Chemistry Common Mistakes Paper 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/92
Last updated 4:46 AM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
behaviour of particles in a solid
* have a fixed shape and cannot flow, because their particles cannot move from place to place
* cannot be **compressed** (squashed), because their particles are close together and have no space to move into
* cannot be **compressed** (squashed), because their particles are close together and have no space to move into
2
New cards
behaviour of particles in a gas
* flow and completely fill their container, because their particles can move quickly in all directions
* can be compressed, because their particles are far apart and have space to move into
* can be compressed, because their particles are far apart and have space to move into
3
New cards
why can transition metals be used as a catalyst
they have a variety of different charged ions
4
New cards
anything using temp changes, what can you use as a control to improve accuracy
polystryene cup
5
New cards
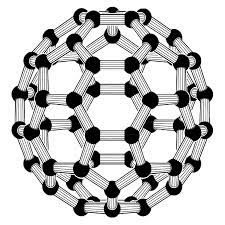
what shape is Buckminster fullerene molecule
spherical
6
New cards
uses of fullerenes
* drug delivery - hollow
* hydrogen storage
* antioxidants
* catalysts (high sa to vol ratio)
* lubricants ( spherical so will roll)
* hydrogen storage
* antioxidants
* catalysts (high sa to vol ratio)
* lubricants ( spherical so will roll)
7
New cards
why does sodium oxide have a high melting point
* giant structure
strong forces of attraction pulling them together
lots of energy needed to break them
strong forces of attraction pulling them together
lots of energy needed to break them
8
New cards
what do you need to mention in practical questions
1. Control variables
2. Risk factors; solution
3. Independent variables
4. Method w/ instruments
5. Evaluative conclusion
6. Dependent variables
9
New cards
what's the difference between electrolysis and chemical cell
electrolysis uses electricity, chemical cell uses a chemical reaction
10
New cards
meaning of accuracy
1. the degree to which the result of a measurement, calculation, or specification conforms to the correct value or a standard
11
New cards
meaning of precision
refinement in a measurement, calculation, or specification, especially as represented by the number of digits given
12
New cards
how are soluble salts made
by reacting a dilute hydrochloric acid with an insoluble solid
13
New cards
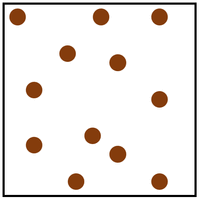
give two limitations of this simple particle model for hydrogen gas
1. it doesn’t show movement
2. they r not 2d irl
14
New cards
1 mega joule = how many j
1,000,000
15
New cards
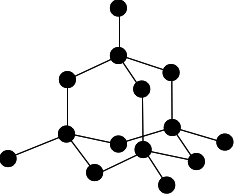
structure of a diamond
In diamond, each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with other carbon atoms in a giant covalent structure, so diamond is very hard, has a very high melting point and does not conduct electricity
16
New cards
why does a diamond have a high MP
Diamond has a very high melting point because a large amount of energy is needed to overcome the many strong covalent bonds.
17
New cards
why does a diamond conduct no electricity
It does not conduct electricity as there are no delocalised electrons in the structure.
