parts of eukaryotic cells + functions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
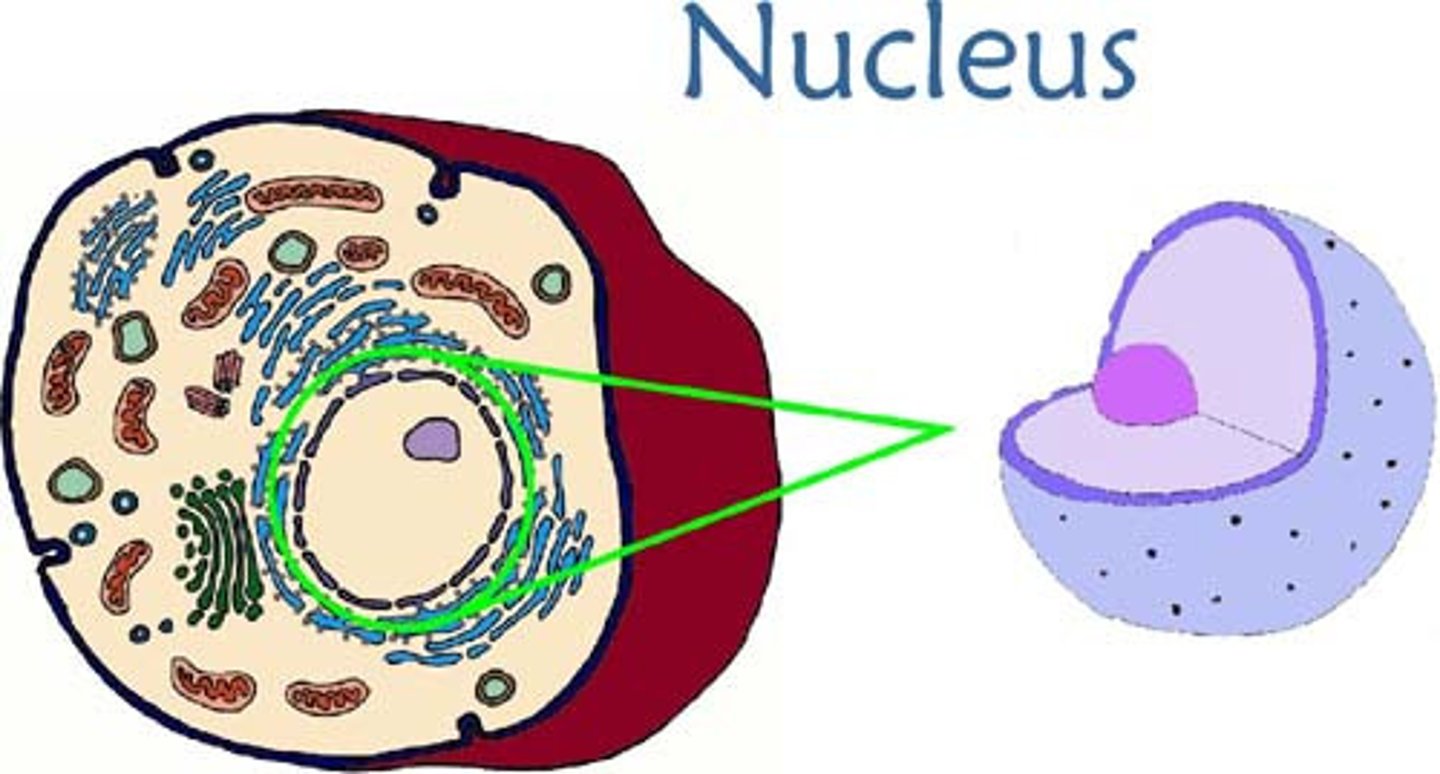
nucleus
- controls cell activities such as cell growth and repair of worn-out parts
- essential for cell division = cells without a nucleus are unable to divide
- controls genetic info (DNA) = DNA molecules contains sequences of nucleotides called genes, which code for polypeptides
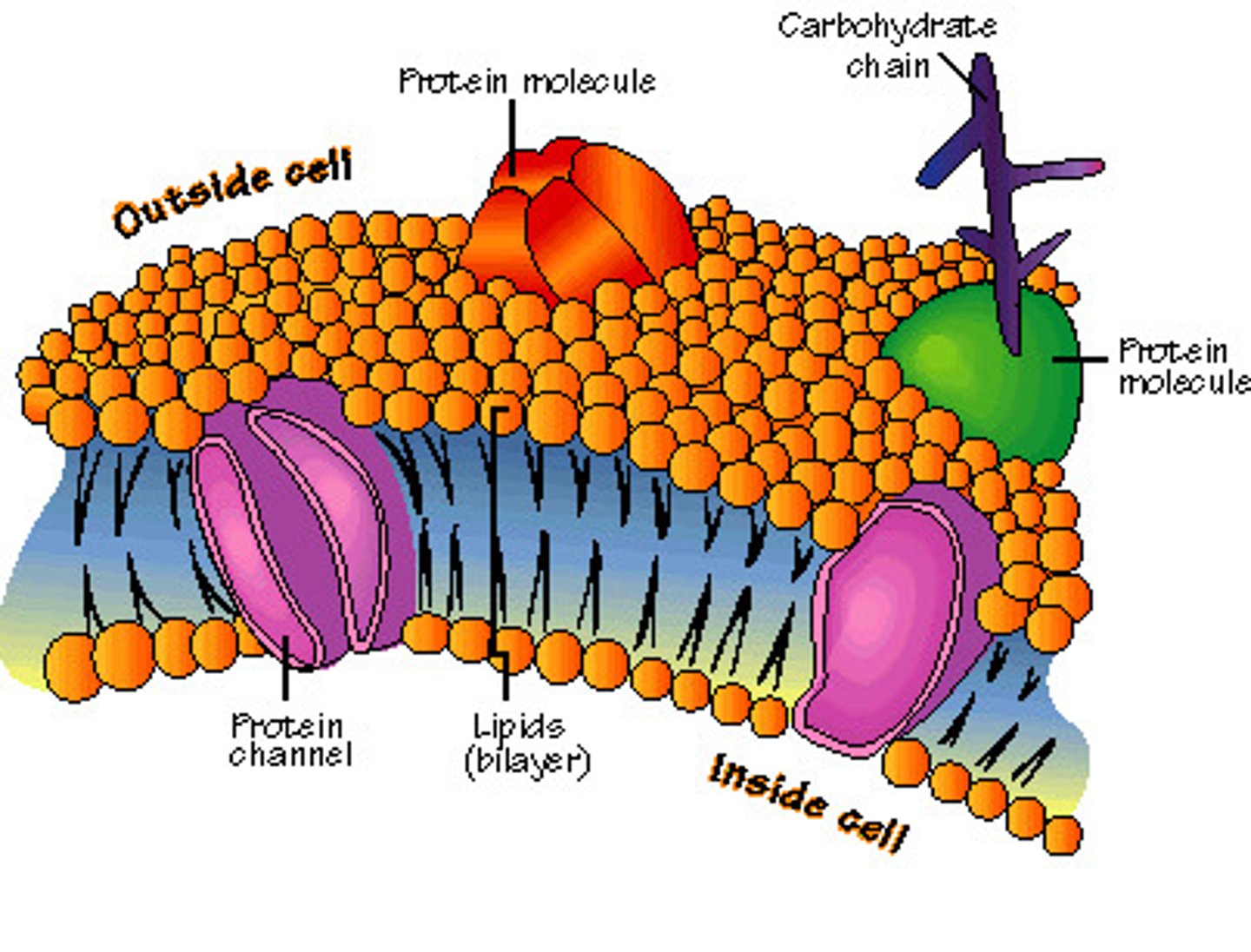
cell surface membrane
