Amerman Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 5 Integumentary System steph
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
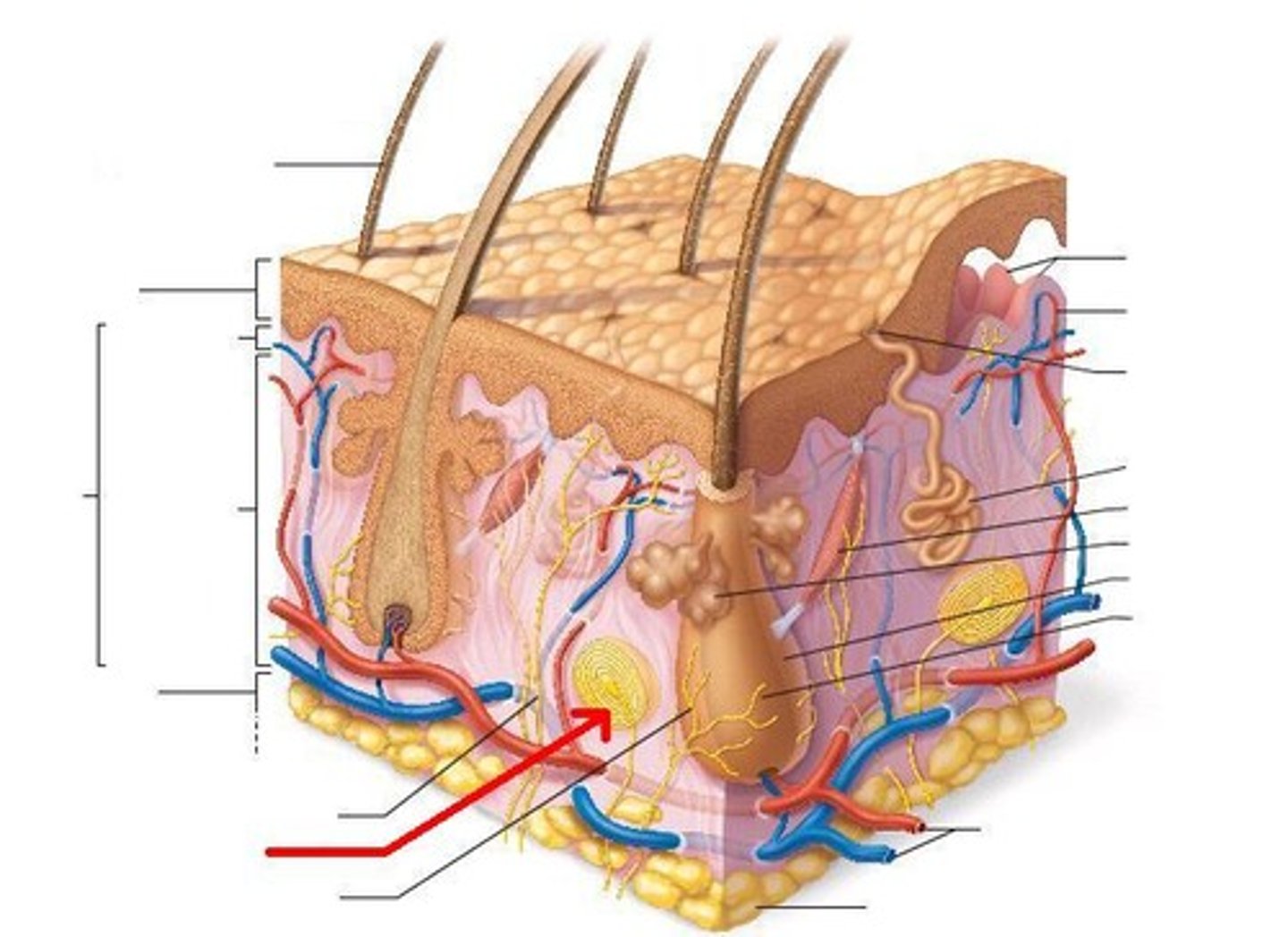
two components of cutaneous membrane
1) epidermis: superficial
2) dermis: deep
epidermis
superficial layer made of keratinized, stratified, squamous epithelium, avascular
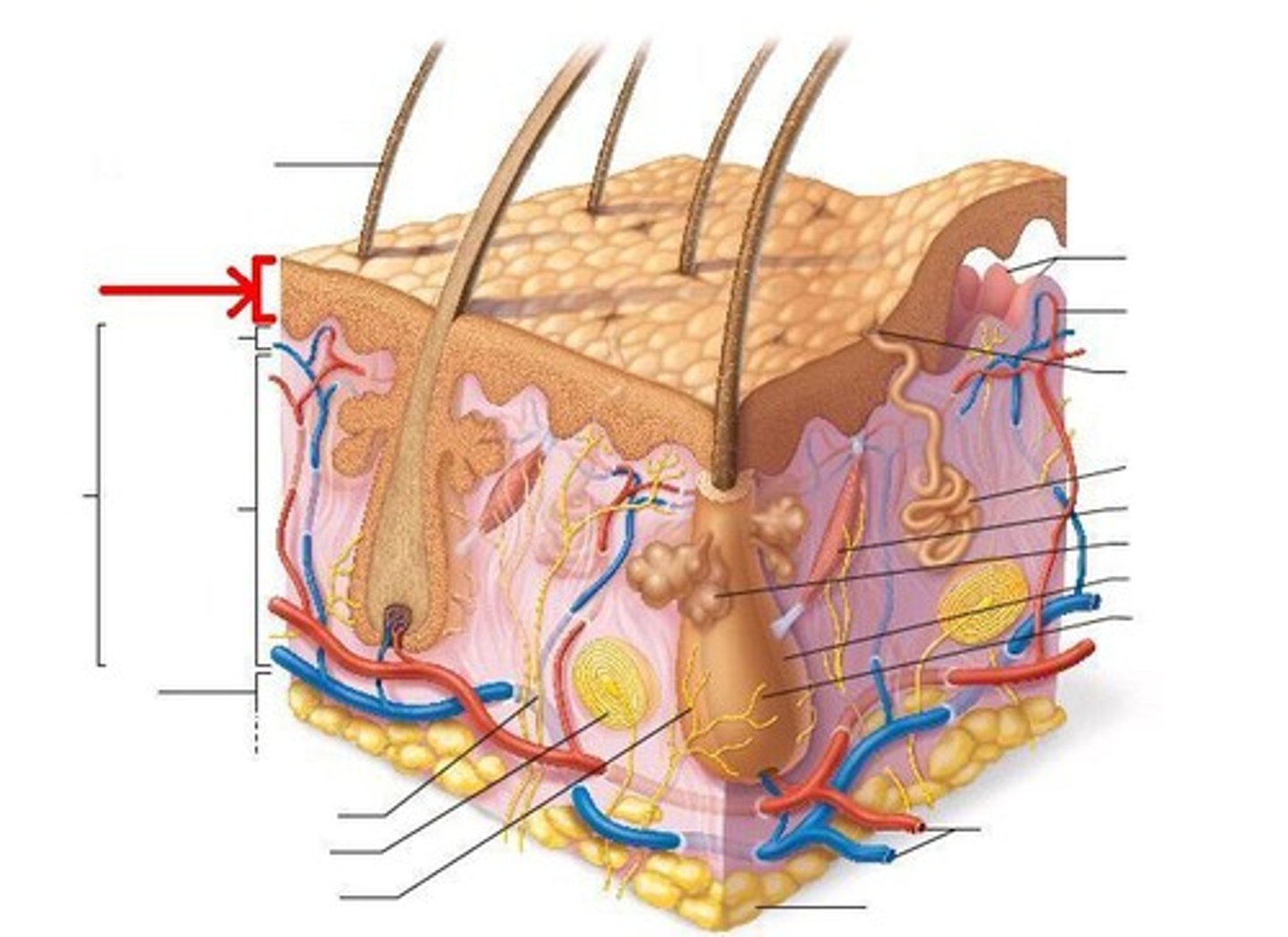
dermis
- deep to epidermis and basement membrane
- made of loose connective tissue and dense irregular CT
- vascular
four accessory structures of skin embedded in cutaneous membrane
1) sweat glands
2) sebaceous glands
3) hair
4) nails
hypodermis
- deep to dermis, also known as superficial fascia or subcutaneous fat
- anchors skin to deeper structures
- has blood vessels
five main functions of integumentary system
1) protection
2) sensation
3) thermoregulation
4) excretion
5) vitamin d synthesis
four ways in which integumentary system provides protection
1) durable but flexible, protects from mechanical trauma
2) continuous barrier to invasion by microorganisms and pathogens, contains immune system cells that destroy pathogens
3) provides protection against UV
4) secretes hydrophobic, lipid based chemicals that protect against salt and water to maintain homeostasis
acid mantle
acidic pH of skin surface created by sebaceous glands, inhibits pathogen growth
how integument functions in sensation
contains sensor receptors that detect stimuli like heat, cold, pain
how integument functions in thermoregulation
negative feedback loops maintain stable internal temperature
sequence of events when body temperature rises above normal range
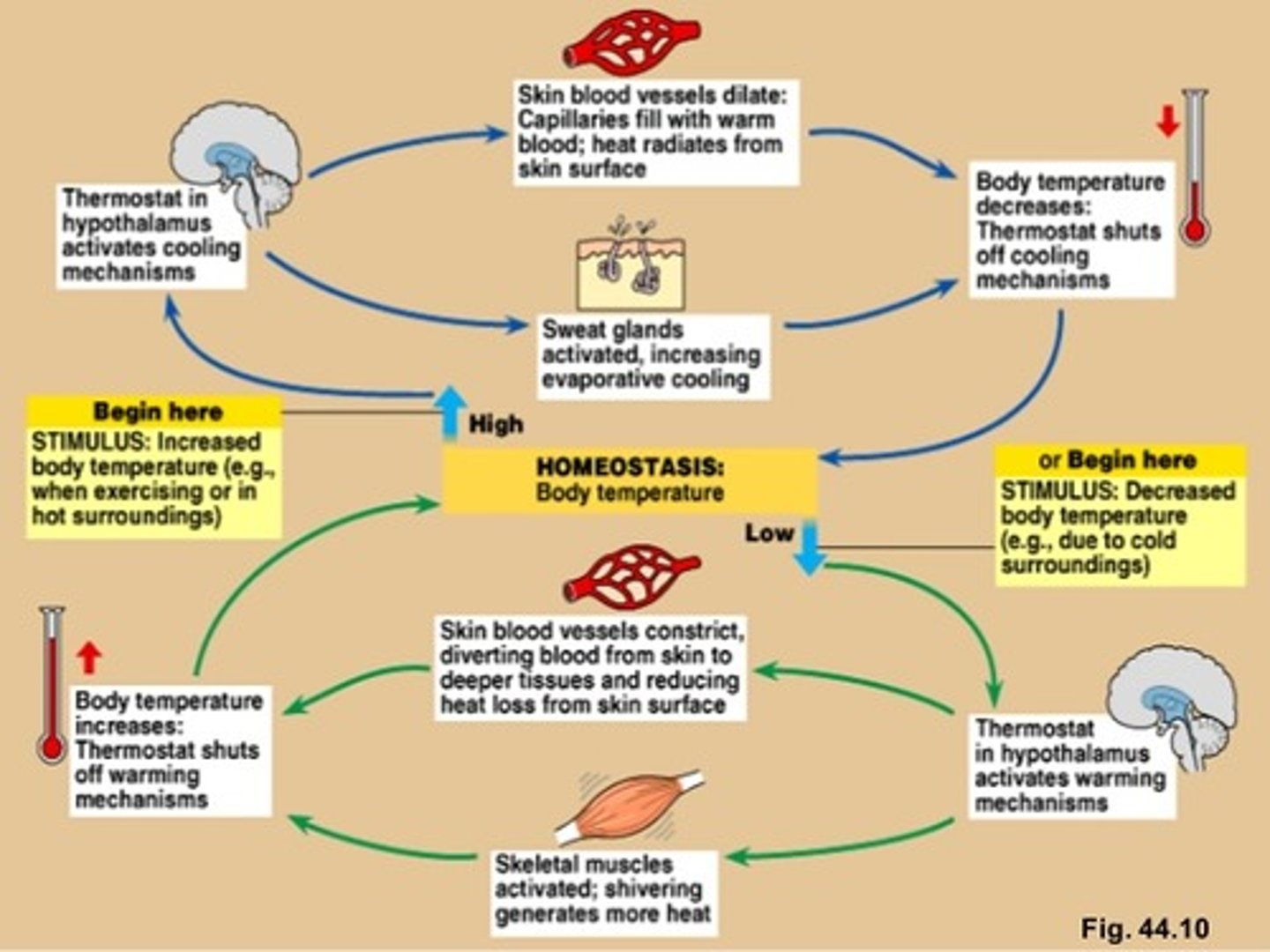
sequence of events when body temperature drops below normal
