Chapter 6 The Skeletal System
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Skeletal system
Consists of 206 bones (in adults), joints, cartilage and ligaments.
Functions of the skeleton
1. support
2. protection of soft body parts
3. Blood cell production
4. Storage of fats & minerals
5. Movement, using muscles & joints.
Classification of bones
-Long
-short
-flat
-irregular
-round
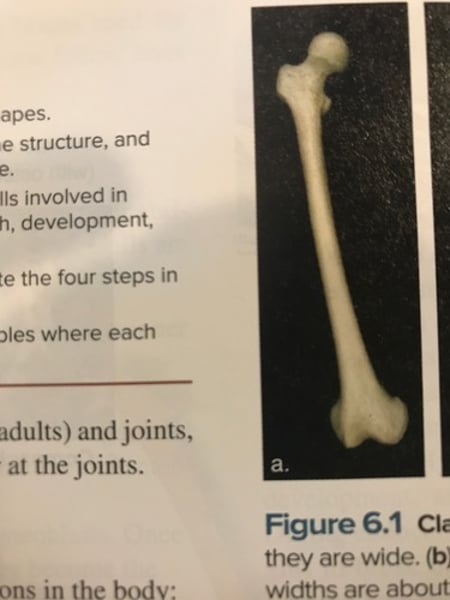
Long bone
longer than they are wide (femur)
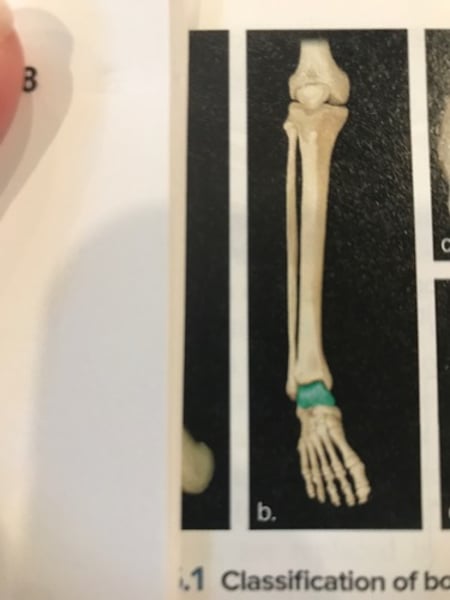
Short bone
Cube shaped (tarsal)
Flat bones
Plate-like, with broad surfaces
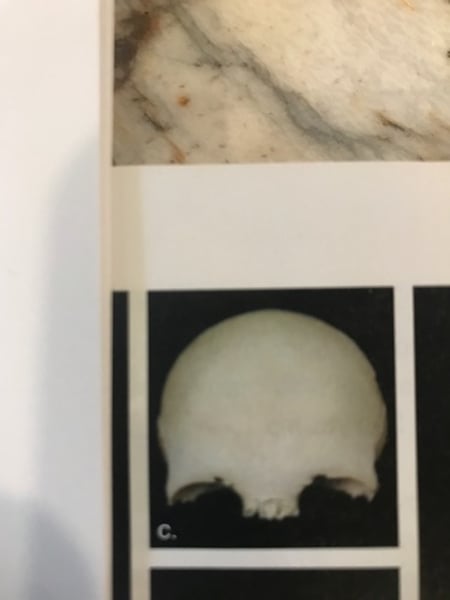
Irregular bone
Varied shapes

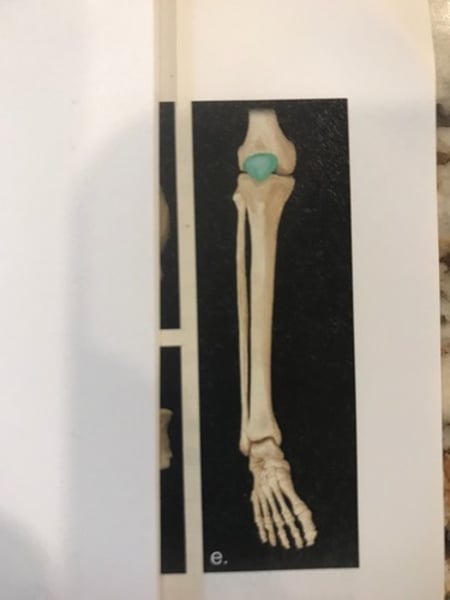
Round bone
Circular in shape (patella)
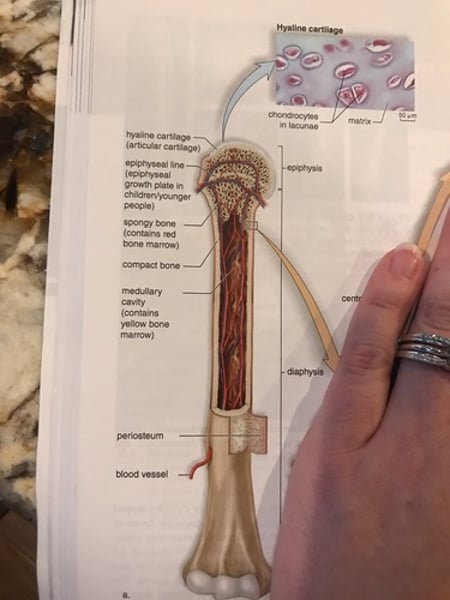
Periosteum (long bone)
Tough, connective tissue covering that contains blood vessels.