- since it is partially permeable, it allows some substances to pass through but not others
- compartmentalization to allow cells and organelles to have specialized functions
cytoplasm
- main site for metabolic activities
- many chemical reactions occur here (due to presence of water)
ribosomes
- sites for polypeptide/protein synthesis
- ribosomes translate (the gene carried by) the messanger RNA (mRNA) into a polypeptide
- the polypeptide then folds to form a protein with a specific 3D conformation
- free ribosomes suspended in the cytoplasm synthesise proteins that function within the cytoplasm
- ribosomes attatched to the RER synthesise proteins that are meant to be secreted out of the cell, packaged within lysosomes or to be embedded into the membranes
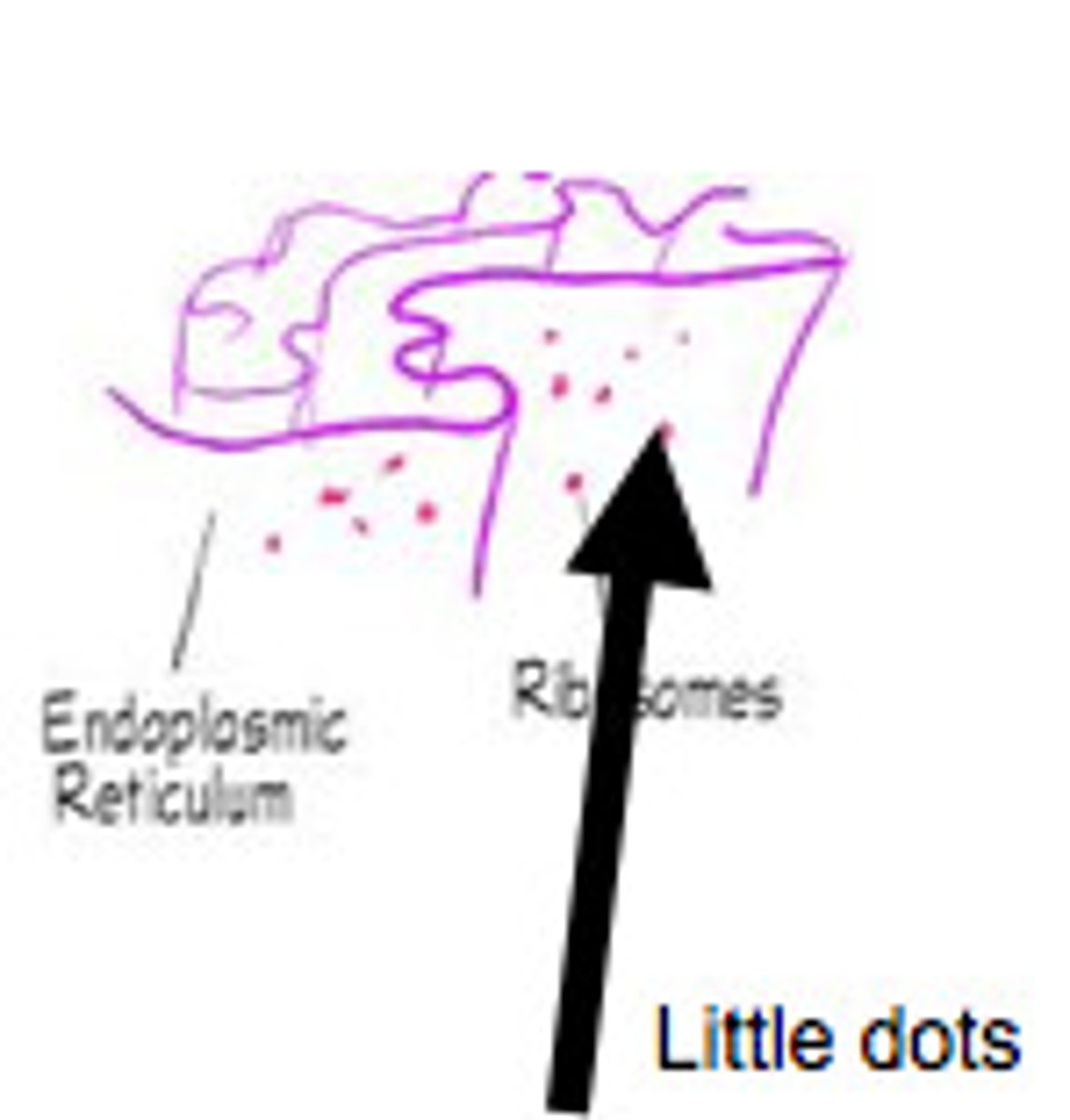
vesticles
- carry substances between membrane compartments
- exocrytosis describes the process of vesticles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell
- endocrytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside of the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane and bring it into the cell
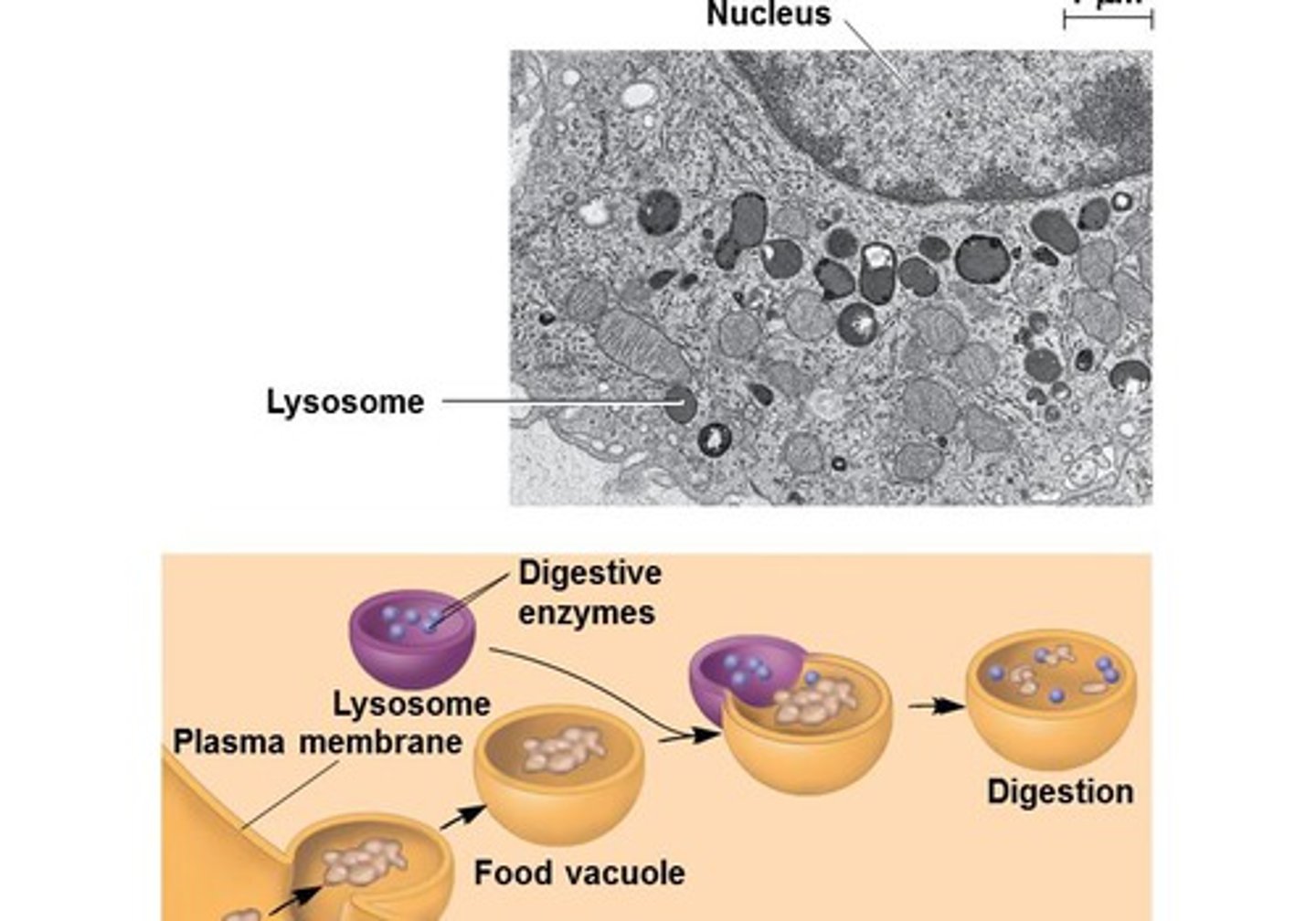
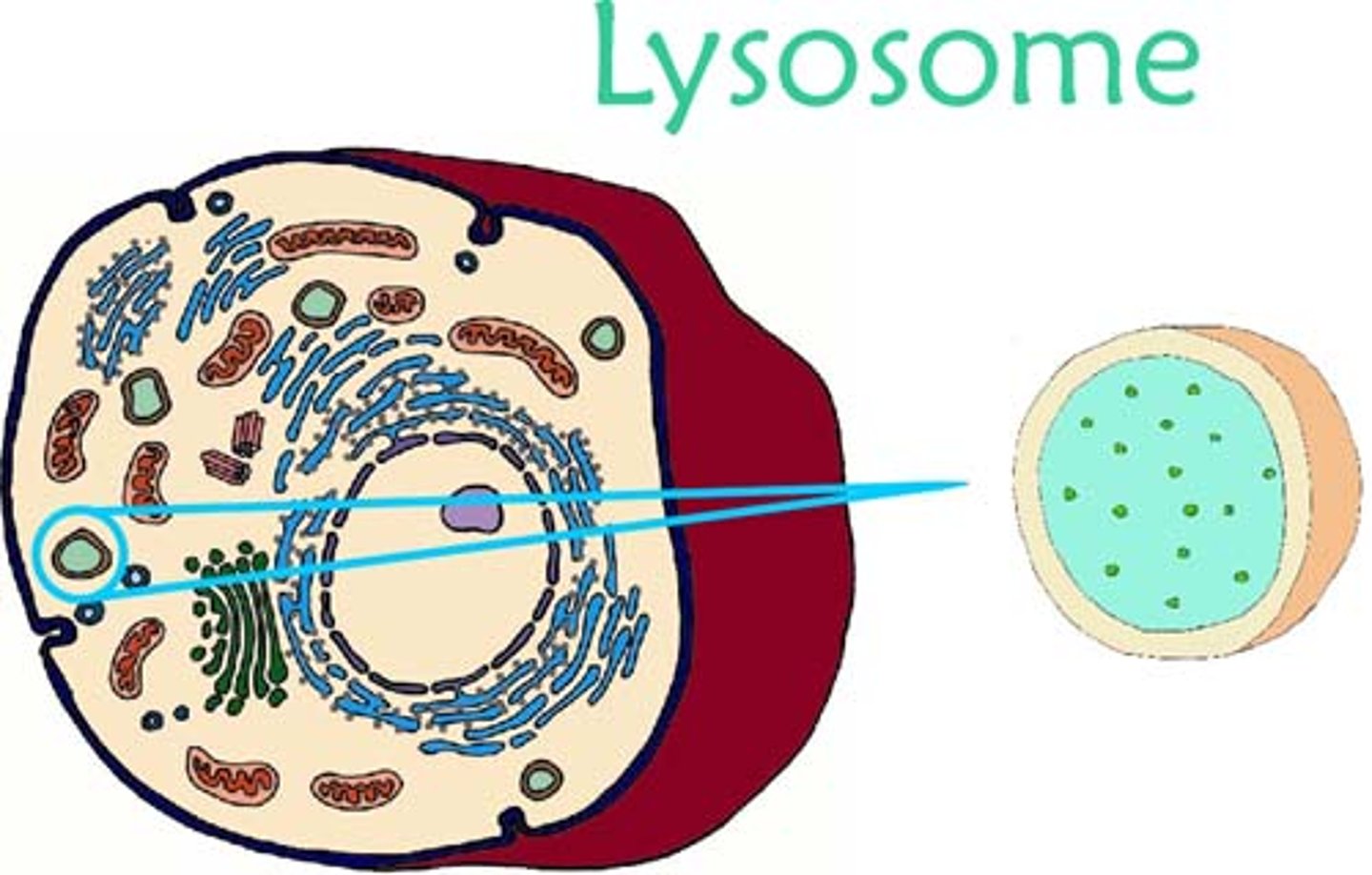
lysosomes
- digestion of food/foreign particles
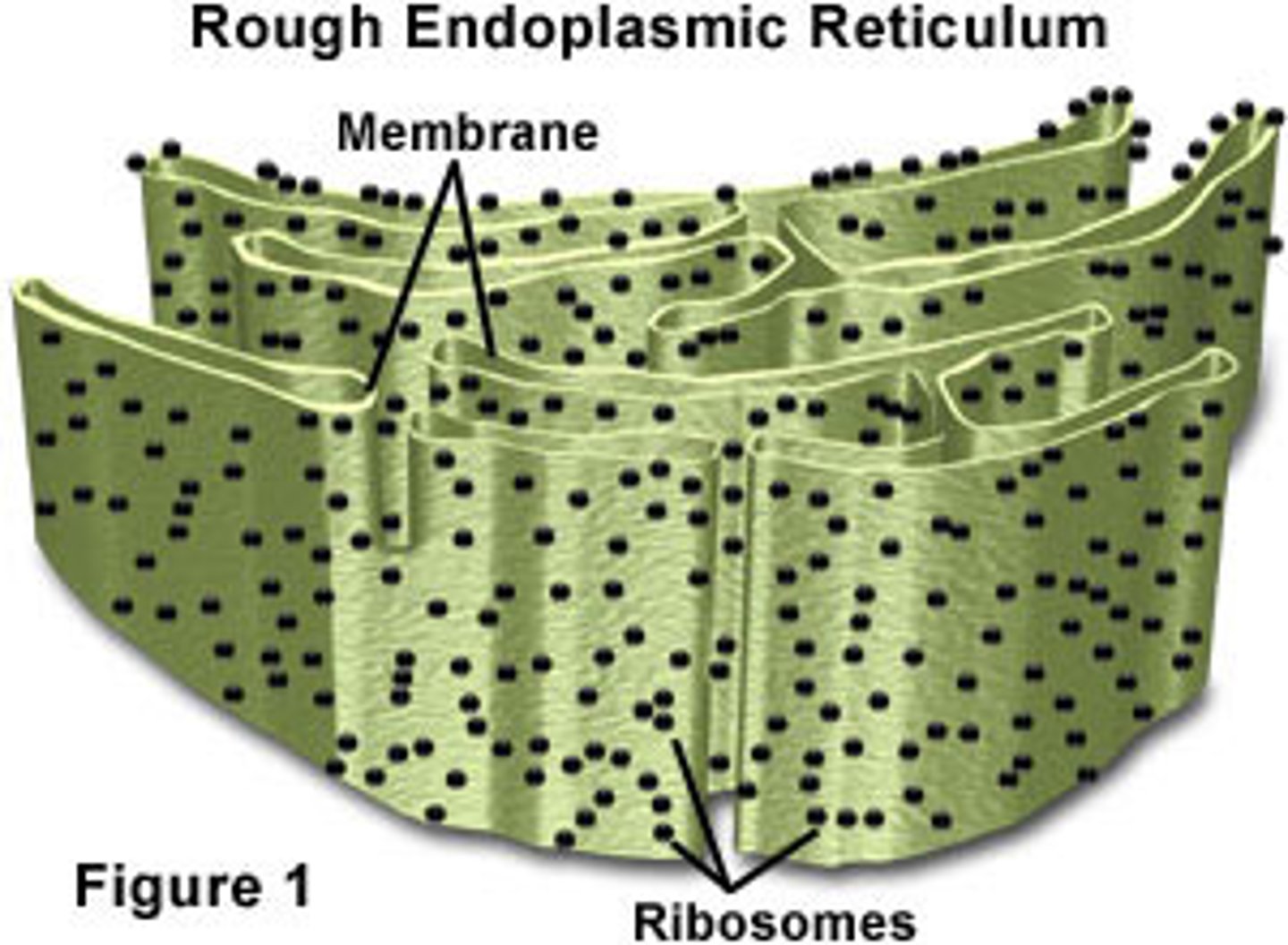
rough endoplasmic reticulum
- folding of polypeptides into proteins