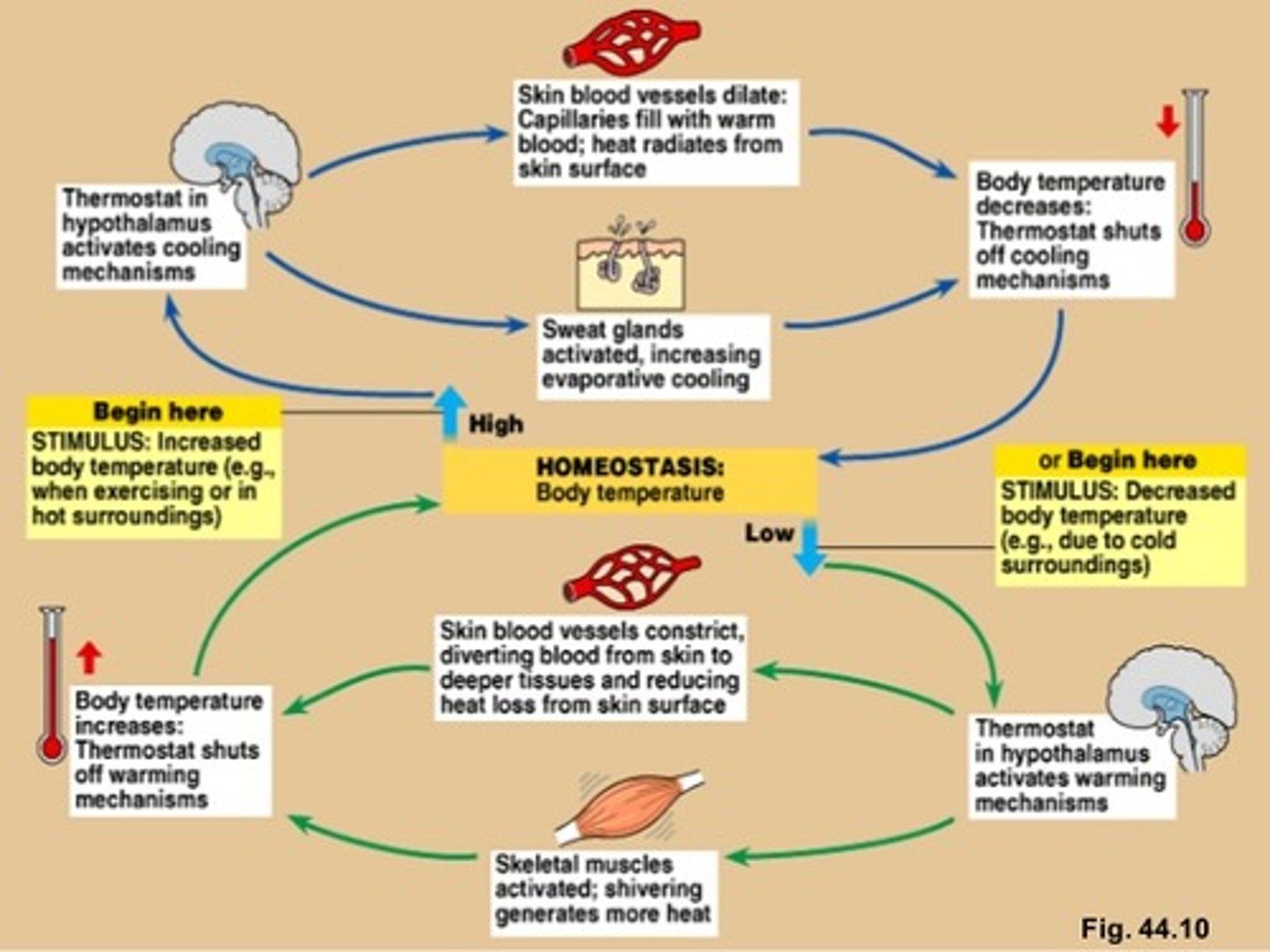
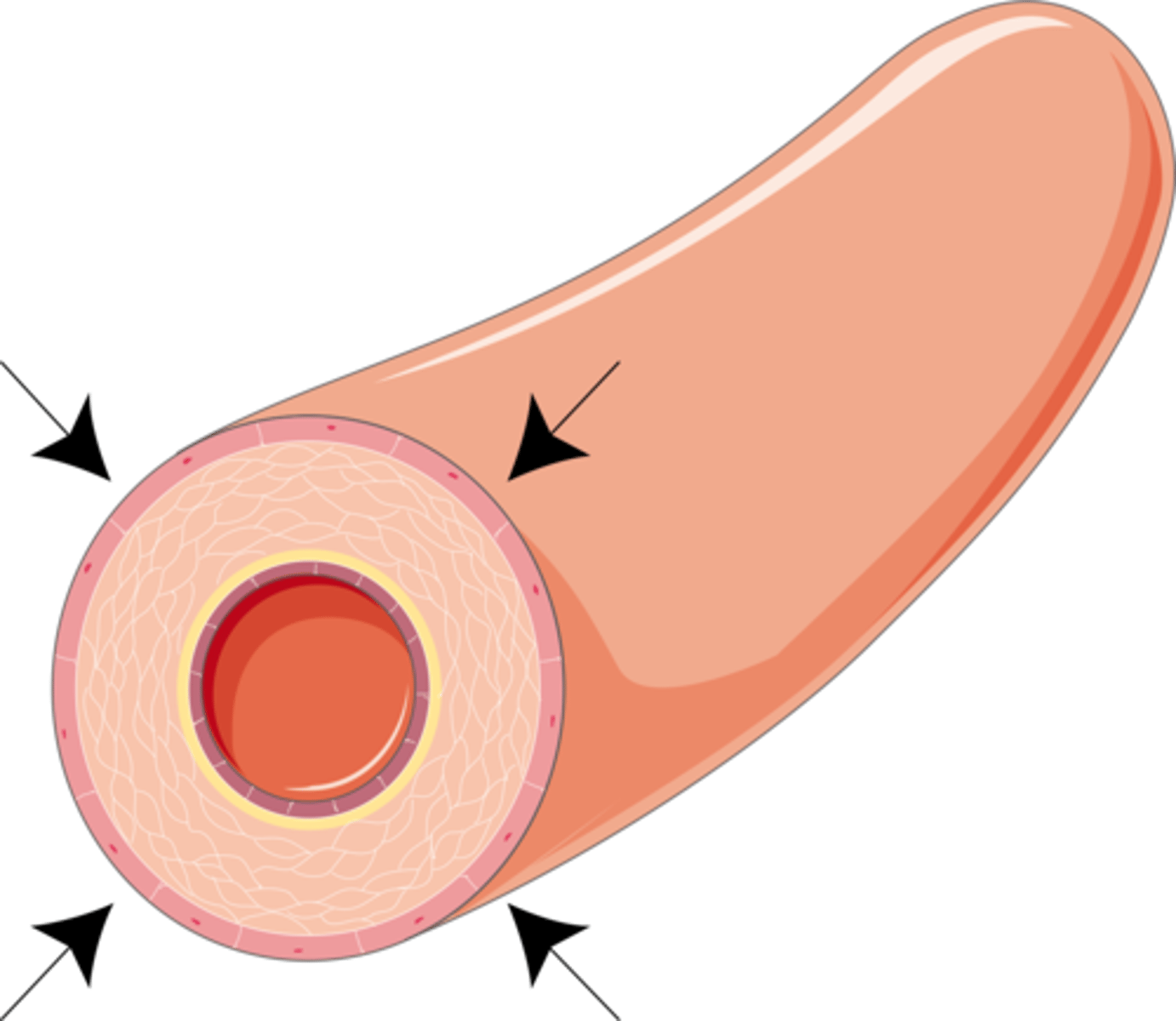
vasoconstriction
narrowing of blood vessels to reduce the amount of blood flow and limit the heat lost to the environment
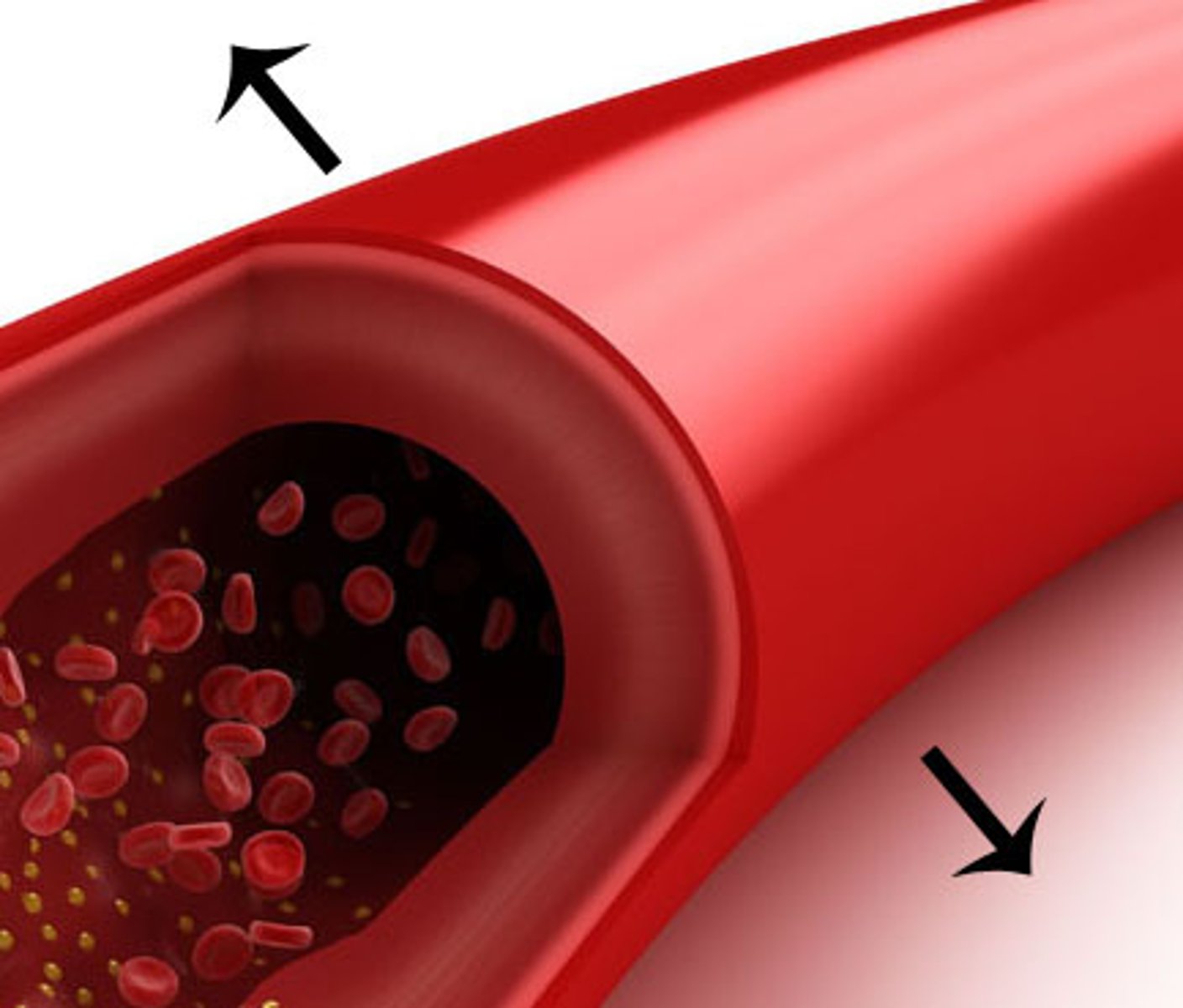
vasodilation
response triggered by hypothalamus causing blood vessels to widen and increase the flood flow and increase the heat radiated away
location and function of control center
hypothalamus
sensory receptors (thermoreceptors)
detect changes in body temperature
role of integument in excretion
waste products and toxins mostly through kidneys, but skin plays a role too
process for vitamin D synthesis
- precursor cholesterol molecule converted to cholecaliferol when epidermis is exposed to UV
- inactive cholecalciferol released to blood then modified by liver and then kidneys to make active calcitriol
- calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) required for absorption of calcium ion in small intestine
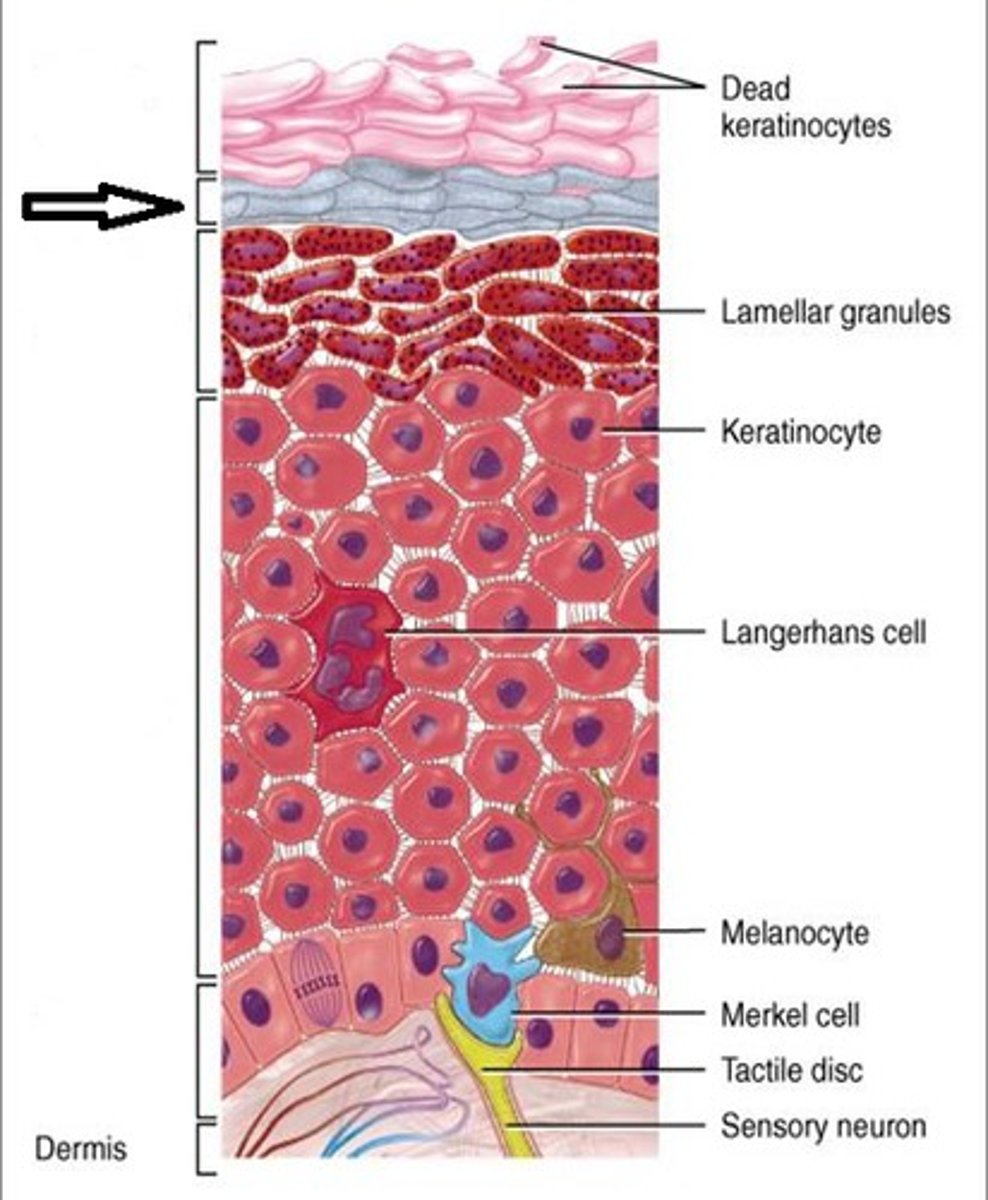
most numerous type of cell in epidermis
keratinocytes
function of keratinocytes
manufacture keratin
two ways keratinocytes make epidermis less susceptible to mechanical trauma
1) they make keratin, a strong protein
2) they're linked by desmosomes
five distinct layers (strata) of keratinocytes
Brilliant Studying Gives Loads of Confidence
deep to superficial:
1) Stratum basale (germanativum)
2) Stratum Spinosum
3) stratum granulosum
4) Stratum lucidum
5) Stratum Corneum
stratum basale
- epidermis layer resting on basement membrane
- most mitotically active, closest to blood supply
- replaces dead keratinocytes and synthesizes vitamin D
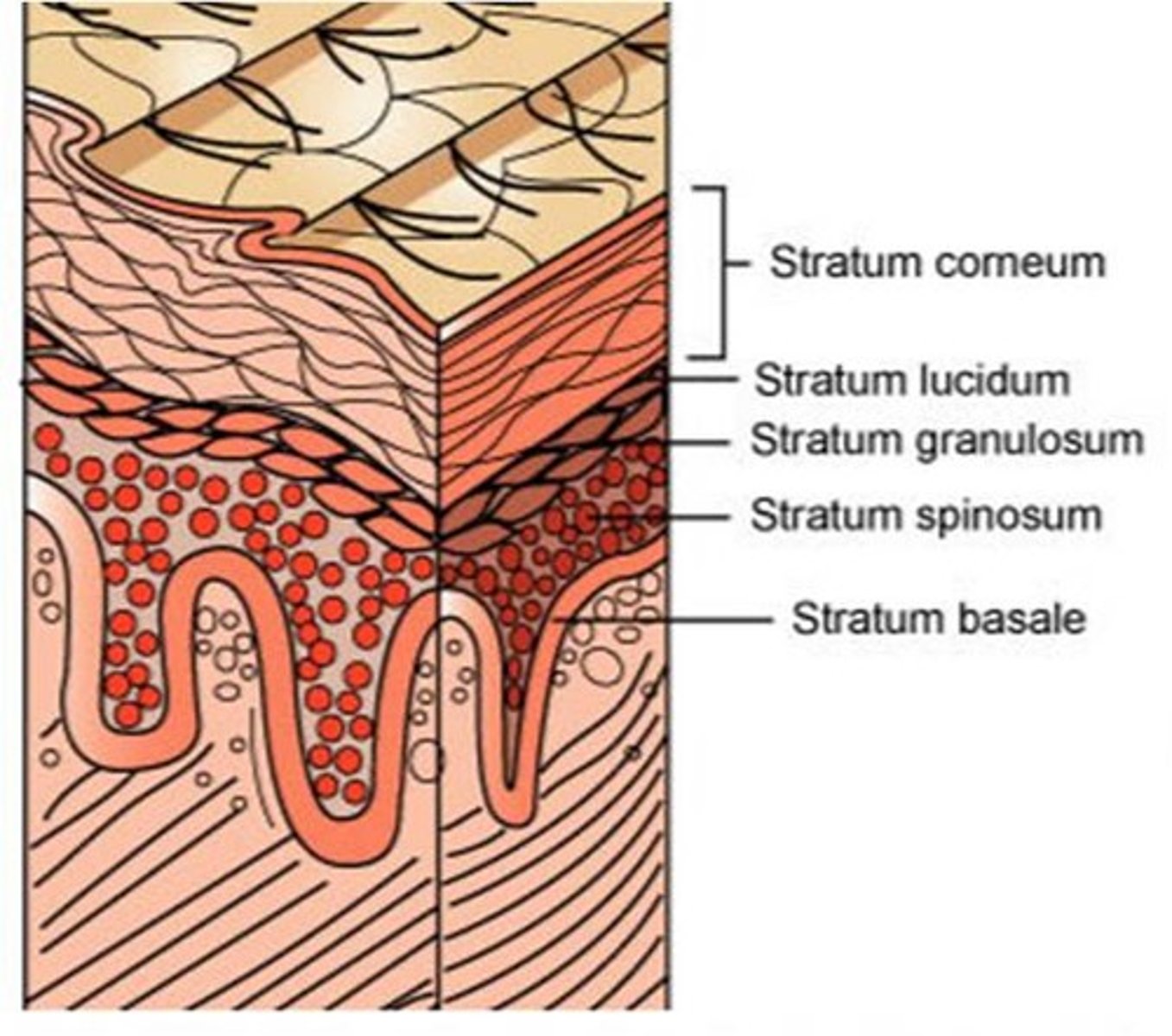
stratum spinosum
- thickest epidermis layer
