MICRO 440: Lab Exam 1 (Weeks 1-4)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/204
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
1
New cards
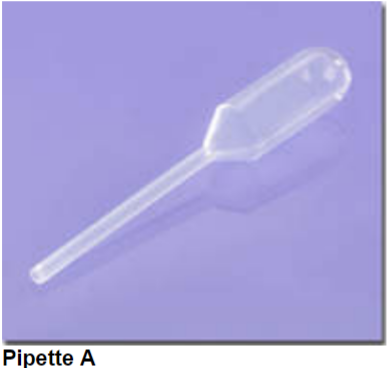
What’s the proper name of pipette A?
Transfer pipette
2
New cards
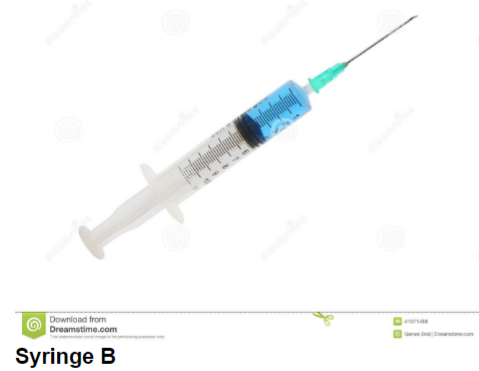
What is the volume of a major gradation of syringe B?
1 mL
3
New cards
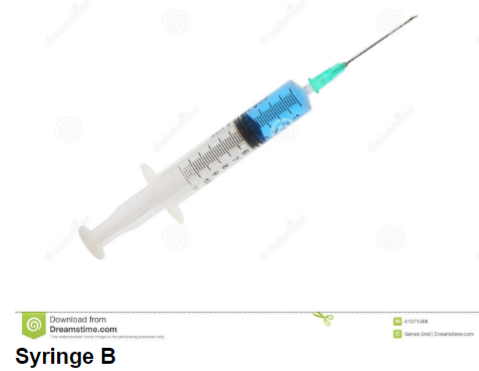
What is the volume of a minor gradation of syringe B?
0\.2
4
New cards
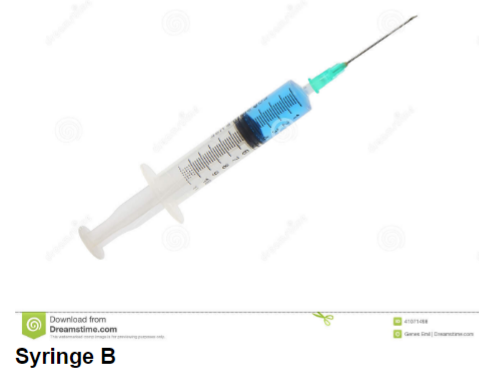
If you dispensed the fluid in syringe B, how much fluid would you have dispensed?
4 mL
5
New cards
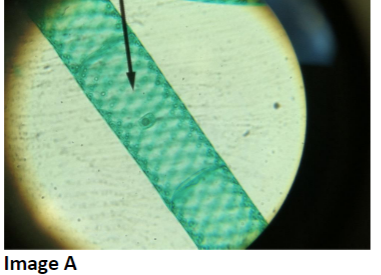
To what domain does the organism in image A belong?
Domain Eukarya
6
New cards
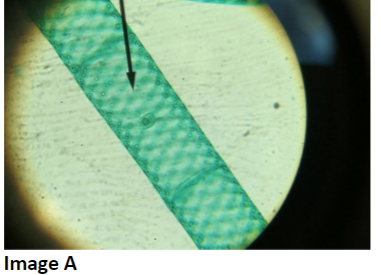
With what disease or process is the organism in picture A associated?
photosynthesis
7
New cards
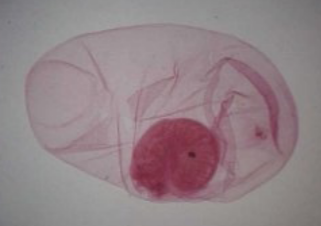
What is the proper name (Genus + specific epithet)?
