organic chem 2 aqa higher (w/ pqs??? why)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what are the number of bonds an atom has determined by?
number of electrons in outer shell, e.g. C - 4 electrons/bonds
what are alcohols?
homologous series - functional group is O-H
general formula: Cn H2n+1 OH
e.g. methanol, ethanol
can be formed by hydration of an alkene, e.g. ethene + water → ethanol
what are the properties of alcohols?
flammable - undergo complete combustion in air to produce CO2 and H2O
react w/ sodium - one of the products is hydrogen
first four alcohols dissolve completely in water to form neutral solutions
can be oxidised by reacting w/ O2 (e.g. from the air) to form carboxylic acids
(react w/ carboxylic acids to form esters + water)
what are the uses of alcohols?
alcoholic drinks (usually ethanol used)
solvents - (e.g. methylated spirit)
fuels (e.g. ethanol is often used in spirit burners)
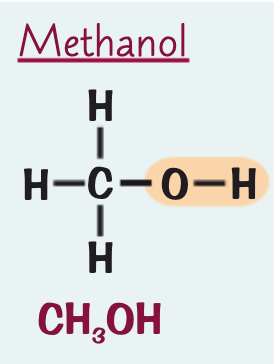
what is the name, formula and structure for the alcohol containing one C atom?
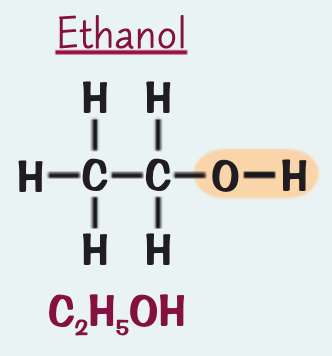
what is the name, formula and structure for the alcohol containing two C atoms?
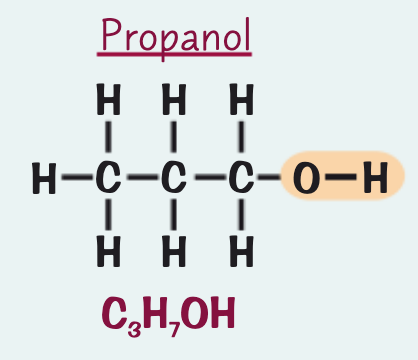
what is the name, formula and structure for the alcohol containing three C atoms?
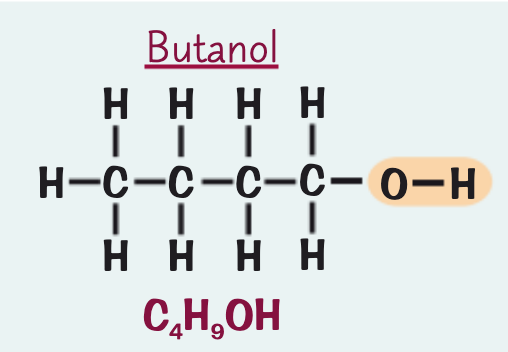
what is the name, formula and structure for the alcohol containing four C atoms?
what is fermentation?
sugar → (w/ yeast) carbon dioxide + ethanol
the ethanol produced is aqueous as the reaction is carried out in a solution
the optimum temperature for this reaction is 37 degrees Celsius in a slightly acidic solution, in anaerobic conditions
what are carboxylic acids?
homologous series - functional group is -COOH
weak acids
forned when an alcohol is reacted w/ an oxidising agent - e.g. ethanol + air OR potassium dichromate → ethanoic acid
suffix is “-oic acid”
why are carboxylic acids weak in terms of ionisation and pH?
do not ionise completely in water
higher pH than aqueous solutions of strong acids of the same concentration
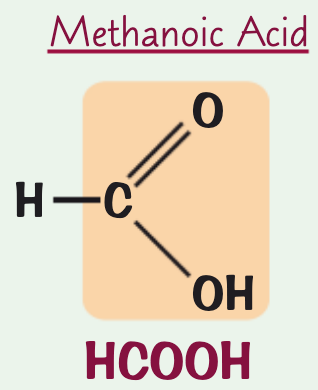
what is the name, chemical/structural formula and structure for the carboxylic acid containing one C atom?