- ribosomes attatched to the RER are sites of protein synthesis
- transport of proteins for secretion
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- synthesis of lipids - enzymes present in the SER synthesise lipids such as phospholipids and steroids
- detoxification - convert harmful substances into harmless ones to be excreted
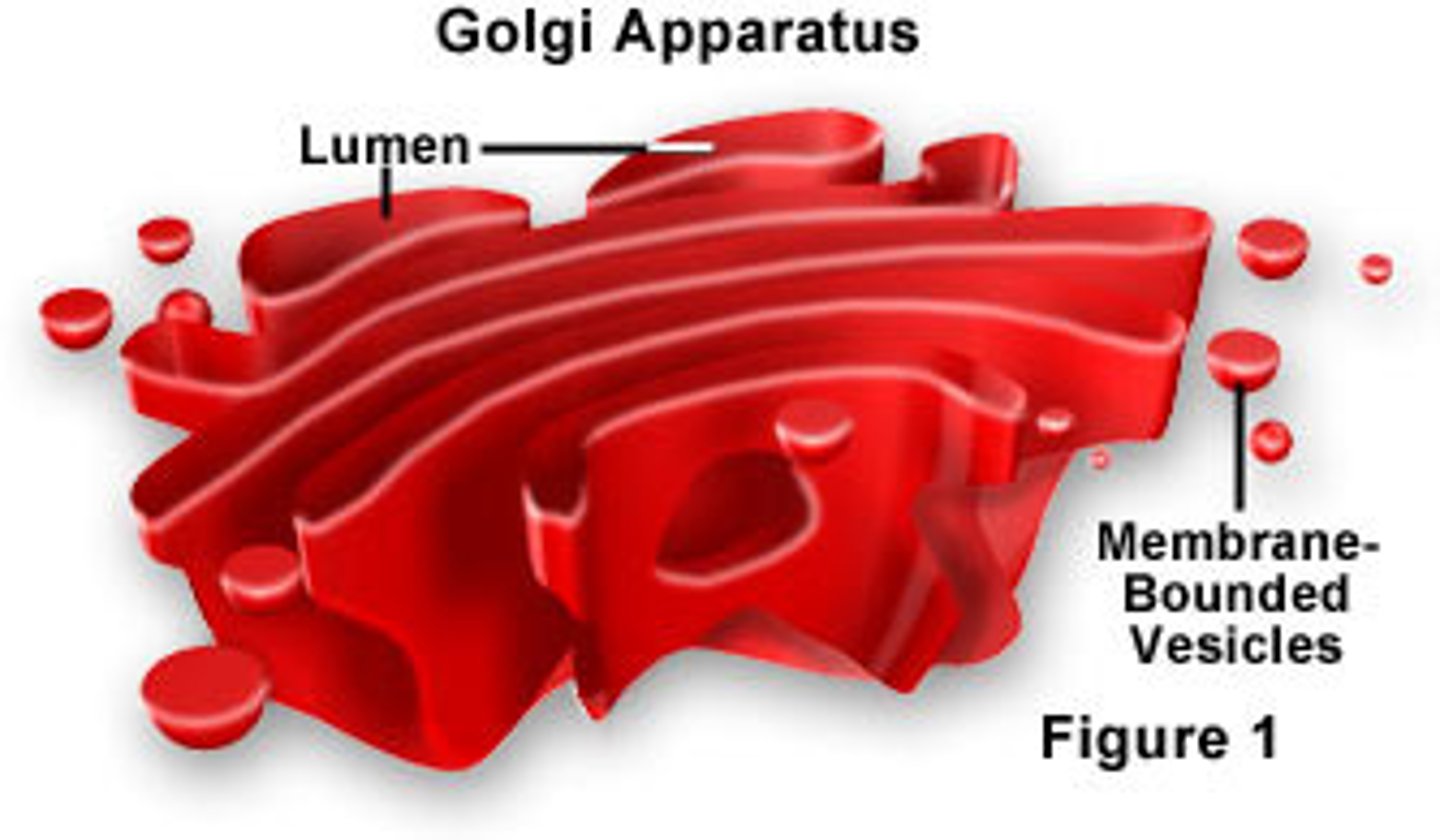
golgi apparatus
- chemical modification - performs chemical modification of proteins and lipids transported from the RER and SER via transport vesticles