-continuous with tendons (connect muscle to bone) and ligaments (connect bones to bones)
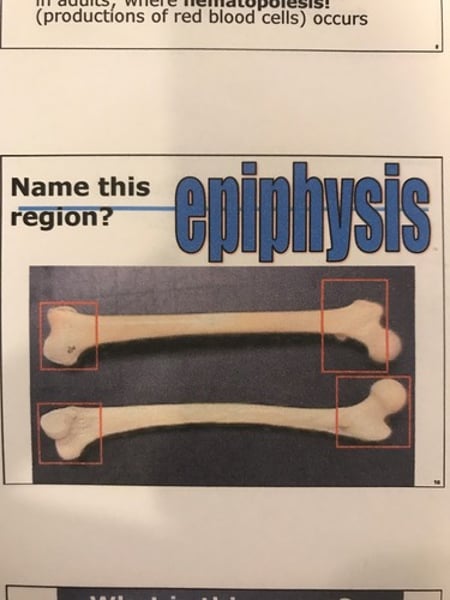
Epiphysis (long bone)
Expanded portion at the ends of bones; made of spongy bone.
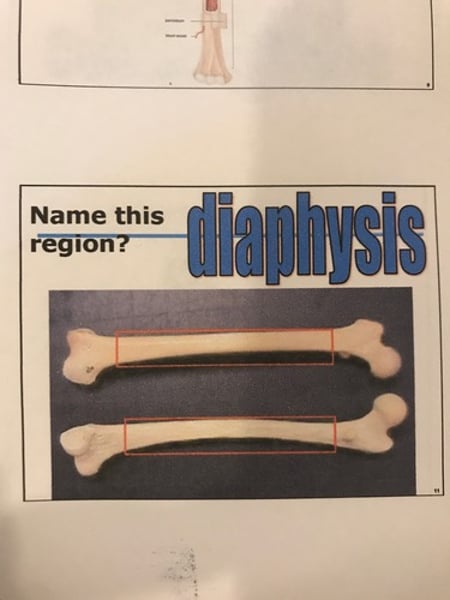
Diaphysis (long bone)
Portion between the epiphysis; the shaft; made of compact bone.
medullary cavity (long bone)
hollow portion of diaphysis containing yellow marrow (fat).
articular cartilage
Layer of hyaline cartilage at articulations (where bones join together).
Endosteum
Lines medullary cavity and the spaces of spongy bone.
Red bone marrow
Found in spongy bone in adults; where hematopoiesis (production of red blood cells) occurs.
Anatomy of a long bone
Epiphysis
Diaphysis
medullary cavity

epiphysial line

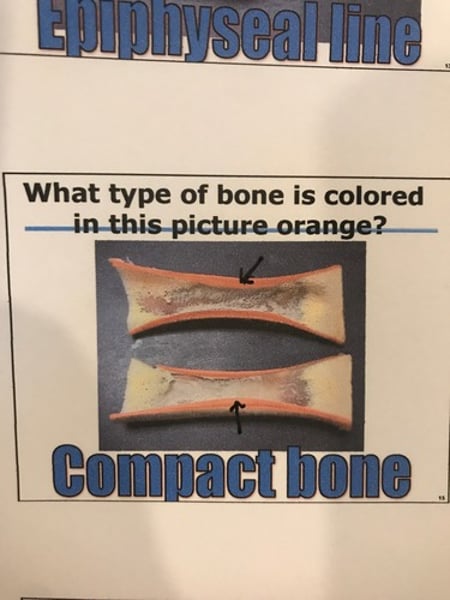
Compact bone
Made of osteons, which are made of lamellae (concentric layers of matrix) containing collagen fibers and mineral salts.
Lacunae
Contain bone cells - osteocytes.
Canaliculi
Small canals that connect osteocytes to each other and blood supply and nerves.
Central canal
contains blood vessels and nerves
perforating canals
run from the periosteum to the central canal of each osteon
Compact bone
compact bone structure
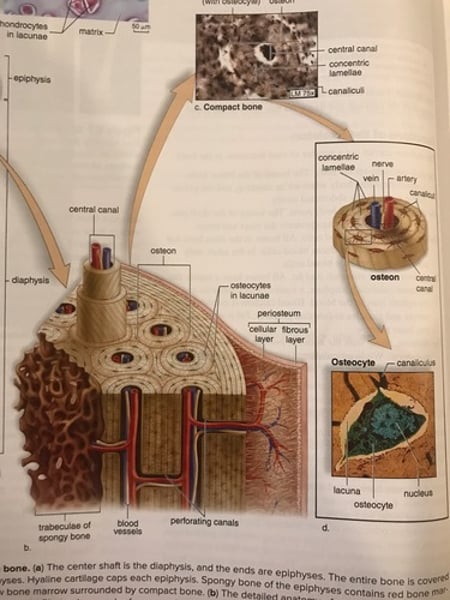
Spongy bone
-Also called cancellous bone.
