Remote Sensing Lecture Midterm
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Problems Associated with In Situ Data Collection
method produced errors introduced by
-sampling design does not capture the spatial variability
-improper operation
-uncalibrated in situ measurement instruments
Remote sensing definition
"the measurement or acquisition of information of some property of an object or phenomenon, by a recording device that is not in physical or intimate contact with the object or phenomenon under study" (Colwell, 1997).
combined formal definition of photogrammetry and remote sensing
"the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment, through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting imagery and digital representations of energy patterns derived from noncontact sensor systems".
IFOV
Instantaneous field of view
EMR
electromagnetic radiation
Remote Sensing scientific activity
Using sensors to measure the amount of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) exiting an object or geographic area from a distance and then extracting valuable information from the data using mathematically and statistically based algorithms
Interaction Model Depicting the Relationships of the Mapping Sciences as they relate to Mathematics and Logic, and the Physical, Biological, and Social Sciences
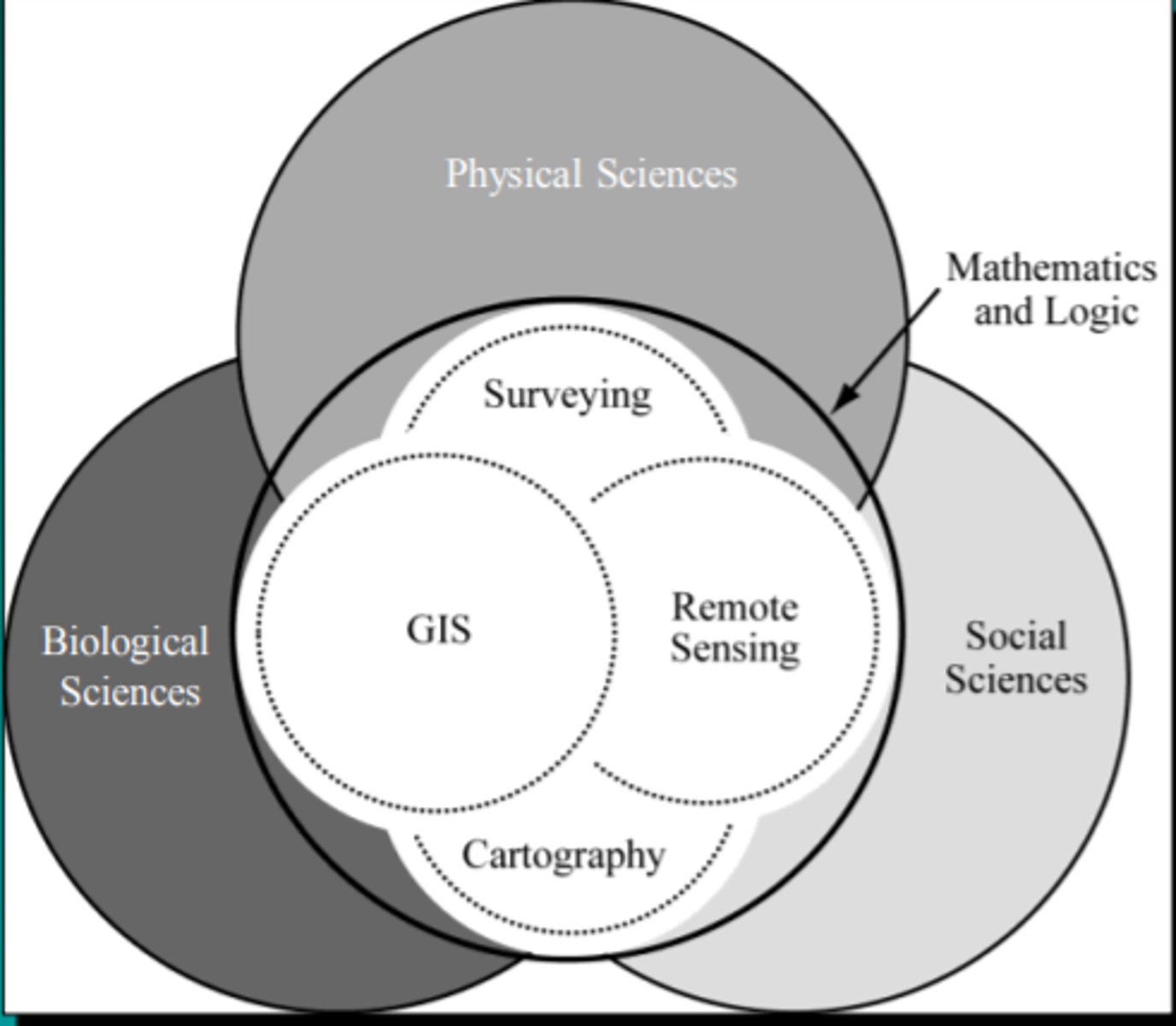
A superior image analyst is able to...
