IMED1003 - Cholesterol Metabolism (3)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Summary so Far
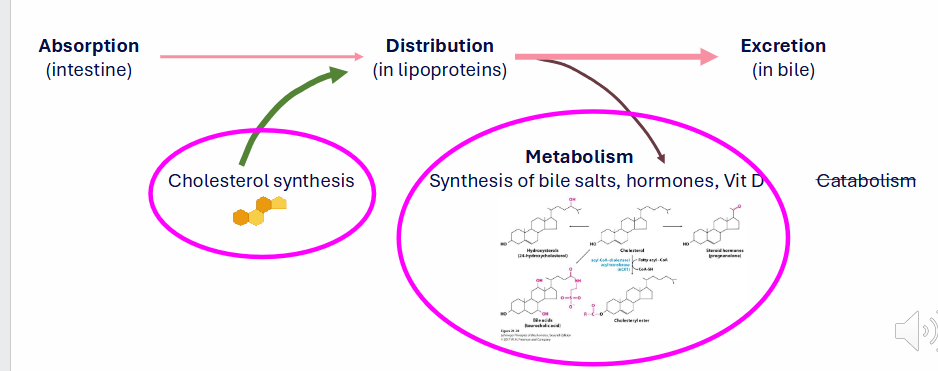
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 3
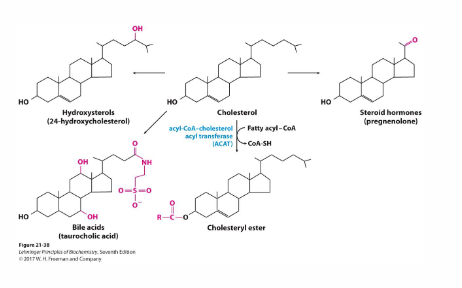
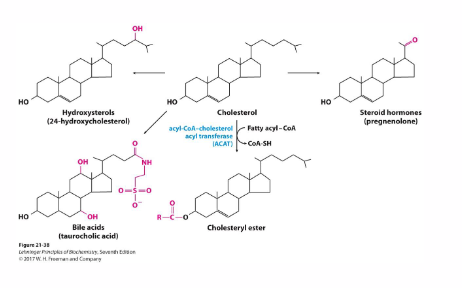
Cholesterol and its derivatives
- Membrane component - free cholesterol
- Storage - cholesteryl esters
- Cholesterol derivatives: Steroid Hormones, Vitamin D, Bile Salts
- Cholesterol transport: lipoproteins
- cholesterol is used to make steroid hormones (in the adrenal glands, gonads etc)
Endogenous Cholesterol Production
- Most cells can synthesise cholesterol
LIVER:
- Production of bile acids
- Produces, mobiles cholesterol for use by peripheral tissues (peripheral tissues e.g gonads, adrenal glands)
ADRENAL GLANDS, GONADS - CHOLESTEROL DERIVATIVES:
- Synthesise 80% of required cholesterol
CNS: USE IN MYELIN PRODUCTION:
- Blood brain barrier: cholesterol cannot be transported to brain
Cholesterol Synthesis
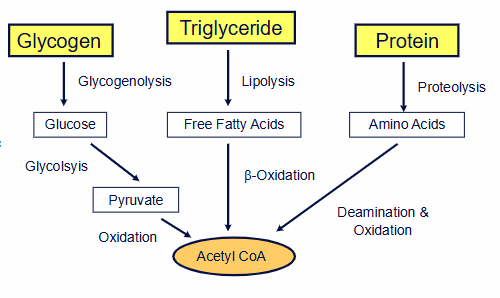
- Requires Acetyl CoA
- important intermediate metabolite
- generated from catabolism of: Carbohydrates, Fatty acids, Amino Acids
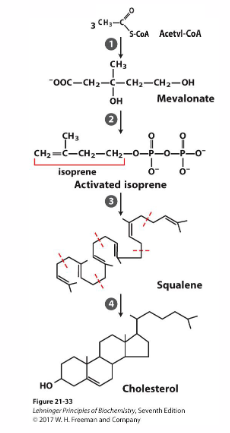
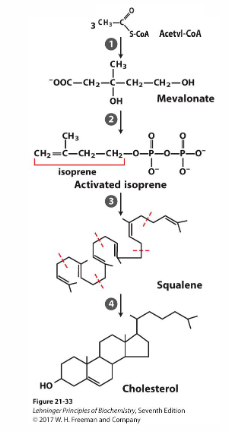
Overview of Cholesterol Synthesis
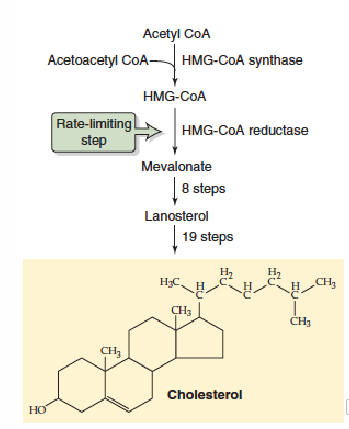
1. 3 Acetyl CoA are condensed to form HMG-CoA (produces water, condensation reaction). HMG-CoA is reduced to form mevalonate
2. Mevalonate converts to phosphorylated 5-C isoprene, requiring 3 ATP
3. Six isoprenes polymerise to form the 30C linear squalene
4. Squalene cyclises to form the 4 rings that are modified to produce cholesterol
Regulation of Cholesterol Synthesis
- HMG-CoA Reductase
3 mechanisms of regulation:
- Phosphorylation - allosterically regulates activity
- Targeted for degredation
- Transcriptionally regulated
Drug Target:
- Statins inactivate HMG-CoA reductase
- most commonly prescribe cholesterol-lowering drug
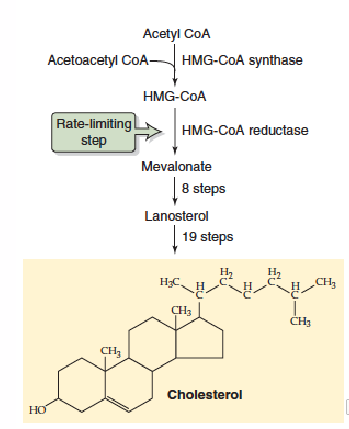
