chapter 23: evolution of populations
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
what evolves?
what doesn’t evolve?
what doesn’t evolve?
populations, individuals
2
New cards
why do individuals not evolve?
individuals acclimate to the environment. they don’t adapt because that’s microevolution. they don’t pass down the acclimation.
3
New cards
what is microevolution?
a change in allele frequencies in a population over generations, not resulting in a new species
4
New cards
what are the 3 widely accepted mechanisms that cause allele frequencies to change? (AKA that causes microevolution)
* which is most effective?
* which is most effective?
natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow. natural selection
5
New cards
these 3 mechanisms cause allele frequency change: natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow
* which of these cause adaptive evolution?
* which of these cause adaptive evolution?
natural selection
6
New cards
what is the name for when darwin’s & mendel’s ideas were combined/reconciled? rather than looking at just changes, incorporated study of genetic changes were included
the modern synthesis (new synthesis)
7
New cards
what is modern synthesis (new synthesis)?
reconciled darwins (NS) & mendel’s (theories of inheritance) ideas
8
New cards
when was the idea of modern synthesis created?
1940s
9
New cards
what is the prerequisite for natural selection?
genetic variation
10
New cards
do clones have genetic variation?
no
11
New cards
what is the source of genetic variation?
mutations
12
New cards
what is genetic variation?
variation in the DNA sequence of genomes
13
New cards
what are the 2 things that genetic variation is measured as?
average heterozygosity & nucleotide variability
14
New cards
what is heterozygosity
has dominant & recessive alleles
15
New cards
genetic variation is measured by 2 things: average heterozygosity & nucleotide variability.
* define both
* define both
average heterozygosity measures the average percent of loci that are heterozygous in a population. nucleotide variability compares the DNA sequences of pairs of individuals
16
New cards
what does sexual reproduction do in regards to alleles?
it shuffles existing alleles into new combinations
17
New cards
______ of alleles is more important than mutation in producing the genetic differences
recombination
18
New cards
recombination of alleles is more important than mutation in producing genetic differences (AKA that cause genetic variation in sexual reproduction).
* what are 2 examples of allele recombination?
* what are 2 examples of allele recombination?
independent assortment & crossing over
19
New cards
describe independent assortment
alleles of different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another
20
New cards
describe crossing over
When two chromosomes — 1 from mom and 1 from dad — line up, parts of the chromosome can be switched. the 2 chromosomes contain the same genes, but may have different forms of the genes
21
New cards
what does sexual reproduction allow for?
natural selection
22
New cards
does sexual or asexual reproduction produce clones?
asexual
23
New cards
does sexual or asexual reproduction have natural selection?
sexual
24
New cards
why does asexual reproduction not have natural selection?
because they’re all clones, they’re genes are all the same and there’s no genetic variation
25
New cards
what are some examples of asexually reproducing organisms?
plants, some microbes, sea anemone
26
New cards
is it harder to reproduce sexually or asexually? why? (AKA which has a reproductive handicap)
sexually, because it’s more costly/more of a process
27
New cards
if sexual reproduction is a handicap, why has it persisted?
it produces genetic variation that may aid in disease resistance
28
New cards
some phenotypic variation does NOT result from genetic differences among individuals.
* what is the main influence that does cause phenotypic variation in these situations?
* what is the main influence that does cause phenotypic variation in these situations?
environment (epigenetics)
29
New cards
only _____ variation can have evolutionary consequences
inherited
30
New cards
what’s an example of non-inheritable variation?
some caterpillars eat leaves & grow to look like leaves/stems. other caterpillars of the same species eat flowers & grow to look like flowers. their appearances aren’t heritable variations. their appearances are influenced by the food they ate/their environments
31
New cards
define mutation
any change in an organism’s dna
32
New cards
mutation has a ____ effect on ____ populations.