-contains bony bars & plates called trabeculae.
-trabeculae follow lines of stress, giving bones strength.
spongy bone

Types of bone cells
1. Osteoprogenitor cells
2. Osteoblasts
3. Osteocytes
4. Osteoclasts
osteoprogenitor cells
Unspecialized cells found in the periosteum, endosteum and central canals.
Osteoblasts
Bone forming cells, created from osteoprogenitor cells.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells, prior osteoblasts.
Osteoclasts
Bone resorption; calcium and phosphorus removed from bone is deposited into the blood.
Ossification
-formation of bone.
1. Instramembranous ossification:
-spongy bone forms between 2 sheets of fibrous connective tissue.
-forms bones of the skull.
2. Endochondral ossification:
-forms most bones of human body.
-hyaline cartilage models are replaced by spongy bone and then compact bone.
Endochondral ossification of a long bone
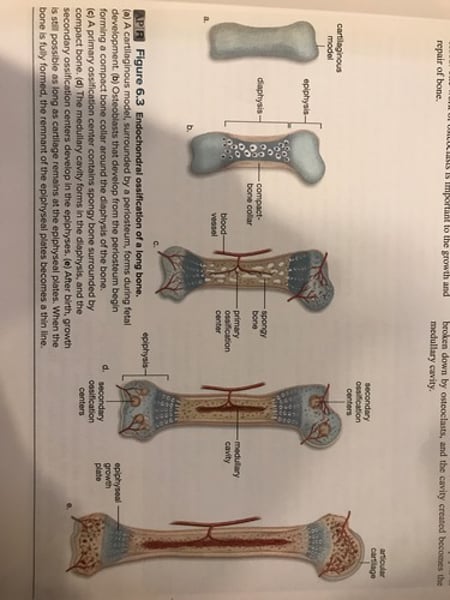
Epiphyseal plate
-band of hyaline cartilage in epiphysis of Long bones.
-allows the bone to grow in length.
-Long bone growth continues until place is ossified.
Appositional growth
Increase in bone diameter.
Remodeling of bones
-bone is continually being broken down and built up again
-osteoclasts remove worn cells and deposit calcium in the blood
-osteoblasts remove calcium from the blood and form new bone
-eventually, they surround themselves with matrix and become trapped in lacunae; they then mature into osteocytes.
-proper levels of calcium needed to prevent osteoporosis.
-Ca promotes the work of osteoblasts.
Surface features of bones
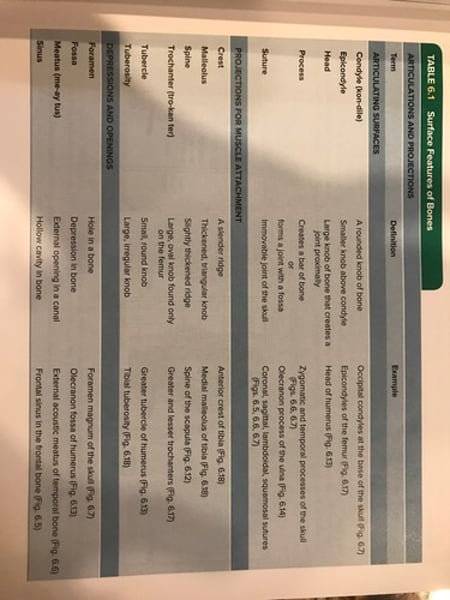
Tissues of the Skeleton
compact and spongy bone, cartilage, and dense connective tissue
Axial skeleton
-lies in midline of body
-bones of axial skeleton:
-skull
-hyoid bone
-vertebral column
-thoracic cage
-middle ear bones
Major bones of the axial skeleton
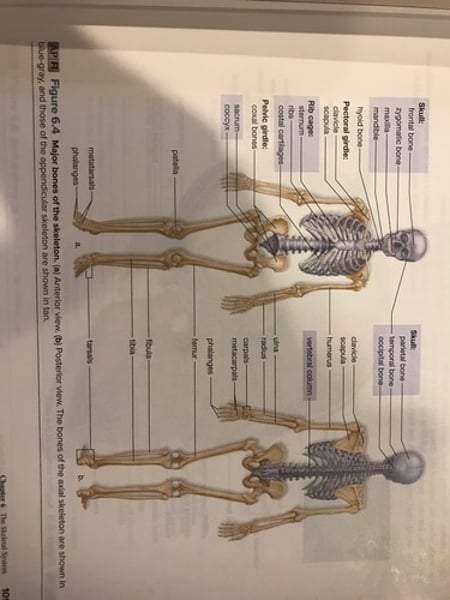
Skull
-formed by the cranium and facial bones.
