Unit 3: Populations (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:32 PM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Survivorship curves
It show age-distribution characteristics of species, reproductive strategies, and life history
2
New cards
Reproductive success
It is measured by how many organisms are able to mature and reproduce, with each survivorship curve representing a balance between natural resource limitations and interspecific and intraspecific competition
3
New cards
Carrying capacity (K)
It refers to the number of individuals that can be supported sustainably in a given area
4
New cards
Population dispersal pattern
It is how individuals or species of animal become distributed in different spaces over certain periods of time
5
New cards
Clumped
Some areas within a habitat are dense with organisms, while other areas contain few members
6
New cards
Random
Occurs in habitats where environmental conditions and resources are consistent
7
New cards
Uniform
Space is maximized between individuals to minimize competition
8
New cards
Biotic potential
The maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimum environmental conditions
9
New cards
Environmental Resistance
Any factor that inhibits an increase in the number of organisms in the population
10
New cards
J-Curve
It represents a population growth occurs in a new environment when the population density of an organism increases rapidly in an exponential or logarithmic form, but then stops abruptly as environmental resistance or another factor suddenly impacts the population growth
11
New cards
S-Curve
It occurs when, in a new environment, the population density of an organism initially increases slowly but then stabilizes due to the finite amount of resources available
12
New cards
Limiting Factor
It can be any resource or environmental condition that limits the abundance, distribution, and/or growth of a population
13
New cards
Density-dependent limiting factors
These are factors whose effects on the size or growth of the population vary with the density of the population
14
New cards
Density-independent factors
These are factors that limit the size of a population, and their effects are not dependent on the number of individuals in the population
15
New cards
Rule of 70
It helps to explain the time periods involved in exponential population growth occurring at a constant rate
16
New cards
Doubling time
It is the amount of time it takes for a population to double in size
17
New cards
Age-structure diagrams
These are determined by birth rate, generation time, death rate, and sex ratios
18
New cards
Pyramid-shaped age-structure diagram
It indicates that the population has high birth rates and the majority of the population is in the reproductive age group
19
New cards
Bell shape age-structure diagram
It indicates that pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups are more nearly equal, with the post-reproductive group being smallest due to mortality
20
New cards
Urn-Shaped age-structure diagram
It indicates that the post-reproductive group is largest and the pre-reproductive group is smallest, a result of the birth rates falling below the death rate, and is characteristic of declining populations
21
New cards
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children that each woman will have during her lifetime
22
New cards
Earth Wisdom
Natural cycles that can serve as a model for human behavior
23
New cards
Frontier Worldview
Viewed undeveloped land as a hostile wilderness to be cleared and planted, then exploited for its resources as quickly as possible
24
New cards
Planetary Management
Beliefs that as the planets most important species, we are in charge of Earth
25
New cards
Earth Wisdom
Beliefs that nature exists for all Earths species and we are not in charge of Earth; resources are limited and should not be wasted
26
New cards
Demographic transition
It is the transition from high birth and death rates to lower birth and death rates as a country or region develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system
27
New cards
Stage 1
Pre-Industrial (High Stationary)
28
New cards
Stage 2
Transitional (Early Expanding)
29
New cards
Stage 3
Industrial (Late Expanding)
30
New cards
Stage 4
Post-Industrial (Low Stationary)
31
New cards
Stage 5
Sub-Replacement Fertility (Declining)
32
New cards
Stage 5: Sub-Replacement Fertility (Declining)
* Some theorists believe a fifth stage is needed to represent countries with sub-replacement fertility.
* Death rates exceed birth rates in most European and East Asian nations.
* Unless mass immigration continues, population aging and decline will occur in this stage.
* Death rates exceed birth rates in most European and East Asian nations.
* Unless mass immigration continues, population aging and decline will occur in this stage.
33
New cards
Stage 4: Post-Industrial (Low Stationary)
* Population growth is zero when birth and death rates are equal.
* The standard of living is higher, and birth and death rates are low.
* In some countries, birth rates are lower than mortality rates, resulting in population losses.
* The standard of living is higher, and birth and death rates are low.
* In some countries, birth rates are lower than mortality rates, resulting in population losses.
