
Osmosis moves molecules from
a low to high concentration
True of false: diffusion can happen only through solid or gas.
false, diffusion can happen through solid, liquid, or gas.
In the body, oxygen and carbon dioxide move by ____.
diffusion
Water is __% of body weight in adults.
60%
Water is __% to __% of body weight in children.
75%-80%
Aging adults experience ____ free fat and ____ mass, and renal decline.
decreased free fat and muscle mass, and renal decline
____ pressure pushes water out of capillaries (____).
Hydrostatic, (filtration).
Hydrostatic pressure is higher during ____.
filtration
____ / ____ pressure puts water into capillaries (____). It holds onto ____ molecules.
osmotic/ oncotic (reabsorption).
water molecules
Oncotic pressure is higher during ____.
reabsorption
____ (osm) is the concentration of salt in the ____ / blood.
osmolality, plasma
The range for serum/ plasma osmolality is ___- ___ mOsm/kg.
280-295 mOsm/kg
____ is the protein responsible for oncotic pressure.
albumin
Forces favoring filtration:
_____ hydrostatic pressure ( ____ pressure)
_____ (in between capillaries, space between cells) oncotic pressure (water- pulling)
capillary hydrostatic pressure (blood pressure)
interstitial (space between cells) oncotic pressure
Forces favoring reabsorption:
capillary ____ pressure (water- pulling)
interstitial ____ pressure
capillary oncotic pressure
interstitial hydrostatic pressure
_____ hormone (ADH) helps retain/ reabsorb the amount of ____ in your body.
antidiuretic hormone, water
ADH works to control the amount of ____ that the ____ reabsorb as they filter out ____ from your ____ (urination).
water, kidneys, waste, blood
A high ADH level causes the body to produce ____ urine.
A low level of ADH results in ____ urine production.
less, greater
The higher the ____ (concentration), the ____ the ADH level.
osmolality, higher
Acid in the body is called
carbon dioxide (CO2)
Alkaline in the body is referred to as
bicarbonate (HCO3)
What is the normal body pH range?
7.35- 7.45
The normal CO2 range in the body is
35-45 mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
The normal partial pressure range of oxygen in the body is __- 100mmHg.
80-100 mmHg
The normal bicarbonate range in the body is 22-__mmHg.
22-26 mmHg
The normal oxygen saturation range is
95-100%
____ - ____ system (RAS) is triggered by a drop in ____ ____ and a drop in ____ volume.
renin- angiotensin system (RAS), drop in blood pressure, fluid
The first step in the RAS system is ____ release from kidneys (increase in ____ volume by ____ fluids).
____ also releases ____.
renin (fluid volume by reabsorbing fluids)
liver, angiotensinogen
2nd step in RAS system:
____ then acts on angiotensinogen to form ____ I.
renin, angiotensin I.
3rd step in RAS system:
ACE (angiotensin- ____ ____) release from ____.
angiotensin- converting enzyme, lungs
4th step in RAS system:
ACE acts on angiotensin to form ____ II.
____ II also acts directly on blood ____ stimulating ____ (narrowing).
angiotensin II.
angiotensin II, blood vessels stimulating vasoconstriction
5th step in RAS system:
Angiotensin II acts on the ____ gland to stimulate the release of ____.
adrenal, aldosterone
(RAS system)
Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to stimulate reabsorption of ____ and ____.
salt and water
The goal of renin- angiotensin system is to raise ____ ____ and ____ ____.
blood pressure and fluid volume
Infarction is
a complete loss of blood supply.
Ischemia is ____ / inadequate blood supply.
reduced
ANP (atrial natriuretic hormone) BNP (brain natriuretic peptide) system counteracts the ___ system.
RAS
ANP increases _____ excretion.
sodium
BNP increases _____ excretion.
fluid
ANP BNP system works by increasing ____ (which decreases ____ volume), performing ____ (which decreases ____ ____), and decreasing ____.
GFR- glomerular filtration rate, blood, vasodilation, blood pressure, renin
The solution with the higher solute concentration is _____.
The solution with the lower concentration is _____.
The solution with the same concentration is _____.
hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic
Edema is the accumulation of _____ within the _____ spaces.
Edema is caused by an increase in _____ _____ pressure, a decrease in plasma ____ pressure, an increase in ____ permeability, and ____ channel obstruction (lymphedema).
fluid, interstitial
capillary hydrostatic pressure, plasma oncotic pressure, capillary permeability, and lymph channel obstruction.
What is the normal sodium range?
135-145 mEq/L
The normal potassium range is 3.5-_ mEq/L.
3.5-5 mEq/L
The normal ____ range is 8.5-10.5 mEq/L.
calcium
Hyperkalemia (high potassium) is categorized by (think tight and contracted):
in the heart: peaked _ waves, _fib or ____ standstill, hypotension, ___cardia.
in the GI tract: diarrhea and ____ bowel sounds.
neuromuscular: paralysis in ____ extremities, increased ____, profound muscle ____.
T waves, Vfib or cardiac standstill, hypotension, bradycardia.
diarrhea and hyperactive bowel sounds
paralysis in lower extremities, increased DTR (deep tendon reflex), profound muscle weakness
Hypokalemia (low potassium) is categorized by (think low and slow):
in the heart: flat _ waves, __ depression, and prominent _ wave.
muscular: decreased ___, muscle ____, and flaccid ____ (paralyzed limbs).
GI tract: decreased _____, _____ to absent bowel sounds, _____, abdominal _____, paralytic ileus, paralyzed intestines.
flat T waves, ST depression, prominent U wave.
decreased DTR, muscle cramping, and flaccid paralysis.
decreased motility, hypoactive to bowel sounds, constipation, abdominal distention (enlargement) paralytic ileus, paralyzed intestines.
Hypernatremia (high sodium) is categorized by (think big and bloated):
____ “red and rosy”
____ “waterbed skin”
___ ___ fever
____ (hyper thirst)
flush, edema, low grade fever, polydipsia
Hyponatremia is categorized by (think depressed and deflated):
neuro: ____ & ____
seizures & coma
Hypercalcemia is categorized by
swollen & slow
moans, groans and stones
Hypocalcemia is categorized by
Trousseau’s sign, Chvostek’s sign
Trousseau’s sign is a sign of _____ and demonstrates
_____ of the thumb, flexion of the _____ joints, extension of the _____ joints, and flexion of the _____.
hypocalcemia, adduction, metacarpophalangeal, interphalangeal joints, wrist
Chvostek’s sign is a sign of _____ and demonstrates _____ of the lip to _____ of all facial muscles.
hypocalcemia, twitching, spasm
Hypovolemia is isotonic fluid _____.
loss
Isotonic fluid excess is known as _____.
hypervolemia
Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of _____ passing through the _____ per _____.
blood, glomeruli, minute
Creatinine is a chemical waste product made as a by-product of normal _____ _____, excreted by the _____.
muscle contractions, kidneys
Blood urea nitrogen is a waste product in the _____ from _____ metabolism.
blood, protein
24- hour urine osmolality range is ___-___ mOsm/kg of water.
500-800 mOsm/kg of water
Random urine osmolality range is ___-900 mOsm/kg of water.
300-900 mOsm/kg of water