- sorting and packing - proteins and/or lipds that are secreted and sorted and packeged into secretory vesticles
- formation of lysosomes
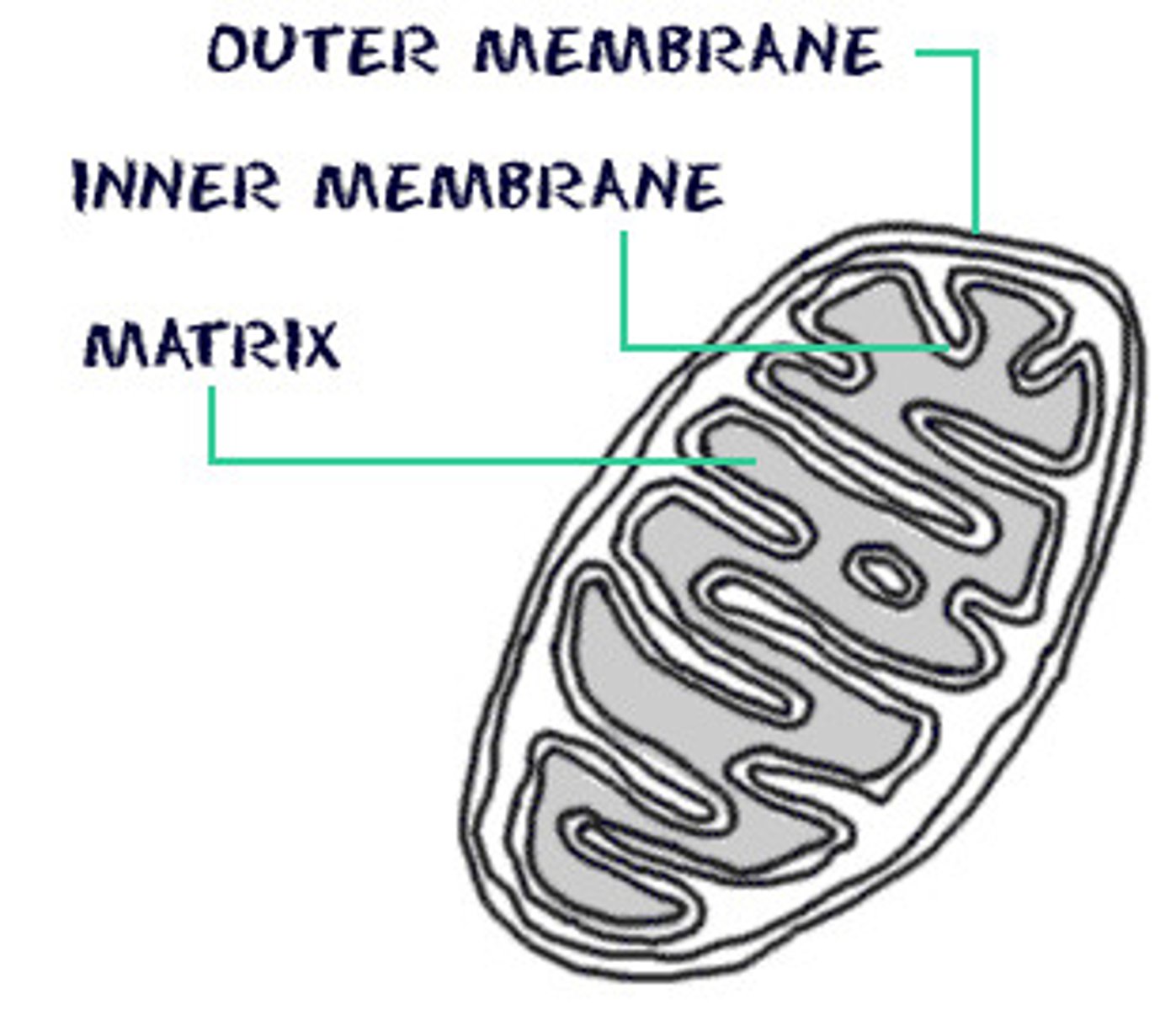
mitochondrion
- site of respiration - mitochondrion performs (aerobic) respiration during which glucose is oxidised to release energy for cell activities
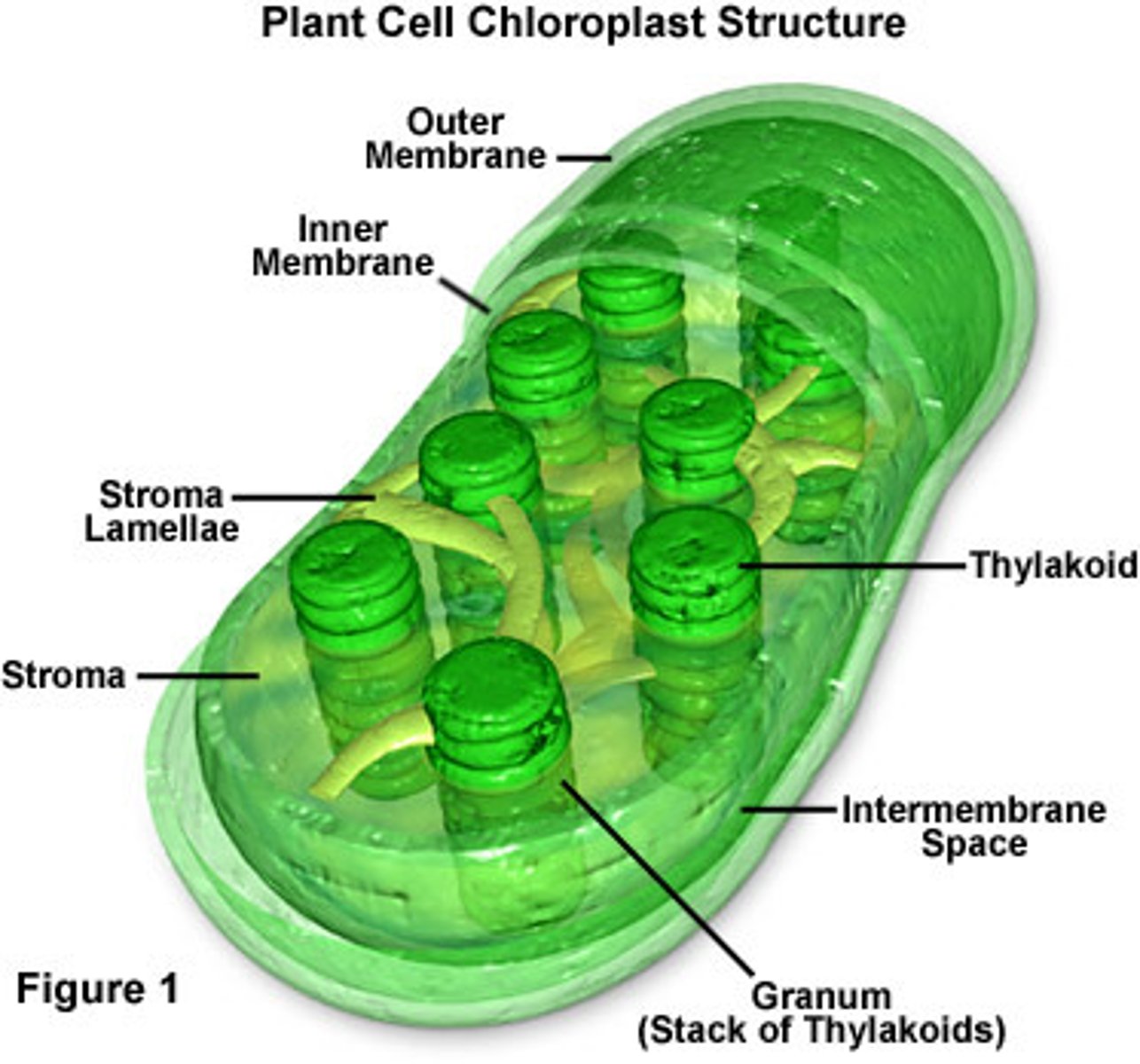
chloroplast