34
New cards
Stage 3: Industrial (Late Expanding)
* Urbanization reduces economic incentives for large families.
* Urban families are increasingly discouraged from having large families as costs rise.
* Female education and employment lower birth rates.
* Leisure time and food are not priorities.
* Urban families are increasingly discouraged from having large families as costs rise.
* Female education and employment lower birth rates.
* Leisure time and food are not priorities.
35
New cards
Stage 2: Transitional (Early Expanding)
* This stage occurs after the start of industrialization.
* Hygiene, medical advances, sanitation, cleaner water, vaccinations, and higher education lower the death rate, resulting in a significant population increase.
* Population rises rapidly.
* Hygiene, medical advances, sanitation, cleaner water, vaccinations, and higher education lower the death rate, resulting in a significant population increase.
* Population rises rapidly.
36
New cards
Stage 1: Pre-Industrial (High Stationary)
* Poor agricultural practices, pestilence, and living conditions make food scarce and medical care is poor.
* High birth rates replace high mortality, resulting in low population growth.
* Sub-Saharan Africa has 54% of the world's AIDS-HIV cases but only 6% of the population.
* High birth rates replace high mortality, resulting in low population growth.
* Sub-Saharan Africa has 54% of the world's AIDS-HIV cases but only 6% of the population.
37
New cards
Present to 2050 C.E.
Estimates are as high as 9.8 billion.
Earth Wisdom
Earth Wisdom
38
New cards
1650 C.E. to present
* Currently \~ 7.5 billion humans.
* In 1650 C.E., the growth rate was \~ 0.1%.
* Today it is \~ 1.2%.
* Planetary Management
* In 1650 C.E., the growth rate was \~ 0.1%.
* Today it is \~ 1.2%.
* Planetary Management
39
New cards
1300 C.E. to 1650 C.E.
* \~ 600 million humans.
* Plagues reduced population growth rate.
* Up to 25% mortality rates are attributed to the plagues that reached their peak in the mid-1600s.
* Plagues reduced population growth rate.
* Up to 25% mortality rates are attributed to the plagues that reached their peak in the mid-1600s.
40
New cards
0 C.E. to 1300 C.E.
* \~ 500 million humans.
* Population rate increased during the Middle Ages because new habitats were discovered.
* Factors that reduced population growth rate during this time were famines, wars, and disease
* Frontier Worldview
* Population rate increased during the Middle Ages because new habitats were discovered.
* Factors that reduced population growth rate during this time were famines, wars, and disease
* Frontier Worldview
41
New cards
5000 B.C.E. to 1 B.C.E.
* \~ 200 million humans.
* Rate of population growth during this period was about 0.03 to 0.05%, compared with today’s growth rate of 1.3%.
* **Frontier Worldview**
* Rate of population growth during this period was about 0.03 to 0.05%, compared with today’s growth rate of 1.3%.
* **Frontier Worldview**
42
New cards
8000 B.C.E. to 5000 B.C.E.
* \~ 50 million humans.
* Increases due to advances in agriculture, domestication of animals, and the end of a nomadic lifestyle.
* Earth Wisdom
* Increases due to advances in agriculture, domestication of animals, and the end of a nomadic lifestyle.
* Earth Wisdom
43
New cards
Before Agricultural Revolution
* \~ 1 million to 3 million humans.
* Hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
* **Earth Wisdom**
* Hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
* **Earth Wisdom**
44
New cards
Birth Rate (%) = \[(total births/total population)\] × 100
Birth Rate Formula
45
New cards
CBR = \[(*b* ÷ *p*) × 1,000\]
Crude Birth Rate Formula
46
New cards
Death Rate (%) = \[(total deaths/total population)\]× 100
Death Rate Formula
47
New cards
CDR = \[(*d* ÷ *p*) × 1,000\]
Crude Death Rate Formula
48
New cards
Doubling Time = 70/% growth rate
Doubling Time Formula
49
New cards
Emigration = number leaving a population
Emigration Formula
50
New cards
Global Population Growth Rate (%) = \[(CBR – CDR)\]/10
Global Population Growth Rate Formula
51
New cards
Immigration = number entering a population
Immigration Formula
52
New cards
National Population Growth Rate (%) = \[(CBR + immigration) – (CDR + emigration)\]/10
National Population Growth Rate Formula
53
New cards
Percent Rate of Change = \[(new # - old #)/old #\] × 100
Percent Rate of Change Formula
54
New cards
Population Density = total population size/total area
Population Density Formula
55
New cards
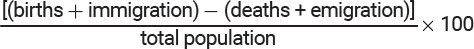
\
Population Growth Rate Formula
56
New cards
dt= 70/r
To find how long it takes for a population to double in size we can use the following formula _________
57
New cards
Liebig’s law of the minimum
Based on _________, even if all other factors are favorable, the one that is least favorable will dictate the growth, abundance, or distribution of the population of a species.