18
New cards
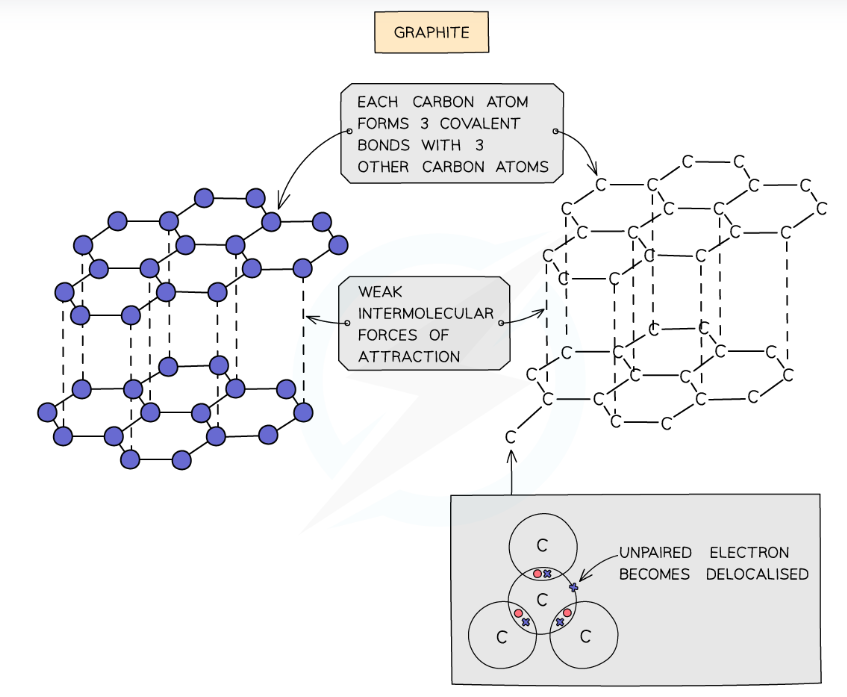
what is the structure of graphite
* In graphite, each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with three other carbon atoms, forming layers of hexagonal rings which have no covalent bonds between the layers.
* In graphite, one electron from each carbon atom is delocalised.
* (graphite is similar to metals in that it has delocalised electrons.)
* In graphite, one electron from each carbon atom is delocalised.
* (graphite is similar to metals in that it has delocalised electrons.)
19
New cards
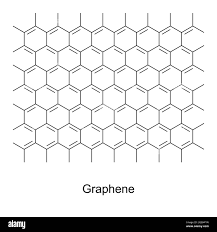
structure of graphene and how this makes it useful
Graphene is a single layer of graphite and has properties that make it useful in electronics and composites.
20
New cards
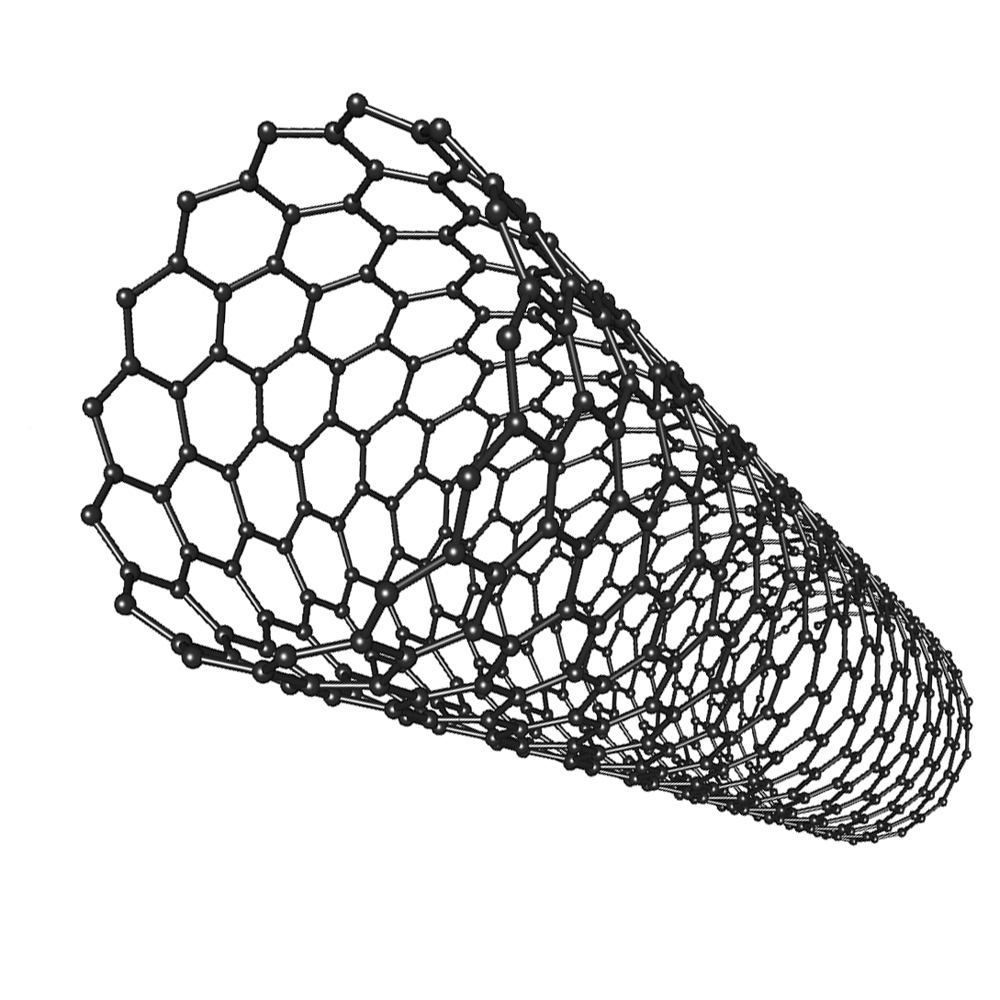
structure of carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical fullerenes with very high length to diameter ratios. Their properties make them useful for nanotechnology, electronics and materials.