-cranium is composed of 8 bones:
1. Frontal bone (1)
2. Parietal bone (2)
3. Occipital bone (1)
4. Temporal Bones (2)
5. Sphenoid bone (1)
6. Ethmoid bone (1)
Skull Anatomy
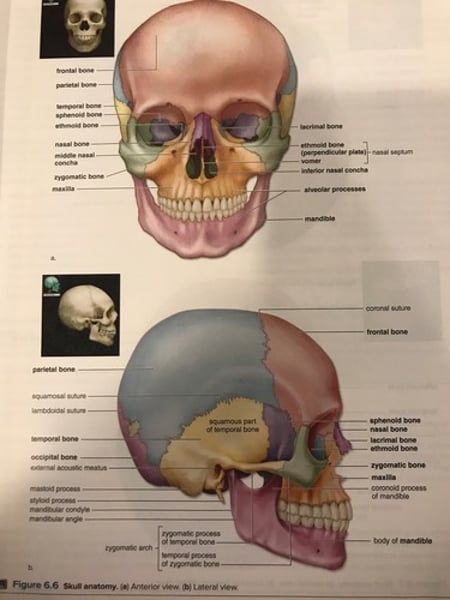
Skull Anatomy
Frontal bone

Parietal bone
Occipital bone
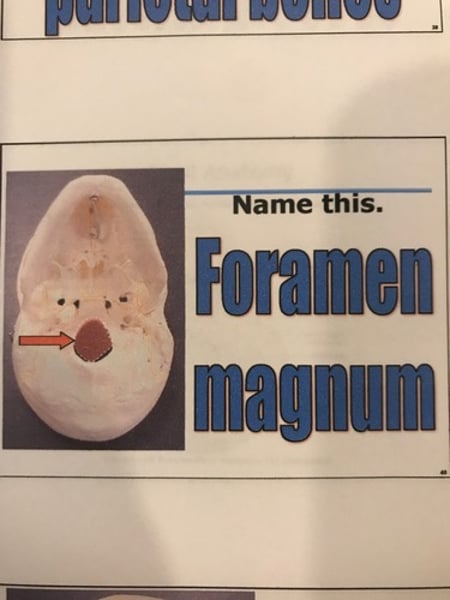
Occipital bone (1)
-foramen (rounded opening) magnum.
-occipital condyles.
Occipital bone
foramen magnum
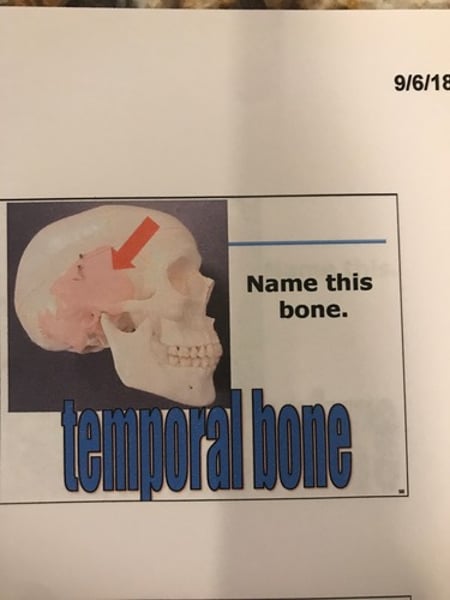
Temporal Bones
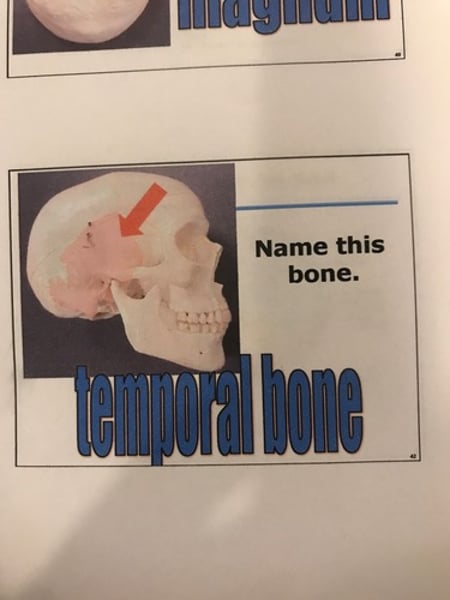
Temporal bones (2)
-external acoustic meatus.
-mandibular fossa
-mastoid process
-styloid process
-zygomatic process.
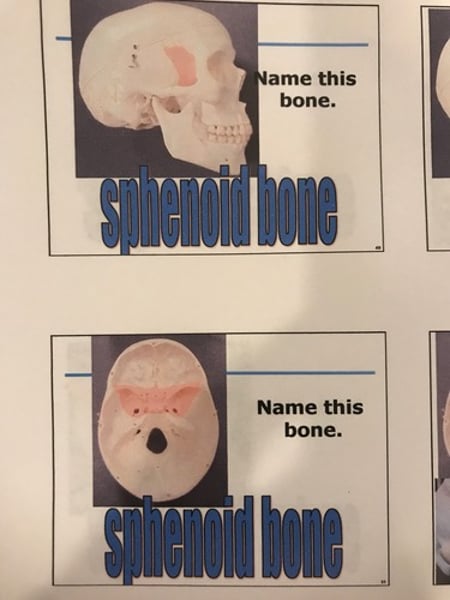
Temporal bone
mastoid process

Sphenoid bone
Sphenoid bone (1) (butterfly)
-sella turcica.