- sits on top of stratum basale and is still mitotically active because it's relatively close to blood
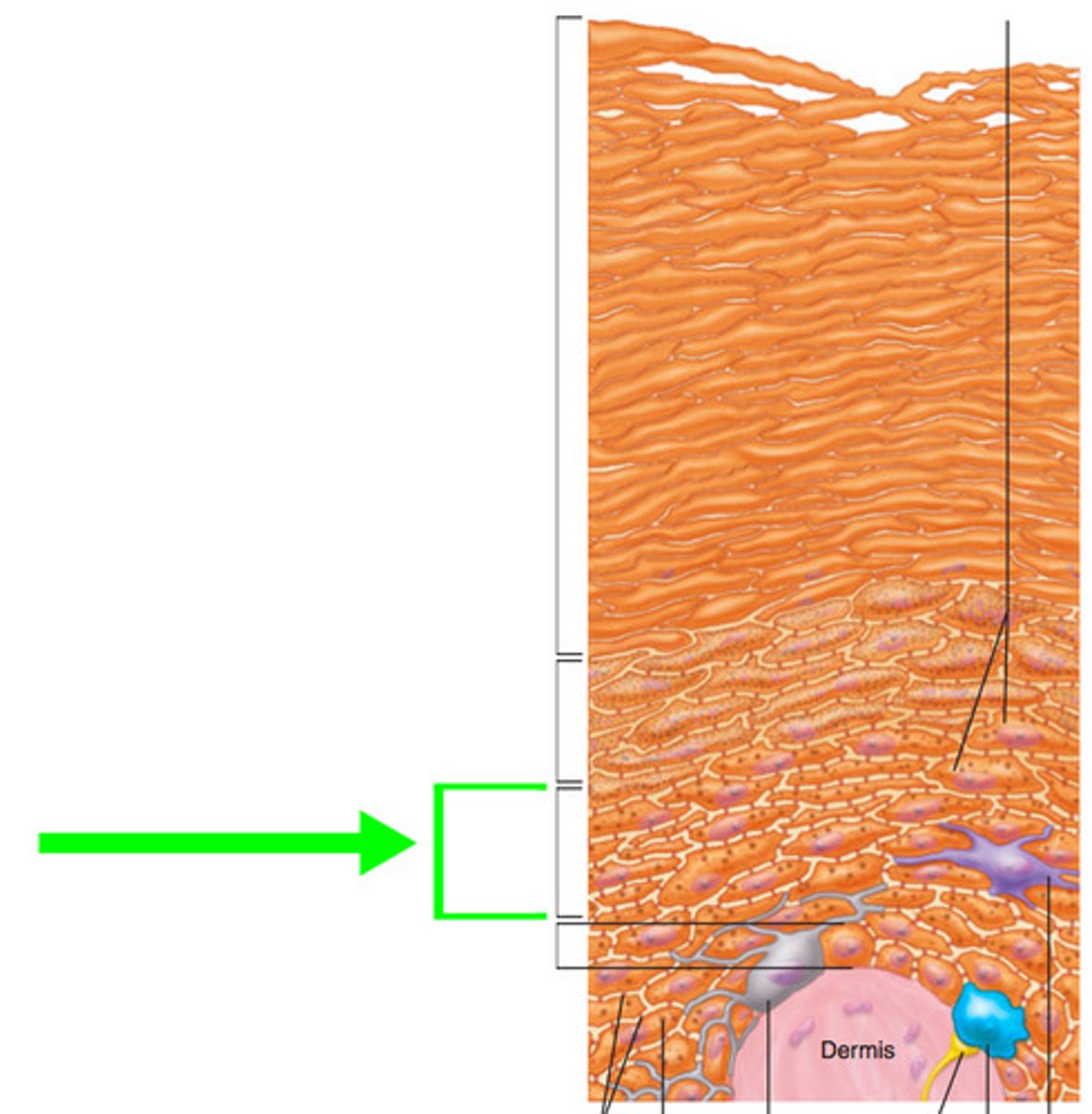
stratum granulosum
- epidermis layer with three to five layers of cells with cytoplasmic granules filled with keratin or lipids
- lipids are important for waterproofing and isolation of dead cells
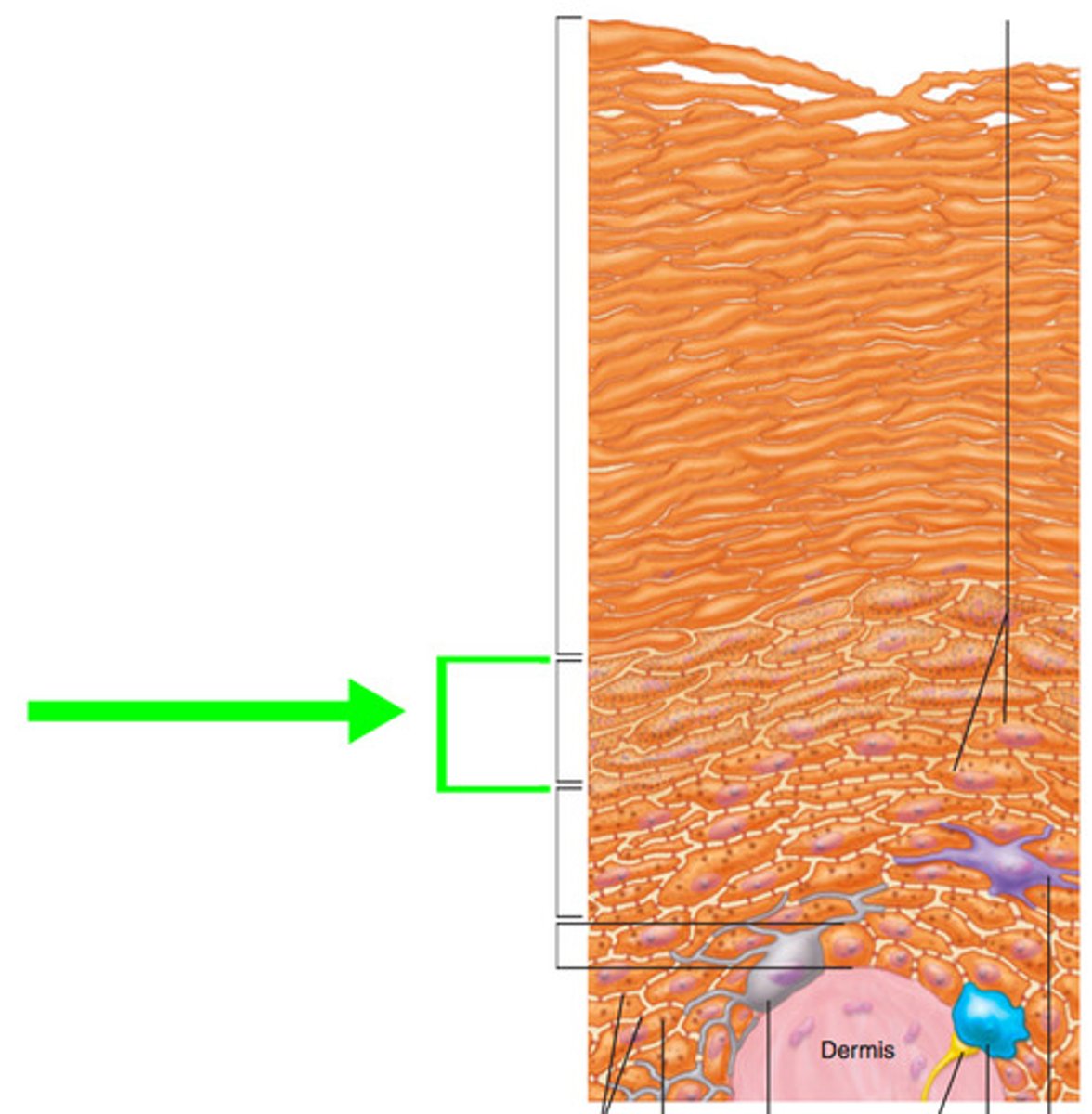
stratum lucidum
- epidermis layer of clear dead keratinocytes, but below stratum corneum
- only in thick skin
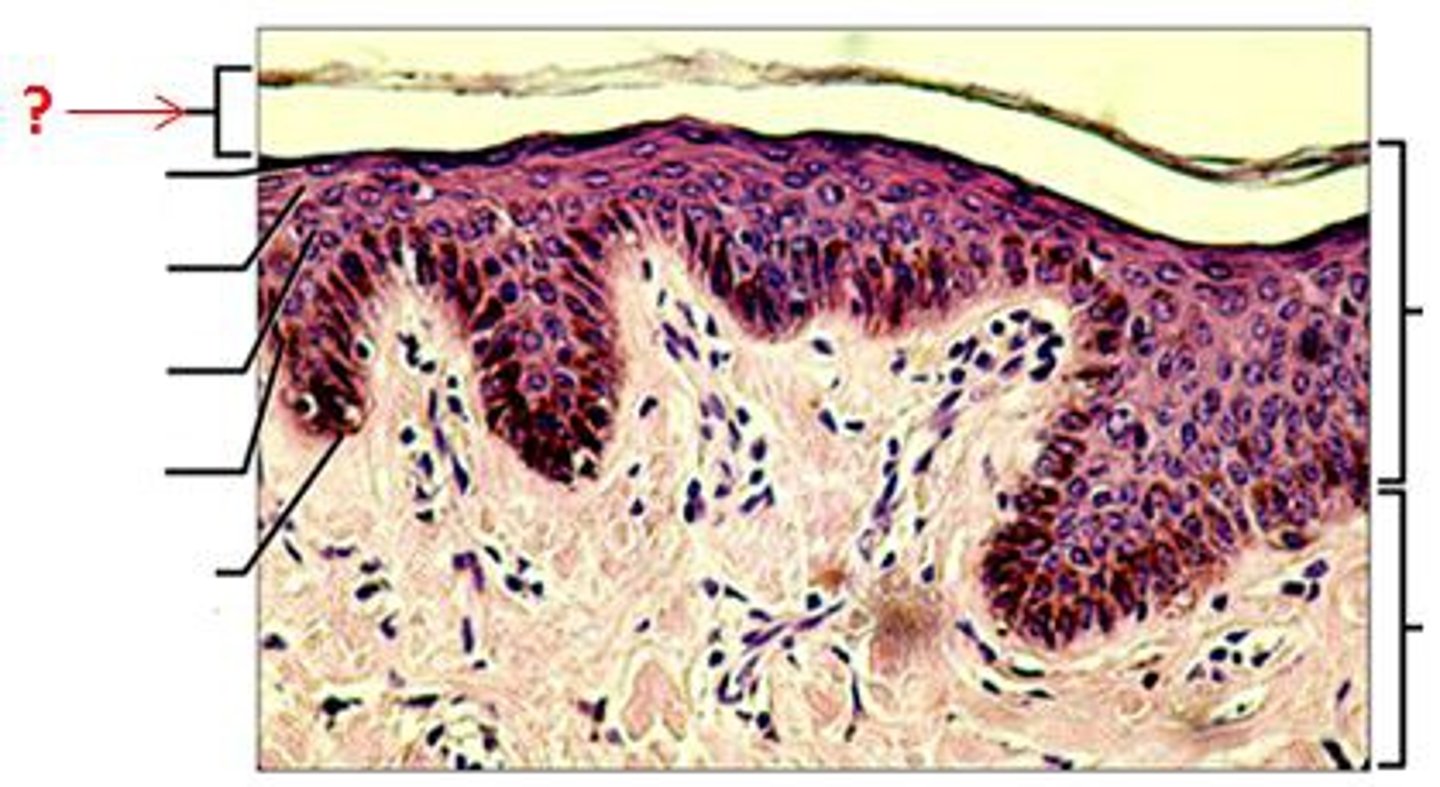
stratum corneum
- outermost epidermis layer
- corned
- dead cells that are all keratin and not much else
- exfoliated mechanically
three types of cells in epidermis other than keratinocytes
1) dendritic (langerhans) cells
2) merkel cells
3) melanocytes
describe life cycle of keratinocytes
- keratinocytes from lower layers pushed up through each epidermal layer until shed from stratum corneum
- takes 40-50 days for this to occur
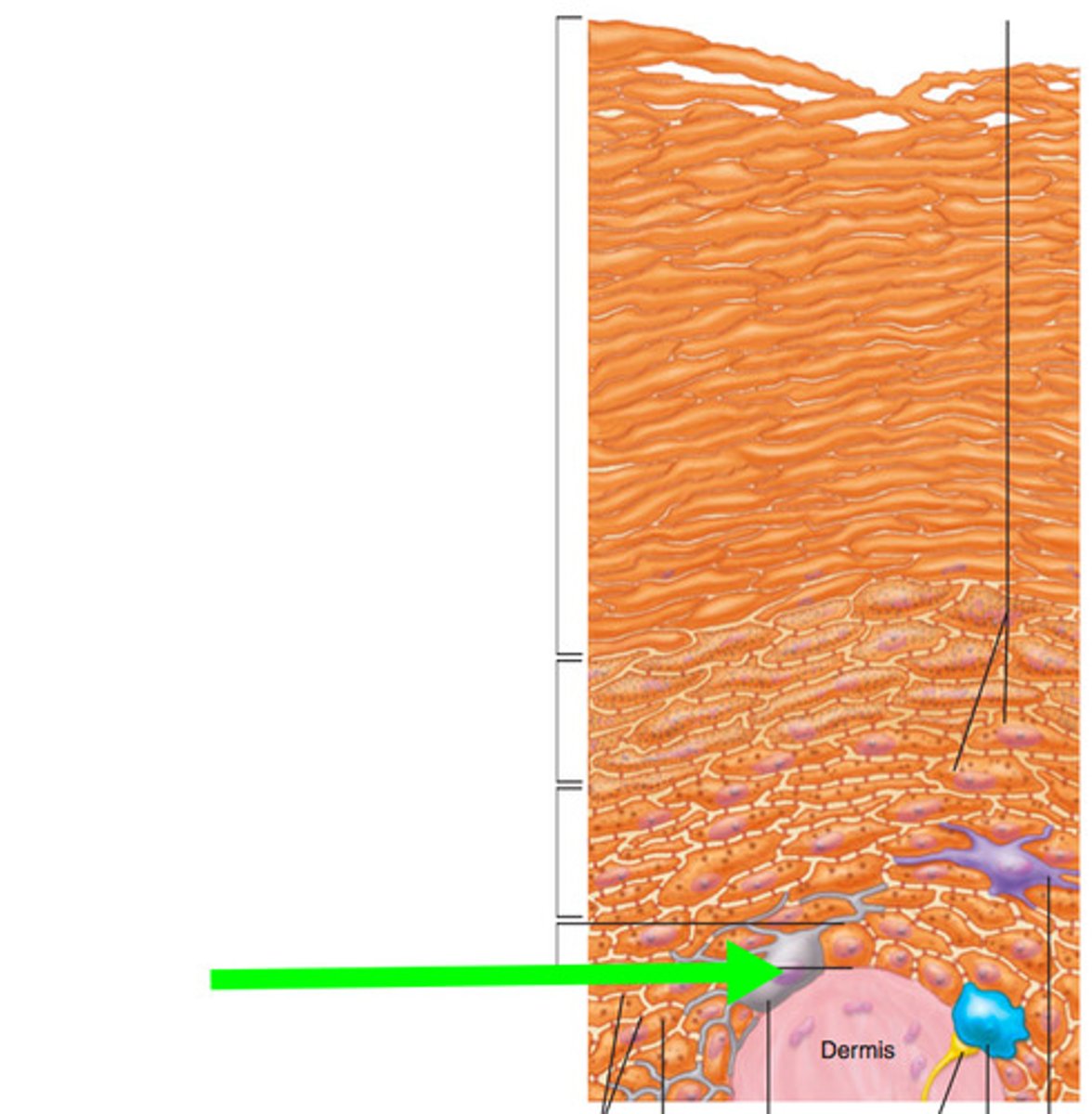
dendritic (langerhans) (astrocytes) cells
- phagocytes of immune system which protect skin and deeper tissues
- located in stratum spinosum
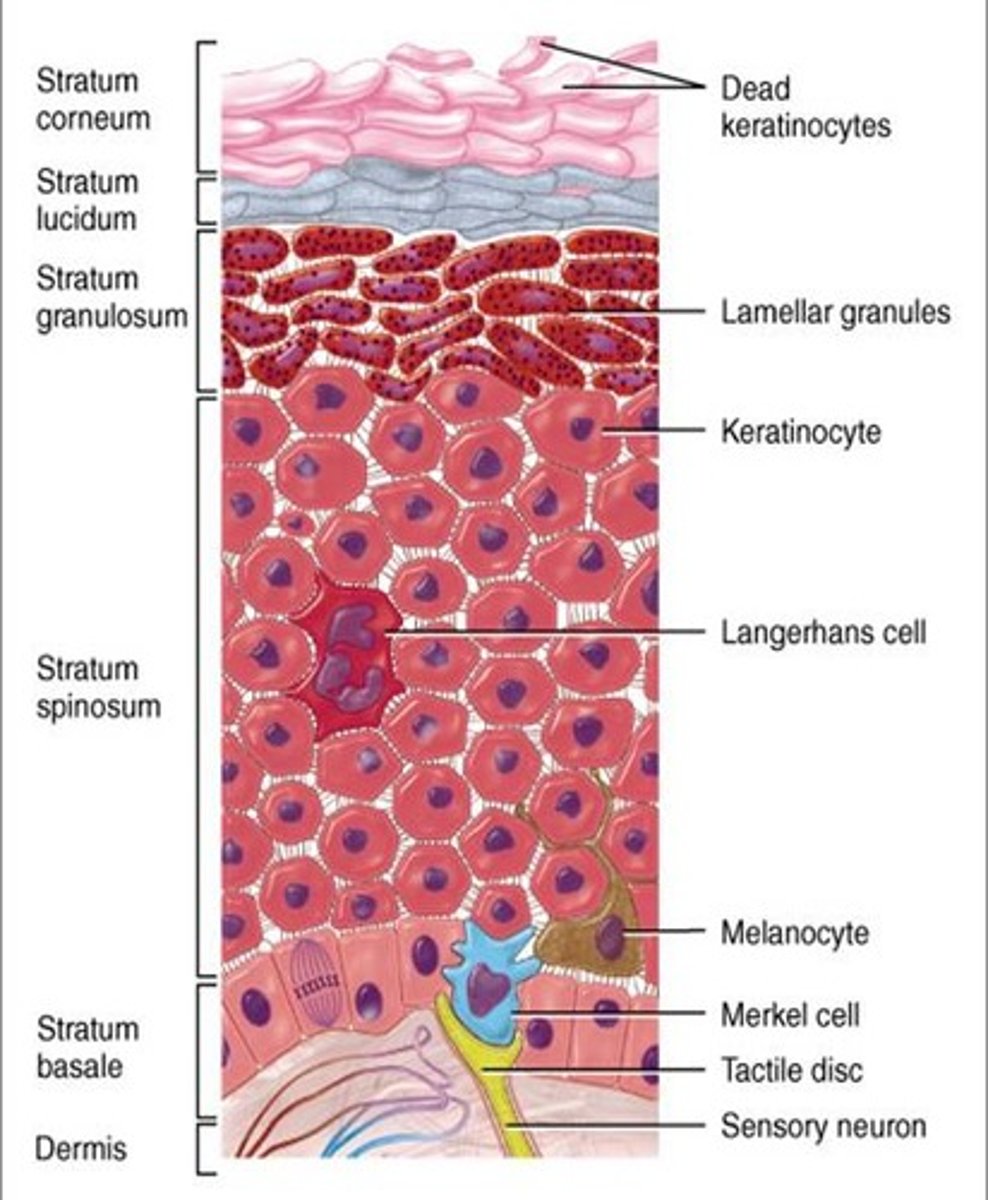
merkel cells
- sensory receptors associated with small neurons
- oval cells in stratum basale
- detect light touch and discriminate shapes and textures
- ton of them in touch regions: fingers lips, base of hairs
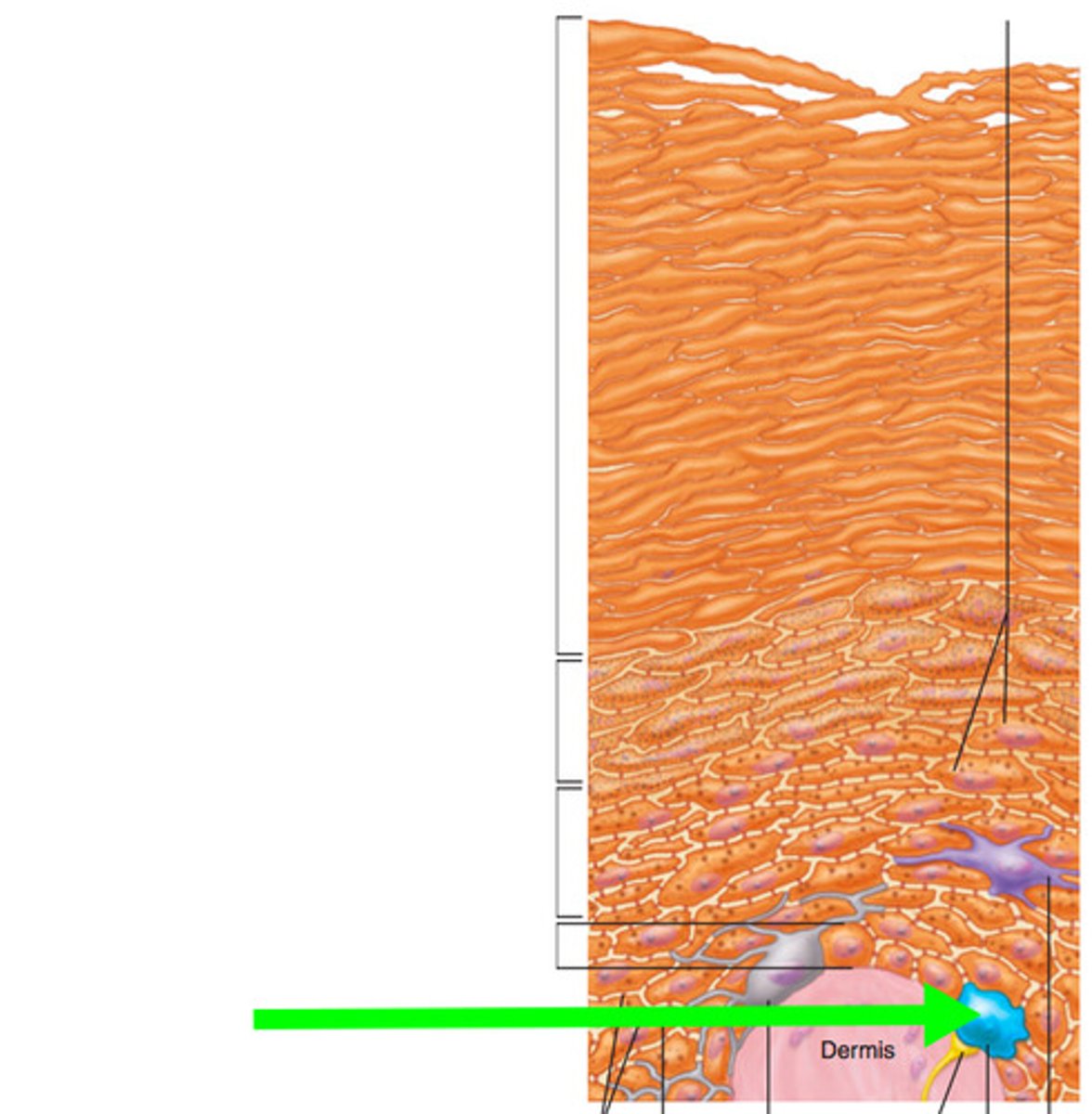
melanocytes
- located in stratum basale, they produce melanin the skin pigment
- ranges in color from orange-red to brown-black
thick skin
- about as thick as a paper towel with all five epidermal layers
- on areas with great deal of mechanical stress: palms, soles of feet
which epidermal layer is missing from thin skin