structural formula: HCOOH
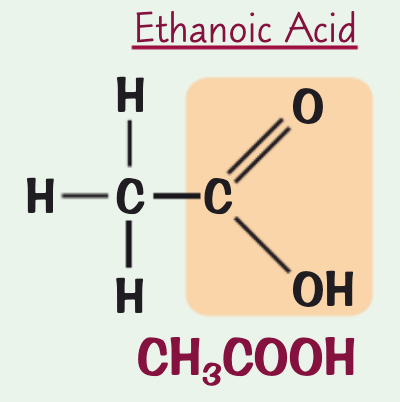
what is the name, chemical/structural formula and structure for the carboxylic acid containing two C atoms?
structural formula: CH₃COOH
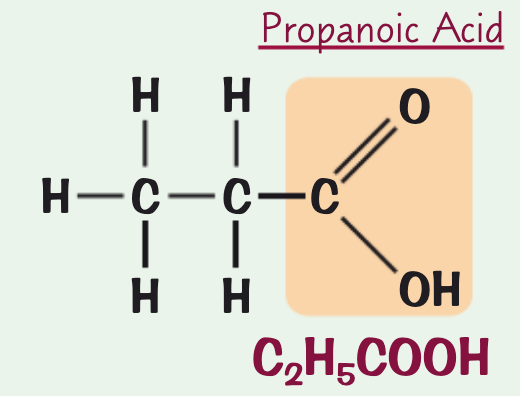
what is the name, chemical/structural formula and structure for the carboxylic acid containing three C atoms?
structural formula: CH3CH2COOH
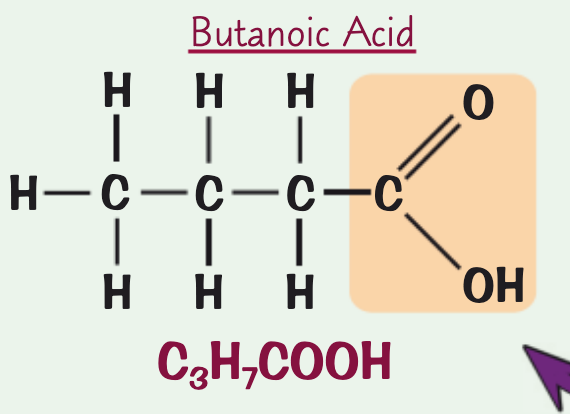
what is the name, chemical/structural formula and structure for the carboxylic acid containing four C atoms?
structural formula: CH3CH2CH2COOH
how do carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates? provide an example of this
(carboyxlic) acid + metal carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water
react in the same way as any other acid!
e.g. ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium ethanoate + carbon dioxide + water
how do carboxylic acids react with alcohols? provide an example of this
alcohol + carboxylic acid (with acid catalyst) → ester + water
(acid catalyst is often H₂SO₄)
ethanoic acid + ethanol → ethyl ethanoate + water
what are esters? what are their typical properties?
formed when a carboxylic acid and polymer (with an acid catalyst) react
sweet smelling compounds - often used in sweets
homologous - functional group is -COOC
e.g. ethyl ethanoate
how do carboxylic acids dissolve in water?
dissolve in water to form acidic solutions with a pH of less than 7
how do carboxylic acids react with metals? provide an example of this
metal + (carboxylic) acid → salt + hydrogen
react in the same way as any other acid!
e.g. aluminium + ethanoic acid → aluminium ethanoate + hydrogen
how do carboxylic acids react with bases? provide an example of this
(carboxylic) acid + base → salt + water
react in the same way as any other acid!
e.g. ethanoic acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium ethanoate + water
what is addition polymerisation? what does the reaction require?