1) understand the scientific principles better
2) are more widely traveled and have seen many landscape objects and geographic areas, and/or
3) have the ability to synthesize scientific principles and real-world knowledge to reach logical and correct conclusions
The EMR reflected, emitted, or backscattered from an object or geographic area is used as a _________ for the actual property under investigation
surrogate
passive remote sensing
-unobtrusive
-sensor passively records the EMR reflected or emitted by the object of interest
-does not disturb the object or area of interest
Remote sensing can provide biophysical information such as...
-x,y location
-z elevation or depth
-biomass
-temperature
-moisture content
Remote sensing devices can be programmed to collect data systematically to remove ________ ____
sampling bias
Remote sensing can be used to model natural processes such as...
-water-supply estimation
-eutrophication studies
-nonpoint source pollution
Remote sensing can be used to model cultural processes such as...
-land-use conversion at the urban fringe
-water-demand estimation
-population estimation
Limitations of Remote Sensing
-Often oversold
-Human method-produced error
-active remote sensor systems can emit intrusive electromagnetic radiation
-uncalibrated instruments
-expensive to collect and analyze
Remote sensing process definition
The remote sensing data-collection and analysis procedures used for Earth resource applications are often implemented in a systematic fashion
Remote sensing process steps
1. Statement of the problem
2. Data Collection
3. Data-to-information conversion
4. Information Presentation
Remote sensing process- Statement of the Problem steps
1. Formulate Hypothesis
2. Select Appropriate Logic
3. Select Appropriate Model
Remote sensing process- Data Collection steps
1. In Situ Measurements
2. Collateral Data
3. Remote Sensing
Remote sensing process- Data-to-Information Conversion steps
1. Analog (visual) image processing
2. Digital Image Processing
3. Hypothesis testing
Remote sensing process- Information Presentation steps
1. Image Metadata
2. Accuracy Assessment
3. Analog and Digital
4. Statistics
5. Graphs
Spatial resolution
the size of the field-of-view
Spectral resolution
the number and size of spectral regions the sensor records data in
Temporal resolution
how often the sensor acquires data
Radiometric resolution
the sensitivity of detectors to small differences in electromagnetic energy.
angle of incidence
the angle of the incoming energy that illuminates the terrain
angle of exitance
angle of energy from the terrain to the sensor system
angular characteristics are a function of
-location in a three-dimensional sphere of the illumination source
-orientation of the terrain facet
-location of the suborbital or orbital remote sensing system
In situ and remotely sensed data are processed using...
a) analog image processing
b) digital image processing
c) modeling
d) n-dimensional visualization.
Information that may be useful for modeling includes
• the global carbon cycle
• biology and biochemistry of ecosystems
• aspects of the global water and energy cycle
• climate variability and prediction
• atmospheric chemistry
• characteristics of the solid Earth
• population estimation
• monitoring land-use change and natural hazards
Examples of shorter wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum
gamma and x rays
Examples of longer wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum
microwaves and broadcast radio waves
Energy conduction
conducted from one object to another by being in direct physical contact
Energy Convection
Sun heats Earth with radiant energy, heating up the air near the surface, hot air rises creating convectional currents in the atmosphere
Radiation
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves (as in from the sun through the vacuum of space)
Wave Model
-Concept of electromagnetic radiation
Wave model- the electromagnetic wave consists of two fluctuating fields at right angles, these fields are ________ and ________
electric, and magnetic
The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation depends upon the length of ____that the charged particle is accelerated
time
frequency of electromagnetic radiation (v) depends on the number of _____________ ___ ______
accelerations per second
Wavelength Definition
the mean distance between maximums (or minimums) of a roughly periodic pattern and is normally measured in micrometers or nanometers (nm).
Frequency definition
the number of wavelengths that pass a point per unit time. A wave that sends one crest by every second (completing one cycle) is said to have a frequency of one cycle per second or one hertz, abbreviated 1 Hz
The longer the wavelength the _____ the frequency
lower
The amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is the ______ of the wave crest above the undisturbed position.
height
The electromagnetic energy from the Sun travels in _ minutes across the intervening __ million miles (150 million km) of space to the Earth.