- stratum lucidum is missing
- about as thin as printer paper
callus
additional layers of stratum corneum built up in response to repetitive pressure
three functions of dermis
1) blood supply for epidermis
2) sensory receptors
3) anchors epidermis in place
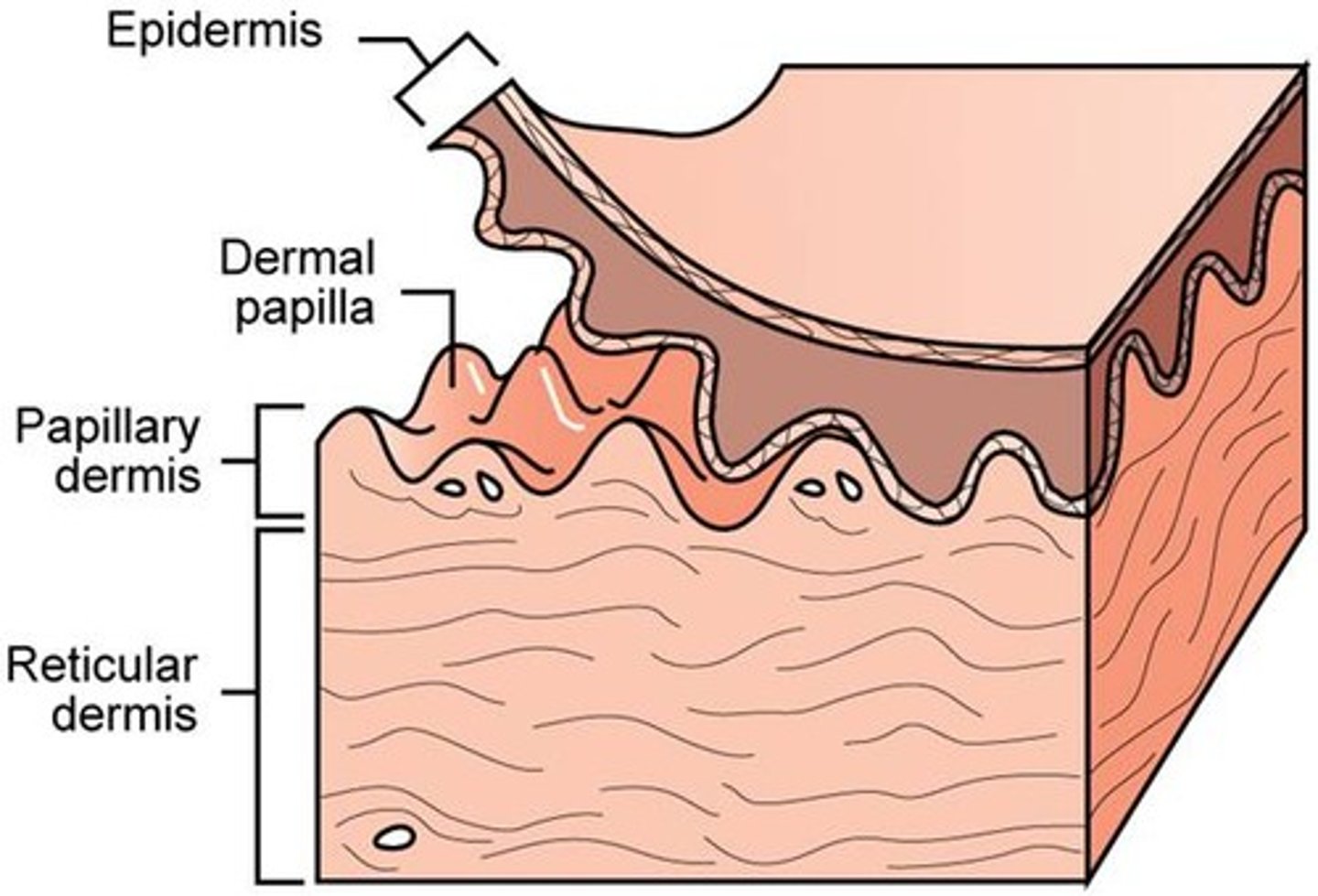
two layers of dermis
1) papillary layer
2) reticular layer
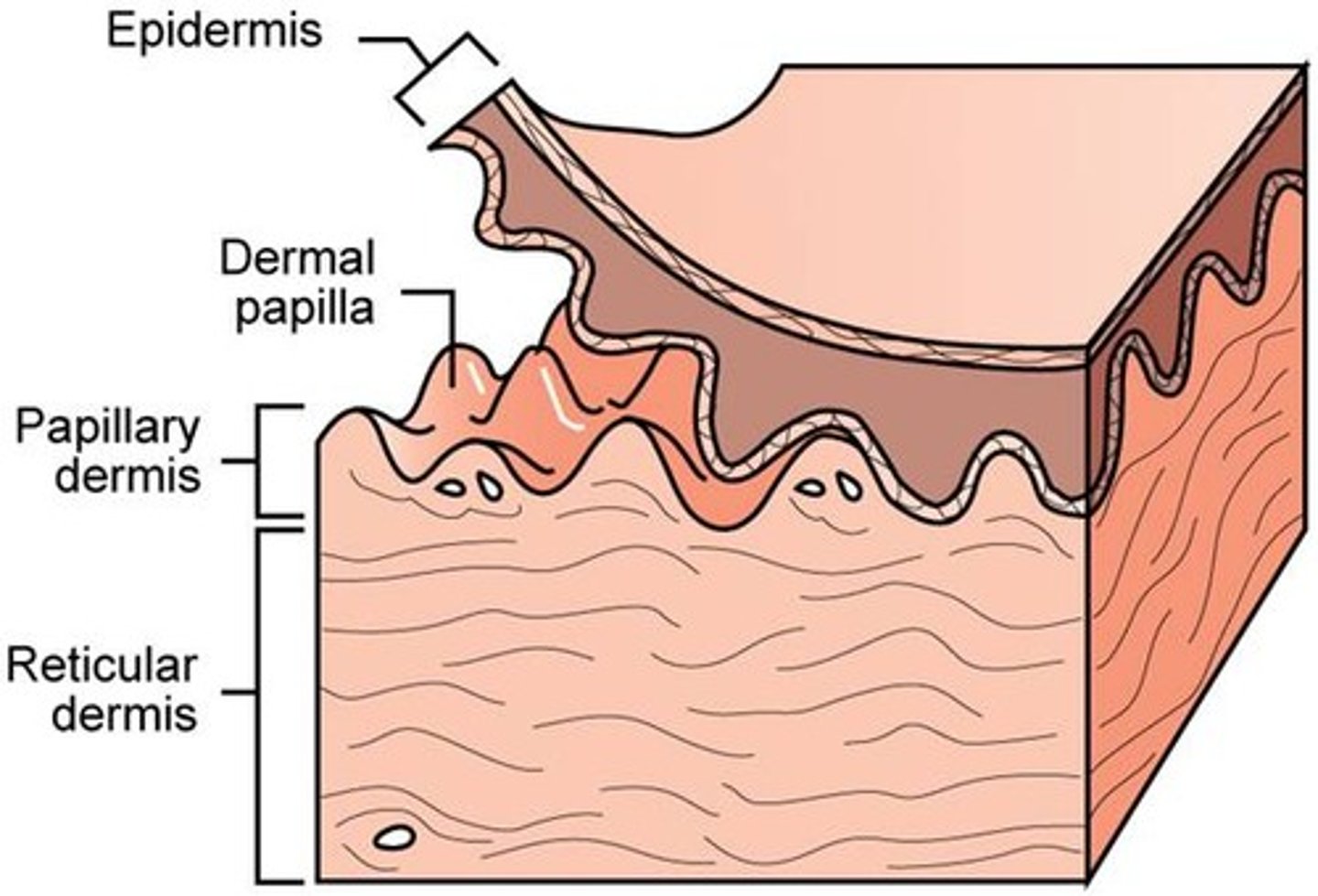
papillary layer
- thinner layer of dermis
- loose connective tissue
- collagen fibers are fond in this layer at the dermis-epidermal junction
- anchors dermis to epidermis
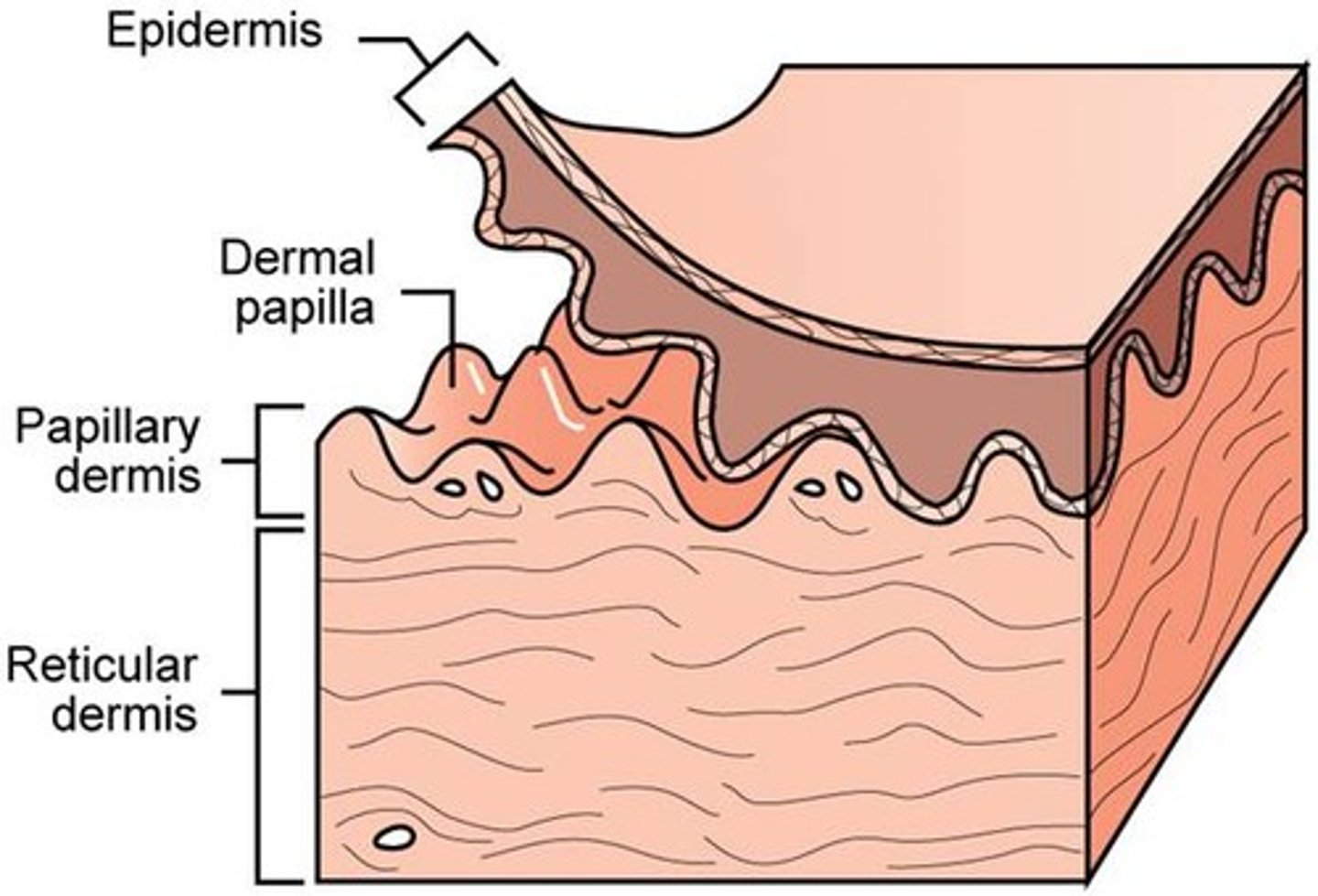
dermal papillae
- tiny projections in surface of papillary layer
- contains capillaries that allow oxygen to diffuse into ECF of dermis and then to avascular epidermis
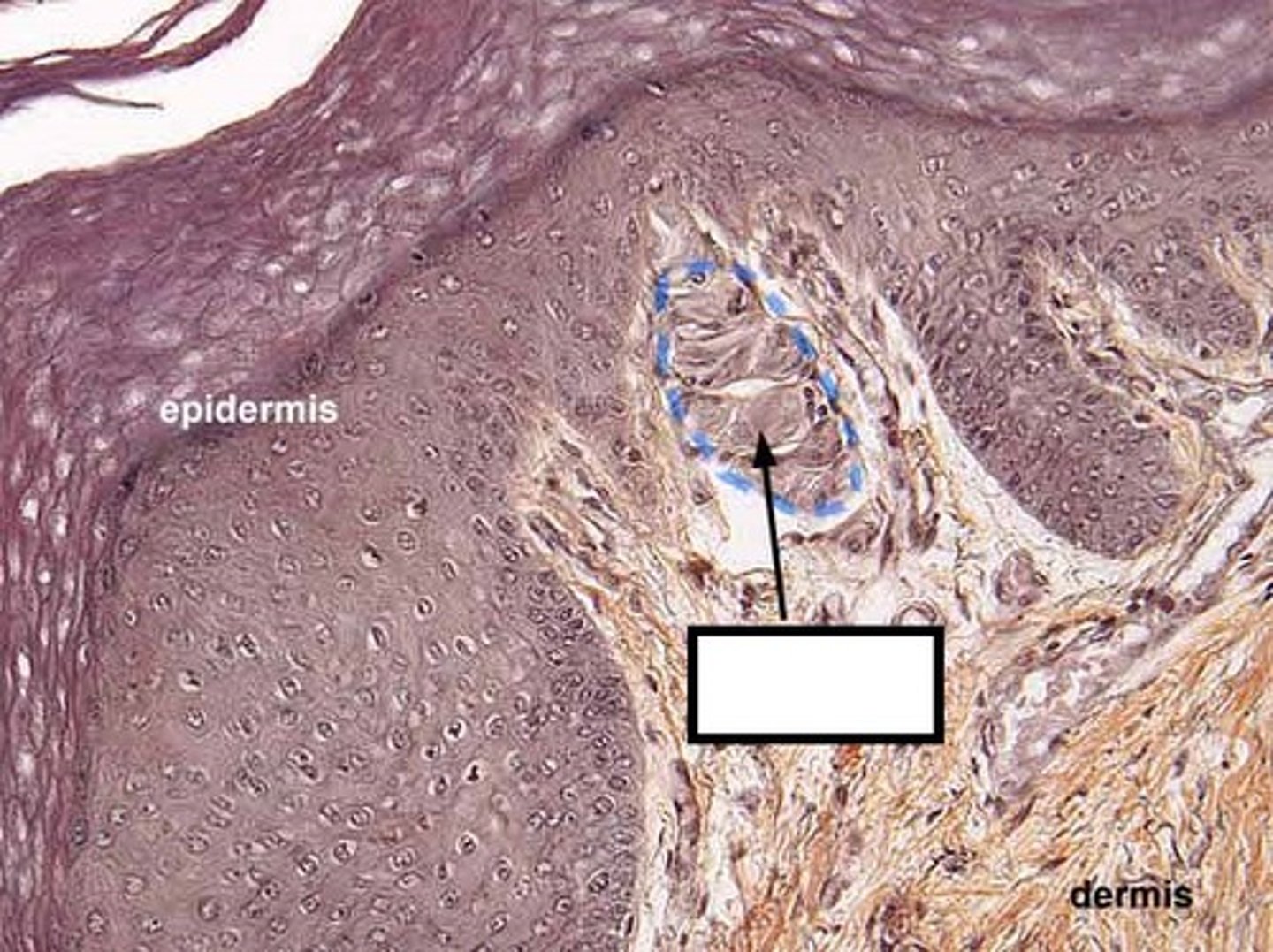
tactile (meissner) corpucles
- sensory receptors that respond to light touch
- found in dermal papillae in dermis
- in skin of fingertips, lips, face, external genitalia
reticular layer
- deeper thicker layer of dermis
- mostly dense irregular connective tissue
- contains collagen bundles and elastic fibers
- rich in proteoglycans that draw water to keep skin firm and hydrated
- also includes blood vessels, sweat glands, hairs, sebaceous glands, adipose
lamellated (pacinian) corpuscles
- sensory receptors in reticular layer of dermis
- respond to changes in pressure and vibration in skin
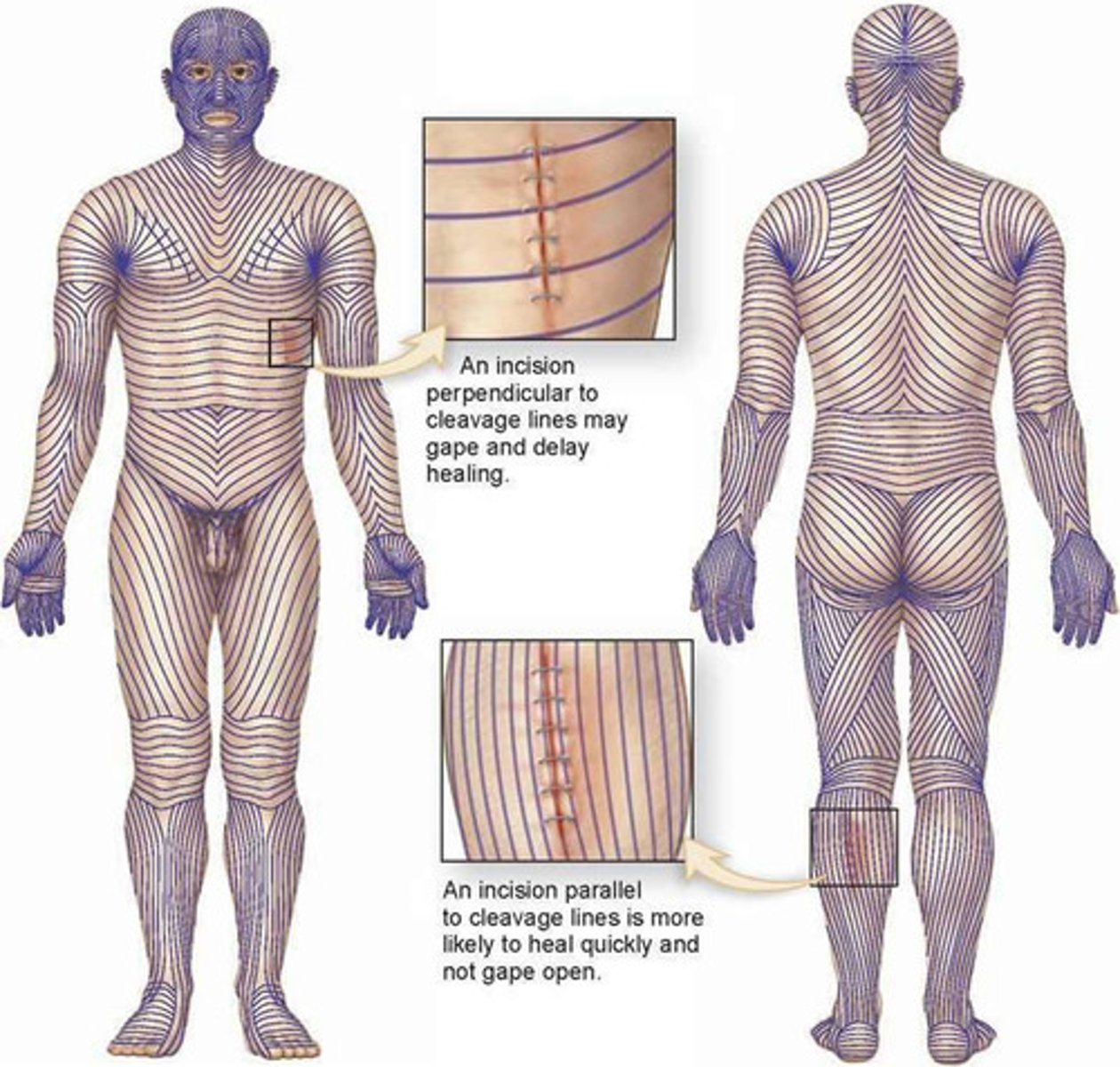
skin markings
- small visible lines created by interaction between dermis and epidermis
- best seen in thick skin of palms and soles of feet
cause of dermal ridges
dermal papillae are more prominent due to thick collagen bundles
- creates epidermal ridges (fingerprints!)