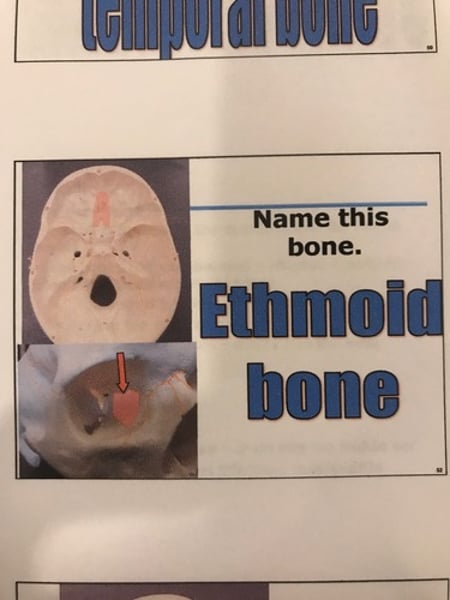
Ethmoid bone
Ethmoid bone (1) (medial sides of orbits, nasal septum)
-Christa Gali
-cribriform plate
-perpendicular plate
-superior & middle nasal conchae
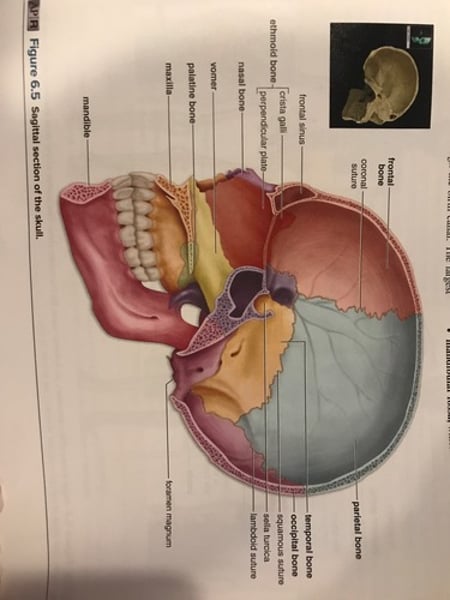
Saggital section of skull
Sphenoid Bone
Temporal bone
ethmoid bone
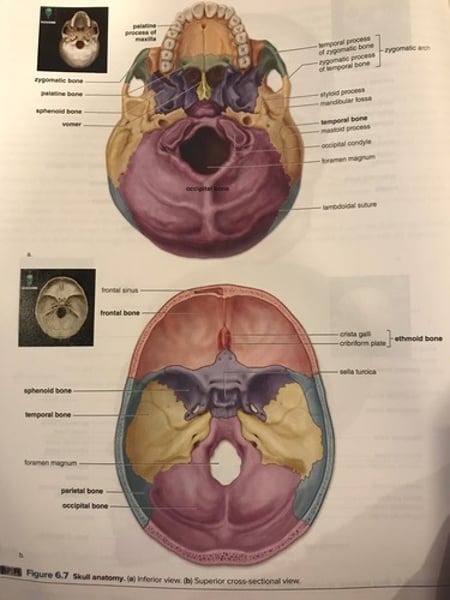
Bones of cranium
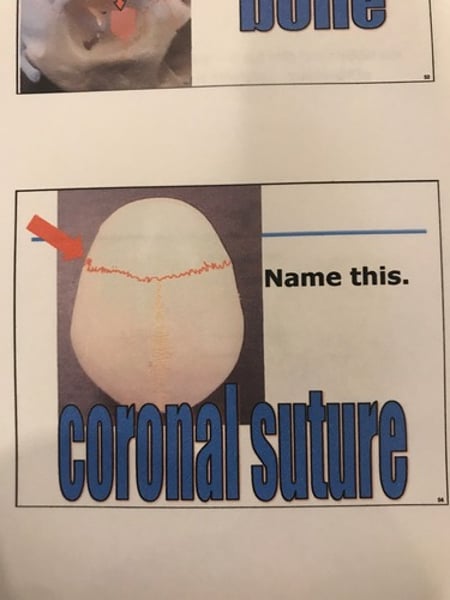
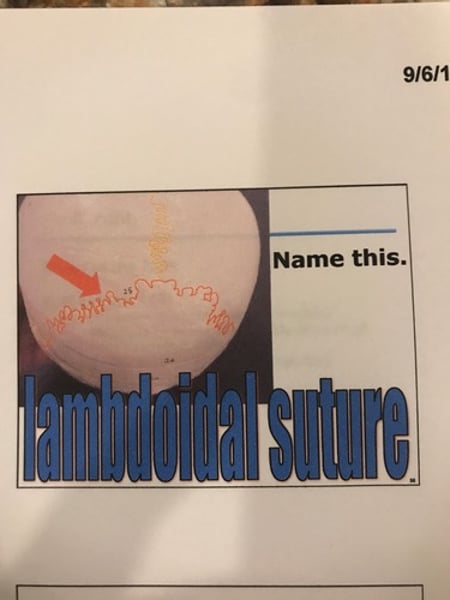
-sutures: immovable joints between cranial bones.