8, 93
The earth approximates a ___ K (__ degrees C) blackbody
300k (27 deg C)
The earth has a dominant wavelength at
9.7
The sun has a ____ K blackbody
6,000
the amount of energy emitted by an object such as the Sun or the Earth is a function of its ___________
temperature
The formula used to determine dominant wavelength
Wein's Displacement law
The sun produces __% of its energy in the visible region (.4-.7)
41%
Quantum Theory of electromagnetic radiation
energy is transferred in discrete packets called quanta or photons
Thus, the energy of a quantum is _________ proportional to its wavelength
inversely
Electrons
the tiny negatively charged particles that move around the positively charged nucleus of an atom.
radiation is produced by changes in the energy levels of the ____ ______ _________
outer, valence electrons
Every time an electron jumps from a higher to a lower energy level, a ______ moves away at the speed of light.
photon
quantum leap
Somehow an electron might disappear from its original orbit and reappear in its destination orbit without ever having to traverse any of the positions in between
________ scattering causes the atmosphere to appear blue
Rayleigh
Atmospheric Scattering is a function of
wavelength and size of gas molecule
Mie scattering takes place when...
there are essentially spherical particles present in the atmosphere with diameters approximately equal to the wavelength of radiation being considered
Atmospheric Layers and Constituents (image)
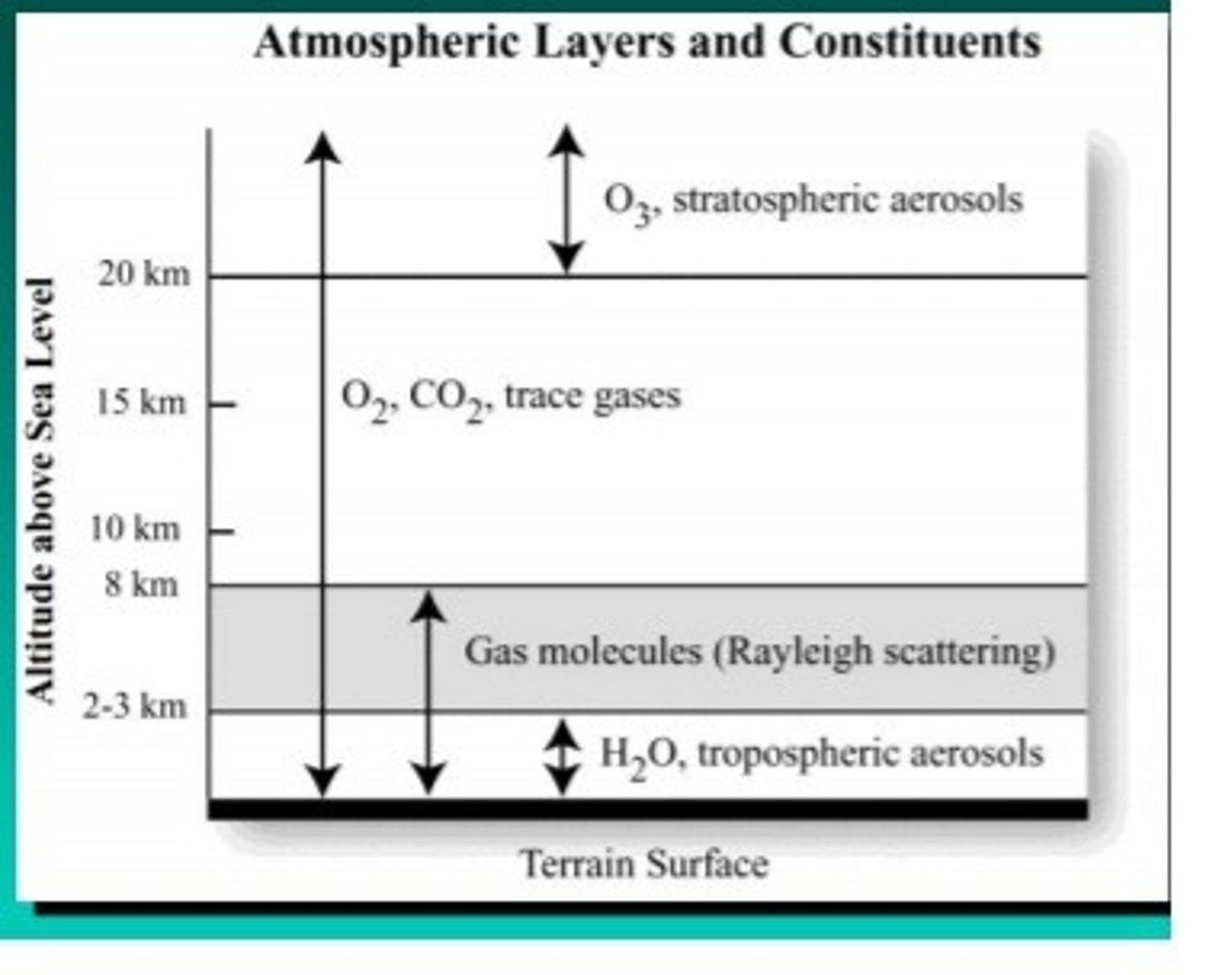
Rayleigh scattering occurs when...
the diameter of the matter (usually air molecules) are many times smaller than the wavelength of the incident electromagnetic radiation.