\
example: it takes 2000 generations for mutation alone to change an allele frequency 1%
\
example: it takes 2000 generations for mutation alone to change an allele frequency 1%
small, large
33
New cards
_____ has a small effect on large populations. BUT there are a lot of genes, so cumulative effects of mutations can be detected.
mutations
34
New cards
**IMPORTANT POINT:**
what provides raw material for natural selection to work on, so ultimate change can be great?
what provides raw material for natural selection to work on, so ultimate change can be great?
mutation
35
New cards
**IMPORTANT POINT:**
what does mutation provide for NS to work on, so that ultimate change can be great?
what does mutation provide for NS to work on, so that ultimate change can be great?
raw material
36
New cards
**IMPORTANT POINT:**
example: some rhinos have horns & some don’t. what role does mutation play? what role does NS play?
example: some rhinos have horns & some don’t. what role does mutation play? what role does NS play?
mutation determines if the rhino has a horn. NS allows the rhino’s horn to get bigger in subsequent generations
37
New cards
what are the 2 things that allow new genes & alleles to arise?
mutation & gene duplication
38
New cards
does mutation or natural selection cause adaptations?
* for the other term - what does it provide for adaptation to happen?
* for the other term - what does it provide for adaptation to happen?
natural selection, a base
39
New cards
only mutations in cells that produce ____ can be passed to offspring
gametes
40
New cards
define point mutation
a change in one base in a gene
41
New cards
mutations in noncoding regions of DNA are harmless…
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
often
42
New cards
mutations in genes can be ____ because of redundancy in the genetic code
neutral
43
New cards
why can mutations in genes be neutral?
because of redundancy in the genetic code
44
New cards
during mutation:
change in protein production is harmful…
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
change in protein production is harmful…
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
often
45
New cards
during mutation:
change in protein production is beneficial…
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
change in protein production is beneficial…
* always
* often
* rarely
* never
rarely
46
New cards
are mutation rates high or low in animals & plants?
low
47
New cards
define population
localized group of individuals of the same species
48
New cards
define gene pool
consists of all the alleles for all loci in a population
49
New cards
define fixed locus
all individuals in a population are homozygous for the same allele
50
New cards
if everyone was homozygous dominant, could natural selection cause the recessive allele to take over?
no
51
New cards
what is the main idea of the HW Theorem? (hardy weinberg theorem)
if the organisms are well-adapted to their environment, then they won’t change or evolve
52
New cards
does HW Theorem describe an evolving or non-evolving population?
non-evolving
53
New cards
HW Theorem:
* allele frequencies & genotype frequencies stay constant from one generation to the next unless… ?
* allele frequencies & genotype frequencies stay constant from one generation to the next unless… ?
there are non-random effects (evolution)
54
New cards
* what is the equation for allele frequency?
* what is the equation for genotype frequencies?
* what is the equation for genotype frequencies?
p+q=1, p^2+2pq+q^2=1
55
New cards
describe the harm in inbreeding
the parents are likely both carriers of certain diseases or tendencies. it is more likely that their offspring is homozygous recessive for those diseases.
56
New cards
HW Equilibrium:
* gene frequencies remain the same throughout generations -- AKA no _____
* gene frequencies remain the same throughout generations -- AKA no _____
evolution
57
New cards
**IMPORTANT POINT:**
what are the 5 conditions for HW Equilibrium that are rarely met in nature? (if these things are in place, nothing will evolve)
what are the 5 conditions for HW Equilibrium that are rarely met in nature? (if these things are in place, nothing will evolve)
extremely large population size, no gene flow, no mutations, random mating, no natural selection
58
New cards
these are the 5 conditions for HW Equilibrium that are rarely met in nature? (if these things are in place, nothing will evolve)
1. extremely large population size
2. no gene flow
3. almost no mutations
4. random mating
5. no natural selection
\
* what is an example of gene flow?
* what is random mating?
* why is it likely that “random mating” would NOT be reached?
1. extremely large population size
2. no gene flow
3. almost no mutations
4. random mating
5. no natural selection
\
* what is an example of gene flow?
* what is random mating?