-fontanels: membranous regions in newborns where cranial bones have not yet fused together.
coronal suture
sagittal suture

Lambdoidal suture
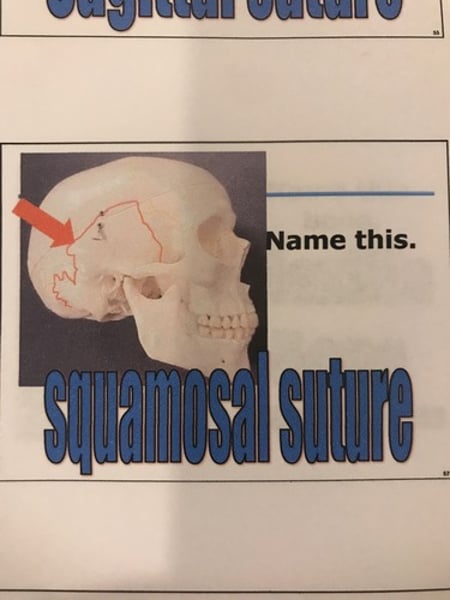
Squamosal suture
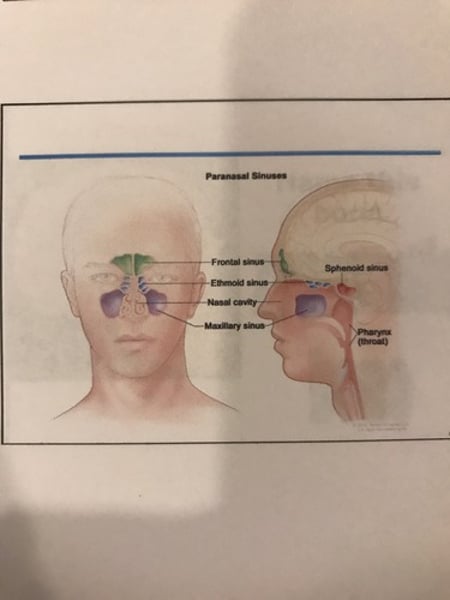
Sinuses in skull bones
-mucous membranes-lines air spaces within the bones.
-reduce the weight of skull.
-give the voice a resonant sound.
-paranasal sinuses - empty into the nose.
Paranasal sinuses
Located in : maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid
paranasal sinuses
Mastoid sinuses
Drain into middle ear.
Mastoid sinuses, mastoiditis
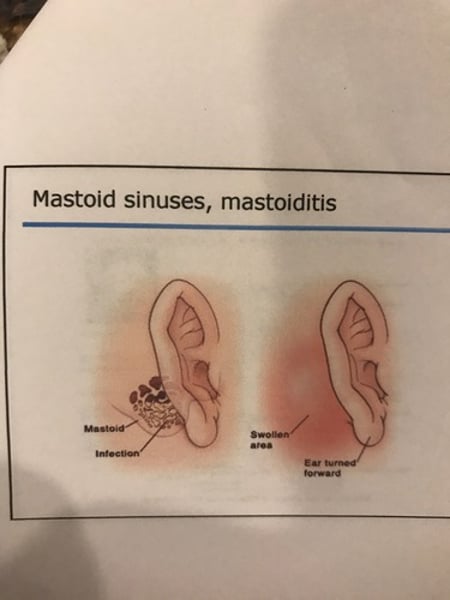
Sinusitis
Sinus infection; mastoiditis.
Bones of the face
1. Maxillae (2)
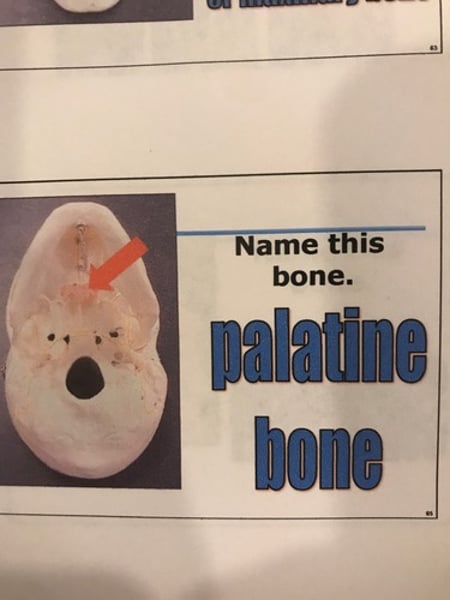
2. Palatine bones (2)
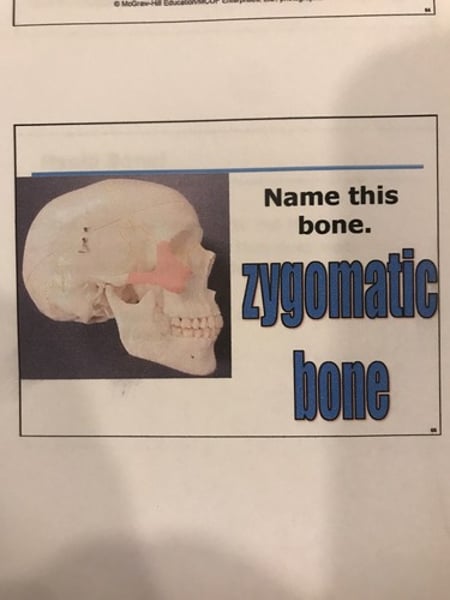
3. Zygomatic bones (2)
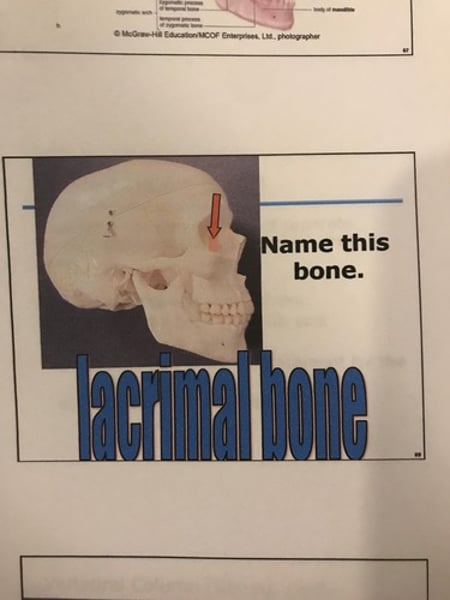