*Taenia solium*
8
New cards
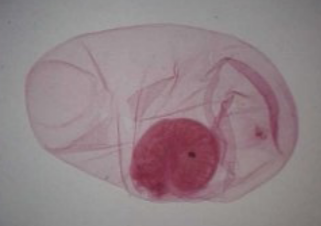
How do humans contract this organism?
Eating undercooked infected pork
9
New cards
What’s the primary stain of the Gram stain?
Crystal violet
10
New cards
If you forgot the Gram’s iodine when staining cells, what would you see and why?
Everything will be pink/red if there’s no CV-iodine precipitates. The CV will get washed from cells by decolorizing.
11
New cards
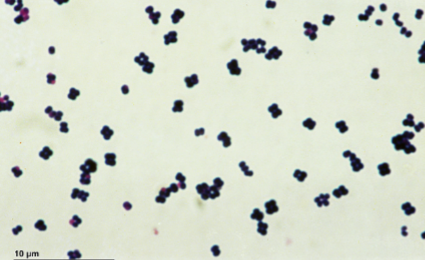
What are the proper technical terms to describe the morphology and arrangement of cells in the image?
Cocci in tetrads and sarcinae
12
New cards
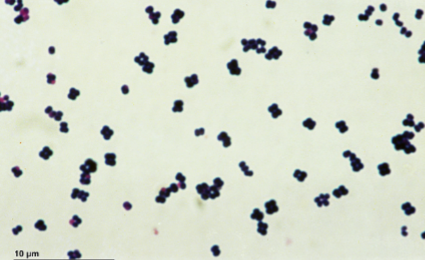
What Gram staining property do the cells in the image have?
Gram positive
13
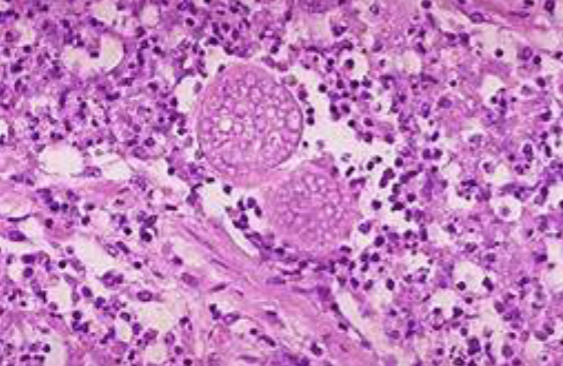
New cards
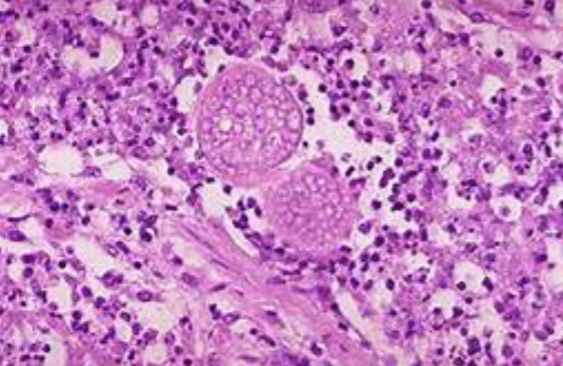
In the San Joaquin Valley Area, patients have developed a wracking cough following a dust storm. Examination of fluid from lungs of patients shows the presence of spherules and fibrocaseous nodules.
\
**Proper name** (Genus + specific epithet) of the organism responsible for patients’ illness?
\
**Proper name** (Genus + specific epithet) of the organism responsible for patients’ illness?
*Coccidiodies immitis*
14
New cards
To what **major group** (eg. Zygomycota) does this organism belong?
Ascomycota
15
New cards
What’s the proper name of the **fleshy fruiting body** produced by some members of the Ascomycota group?