* why is it likely that “random mating” would NOT be reached?
migration, no selection, because animals are choosy and selective about their partners
59
New cards
if all of the factors for HW Equilibrium are met, will evolution occur?
no
60
New cards
what are the 8 mechanisms that could cause evolutionary changes? (AKA Hypothesized Evolutionary Mechanisms)
* these prove that Darwinian NS isn’t the only theory
* these prove that Darwinian NS isn’t the only theory
natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, species selection, self organization, neutral theory, natural genetic engineering, intelligent design
61
New cards
natural selection:
* differential ____ success (some live, some don’t)
* this is the only method that causes ____
* accumulates & maintains favorable _____
* differential ____ success (some live, some don’t)
* this is the only method that causes ____
* accumulates & maintains favorable _____
reproductive, adaptation, genotypes
62
New cards
what is phenotypic polymorphism?
describes a population in which 2+ distinct morphs for a character are each represented in high enough frequencies to be readily noticeable
63
New cards
what does phenotypic polymorphism prove?
environment affects appearance
64
New cards
what is genetic polymorphism?
heritable components of characters that occur along a continuum in a population
65
New cards
_____ conditions make it difficult to determine what traits are inherited & what isn’t
environmental
66
New cards
an example of genetic polymorphism is the yarrow plant. it’s seeds were taken from a mountain range at a variety of altitudes & placed in a level field. they grew at different heights. the flowers grew at different heights on the level field. was this genetic or environmental? why?
genetic because the seeds were moved
67
New cards
define a cline
change in organism by geography
68
New cards
what are the 2 factors of individual fitness?
survival & reproduction
69
New cards
define individual fitness
the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals
70
New cards
is having 9 kids an example of high individual fitness or low individual fitness?
high
71
New cards
define relative fitness
contribution of a genotype to the next generation as compared to the contributions of alternative genotypes for the same locus
72
New cards
is it high or low relative fitness if the genotype shows up more in the next generation?
high
73
New cards
natural selection increases the frequencies of alleles that enhance survival & reproduction. therefore, the adaptive match between an organism & it’s environment _____
\
* increase or decrease?
\
* increase or decrease?
increase
74
New cards
define niche
role an organism plays (ex: predator vs prey)
75
New cards
what are 5 types of natural selection?
directional selection, diversifying selection, stabilizing selection, sexual selection, frequency dependent selection
76
New cards
define stabilizing selection
loses extreme phenotypes
77
New cards
define directional selection
favors one phenotype extreme over the other, causing the mean to shift
78
New cards
define diversifying selection
intermediate phenotype disfavored, causing phenotype divergence (2 extreme phenotypes left)
79
New cards
sexual selection is based on _____ ____
sexual dimorphism
80
New cards
sexual selection is based on sexual dimorphism. define this term
distinct secondary characteristic differences between males & females
81
New cards
sexual selection is a type of _____ mating
nonrandom
82
New cards
sexual selection is a type of nonrandom mating. what are 3 types of nonrandom mating? define each
inbreeding (close relatives), selfing (asexual reproduction), assortative mating (females prefer to mate with males with certain phenotypes)
83
New cards
what may be the cause of inbreeding? why is it bad?
geographic location or lack of other opportunities. elevates frequency of homozygous recessive/decreases diversity
84
New cards
sexual selection emphasizes mating over ____
survival
85
New cards
what is the good genes hypothesis?
if a trait is related to male health, females use the selected feature to evaluate overall health & superior genes of the male
86
New cards
what are 3 types of sexual selection?
intrasexual, intersexual selection, male showiness
87
New cards
define intrasexual selection
competition among individuals of one sex for mates of the opposite sex
88
New cards
define intersexual selection (AKA mate choice)
occurs when individuals of one sex are choosy in selecting their mates
89
New cards
define male showiness
due to mate choice. increases a male’s chances of attracting a female, while decreasing his chances of survival
90
New cards
why are females often more picky about who they mate with than males?