21
New cards
A different student produced a pure, dry sample of copper chloride using the same reaction.
How should the solution be heated gently in step 3; “Heat the solution gently until crystals start to form.”
How should the solution be heated gently in step 3; “Heat the solution gently until crystals start to form.”
using a (boiling) water bath or using an electric heater
22
New cards
state the law of conseration of mass
mass of products = mass of reactants
23
New cards
explain why the student should use a **pipette** to measure the dilute sulfuric acid and a **burette** to measure the sodium hydroxide volume
* pipette measures a fixed volume (accurately)
* burette measures variable volume
* burette measures variable volume
24
New cards
why is sodium chloride a strong electrolyte
The solution will have the maximum number of ions available to conduct electricity.
25
New cards
equation for a hydrogen fuel cell
2H2 + O2 ⟶ 2H2O
26
New cards
in refreence to bond energies, explain why something would be an exothermic reaction
* energy released forming (new) bonds is greater than energy needed to break (existing) bonds
* (so) energy is released (to the surroundings)
* (so) energy is released (to the surroundings)
27
New cards
half equation for the reaction occurring at an electrode in 1 type of hydrogen fuel cell
H2 + 2OH− → 2H2O + 2 e−
28
New cards
why would a feul cell be described as an alkaline cell
contains OH− ions
29
New cards
how to find out how many protons there are
small #
30
New cards
how to find out how many neutrons there are
big number - small number
31
New cards
properties of the alkali metals (GROUP 1 METALS)
* are soft (they can be cut with a knife)
* have relatively low **melting points**
* have low densities
* have relatively low **melting points**
* have low densities
32
New cards
Give two differences between the properties of iron and sodium.
1. • iron has a higher MP/BP
2. • iron is dense(r)
3. • iron is hard(er)
4. • iron is strong(er)
5. • iron is less reactive
6. • iron has ions with different charges
7. • iron forms coloured compounds
8. • iron can be a catalyst
33
New cards
Chadwick’s experimental work on the atom led to a better understanding of isotopes.
Explain how his work led to this understanding.
Explain how his work led to this understanding.
1. Chadwick provided the evidence to show the existence of neutrons
2. (this was necessary because) isotopes have the same number of protons
3. but with different numbers of neutrons
34
New cards
what should you do when listing methods
independent, dependent, control,
35
New cards
when identifiying problems for 2&3 markers what should you do
1. identify the problem
2. give a solution
36
New cards
in graphite, each carbon forms _____ (covalent) bonds
3
37
New cards
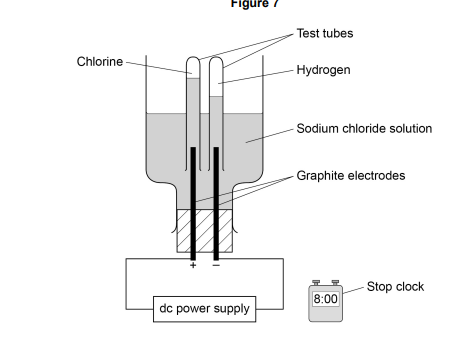
The student made an error in selecting the apparatus for this investigation. How should the apparatus be changed?