when lots of small alkene monomers open up the double bonds to join and form polymers
requires high pressure & a catalyst
what are the features of addition polymers? provide some examples
addtion polymer contains the same type and number of atoms as the monomers that formed it because no other molecule is formed in the reaction
have repeating units (four groups arranged around a main chain w/ 2 C atoms)
e.g. ethene → poly(ethene), propene → poly(propene)
what is condensation polymerisation? give an example
involves monomers which contain two functional groups
produced from two different monomers w/ two of the same functional group on each monomer OR two monomers of the same type w/ two different functional groups on each monomer
when the momomers react, they join and lose small molecules (usually water)
e.g. ethanediol + hexanedioic acid → polyester + water
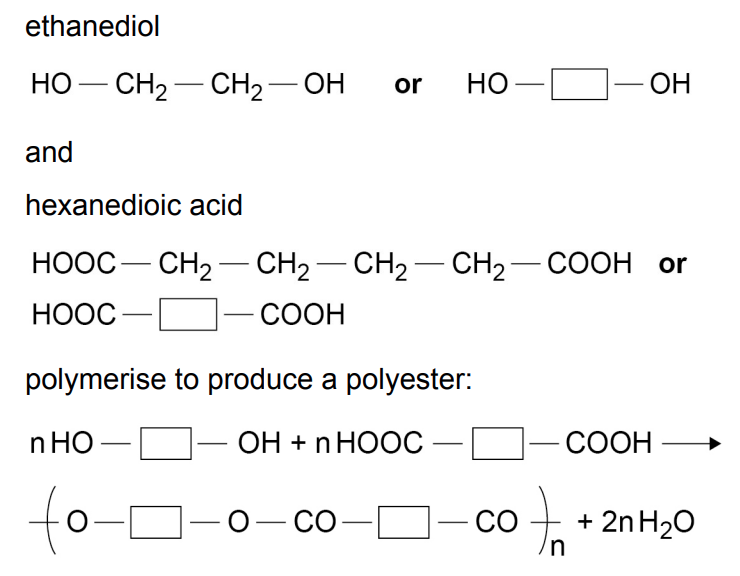
how is a polyester formed?
dicarboxylic acid + diol → polyester + water
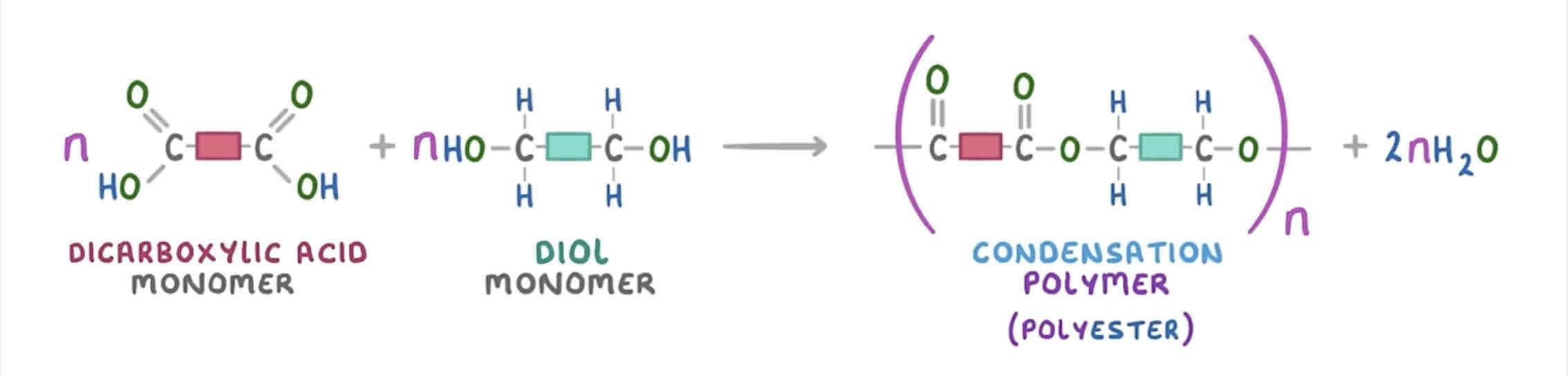
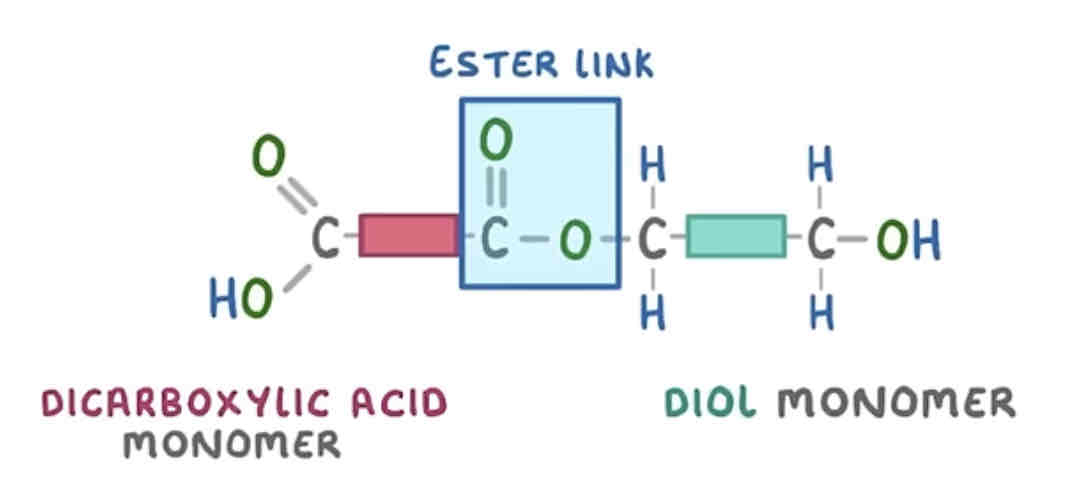
how do you write the repeating pattern of this polyester?
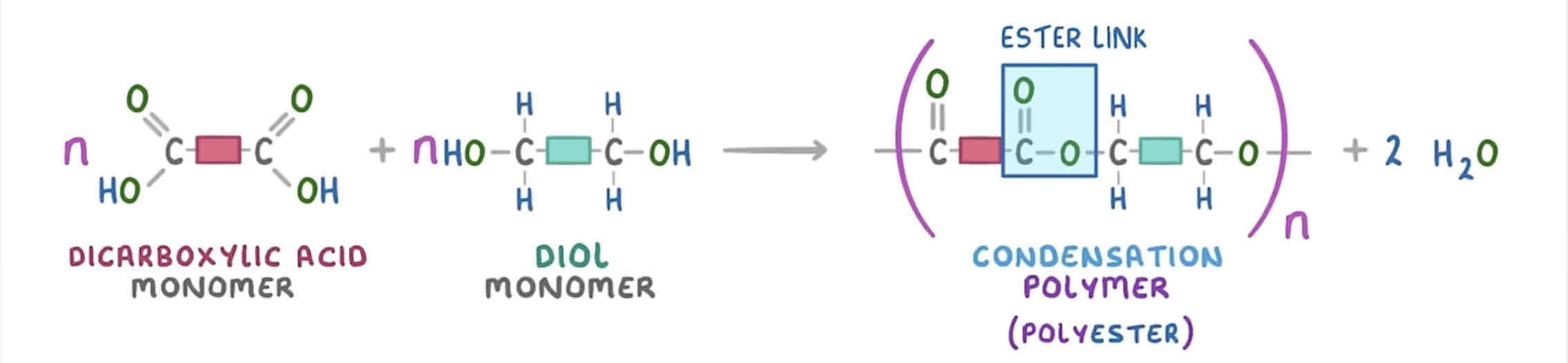