All scattering is accomplished through absorption and re-emission of _________ by atoms or molecules
radiation
The amount of scattering is _________related to the fourth power of the radiation's wavelength.
inversely
Non-selective scattering is produced when...
there are particles in the atmosphere several times the diameter of the radiation being transmitted.
Absorption....
the process by which radiant energy is absorbed and converted into other forms of energy
absorption band
a range of wavelengths (or frequencies) in the electromagnetic spectrum within which radiant energy is absorbed by substances such as water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2 ), oxygen (O2 ), ozone (O3 ), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
The cumulative effect of the absorption by the various constituents can cause the atmosphere to _____ ____ in certain regions of the spectrum
close down
atmospheric windows
Parts of the spectrum that transmit energy effectively
Absorption occurs when...
-energy of the same frequency as the resonant frequency of an atom or molecule is absorbed, producing an excited state
-the energy is transformed into heat motion and is reradiated at a longer wavelength,
When dealing with a medium like air, absorption and scattering are frequently combined into an __________ ___________
extinction coefficient
Simplified definition of reflectance
Reflectance is the process whereby radiation "bounces off" an object like a cloud or the terrain
Process of Reflectance
re-radiation of photons in unison by atoms or molecules in a layer one-half wavelength deep.
Specular reflection occurs when
the surface from which the radiation is reflected is essentially smooth (i.e. the average surface profile is several times smaller than the wavelength of radiation striking the surface).
diffused radiation
when the reflecting surface is rough, the reflected rays go in many directions, depending on the orientation of the smaller reflecting surfaces.
- white paper
-white powder
a perfectly diffuse surface (Lambertian surface)
-the radiant flux leaving the surface is constant for any angle of reflectance to the surface normal.
-the surface is so rough that there are no individual reflecting surfaces
Radiation Budget Equation
the total amount of radiant flux in specific wavelengths (l) incident to the terrain ( ) must be accounted for by evaluating the amount of radiant flux reflected from the surface ( ), the amount of radiant flux absorbed by the surface ( ), and the amount of radiant flux transmitted through the surface ( ):
radiant flux
The time rate of flow of energy onto, off of, or through a surface. Measured in watts
Hemispherical Reflectance
the dimensionless ratio of the radiant flux reflected from a surface to the radiant flux incident to it
Hemispherical transmittance
the dimensionless ratio of the radiant flux transmitted through a surface to the radiant flux incident to it
hemispherical absorptance
dimensionless relationship
Irradiance
The amount of radiant flux incident upon a surface per unit area of that surface
Exitance
The amount of radiant flux leaving per unit area of the plane surface
Radiance
s the radiant flux per unit solid angle leaving an extended source in a given direction per unit projected source area in that direction and is measured in watts per meter squared per steradian
Radiance from paths 1, 3, and 5 contains....
intrinsic valuable spectral information about the target of interest.
path radiance (Lp ) from paths 2 and 4 includes
diffuse sky irradiance or radiance from neighboring areas on the ground.
index of refraction (n)
a measure of the optical density of a substance. This index is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum, c, to the speed of light in a substance such as the atmosphere or water, cn
The speed of light in a substance can never reach the speed of light in a vacuum. Therefore, its index of refraction must always be greater than....
1
Anytime energy is propagated through the atmosphere for any appreciable distance at any angle other than vertical, __________occurs.
refraction
The amount of refraction is a function of the
angle made with the vertical , the distance involved (in the atmosphere the greater the distance, the more changes in density), and the density of the air involved
Serious errors in location due to refraction can occur in images formed from energy detected at high altitudes or at acute angles. ______ ___ can predict this and be removed
Snells Law
Types of aerial cameras:
1. single-lens mapping (metric) camera
2. multiple-lens (multiple-band) camera
3. digital camera
4. miscellaneous cameras
The ability of a portion of a developed film to pass light is called its
transmittance
RS Data must be calibrated in two ways:
1. geometrically and radiometrically
2. calibrated to characteristics on the ground
Remote Sensing process:
1. statement of the problem
2. data collection
3. data-to-information conversion
4. information presentation
Types of resolution:
1. spatial
2. spectral
3. temporal
4. radiometric
5. thematic
Angular characteristics associated with each pixel are a function of:
1. location of the source of illumination (sun if passive, sensor if active)
2. orientation of the terrain
3. location of the sensor
Data processing types:
1. analog image processing
2. digital image processing
3. modeling
4. n-dimensional visualization (2D or 3D?)
GPS devices can be accurate to
10 cm
Aim for __% accuracy
80
Types of reflection:
1. specular reflectance (smooth)
2. diffused reflectance (rough)
3. Lambertian reflectance (perfectly rough)