4. Lacrimal bones (2)
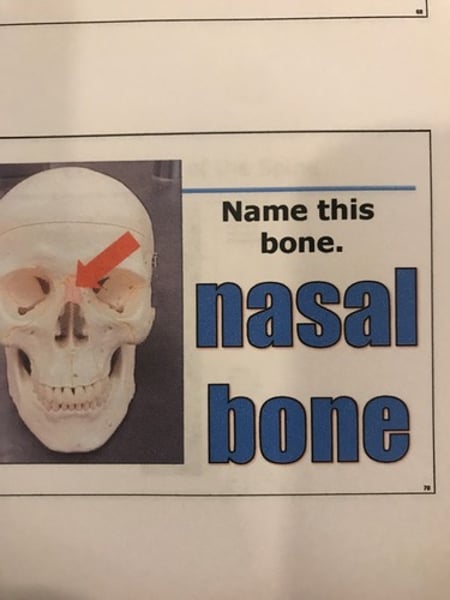
5. Nasal bones (2)
6. Vomer bone (1)
7. Inferior nasal conchae (2)
8. Mandible (1)
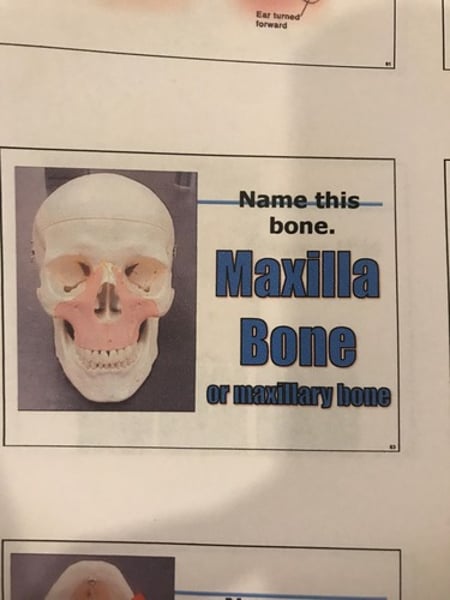
Maxillae (2)
-alveolar process (tooth sockets)
-palatine process (hard palate-roof of mouth) (cleft palate)
Zygomatic bones (2)
-temporal process
-zygomatic arch
Maxillae (maxillary bones)
palatine bone
Zygomatic bone
Lacrimal bone
Nasal bone
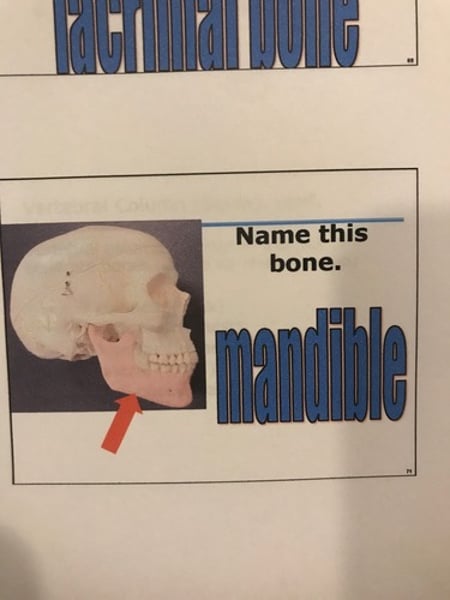
Mandible
-only movable bone of the skull.
-mandibular condyle
-coronoid process
-alveolar process
Mandible
Hyoid bone
-superior to larynx.
-only bone In the body that does not articulate with another bone.
-anchors to the tongue.
-site of attachment for muscles associated with swallowing.
Hyoid bone

Vertebral column
Consists of separate vertebrae separated by intervertebral disks.