58
New cards
Positive feedback loops
_________ stimulate change and are responsible for sudden or rapid changes within ecosystems.
59
New cards
**Negative feedback loops**
**This** often provide stability.
* Limiting factors can cause a negative feedback loop because populations cannot exceed the ecosystem's carrying capacity.
* Limiting factors can cause a negative feedback loop because populations cannot exceed the ecosystem's carrying capacity.
60
New cards
carrying capacity
This *point of stabilization* is known as the _____ of the environment, and it denotes the point at which the upward growth curve begins to level out
61
New cards
density-dependent
This type of population growth is termed “_________” since the growth rate depends on the number of organisms in the population.
62
New cards
density-dependent
This type of population growth rate is known as “_______,” a regulation of the growth rate is not tied to the population density until the resources are exhausted and the population growth crashes.
63
New cards
Type I - Late Loss
Reproduction occurs fairly early in life, with most deaths occurring at the limit of biological life span.
64
New cards
Type I - Late Loss
Low mortality at birth with a high probability of surviving to advanced age.
65
New cards
Type I - Late Loss
Death rates decrease in younger years due to advances in prenatal care, nutrition, disease prevention, and cures, including immunization.
66
New cards
Type II - Constant Loss
Individuals in all age categories have fairly uniform death rates, with predation being the primary cause of death.
67
New cards
Type II - Constant Loss
Typical of organisms that reach adult stages quickly.
68
New cards
Type III - Early Loss
Typical of species that have great numbers of offspring and reproduce for most of their lifetime.
69
New cards
Type III - Early Loss
Death is prevalent for younger members of the species due to environmental loss and predation and declines with age.
70
New cards
r-Strategists
* Not endangered
* Have many offspring and tend to overproduce
* Low parental care
* Mature rapidly
* Have many offspring and tend to overproduce
* Low parental care
* Mature rapidly
71
New cards
r-Strategists
* Population size limited by density-independent limiting factors, including climate, weather, natural disasters, and requirements for growth
* Short-lived
* Tend to be prey
* Tend to be small
* Short-lived
* Tend to be prey
* Tend to be small
72
New cards
r-Strategists
* Type III survivor curve
* Wide fluctuations in population density
* Wide fluctuations in population density
73
New cards
K-Strategists
* Most endangered
* Have few offspring
* High parental care
* Mature slowly
* Have few offspring
* High parental care
* Mature slowly
74
New cards
K-Strategists
* Density-dependent limiting factors to population growth stem from intraspecific competition and include competition, predation, parasitism, and migration
* Long-lived
* Tend to be predator and prey
* Tend to be larger
* Long-lived
* Tend to be predator and prey
* Tend to be larger
75
New cards
K-Strategists
* Type I or II survivor curve
* Population size stabilizes near the carrying capacity.
* Population size stabilizes near the carrying capacity.
76
New cards
Generalists
* Able to use a variety of environmental resources
* Adaptable to a wide range of environments
* Have a high level (range) of tolerance
* Adaptable to a wide range of environments
* Have a high level (range) of tolerance
77
New cards
Generalists
* Have an advantage when environmental conditions change
* Less likely to be extinct
* Less likely to be extinct
78
New cards
Specialists
* Use specific set of resources
* Less adaptable due to specialized needs
* Have a low level of tolerance
* Less adaptable due to specialized needs
* Have a low level of tolerance
79
New cards
Specialists
* Easily affected when environmental conditions change
* More likely to become extinct
* More likely to become extinct