3 types of epidermal ridge patterns
1) loops
2) whorls
3) arches

two types of skin markings created by reticular layer
1) cleavage lines
2) flexture lines - around joints
melanin
protein pigment, orange-red to brown-black
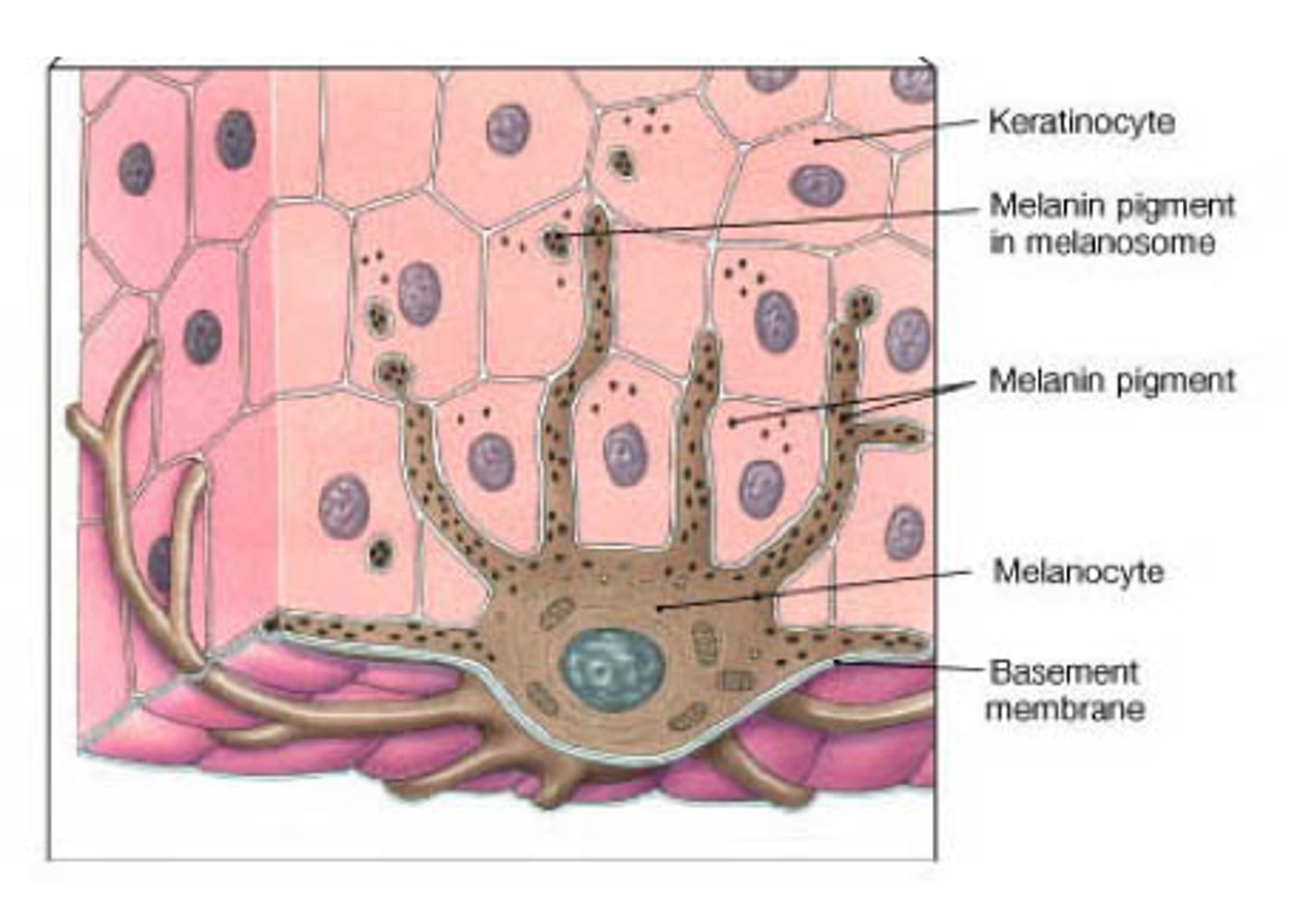
components of melanin
two molecules of amino acid tyrosine bonded by reactions catalyzed by enzyme tyronsinase
tyrosine
amino acid that composes melanin
tyrosinase
enzyme that catalyzes reactions that bond tyrosine to make melanin
melanosome
vesicle where melanin is synthesized
primary purpose of melanin
protect keratinocyte DNA from mutations induced by UV radiation
secondary function of melanin
- reduce synthesis of vitamin D in response to UV radiation resulting in less calcium ion absorption and maintenance of calcium ion homestasis
theory on lighter and darker skin
dark skin maybe to prevent excess vitamin D, light skin to encourage more vitamin D
melanocytes on palms and soles of feet
fewer melanocytes mean lighter skin
number of melanocytes in different people
- identical in all individuals irrespective of skin color
- differences in skin tones are due to difference in tyrosinase ctivity and type (color) of melanin produced
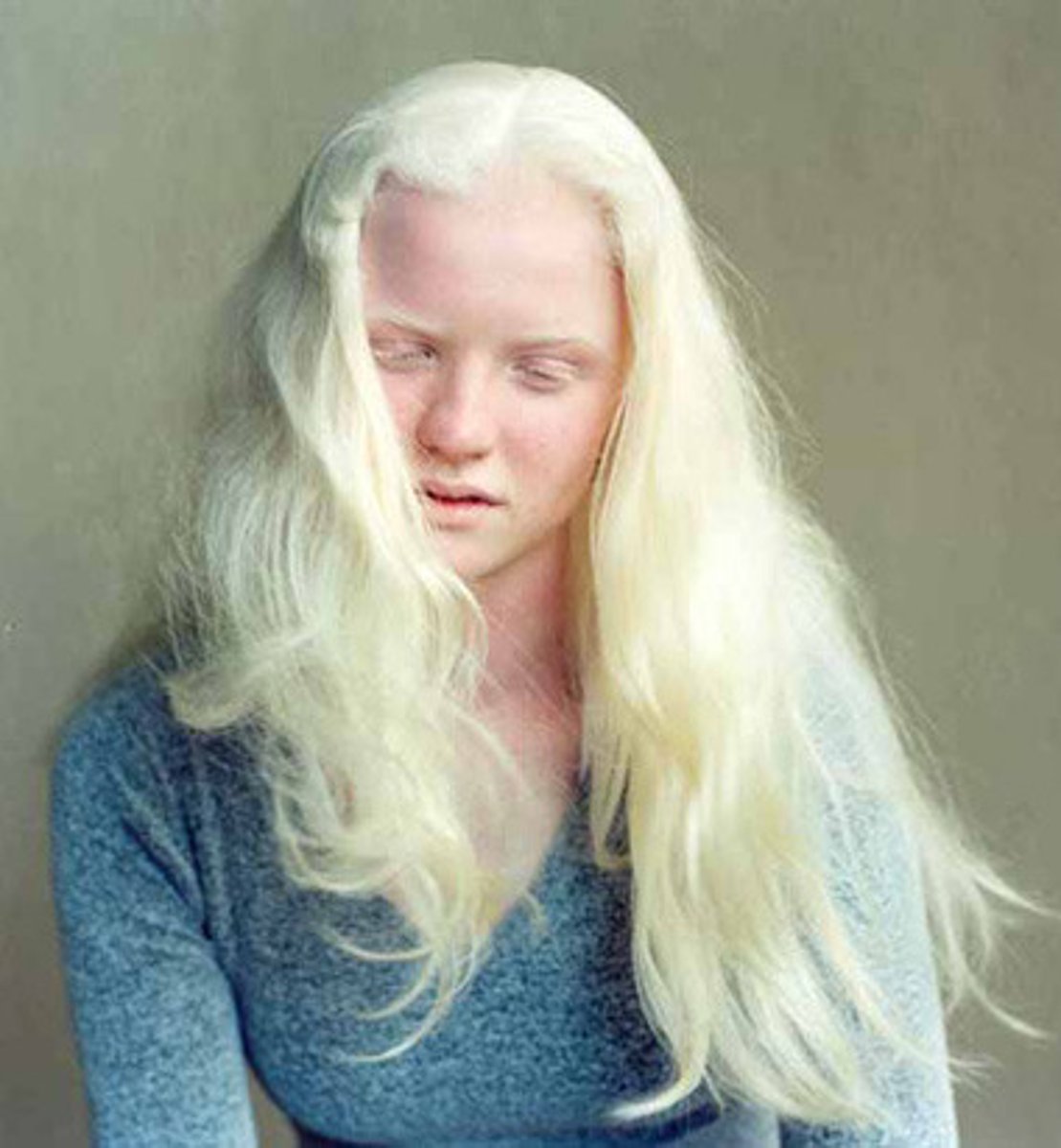
albinism
failure to manufacture tyrosinase resulting in lack of pigmentation

mole (nevus)
area of increased pigmentaiton due to a local proliferation of melanocytes, not an increase in melanin production
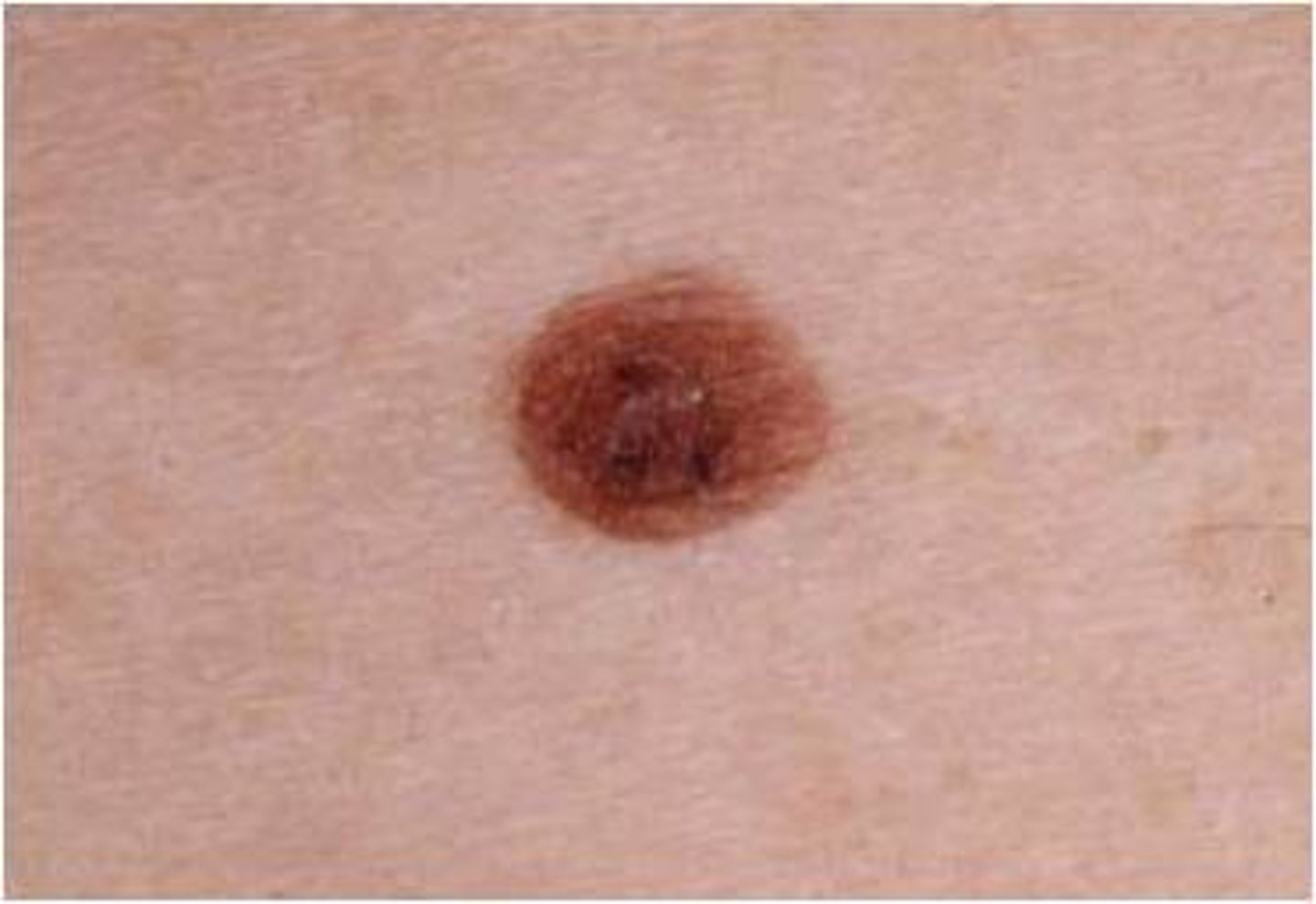
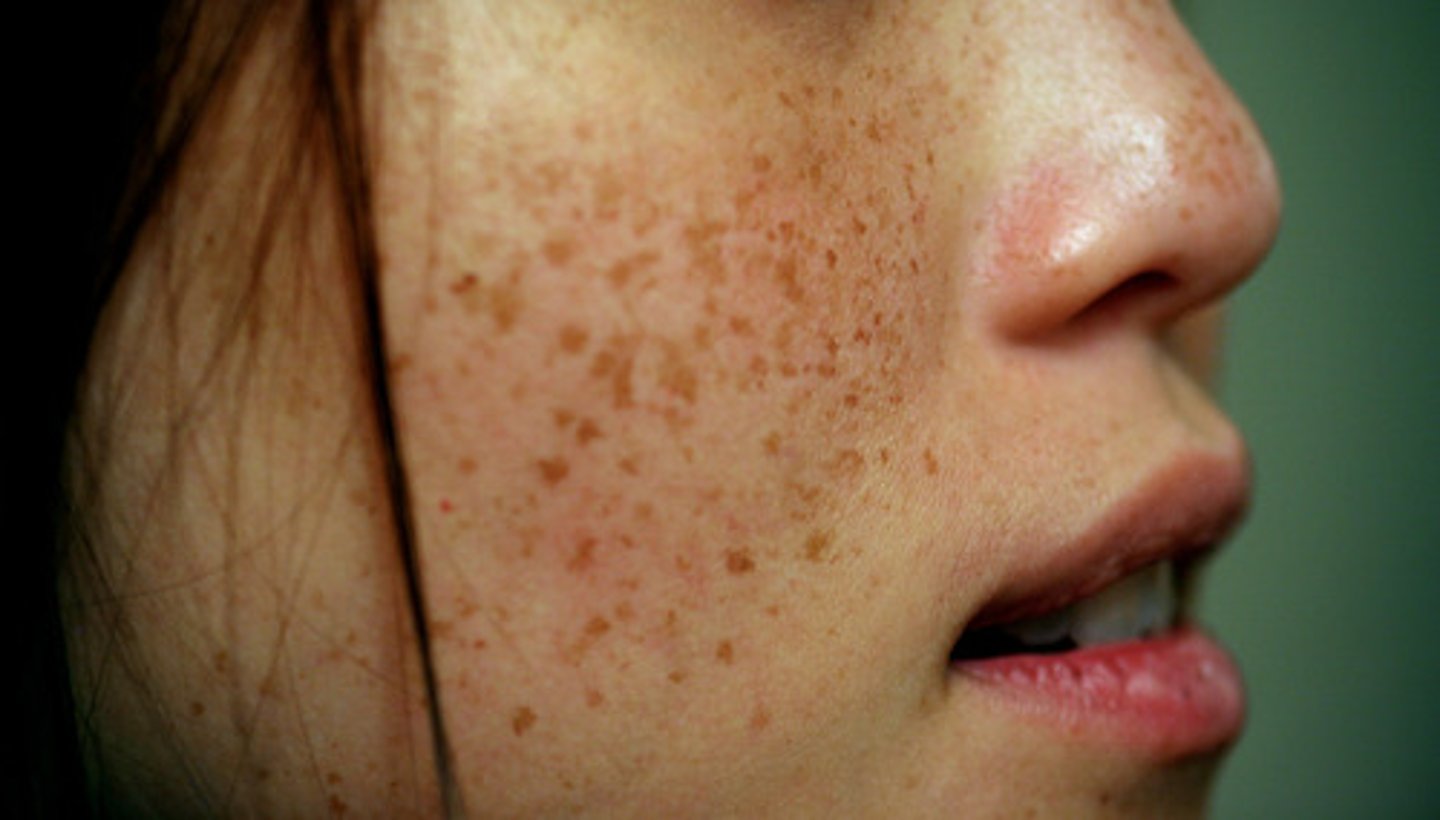
freckle
small area of increased pigmentation from increased melanin production in a localized spot