Ascocarp
16
New cards
Bacteria examples?
*Bacillus anthracis; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Nostoc; Rhizobium* (in root nodules)
17
New cards
Fungi ==Ascomycetes== (Ascomycota) examples?
1. *Saccharomyces cerevisiae* budding and sporulating
2. *Claviceps purpurea* - perithecial head, ergot images
3. *Candida albicans*
4. *Coccidioides imitis*
5. *Ophiocordyceps unilateralis*
6. *Sporothrix spp.*
7. *Trichophyton mentagrophytes*
8. morels
18
New cards
Fungi Basidiomycetes (Basidiomycota) examples?
1. button mushroom
2. *Filobasidiella neoformans (Cryptococcus neoformans)*
3. *Ustilago* maydis (huitlacoche)
19
New cards
Fungi ^^Zygomycetes^^ (Zygomycota) examples?
*Rhizopus* sporangia/sporangiophores and zygosporangia
20
New cards
Fungi examples?
Ectomycorrhizae, lichens, onychomycosis (nail fungus image), sporotrichosis; coccidioidomycosis;
ergot/ergotism
ergot/ergotism
21
New cards
Protists examples?
1. **Plant-like (algae):** *Spirogyra*
2. **Fungus-like (water & slime molds):** *Physarum* plate; *Phytophthora* infestans
3. **Amoebozoa (amoebas):** *Amoeba proteus, Entamoeba histolytica, Amoeba* model
4. **Ciliophora (“ciliates”):** *Paramecium* model, *Paramecium, Balantidium* coli
5. **Mastigophora (“flagellates”):** *Euglena* model, *Euglena, Trypanosoma brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi, Giardia lamblia; Trichomonas vaginalis; Trichonympha*
6. **Apicomplexa (“sporozoa”):** *Plasmodium gametocyte & merozite*s (lab manual); *Toxoplasma gondii*
22
New cards
Animalia examples?
*Taenia solium* cysticercus larva, *Aedes*
23
New cards
Acellular examples?
prions (image), prion disease brain sample (image), influenza virus (image)
24
New cards
Spill management
1. Announce spill & stay in place; colleagues will help
2. Treat spill & dispose of material properly (glass in sharps container; towels & gloves in biobin)
3. Eyewash station: help colleagues
4. Shower in autoclave room
25
New cards
Autoclaving conditions (kills all cellular organisms, viruses)
121\*C, 15 psi, 15-20 mins
26
New cards
What can cause a host to be compromised?
immunosuppression or breaches in the skin
27
New cards
What are portals of entry?
eyes, nose, mouth, and mucous membranes
28
New cards
What important safety precautions should be taken when incubating screw-cap tubes? When placing tubes in the “kill area”?
1. incubation: tube caps loosened
2. tubes in “kill area”: caps loosened ¼ turn, tape labels removed
29
New cards
What info should be placed on labels? Where should labels be placed on tubes and plates?
1. name, date, and microbe.
2. Labels placed at the top of tubes
3. Plates inverted with the agar side up; label on the agar side.
30
New cards
How should spent cultures be prepared for disposal? Where should they be placed for disposal?
1. Plates taped shut with masking tape.
2. Tubes: tape removed, caps loosened. Autoclaving conditions are **121*C, 15 psi, and 15-20 mins** = kill all cellular organisms and viruses. Placed in the **Kill Area.**
31
New cards
What are opportunistic pathogens?
microbes in the soil, water, and on/in in the body that take advantage of opportunities (a compromised host) = result in disease
32
New cards
Amplification & infectious dose
Many microbes grow from a few, leading to infectious dose = sufficient microbes can cause a disease
33
New cards
Compromised hosts/events
1. Healthy pregnant woman
2. Healthy student with a cut on their hand
3. HIV-positive person
4. Person undergoing cancer chemotherapy
34
New cards
Inoculating loop function
Collecting and transferring small amount of culture, especially liquid culture; streaking plates to perform “dilution over distance”
35
New cards
Inoculating needle function
For solid cultures, moving very small amounts, stab inoculation
36
New cards
Bacticinerator
Gasless, flameless sterilizer used with inoculating loops and needles
37
New cards
Syringes
Measuring volume to transfer larger amounts
38
New cards
Serological pipette measures?