1. use measuring cylinders, or gas syringes (instead of test tubes)
2. (Because) test tubes cannot measure the volume
38
New cards
Name the products formed when chlorine solution reacts with potassium iodide solution.
potassium chloride and iodine
39
New cards
Chlorine reacts with hydrogen to form hydrogen chloride.
Explain why hydrogen chloride is a gas at room temperature.
Explain why hydrogen chloride is a gas at room temperature.
* hydrogen chloride is made of small molecules
* so has weak intermolecular forces
* that require little energy to overcome
* so has weak intermolecular forces
* that require little energy to overcome
40
New cards
Give one reason why it would be hazardous if water came into contact with sodium
* • very exothermic reaction
* • produces a corrosive solution
* • produces hydrogen, which is explosive / flammable
* • produces a corrosive solution
* • produces hydrogen, which is explosive / flammable
41
New cards
Explain why you would not expect titanium chloride to be a liquid at room temperature
* metal chlorides are usually ionic
* solid at room temperature / have high melting points
* due to them having strong (electrostatic) forces between the ions
* solid at room temperature / have high melting points
* due to them having strong (electrostatic) forces between the ions
42
New cards
why is graphite used for electrodes in electrolysis
its unreactive, can conduct electricity
43
New cards
what is a neutralisation reaction
A neutralisation reaction is a reaction between an acid and a base. Acids in solution are sources of hydrogen ions , H. + alkalis in solution are sources of hydroxide ions, OH.
44
New cards
write the ionic equation for the neutralisation reaction of hydrochloric acid with potassium hydroxide
H+ + 0H- → H2O
45
New cards
what is the ammonia from the Haber process used for
nitrogen based fertilisers
46
New cards
what does an ester bond look like
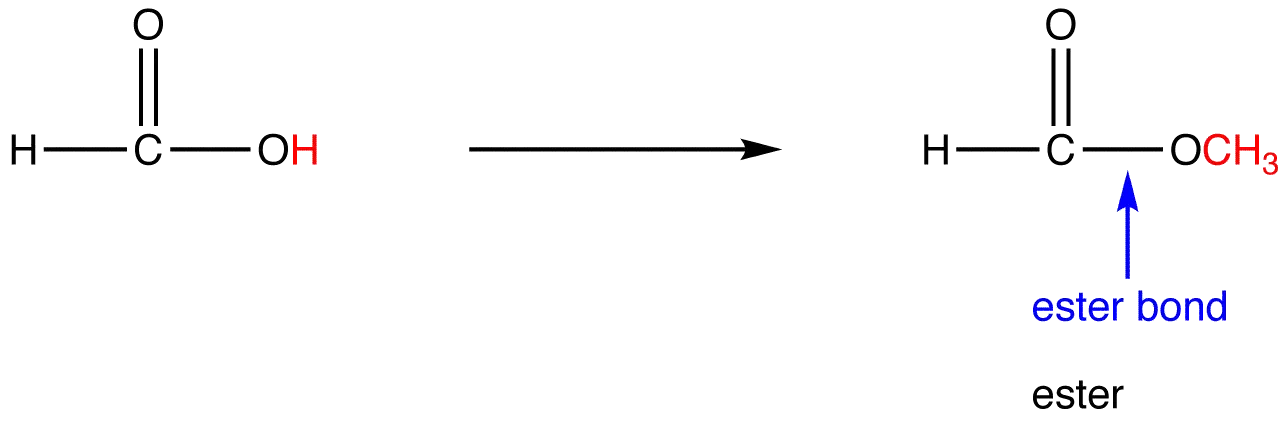
47
New cards
meaning of affinity
Affinity is the **tendency of a chemical species such as an atom or molecule to react with another to form a chemical compound**.