two other pigments that affect skin pigmentation
1) carotene
2) hemoglobin
carotene
- yellow-orange pigment
- lipid soluble molecule that accumulates in stratum corneum
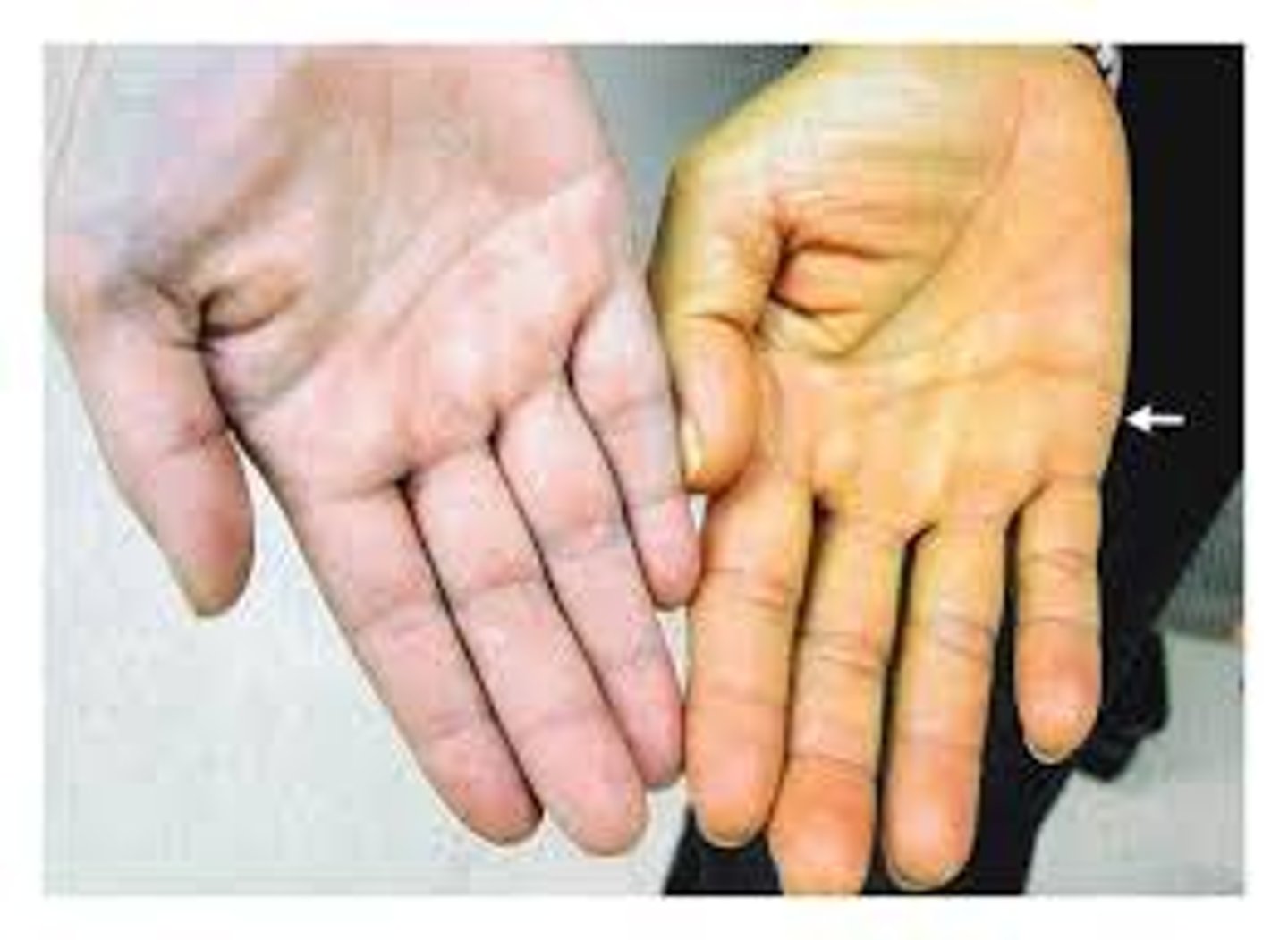
hemoglobin
- found in red blood cells, it transports oxygen
- oxygen binds to iron giving it a bright orange-red color
- affects skin color in areas of increased blood flow
erythema
- color change to be more reddish when blood flow increases in dermis
- regular response to exercise
- also response to trauma, fever, infection
pallor
- color change due to decreased blood flow in dermis resulting in loss of pinkish hue
- response to cold environment
-
cyanosis
- color change resulting from low hemoglobin levels in blood in dermis
- blood turns reddish purple and skin becomes bluish
- also if hemoglobin can't bind to oxygen
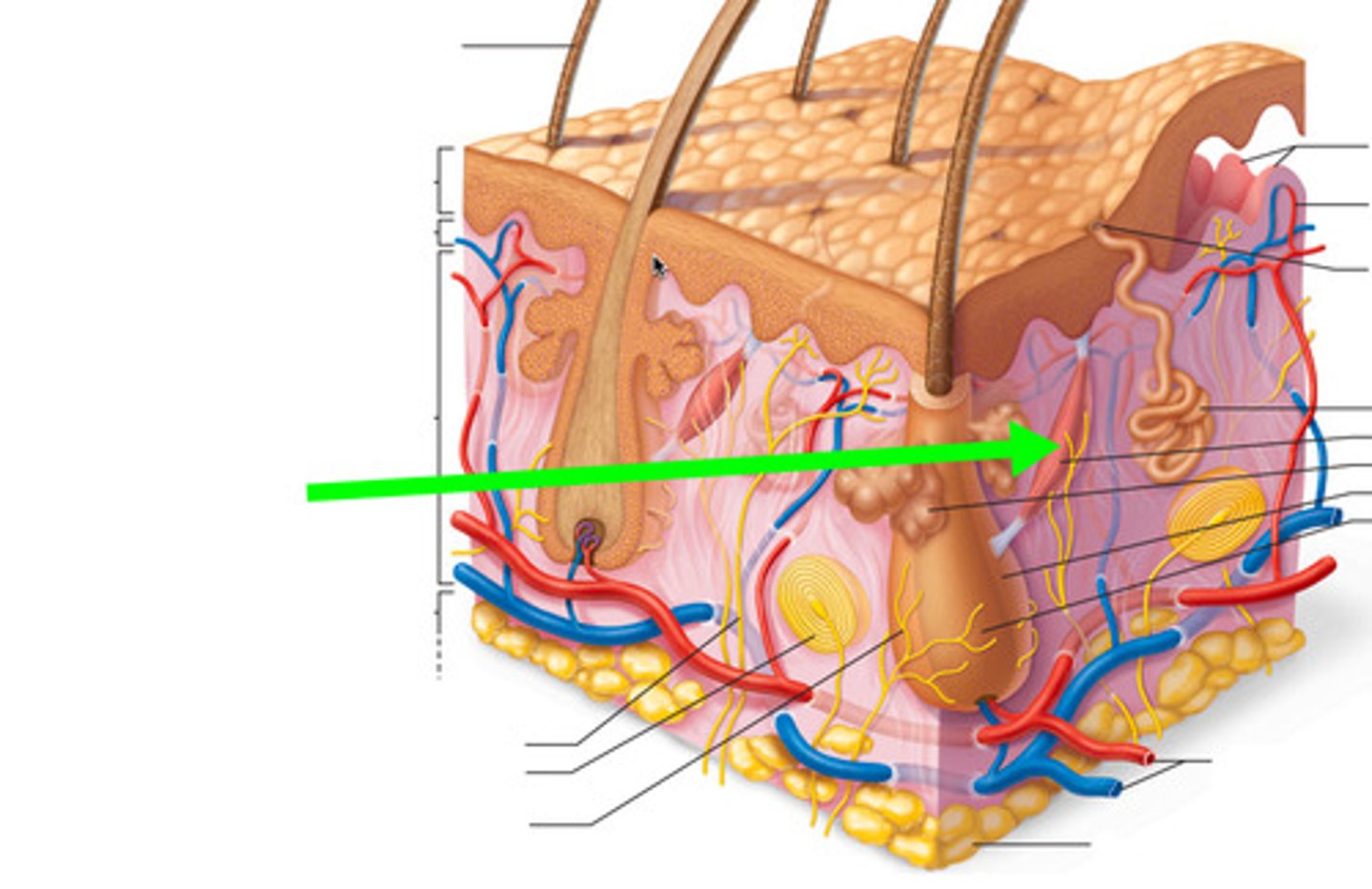
three accessory structures of integument
1) hair
2) nails
3) glands
these are derived from epithelium only
functions of hair (pili)
- protects by preventing subsances and organisms from entering eyes and nose
- protects skin from UV radiation and mechanical trauma
- associated with small sensory neurons that detect changes in environment
- too sparse in humans to affect thermoregulation
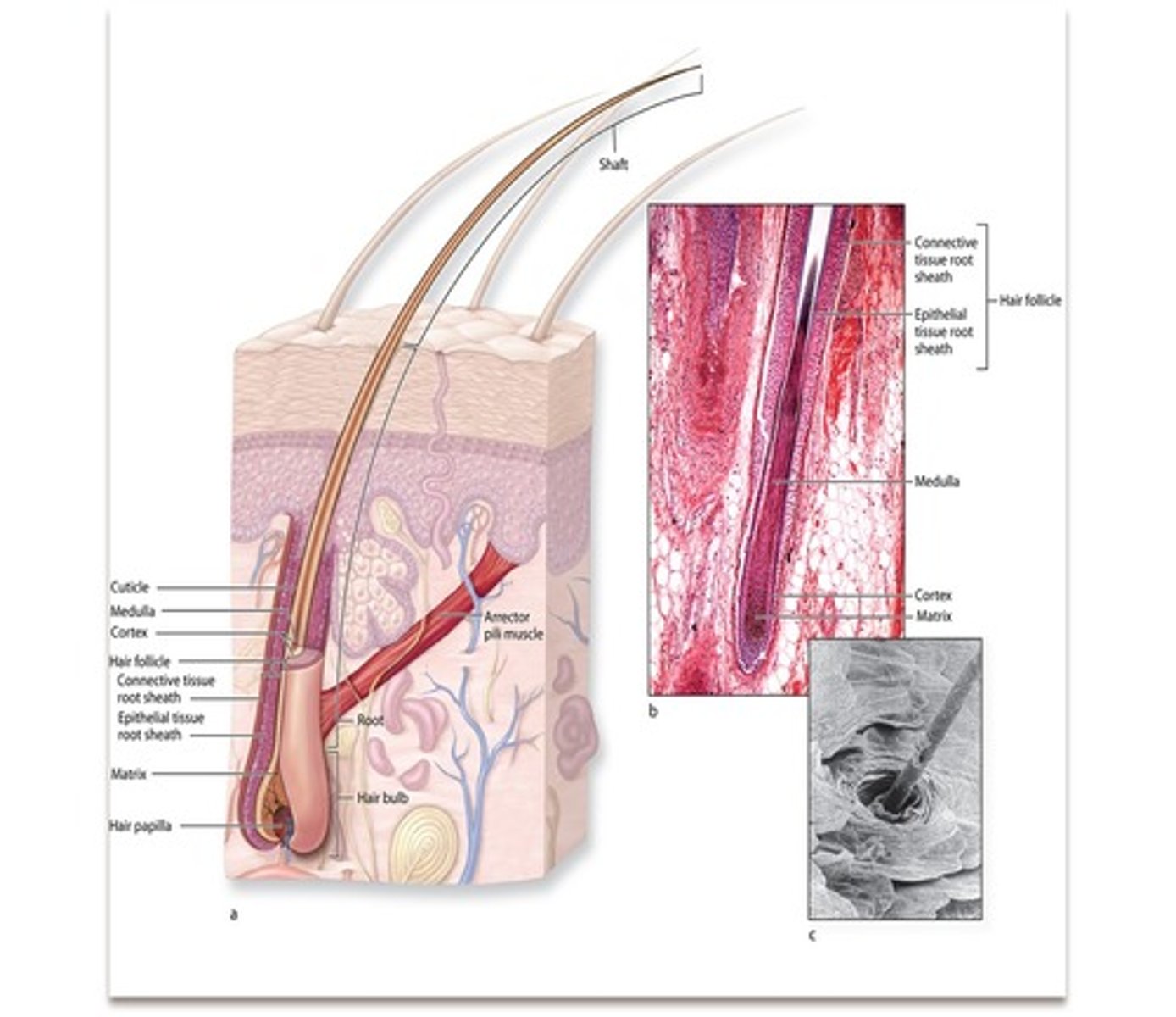
two main parts of hair
1) shaft
2) root
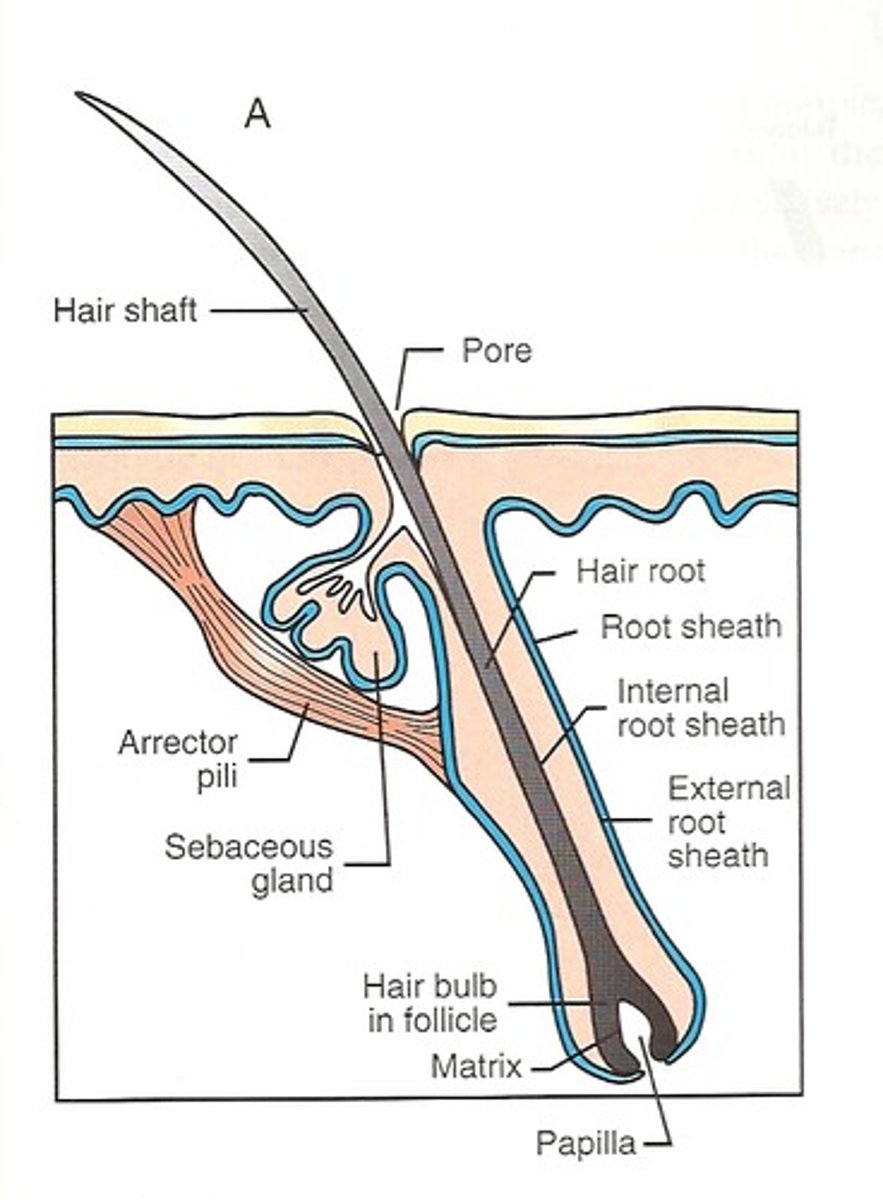
hair papilla
combined with root, known as hair bulb
composition of hair shaft
columns of dead keratinized epithelial cells
composition of hair root
- part of hair embedded in dermis
- surrounded by sensory neuron
- indented at its base by blood vessels called hair papilla
hair bulb