Major (5 mL) & minor (1 mL) gradations
39
New cards
Incubators
Controls metabolism and growth through temperature to culture microbes
40
New cards
Tubes
Culture and handle microbes, store samples; either agar slants, agar deep, broth, or plates
41
New cards
Plates
Grow bacteria/etc. on a medium
42
New cards
What is sterile or aseptic technique? What is the purpose of practicing sterile/aseptic technique?
1. When any microorganisms are removed by inducing heat; using Bacti-Cinerator to sterilize an inoculating needle or loop
2. Avoid contamination; keep pure cultures pure.
43
New cards
Media
plural for medium; microbe food
44
New cards
Broths
liquid (“soup”)
45
New cards
Solid
broth + gelling agent (agar)
46
New cards
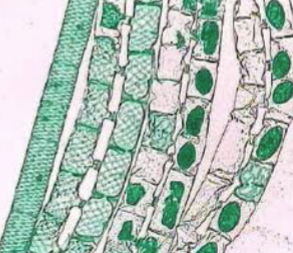
What is this specimen and the green dots?
*Spirogyra* (protist), chloroplasts
47
New cards
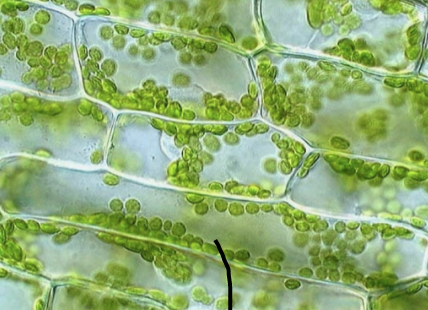
What is this specimen?
*Elodea* (plant)
48
New cards
Photosynthesis equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
49
New cards
Define resolution & its advantage?
clarity of object’s image; ability to distinguish between close objects
50
New cards
Define par centrality & its advantage?
1. Lenses centered relative to each other; objects in the center of the field using one lens will be centered in the other lens. (Center the object you’re observing before switching lenses)
51
New cards
Define parfocality and its advantage?
Lenses %%focused%% relative to each other; only small adjustments in focus are needed when changing lenses (objectives)
52
New cards
Rheostat function
adjust light intensity
53
New cards
Condenser function
When opened & raised, it increases light focused on specimen thus increasing resolution
54
New cards
Fine focus function
Small-scale movements with 40x (high dry) or 100x (oil immersion) objective lenses
55
New cards
Condenser function
Focuses all of the light rays on specimen to maximize illumination
56
New cards
How to increase & adjust resolution?
1. Increase numerical aperture (measure of a lens’s ability to gather light).
2. Use **rheostat to increase light intensity,** raise the substage condenser, and open the iris diaphragm.
57
New cards
Contrast adjustment involves:
Increase light intensity with rheostat, lower the substage condenser, and close the iris diaphragm.
58
New cards
Describe the proper way to examine a bacterial smear, beginning with the scanning lens and working up to the oil immersion lens.
1. place the slide on the stage in the mechanical slide holder, center the specimen over the opening in the stage and make any distance adjustments between the two oculars to account for one’s own interpupillary distance.
2. 4x scanning lens: adjustments to the iris diaphragm for optimum illumination, contrast, and image
3. coarse-focus adjustment knob to focus the image and use fine-focus so it is in the sharpest focus, then work through the low (10x) and high-dry (40x) objectives.