Functions of vertebral column
1. Forms body's vertical axis.
2. Supports rib cage.
3. Serves as point of attachment for pelvic girdle.
4. Protects spinal cord.
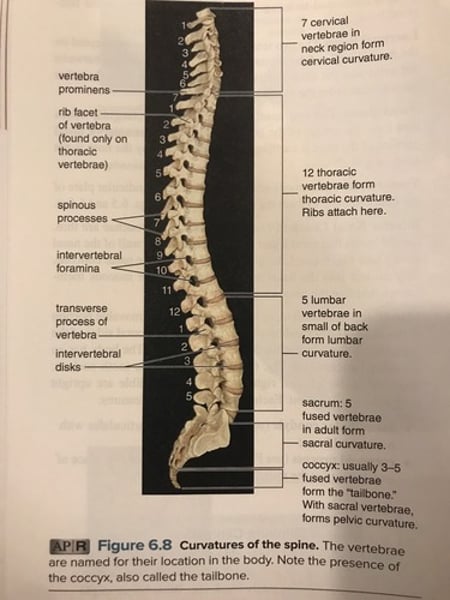
Curvatures of spine
Vertebral bones
- 7 cervical (neck)
- 12 thoracic (chest)
- 5 lumbar (lower back)
- 5 sacral (fused)
- 3 to 5 coccygeal (fused)
Normal curvatures of spine
-cervical & lumbar : convex anteriorly
-thoracic & sacral : concave posteriorly
-provide support & balance.
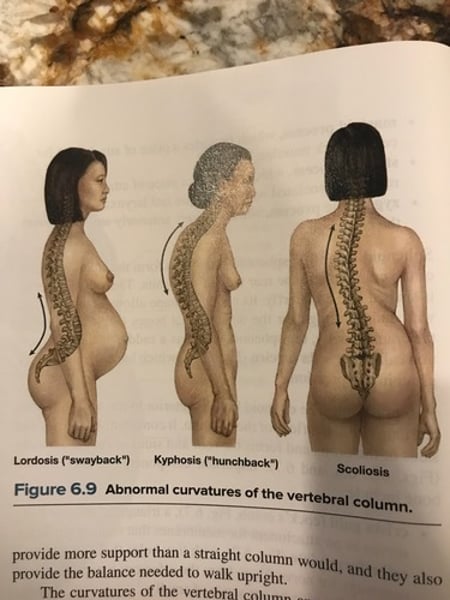
Abnormal curvature of spine
1. Lordosis : exaggerated lumbar curvature.
2. Kyphosis : increased roundness of thoracic curvature.
3. Scoliosis : lateral curvature; occurs most often in thoracic region.
Abnormal curvatures of spine
intervertebral discs
fibrocartilage pads between vertebrae.
-prevent vertebrae from grinding against one another.
-absorb shock
-allow motion between vertebrae
-can slip or rupture (herniated disk).
intervertebral discs

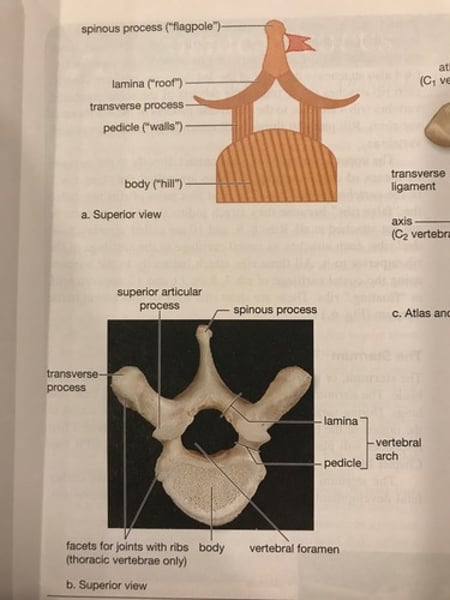
Vertebrae structure
-Body : large, anterior portion.
-vertebral foramen : canal for spinal cord
-bony projections : sites for muscle attachment.
-spinous process (spine) : posterior projection (c7-chin to chest)
-transverse process : lateral projections.
Vertebrae
Cervical Vertebrae
-C1-C7
-C7 also called the vertebra prominens.
-have transverse foramina & short spines.
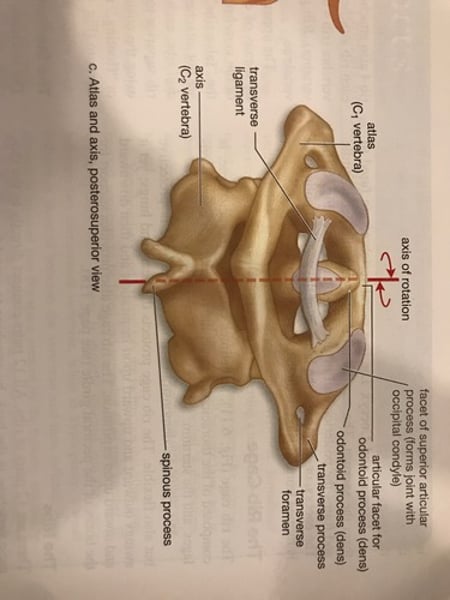
-Atlas (c1) : supports head; allows head movement up and down.
-Axis (c2) : serves as pivot for atlas; allows head movement from side to side. (has odontoid process, or dens!)
C1 Atlas

C2 Axis

Atlas & Axis
thoracic vertebrae
-T1-T12
-Long slender spines and costal facets.
lumbar vertebrae
-L1-L5
-massive bodies & square spines.