hair root + hair papilla
matrix
at base of root, kertainocytes that actively divide
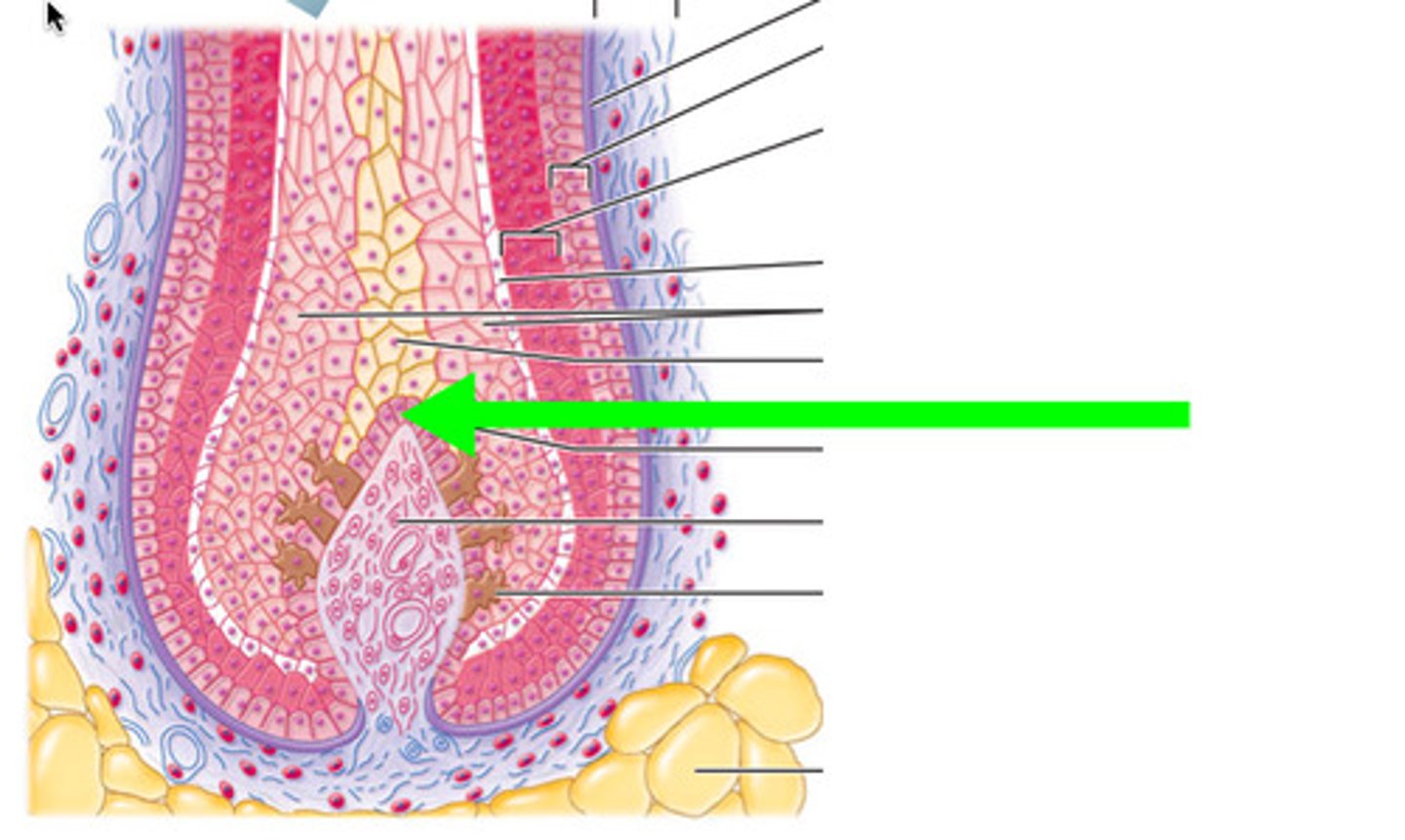
epithelial root sheath
- infolding of the epidermis which extends down into the dermis and hypodermis
- makes up the hair follicle
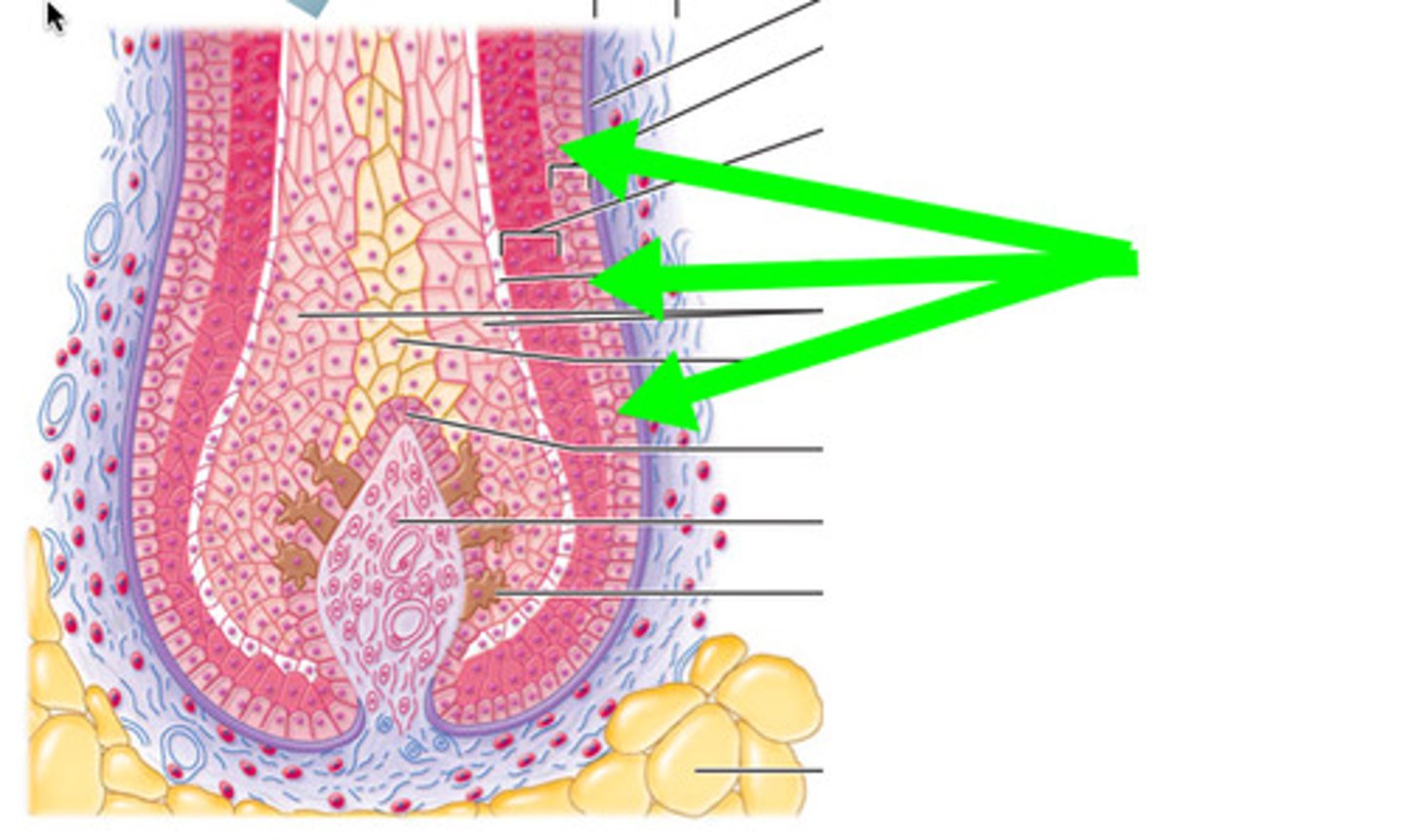
three visible regions in a transverse section of a hair strand
1) inner medulla
2) middle cortex
3) outermost cuticle
dermal root sheath
connective tissue that surrounds the follicle and separates it from the dermis
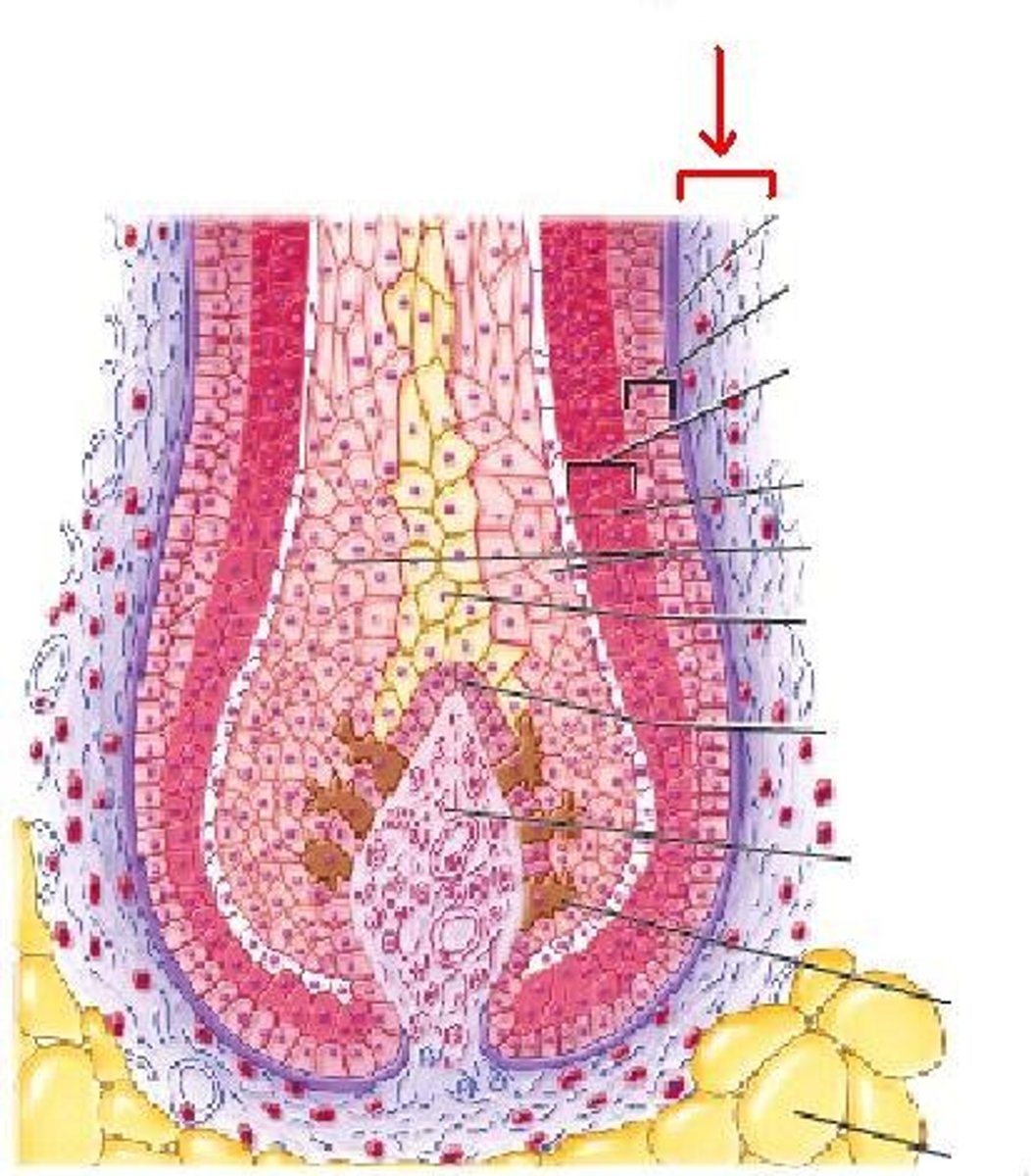
arrector pili muscles
small bands of smooth muscles attached to dermal root sheath and dermal papillary layer
piloerection
when hair stands up because of contraction of arrector pili muscles. causes goosebumps

average hair growth
- about 1-1.5cm per month
- varies between individuals
- not continuous
two stages of hair growth
1) growth stage - mitosis happens in matrix and are pushed further away
2) resting stage - mitosis in matrix ends, follicle shortens and hair is pushed toward surface
composition of nails
made of stratified squamous epithelial cells filled with hard keratin
structure of nail plate and nail bed
nail plate - sits on top of nail bed
nail body - visible part of nail plate
nail root - under the skin where the nail matrix is
nail matrix - newly dividing cells
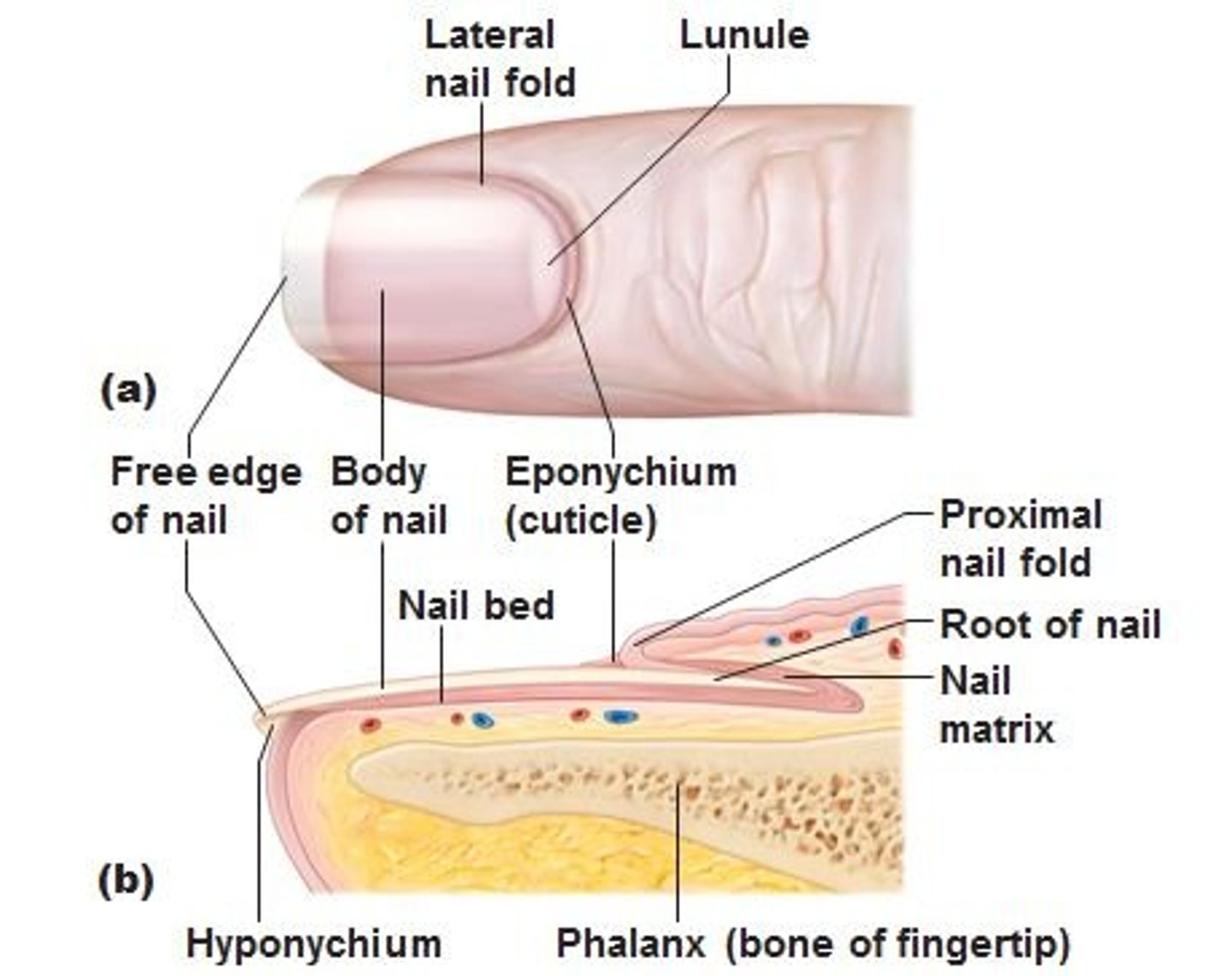
folded regions of skin surrounding nail plate
proximal nail fold
distal nail folds
eponychium
cuticle, consists only of stratum corneum
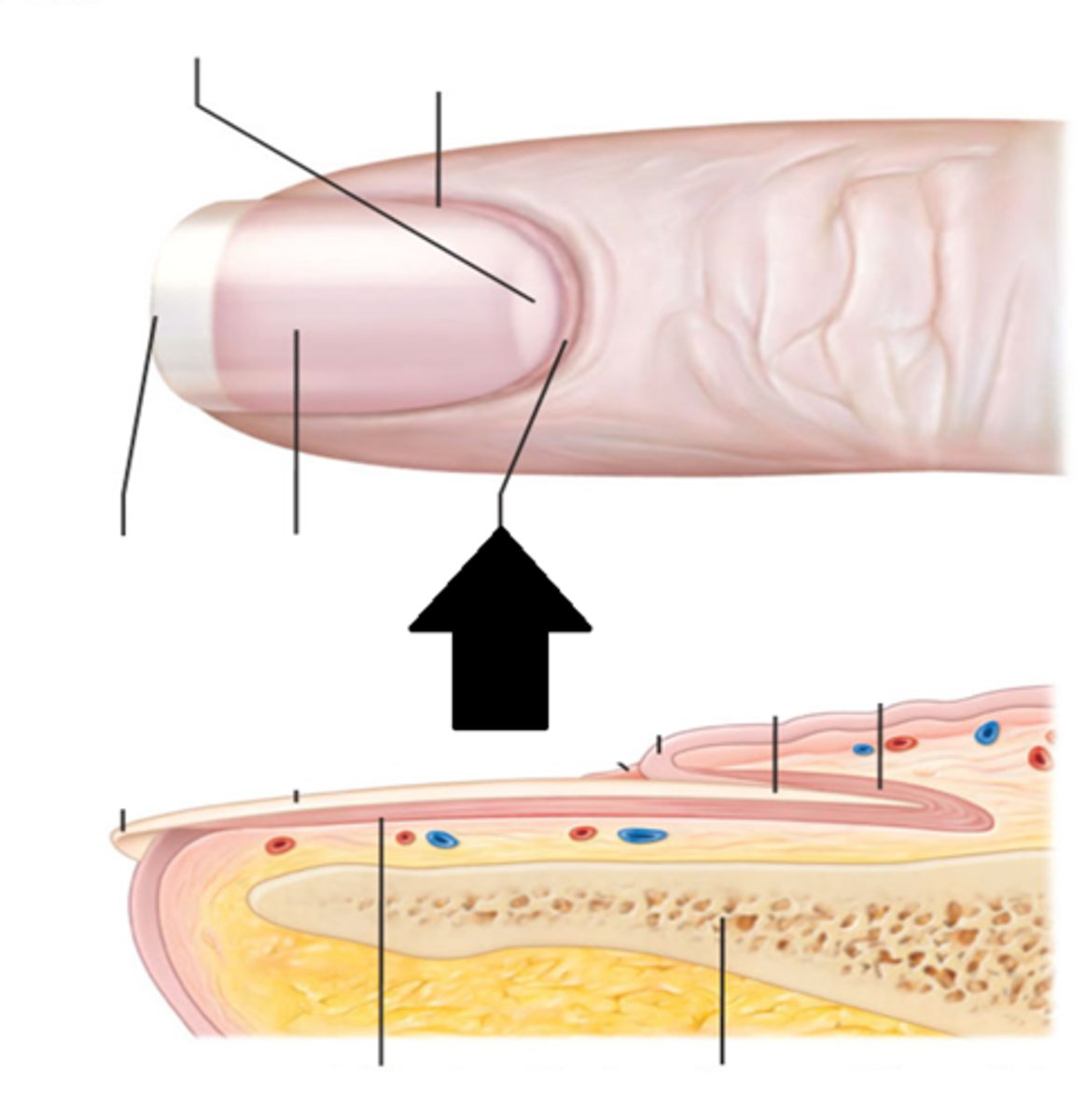
hyponychium
stratum corneum underlying nail bed on free edge of nail plate