4. Ensure specimen is desirably positioned before moving to the next objective, so it’s not lost at higher magnification
5. focused under high dry = rotate the nosepiece to a midway position between the high-dry and oil-immersion lenses, drop immersion oil on the specimen, and ensure oil doesn’t get on the microscope or lenses.
6. Rotate oil lens so its tip is submerged in the oil drop, pass through it, and return the oil lens into the oil to minimize air bubbles.
59
New cards
With which objective lenses may the coarse focus adjustment knob be used? With which objective lenses may the ^^fine focus adjustment knob^^ be used?
1. 4x and 10x lenses
2. ^^40x and 100x lenses^^
60
New cards
How to make a wet mount?
1. drop of water placed on the slide and organisms are introduced to it, or if the organism is already in a liquid medium then a drop of medium is placed on the slide
2. cover glass is placed over the preparation to flatten the drop and keep the objective lens from getting wet.
61
New cards
What are the advantages of a %%wet mount%% over a ==heat fixed and stained smear?==
1. %%quick prep;%% can flatten specimen to make it easier to see its size and shape, characteristic arrangement/grouping of cells in natural color, motility
2. ==**stained and heat-fixed smears**== can distort size, shape, and arrangement of cells making it **difficult** to identify motility b/c organism is dead.
62
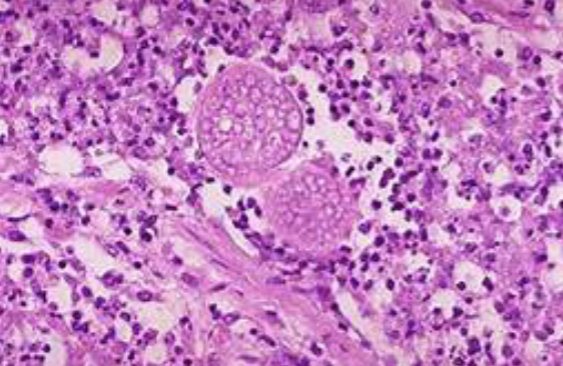
New cards
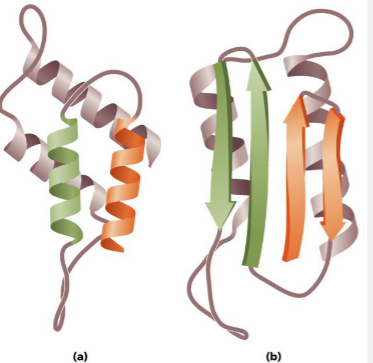
Prion proteins; What forms are A & B in?
normal (alpha), pathogenic (beta)
63
New cards
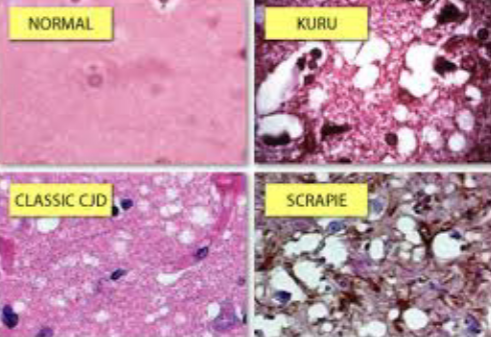
What is this image depicting?
Normal brain tissue and prion-affected tissue
64
New cards
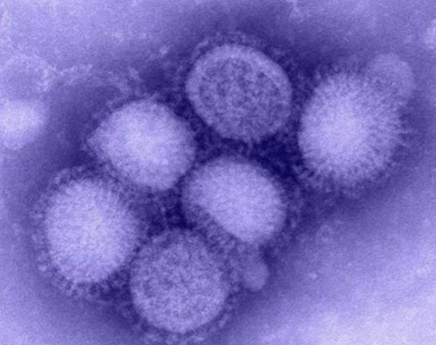
What virus is this?