name three differences between addition and condensation polymerisation
addition - polymers produced from one monomer wheareas condensation - produced from two different monomers
addition - polymers produced from ethene / alkene whereas condensation - polymers produced from diarboxylic acid and diol
addition - polymer only product formed whereas condensation - small molecules such as water also
addition - repeating unit is a hydrocarbon whereas condensation - repeating unit has an ester link and carbon chain
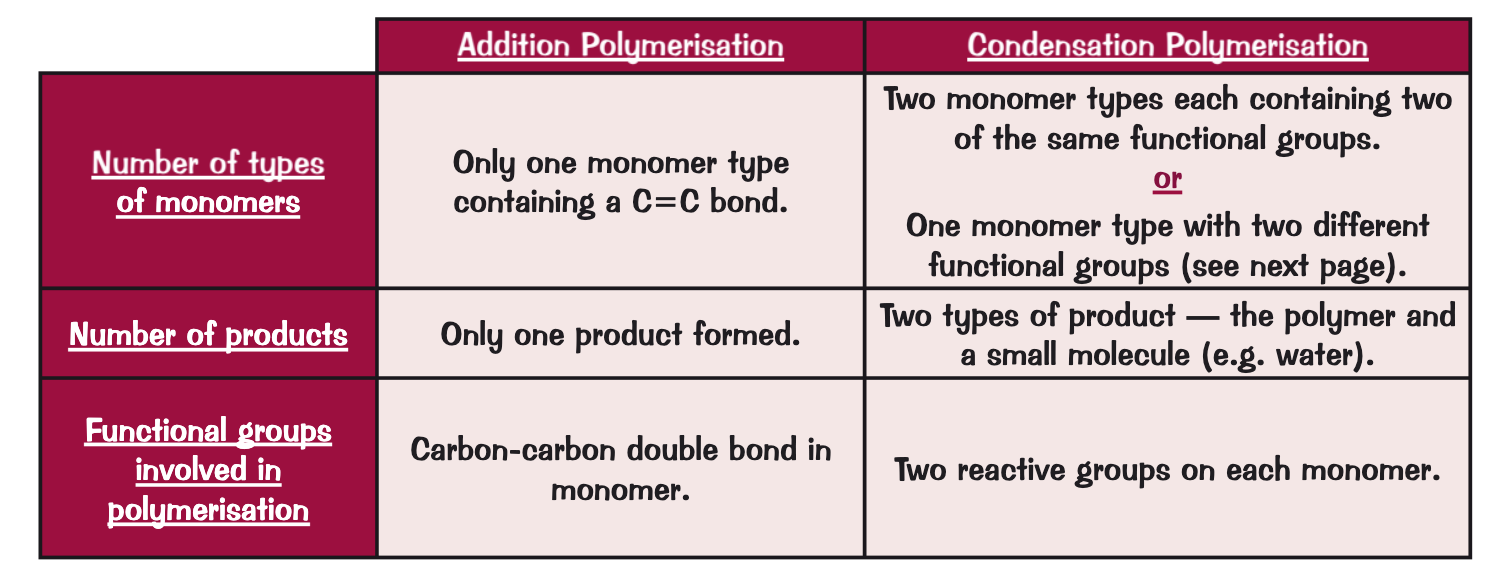
what is an amino acid? provide an example
how can they react?
