Forensic Biology: Lecture 6 – STRs & Problems in Forensic Analysis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
DNA degradation variables:
time, temperature, humidity, light (esp. UV radiation), substrate, specific chemicals, presence of bacteria
RFLPs require greater than [blank] ng of High Molecular Weight DNA.
10-50
1
PCR-based methods can work with less than [blank] ng of highly degraded DNA.
When working with degraded samples, the shorter the amplicon:
the better (SNPs > short STRs > long STRs)
mtDNA can work with
highly degraded DNA
unsuccessful PCR
Typically, DNA degradation =
True/False: Markers with larger amplicon sizes are more affected.
True; Even within one locus, large alleles may be missing.
True/False: DNA degradation can cause one allele to mutate into another.
False; Very unlikely that one multilocus genotype could ever convert into another as the result of DNA degradation.
PCR inhibitors
Heme, phenol, blue dye from blue jeans, heparin, xylene, cyanol
PCR contamination sources
other human DNA within the lab, or previously amplified samples
Laminar flow hood
contained, controlled area designed to produce laminar columns of sterile, pyrogen-free air as a sterile environment for aseptic production of parenteral products
pyrogen
fever-producing agent
parenteral
taken into the body or administered in a manner other than through the digestive tract
Avoiding Contamination:
Pre and post-PCR sample processing areas should be physically separated. Aerosol-resistant (filter) pipette tips should be used and changed on every new sample to prevent crosscontamination during liquid transfers. UV irradiation of laboratory PCR set-up space, plus cleaning workspaces and instruments with isopropanol and/or 20% bleach solutions helps to insure that extraneous DNA molecules are destroyed prior to DNA extraction or PCR setup.
STR mutations have important practical consequences for:
Paternity testing and mass disaster investigations, where conclusions are being drawn from genetic data across generations. This is why in paternity tests at least two differences are conventionally required for exclusion..
SWGDAM stands for
Scientific Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods
SWGDAM Analytical Threshold:
value above which it is assumed allelic dropout has not occurred within a single-source sample
stochastic