Influenza
65
New cards
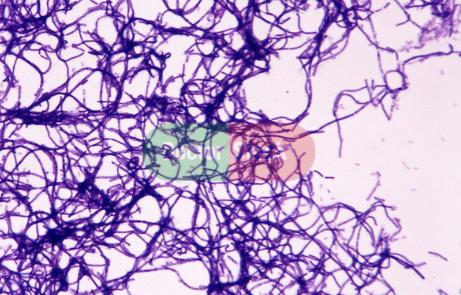
What is this bacteria?
*Bacillus anthracis,* endospore former
66
New cards
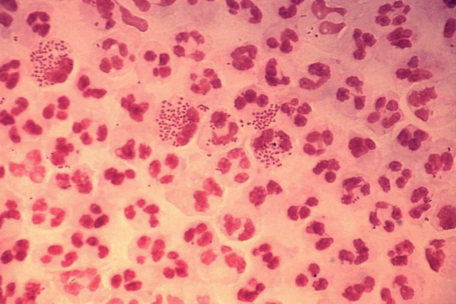
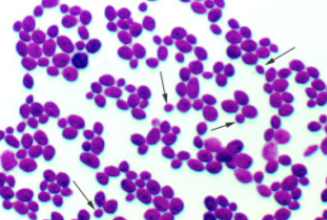
What is this bacteria?
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae* in pus (cocci in neutrophils)
67
New cards
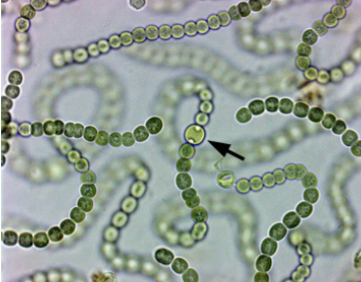
*Nostoc*: What is the name of the structure at the tip of the pointer/arrow, and which unique chemical reaction occurs within such structures?
heterocyte; N2 -> NH3
68
New cards
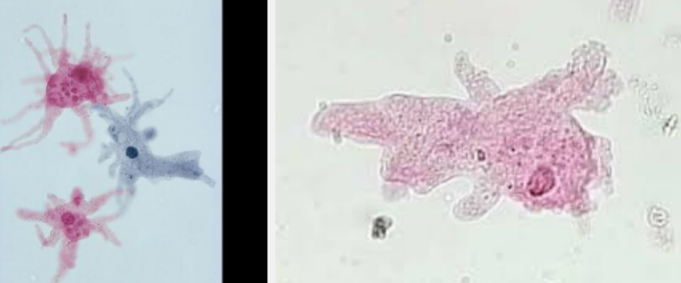
What is the name of this protist?
*Amoeba proteus*
69
New cards
What’s this asexual specimen?
*Saccharomyces cerevisiae* (buds at ends of arrows)
70
New cards
What is this specimen?
*Spirogyra* (vegetative at far left; rest are conjugating)
71
New cards
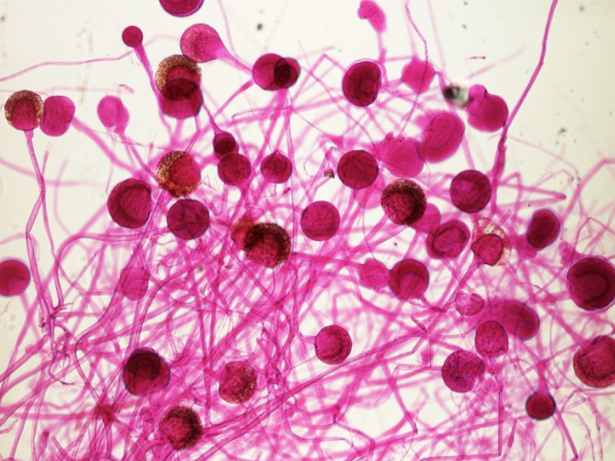
What’s this specimen?
*Rhizopus* sporangia
72
New cards
What subcellular structure carries out photosynthesis in plants?