- Site of photosynthesis- light energy absorbed by chlorophyll is converted into chemical energy for glucose formation
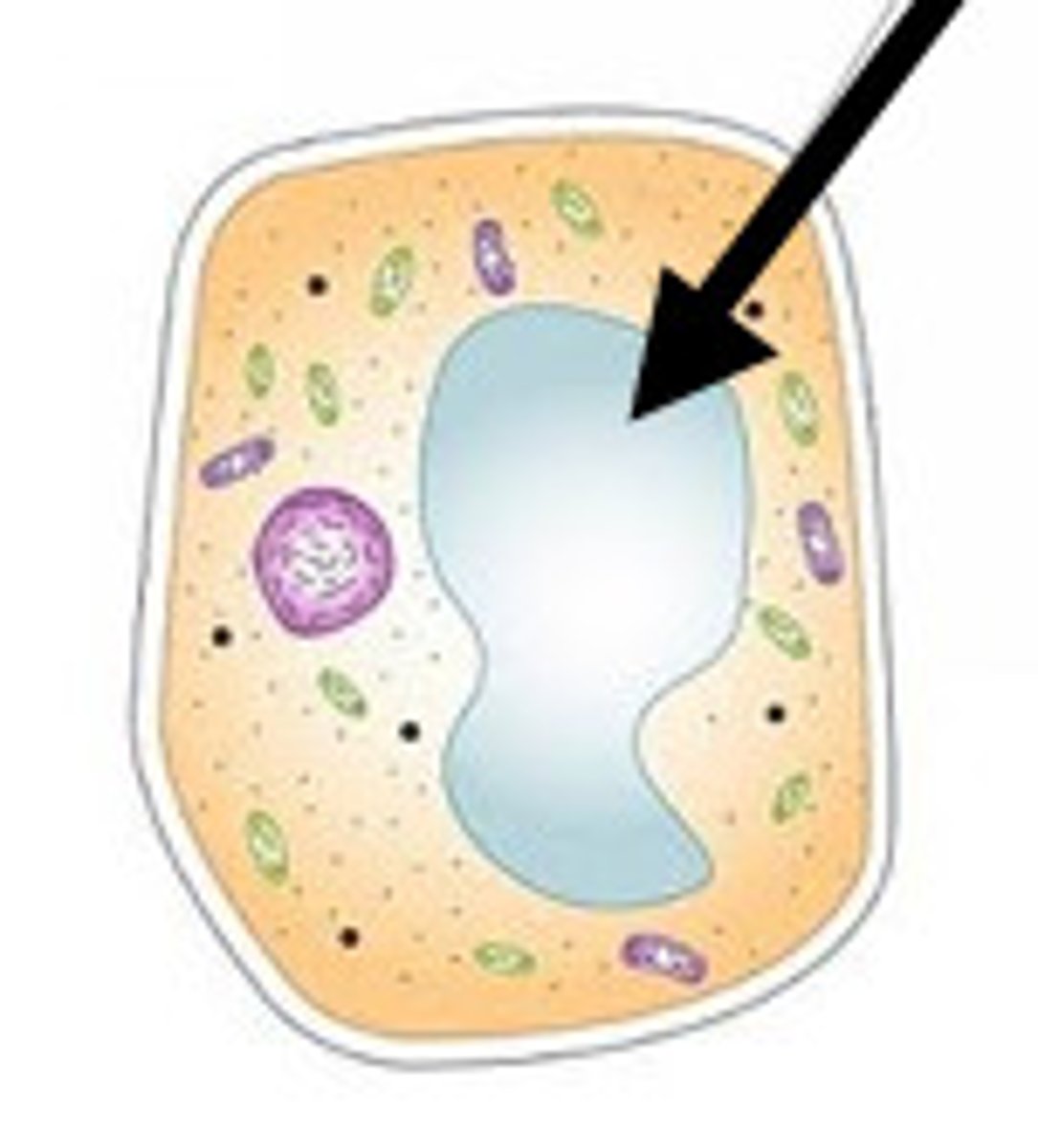
vacuole
- helps develop turgidy of plant cell as water molecules enter the cell sap by osmosis when vacuole volume increases
- storage of starch converted from excess glucose
- storage of pigments which gives flowers or fruits its colour to attract insects and birds for pollination and seed dispersal
- storage of defensive compounds for protection by making plants deadly or unpalatable for hebivores to consume
- deposition site for metabolic waste materials
cellulose cell wall
- highly rigid to provide mechanical support for individual cells, lignin deposition further increases the strength in some of the xylem walls
- prevevents cell lysis when the cell is placed in a medium of less negative water potential
deleop a coat of waxy cuticle which reduces excessive water loss and reduces rate of infection by plant pathogens