because they invest more energy into childbirth & childrearing than the males
91
New cards
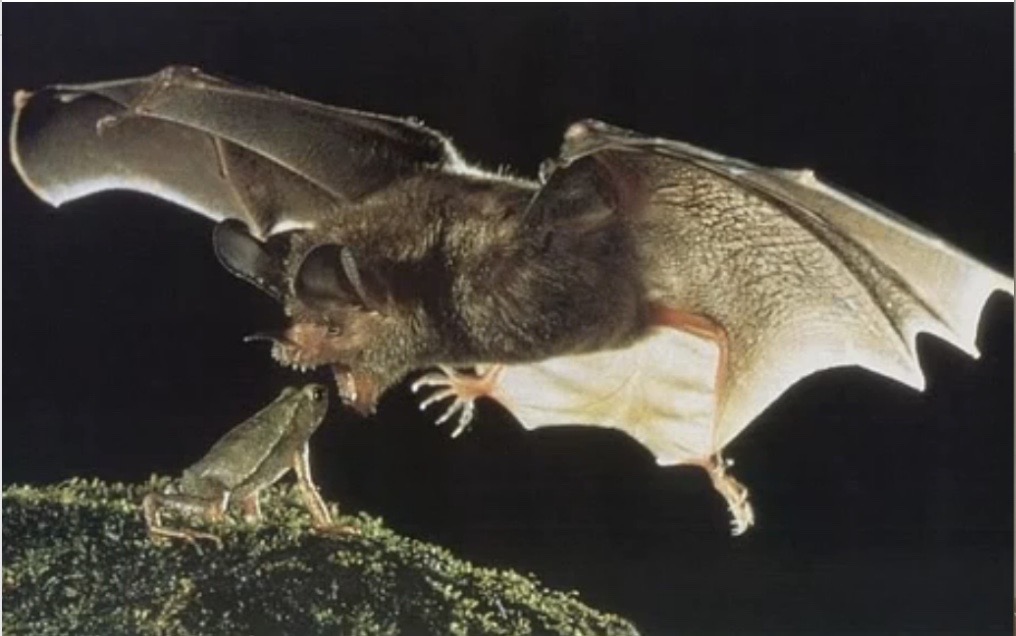

describe the significance of this picture
male frogs call to attract females. but bats hear the calls and go to eat the male frog. the benefit is that the female frogs like the male frog’s call. the more the male frog calls, though, the more likely it is to get eaten by the bat. over generations, if the females started being picky about features of the male frog over their call, then bats would have less food since frogs would stop calling
92
New cards
what is frequency-dependent selection?
the fitness of a phenotype declines if it becomes too common in the population. selection favors whichever phenotype is less common in a population
93
New cards
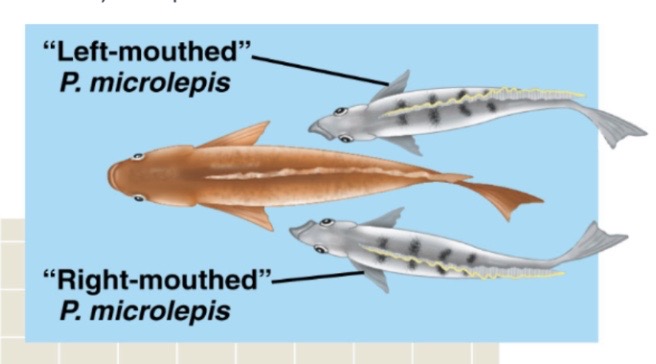
describe the significance of this picture and what it leads to
if there are more left-mouthed than right-mouthed fish in an area: the more often the big fish is attacked on the left side (with left-mouthed fish), the better the big fish gets at dodging the left-mouthed fish. this leaves left-mouthed fish without food, so they’ll die out. right-mouthed fish (previously in the minority) become more popular
94
New cards
what does balancing selection lead to?
a state called balanced polymorphism - AKA heterozygous advatage
95
New cards
define heterozygote advantage
some individuals who are heterozygous at a particular locus have greater fitness than homozygotes
96
New cards
what’s an example of heterozygote advantage? give a thorough description
sickle cell anemia & malaria resistance. if someone is homozygous recessive for sickle cell, it’s often lethal. if someone is homozygous dominant, less of their kids will have sickle cell, and fewer will die of malaria. if someone is heterozygous, they’ll be a carrier of sickle cell & have resistance to malaria. if malaria increases, sickle cell decreases. because with malaria, all die. & with sickle cell, some kids might die if marrying a carrier
97
New cards
does natural selection work on neutral variation?
no
98
New cards
what are some examples of natural selection?
darwin’s finshes, soapberry bugs, antibiotic resistance
99
New cards
describe how natural selection worked for the cane toad & its selection for longer legs.
introduced to australia to eat bugs. for the first 20 years, they spread at 6 miles/year. they now spread at average 30 miles/year. allows them to secure the best habitat at the new terrain. migration = no competition with other toads because none are there yet
100
New cards
give a short example of how butterflies experienced natural selection
evolved resistance to a killer bacteria in one year