Retulation of Cholesterol Synthesis: HMG-CoA reductase
1. Phosphorylation - allosterically regulates activity:
- [ATP]:[AMP] low, enzyme is phosphorylated - inactive
- Decreases cholesterol synthesis in low energy state (since synthesis needs energy)
2. Proteolytic Degredation:
- High [cholesterol], protein marked for degredation (ubiquinated)
- degraded by proteosomes
- decreases cholesterol synthesis when cholesterol levels are high
3. Transcriptional regulation of HMG-CoA gene
- Low [cholesterol], increased transcription of gene encoding HMG-CoA reductase
- Promotes cholesterol synthesis when cholesterol levels are low
Storage and Transport - Cholesterol
- Membrane component: free cholesterol
- Storage: cholesteryl esters
- Cholesterol derivaties: Steroid hormones, Vitamin D, Bile Salts
- Cholesterol Transport: Lipoproteins
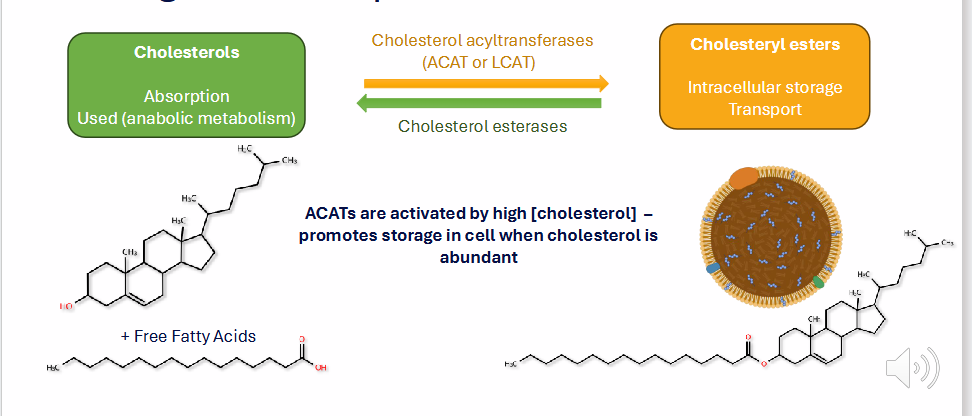
Cholesterol is esterified with fatty acids for storage and transport
- Free cholesterol is used in absorption (anabolic metabolism)
- Cholesterol acyltransferases (ACAT or LCATs) are activated by high [cholesterol] - promotes storage in cell when cholesterol is abundant
- this forms cholesteryl esters (intracellular storage and transport)
- Cholesterol esterases go the other way
![<p>- Free cholesterol is used in absorption (anabolic metabolism)</p><p>- Cholesterol acyltransferases (ACAT or LCATs) are activated by high [cholesterol] - promotes storage in cell when cholesterol is abundant</p><p>- this forms cholesteryl esters (intracellular storage and transport)</p><p>- Cholesterol esterases go the other way</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/78c96b31-7844-47b6-8d1d-4892cae479e7.png)
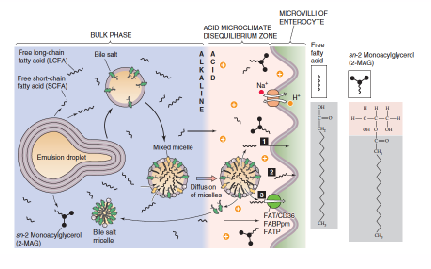
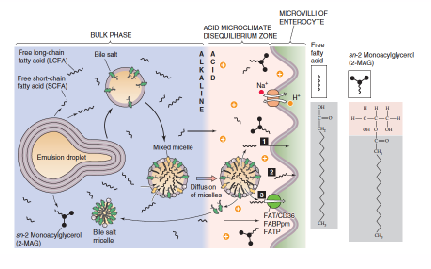
Bile Acids emulsify cholesterol in GI tract
- Exogenous cholesterol - absorbed in GI tract
- excess cholesterol - excreted into GI tract
- Bile Acids
- Produced in hepatocytes (liver)
- Stored in gall bladder
- secreted into small intestine