48
New cards
how did mendeleev organise the elements
arranging them in order of their atomic weight
49
New cards
what did mendie do with his version of the periodic table
* had gaps in it
* showed elements with similar chemical properties lined up in groups
* showed elements with similar chemical properties lined up in groups
50
New cards
properties of g7 metals
* simple **molecules**
* coloured vapours
* diatomic molecules
* form ionic salts w metals
* form molecular compounds with non metals
* \
* coloured vapours
* diatomic molecules
* form ionic salts w metals
* form molecular compounds with non metals
* \
51
New cards
characteristics of transition metals
* form coloured compounds
* catalytic properties
* ions w different charges
* catalytic properties
* ions w different charges
52
New cards
what’s the modern name for atomic weight
relative atomic mass
53
New cards
formula of molecule X in group 7
X2
54
New cards
Describe what you would see when sodium reacts with chlorine.
flame
white precipitate
white precipitate
55
New cards
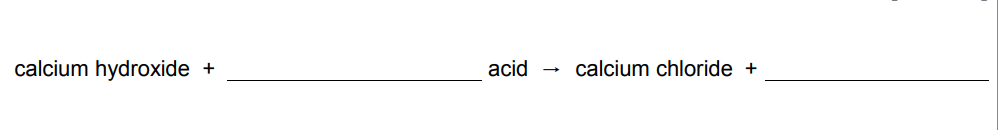
Calcium hydroxide solution reacts with an acid to form calcium chloride. Complete the word equation for the reaction
hydrochloric (acid) water
56
New cards
Suggest one reason why it costs less to use nanoparticles rather than fine particles in suncreams
1. • less can be used (for the same effect)
2. • greater surface area (to volume ratio)
57
New cards
uses of nanoparticles
* catalyst
* electronics
* deoderant
* sun creamal
* electronics
* deoderant
* sun creamal
58
New cards
Give one limitation of using a dot and cross diagram to represent an ammonia molecule.
does not show the shape or only two-dimensiona
59
New cards
Hydrogen fuel cells can be used to power different forms of transport. Some diesel trains are being converted to run on hydrogen fuel cells.
**A newspaper article referred to the converted trains as the new ‘steam trains’. Suggest why.**
**A newspaper article referred to the converted trains as the new ‘steam trains’. Suggest why.**
1. (in a fuel cell) hydrogen is oxidised (to produce water)
2. water is produced / released as gas / vapour / steam
60
New cards

Explain why a mixture is used as the electrolyte instead of using only aluminium oxide
1. mixture has a lower melting point (than aluminium oxide)
2. (so) less energy needed
61
New cards

Explain why sodium chloride solution cannot be used as the electrolyte to produce sodium metal.
1. hydrogen (gas) would be produced (instead of sodium)
2. (because) sodium is more reactive than hydrogen
62
New cards
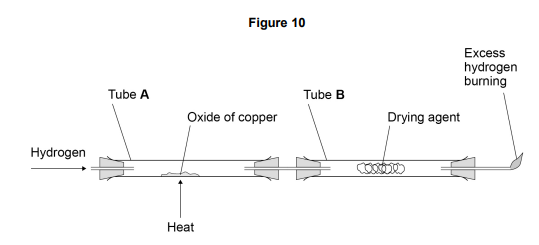
Explain why the excess hydrogen must be burned off.
* to prevent hydrogen escaping (into the air)
* (because) hydrogen is explosive
* (because) hydrogen is explosive
63
New cards
John Dalton; Before the discovery of the electron, atoms were thought to be …..
tiny spheres that could not be divided.
64
New cards
John Dalton The discovery of the electron led to the ….
plum pudding model of the atom.
65
New cards
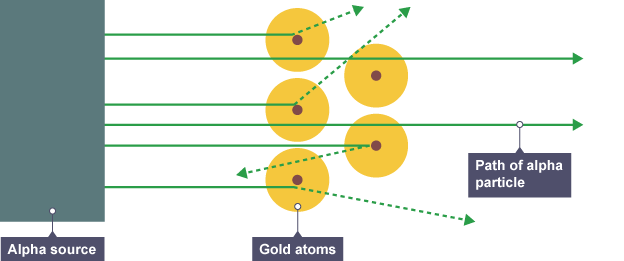
The results from the alpha particle scattering experiment led to….
nuclear model replaced the plum pudding model
66
New cards
how did the alpha particle scattering experiment change the model
Most alpha particles went straight through the foil. But a few were scattered in different directions.