a random probability distribution or pattern that may be analyzed statistically but may not be predicted precisely
If just a few cells are present in the evidence sample, it is possible that:
during sampling, an allele could be lost by chance (this is not a problem when enough template DNA is used in the PCR reaction)
Stutter Products
Peaks that show up primarily one repeat less than the true allele as a result of strand slippage during DNA synthesis
strand slippage
can occur when one nucleotide strand forms a small loop
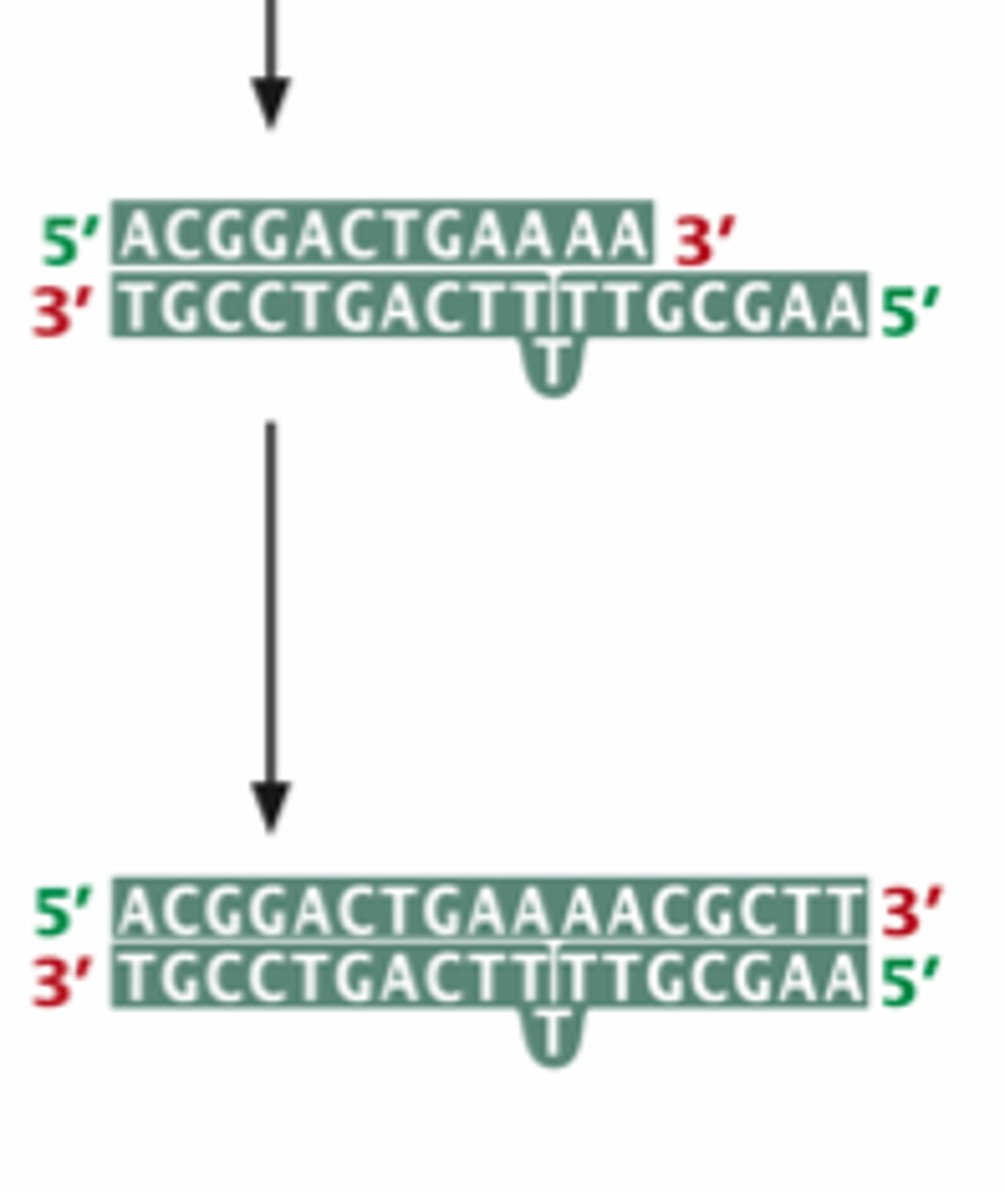
Non-template A Addition
Terminal 3' A that is often added to the growing PCR product changes allele size
allelic dropout
PCR amplification may fail due to sequence changes in a primer binding region of genomic DNA template, making it impossible to detect an allele that exists in the template DNA. This results in what is known as null alleles.
degenerate primers
A mixture of PCR primers that are similar but not identical. They may be designed based on a consensus sequence derived from similar organisms, with substitutions of different bases at one or more locations in the primers.
Mixed profile analysis
1. identify the presence of a mixture
2. designate allele peaks
3. identify the number of potential contributors
4. estimate the relative ratio of the individuals contributing to the mixture
5. consider all possible genotype combinations
compare reference samples
Given the large number of alleles, the forensic analysis of mixed samples with STRs is possible. Often it will be possible to determine if a suspect is:
excluded
Unrestricted
ignores relative peak height differences; all combinations of alleles are deemed possible
Restricted
based on relative peak heights; alleles are only paired where specific combinations are deemed possible
Heterozygote alleles should be:
>70% of highest allele
<15%; 4bp (for tetra repeats)
Stutter products are usually [blank] of corresponding allele peak & shorter by [blank]
Cybergenetics TrueAllele
A fully continuous probabilistic approach that analyzes electropherograms and considers the genotypes at every locus of each contributor, taking into consideration:
- the mixture weights of the contributors
- the DNA template mass
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) stutter
- relative amplification
- DNA degradation, and the uncertainties of all these variables