have two functional groups - amine group -NH2 and carboxyl group -COOH
e.g. glycine
can react together in condensation polymerisation to form a polypeptide, a type of polyamine
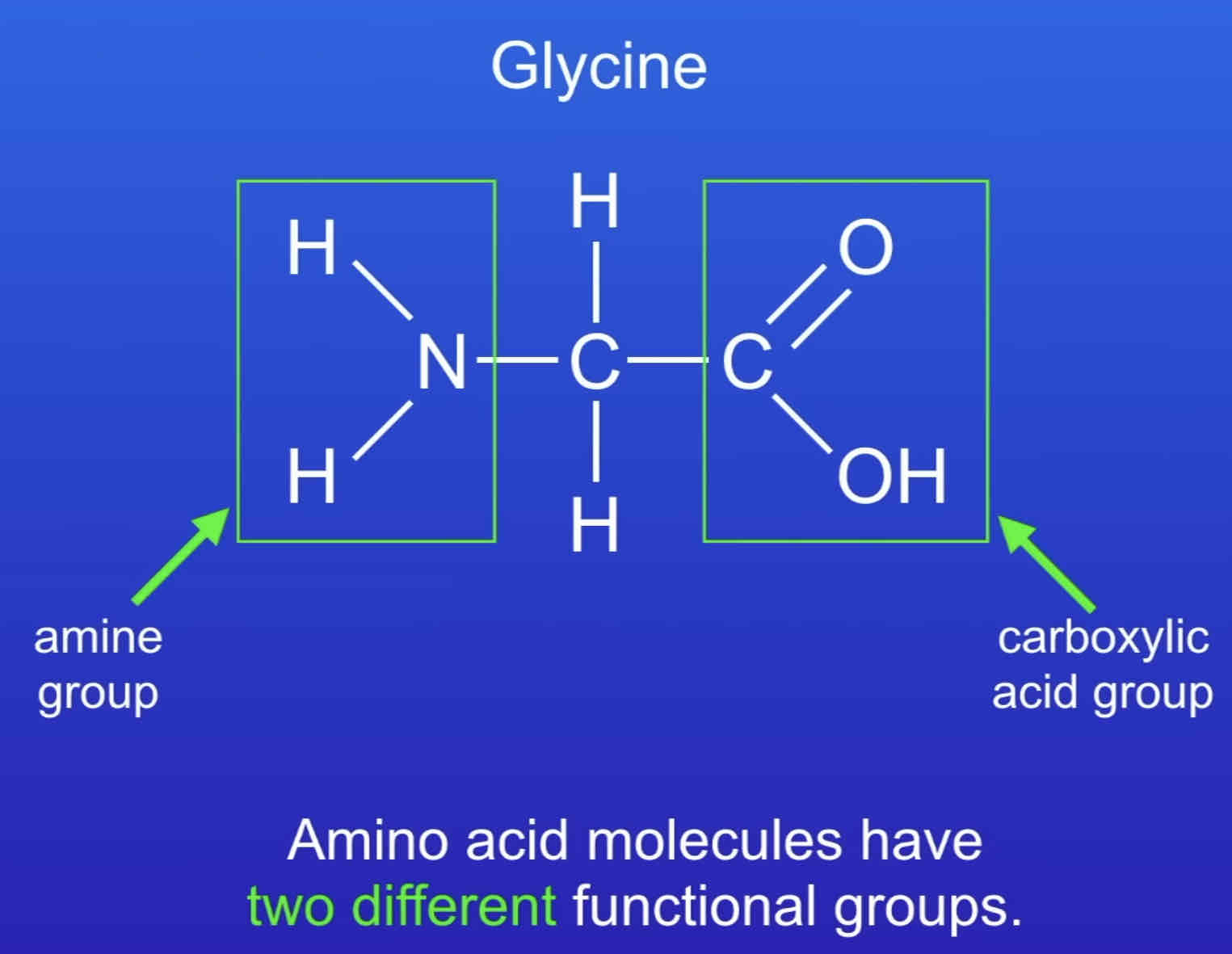
how are polypeptides formed?
condensation polymerisation reaction between two amino acids (acid group of one reacts with amine group of the other)
water formed as a by product for every bond formed
e.g. glycine → poly(glycine):
what is the difference between a polypeptide and a protein?
polypeptides made up of chains of the same amino acid
proteins made up of chains of different amino acids
give two reasons why proteins are important in the body
enzymes - catalyse biological reactions
haemoglobin - transports oxygen
name two polymers of sugars
starch
cellulose
what is a carbohydrate? provide 2 examples
a biological molecule containing C,H and O
e.g. starch and cellulose
what is DNA? what does it stand for?
DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid
large molecule essential for life
encodes genetic instructions for development and functions of living organisms and viruses
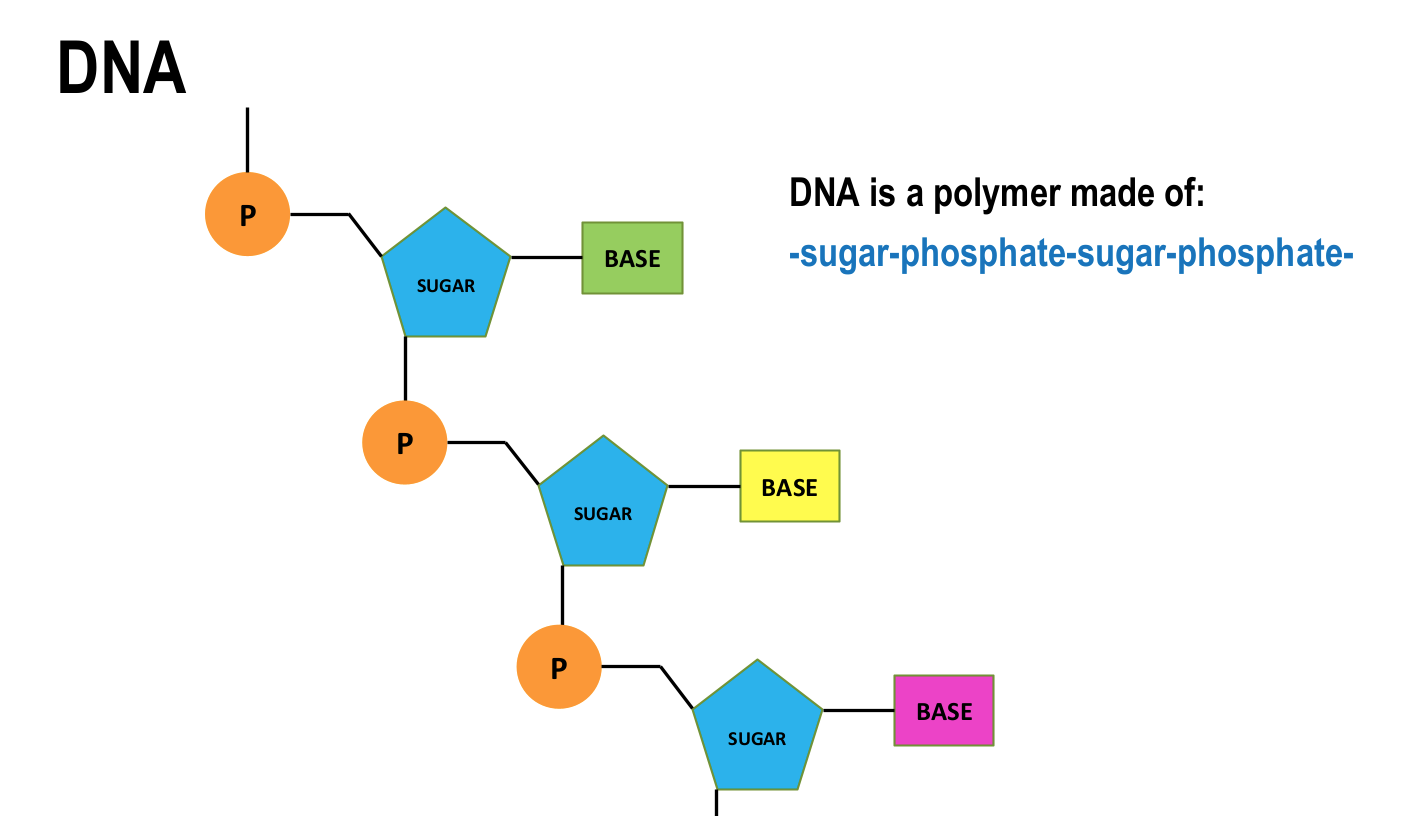
describe the shape and structure of DNA
most DNA molecules are 2 polymer chains, made from 4 different monomers called nucleotides
double helix structure
base pairs are A-T and C-G and form cross links holding the 2 nucleotide chains together
what does volatile mean?
evaporates easily