* the mass of an atom is concentrated at its centre, the **nucleus**
* the nucleus is positively charged
* the mass of an atom is concentrated at its centre, the **nucleus**
* the nucleus is positively charged
67
New cards
Niels Bohr adapted the nuclear model by suggesting that ….
electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances. The theoretical calculations of Bohr agreed with experimental observations.
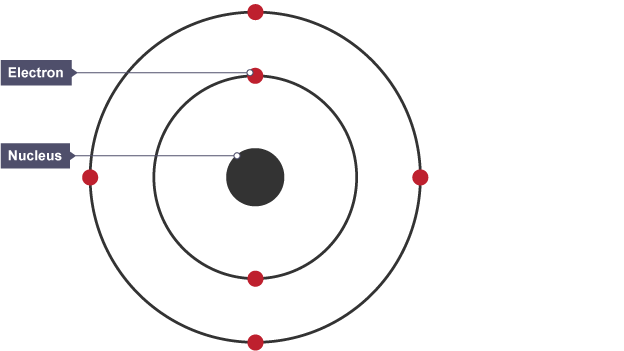
68
New cards
physical properties of group 1 elements
* soft
* low mp
* malleable
* not useful as cataylyst
* low mp
* malleable
* not useful as cataylyst
69
New cards
physical properties of transition metals
* they are good conductors of heat and electricity.
* high mp
* dense
* strong
* high mp
* dense
* strong
70
New cards
what kind of cup should you use for investigations that measure temp
polystyrene
71
New cards
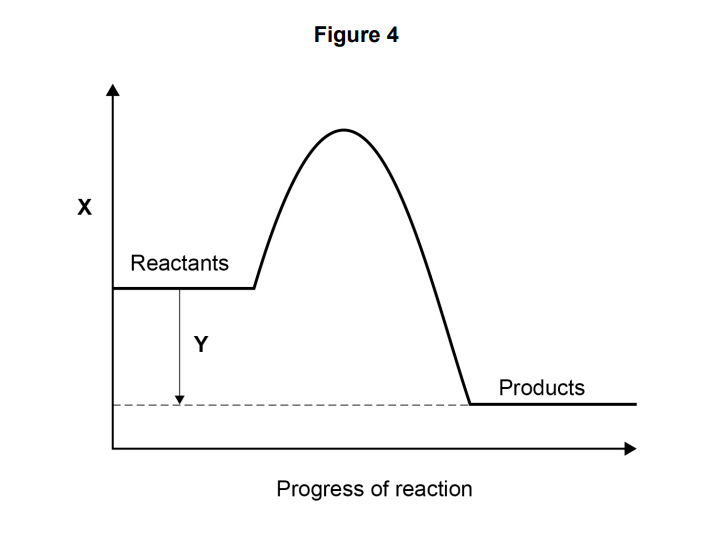
what do labels x and y rep
(X) energy (Y) (overall) energy change
72
New cards
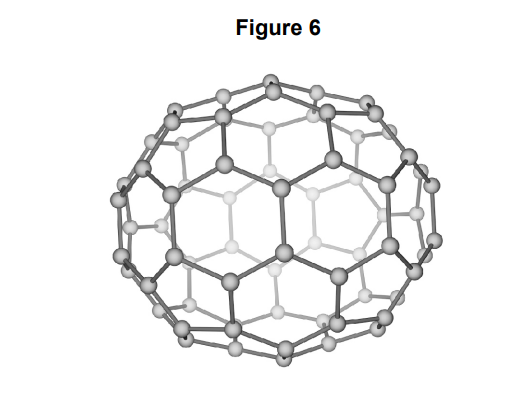
why is it suitable for drug delivery
* hollow
* unreactive
* non toxic
* high sa to vol ratio
* \
* unreactive
* non toxic
* high sa to vol ratio
* \
73
New cards
why is the solid in excess rather than the liquid
excess) zinc oxide can be filtered off
74
New cards
the noble gases have boiling points that increase going down the trt/f
true
75
New cards
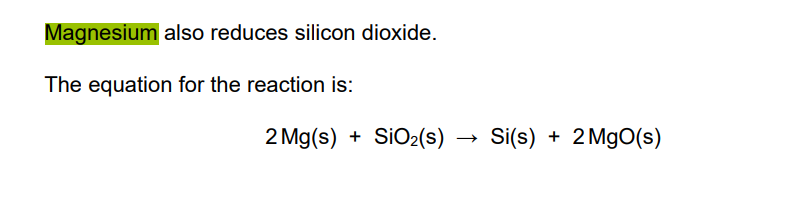
Give one reason why the products are difficult to separate if magnesium is used to reduce silicon dioxide.