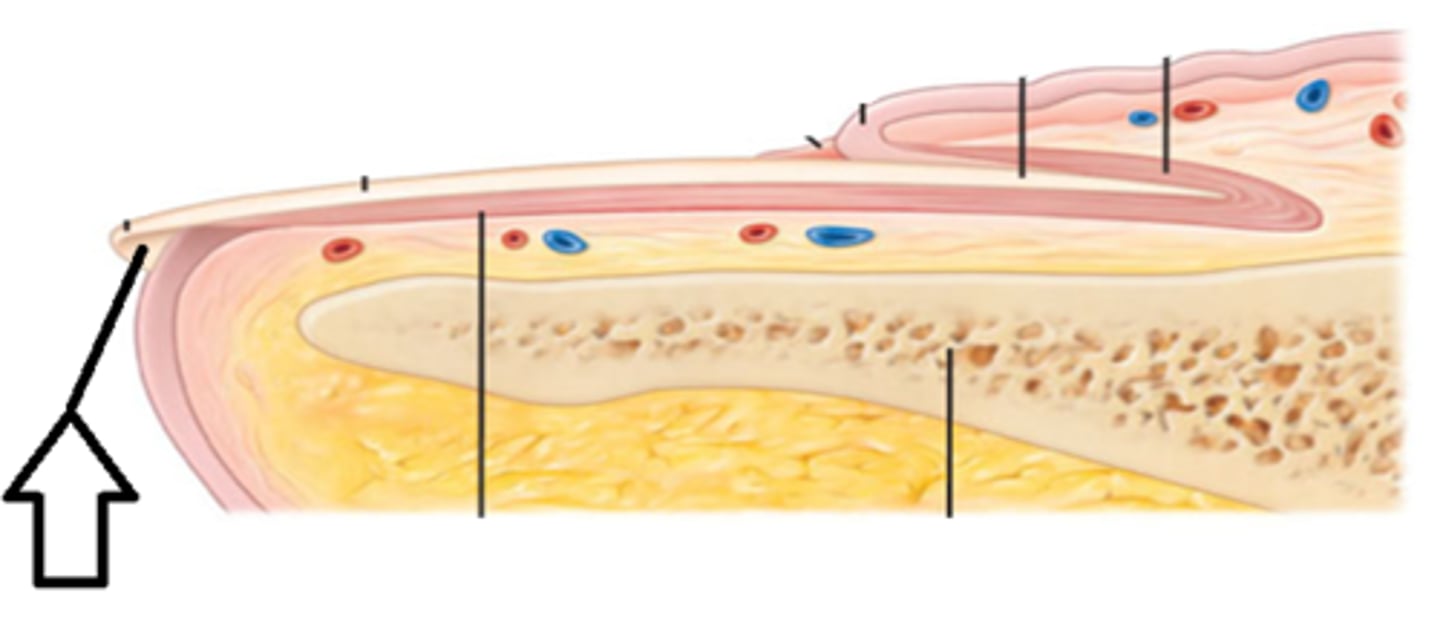
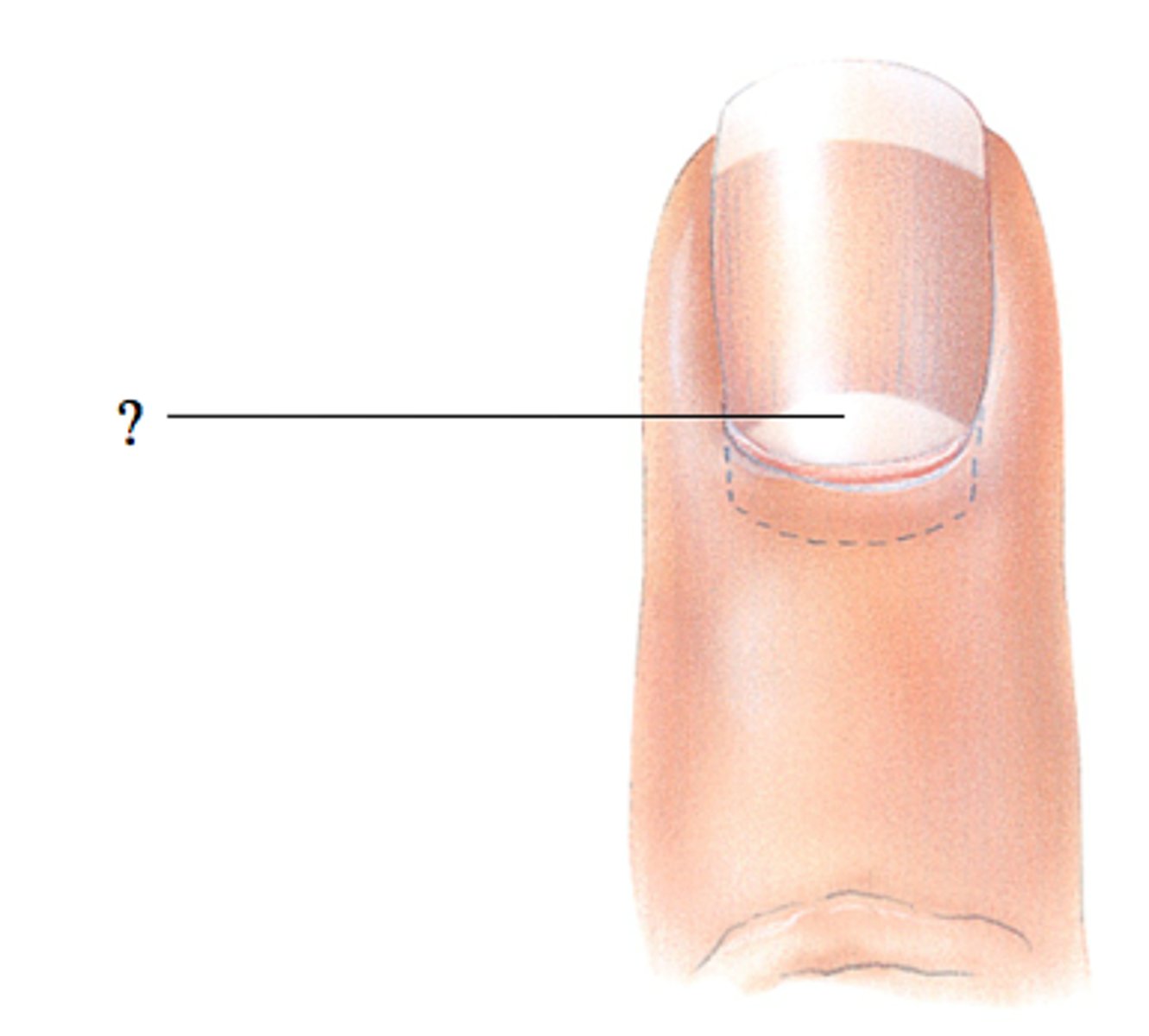
lunula
half mooned shaped region of proximal nail plate that represents an acculation of keratin
nail growth
finger nails grow .5mm per week. toe nails more slowly
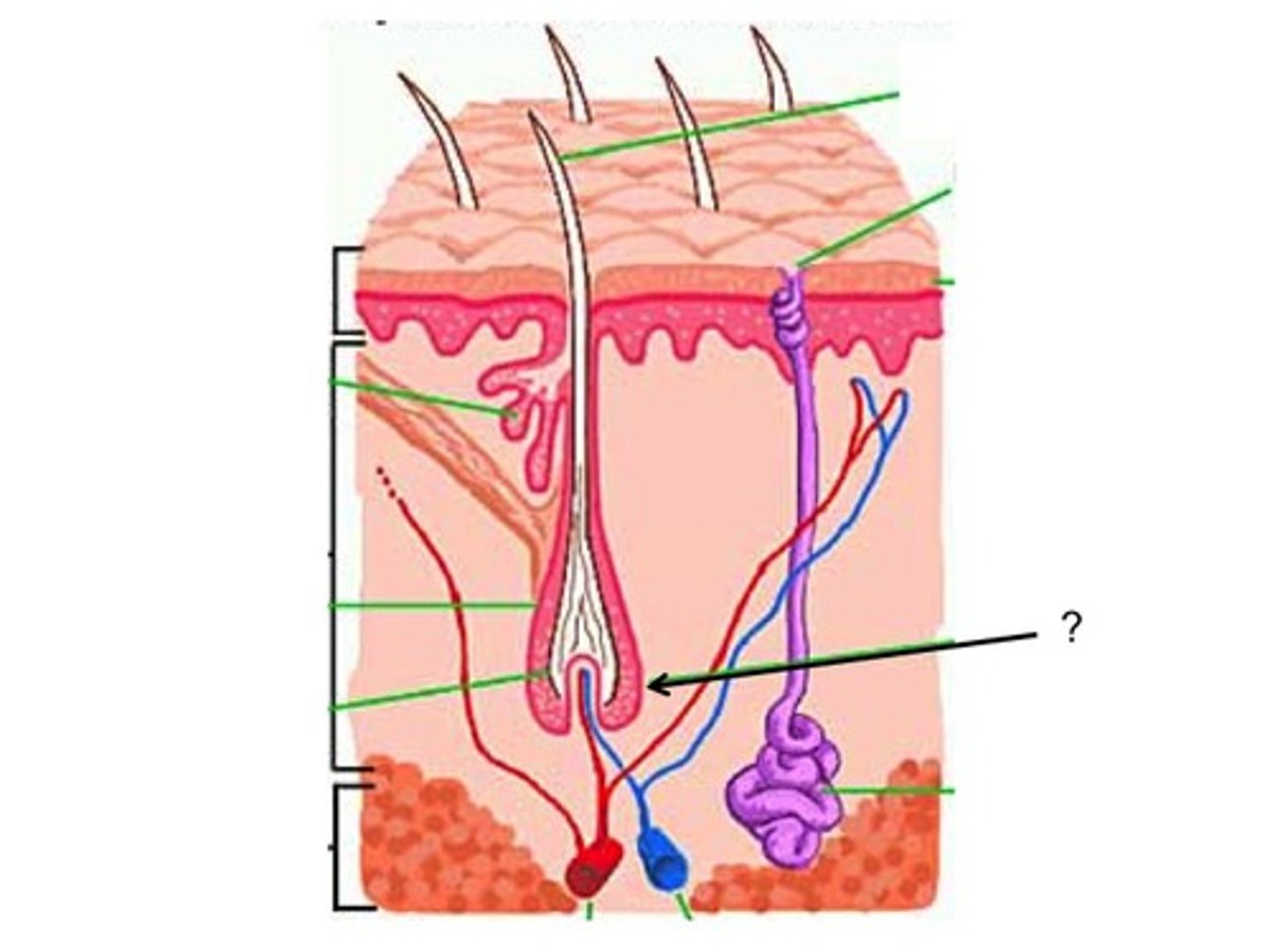
two basic types of glands
1) sweat (sudoriferous)
2) sebaceous - produce oily sebum
four types of sweat glands
1) eccrine
2) apocrine
3) ceruminous
4) mammary
what kind of secretion in sweat glands
merocrine exocytosis NOT holocrine
eccrine sweat glands
- most prevalent type
- coiled glands found in dermis
- small amount of excretion through
- goes through duct to a sweat pore
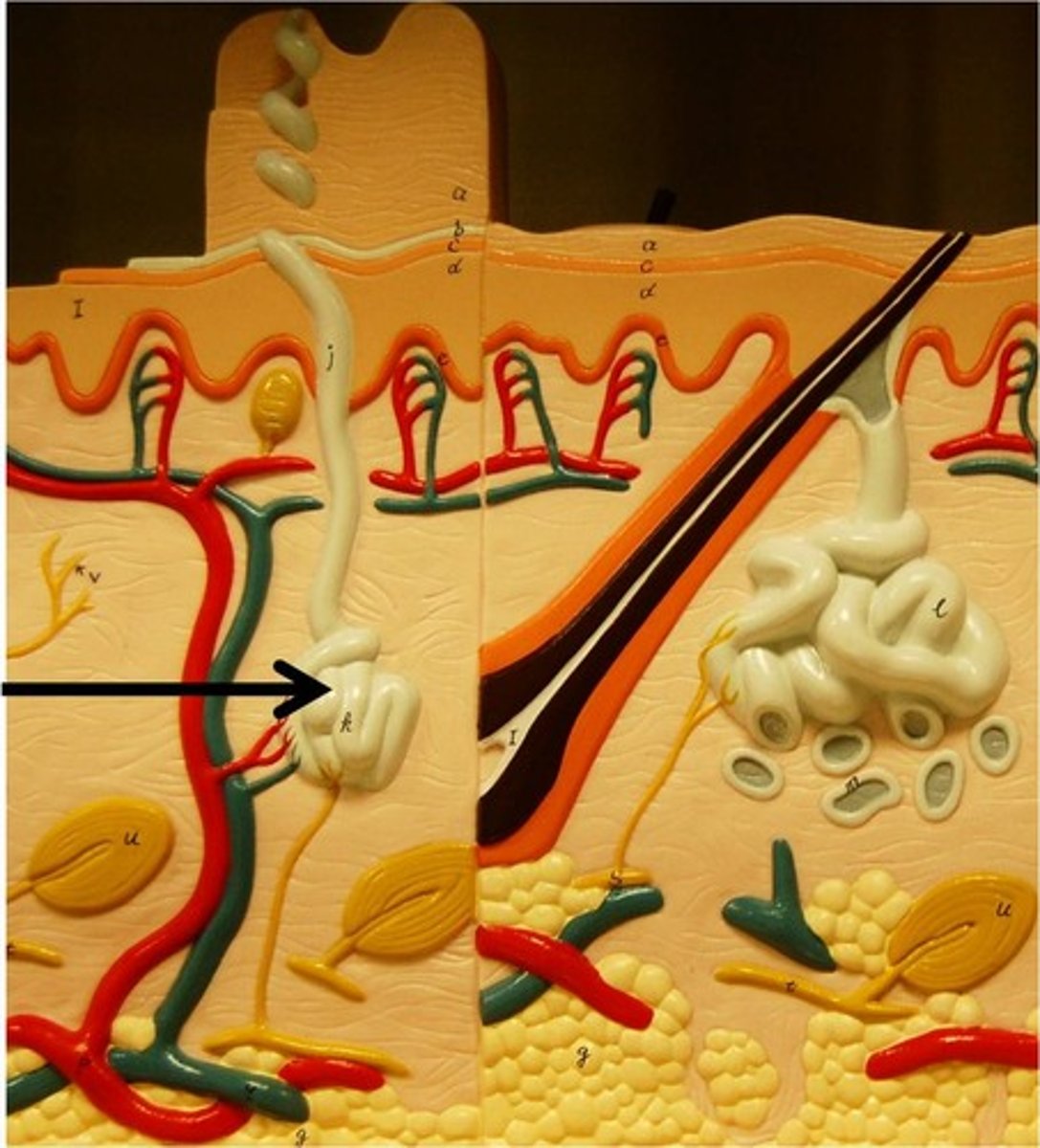

apocrine sweat glands
- only found in axillae, anal area, and areola
- releases protein rich secretion into a hair follicle
- can become odiferous once skin bacteria metabolize them
- influenced by sex hormones, active after puberty
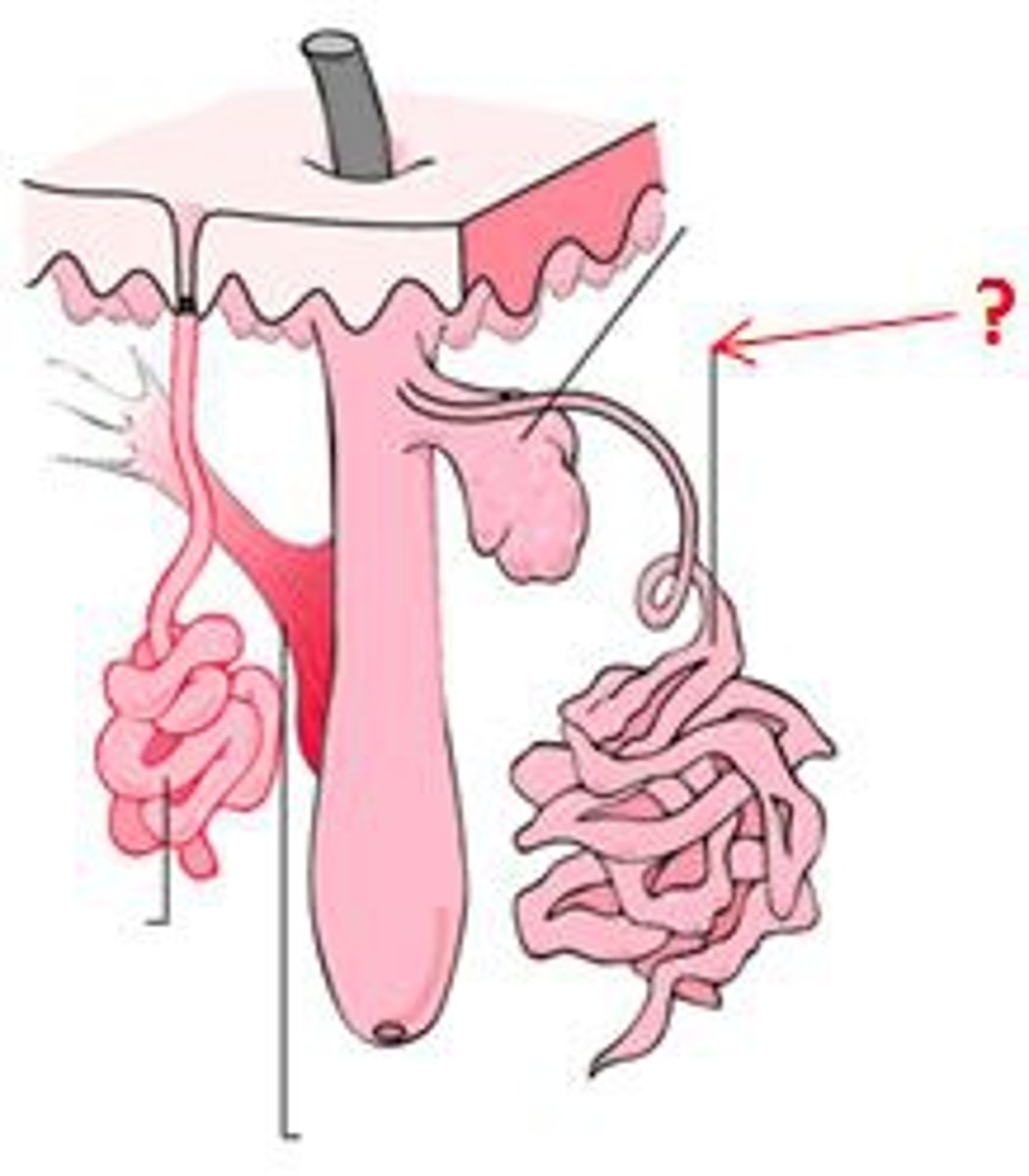
ceruminous glands
- release ear wax into hair follicles in ear
- modified apocrine glands
cerumen
ear wax. lubricates and traps particles leading to tympanic membrane
mammary glands
specialized type of sweat gland, makes MILK
sebaceous glands
- found everywhere on body except palms and soles
- most number found on face and scalp
- influenced by sex hormones, especially testosterone
- dramatic increase after puberty
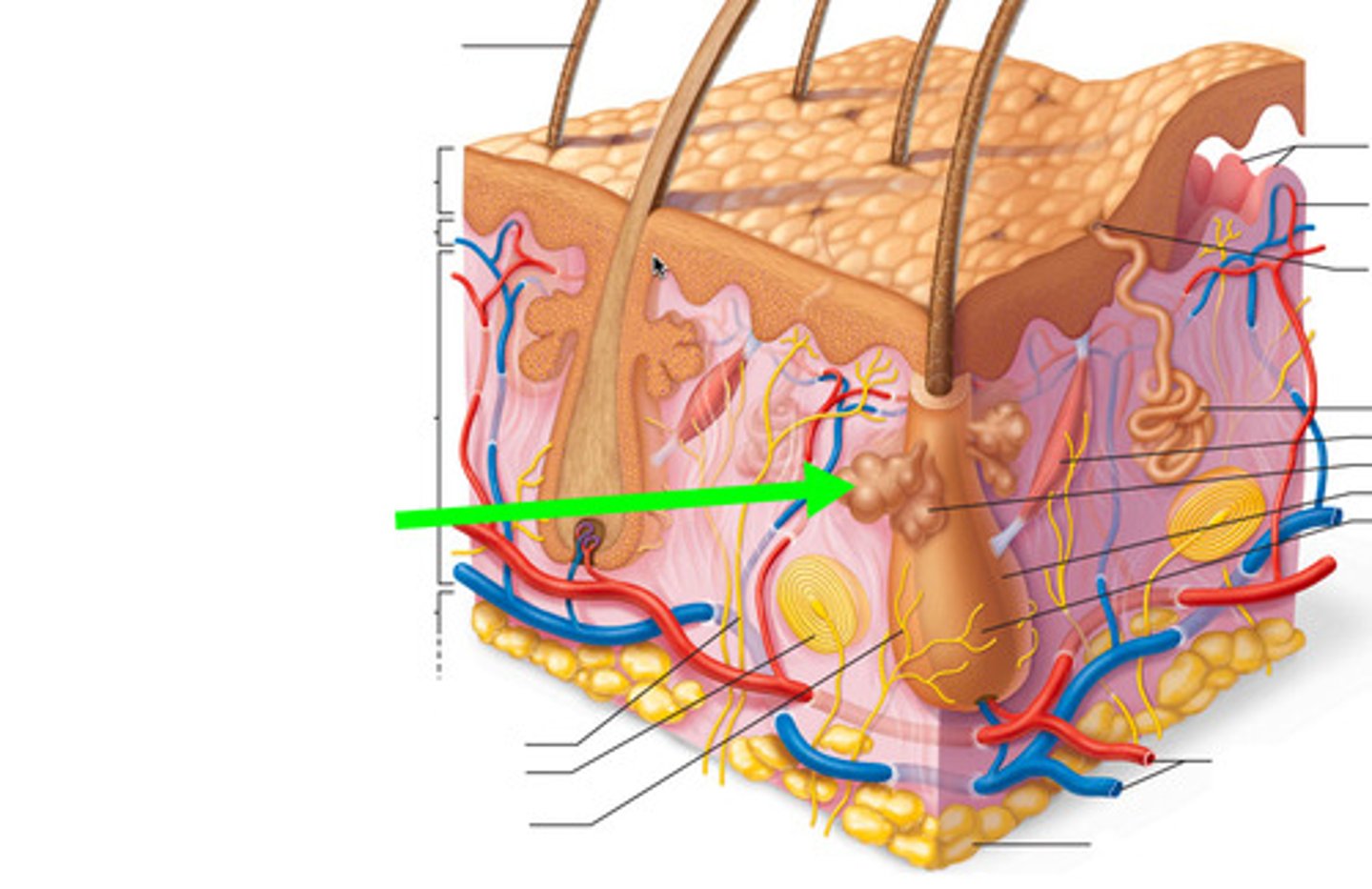
acini
secretory cells in sebaceous glands, ducts converge to form a central duct
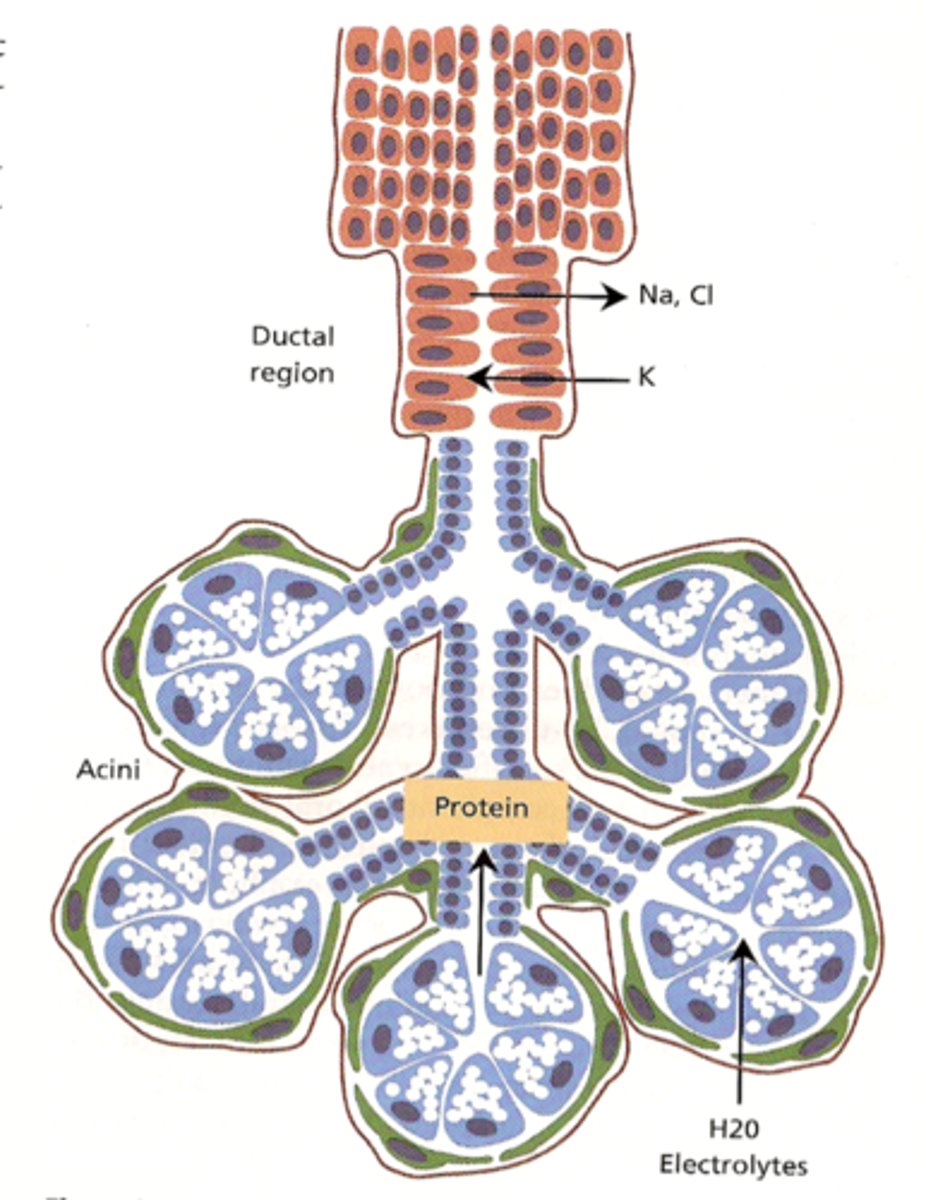
composition and origin of sebum
sebaceous glands
function of sebum
coats hair, inhibits growth of bacteria