both products are solid
76
New cards
what does higher strength of an acid mean
• the stronger an acid the greater the ionisation / dissociation (in aqueous solution) • (so) the stronger the acid the lower the pH
77
New cards
what does higher conc of an acid mean
* • the higher the concentration of an acid the more acid / solute in the same volume (of solution)
* • (so) the higher the concentration of the acid the lower the pH
* • (so) the higher the concentration of the acid the lower the pH
78
New cards

why is there no electrical conductivity in barium sulphate
* there are no ions that are free to move (
* because) barium sulfate is solid / insoluble
* (and) hydrogen ions have reacted with hydroxide ions to produce water
* because) barium sulfate is solid / insoluble
* (and) hydrogen ions have reacted with hydroxide ions to produce water
79
New cards
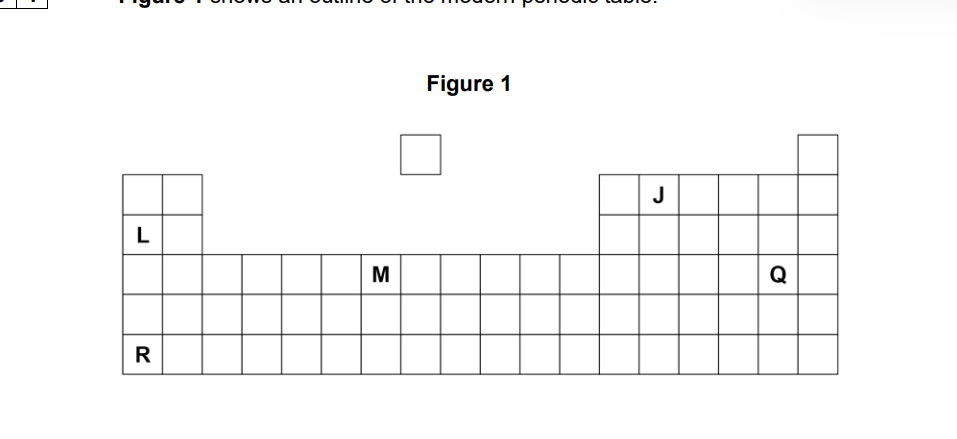
which are in the same period
m &q
80
New cards
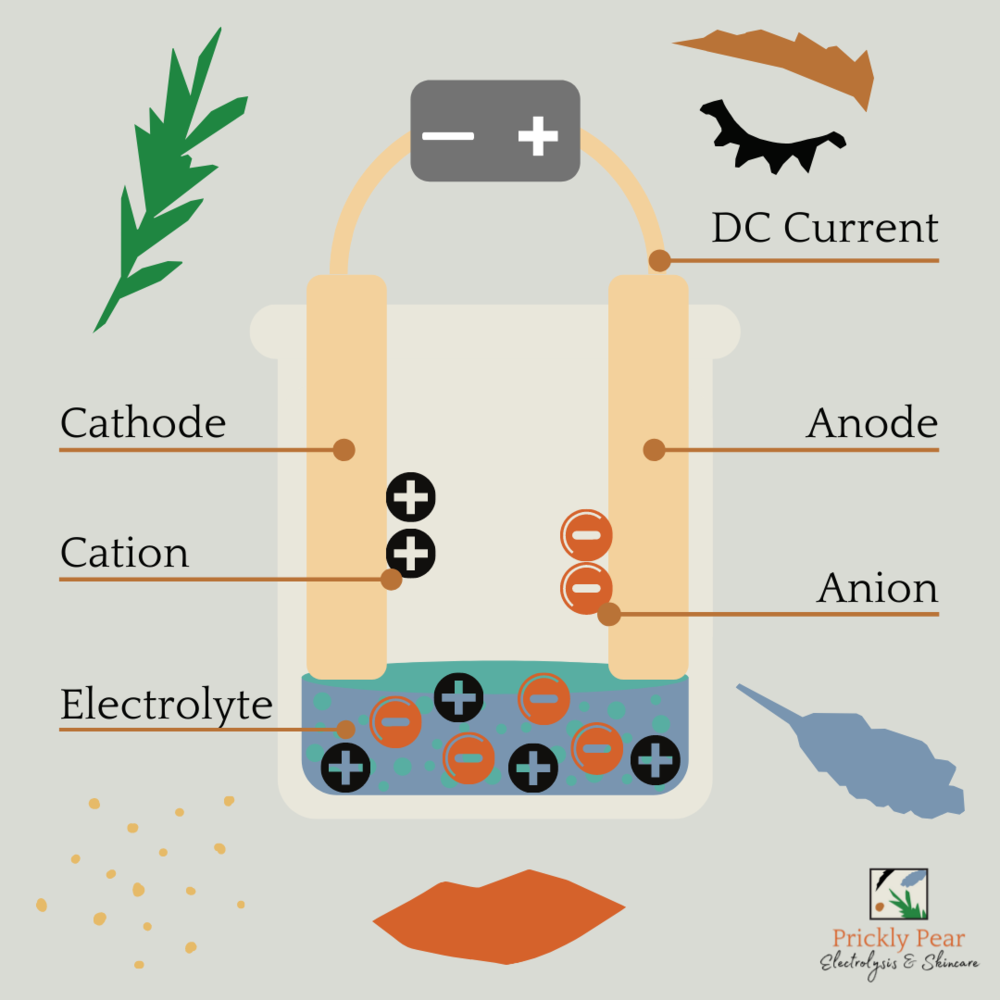
electrolysis materials
81
New cards
behaviour of particles in a liquid
* flow and take the shape of their container, because their particles can move around each other
* cannot be compressed, because their particles are close together and have no space to move into
* cannot be compressed, because their particles are close together and have no space to move into
82
New cards
how can the atom economy of a reaction be improved
find a use for the waste
change reaction to reduce waste
change reaction to reduce waste
83
New cards
why does iodine have a higher bp than chloring
the FORCES between iodine molecules are stronger
84
New cards
why does potassium iodide conduct electricity
it contains IONS which are free to move
85
New cards
why is X positioned in group Y of the periodic tablle
it has Y outer electrons
86
New cards
how can ionic compound conduct electricity when molten
IONS are free to move
87
New cards
saftey precautions when heating contents in an evaporating dish
wear googles
88
New cards
what is the half equation for what happens at the negative electrode in fuel cells (anode)
**2H2 → 4H+ + 4e–**
89
New cards
what is the half equation for what happens at the positive electrode in fuel cells (cathode)
4H+ + O2 + 4e– → 2H2O
90
New cards
what is the total equation for what happens in hydrogen fuel cells
2H2 + O2→ 2H2O
91
New cards
what is meant by a strong acid
fully ionised when disolved in water
to form h+ ions
to form h+ ions
92
New cards
how does a covalent bond hold atoms together
the positive nuclei from two different atoms are held together by their common attraction for the shared pair of electrons held between them.
93
New cards
how does an ionic bond hold atoms together
strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions. The forces act in all directions in the lattice. This is called ionic bonding .