Chloroplasts
73
New cards
Function of heterocyte in Nostoc?
1. Colorless specialized cells in cyanobacteria that provide the anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment necessary for the operation of the **nitrogen-fixing** enzymes.
2. Cyanobacteria’s properties allow them to thrive in various habitats like marine and freshwater environments, soil, and rocks in different temperatures, live as unicellular organisms or in colonies, and can be filamentous (form sheaths or biofilms).
74
New cards
Taxonomy is?
classification, description, identification, and naming of living organisms
75
New cards
Phylogeny is?
grouping organisms to reflect derivation from a common ancestor; reflect evolutionary history/relations of a group of organisms
76
New cards
Eukaryote: Kingdom Fungi (yeasts, molds, mushrooms) examples
1. ***Saccharomyces cerevisiae:*** budding (cells at ends of arrows) = asexual reproduction; Genus name: sugar fungus; Cerevisiae: beer maker
2. ***Rhizopus sporangia:*** sporangia (look like candy part of a lollipop) = asexual reproduction structures. Brown material are spores, cause bread mold.
77
New cards
Eukaryote: Kingdom Animalia (multicellular, no cell wall, motile, nutrition – ingestion) examples
1. ***Taenia solium cysticerus:*** pork tapeworm, photomicrograph of a cysticerus larva; dark pink part (infectious for humans)
2. ***Aedes:*** mosquitos can be vectors for pathogens like malaria or Zika virus.
3. ***Helminths:*** multicellular parasitic worms; diseases caused involve microscopic eggs and larvae (guinea worm/Dracunculus medinensis: dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, painful ulcers on legs & feet)
4. ***Arthropods:*** animal with no internal spine, a body made of joined segments, and a hard covering, like a shell. EX: mosquitoes, ticks, flies are typical vectors for viral diseases (either mechanical or biological)
78
New cards
Eukaryote: Kingdom Protista (protozoa & algae) examples
1. ***Amoeba proteus:*** protist, used to be called Kingdom Protista. Animal-like protists = protozoa. In watery environments, extrudes pseudopods from cell which engulfs its prey. Free living; doesn’t cause disease.
2. ***Spirogyra:*** vegetative at far left, rest are conjugating. Have spiral chloroplasts. Filamentous algae having thin unbranched chains of cylindrical cells.
79
New cards
Prokaryotes: Domain Bacteria examples
1. ***Bacillus*** (rod-shaped) ***anthracis*** (anthrax): gram-positive, endospore-former, endospores can be weaponized for bioterrorism (resistant to heat, radiation, chemicals); causes 90% fatal disease anthrax.
2. ***Neisseria gonorrhoeae*** in pus: gram-negative, cocci in neutrophiles (phagocytes). Disease: gonorrhea, sexually transmitted disease (STD)
3. ***Nostoc:*** cyanobacteria, fix nitrogen in heterocytes. Photosynthetic. Is green because it contains chlorophyl.
80
New cards
Viruses are?
acellular microorganisms (not composed of cells) consisting of proteins and genetic material (DNA or RNA, but never both) that are inert outside of a host organism
\
EX: Influenza, HIV, ebola
\
EX: Influenza, HIV, ebola
81
New cards
Prions are?
acellular proteinaceous infectious particles. Alpha-helix (normal) or B-sheet (rogue)
\
EX: TSE (Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy) Mad Cow Disease, Kuru, CJD, Scrapie
\
EX: TSE (Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy) Mad Cow Disease, Kuru, CJD, Scrapie
82
New cards
Major taxa
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
83
New cards
Is an arthropod vector involved in the transmission of the pathogen?
Yes, injection into the bloodstream of the host by the bite of an infected arthropod species like mosquitoes or ticks.
84
New cards
Cell morphology (shape)
1. sphere = coccus/cocci
2. rod = bacillus/bacilli
3. spiral = spirillum/spirilla (rigid) or spirochaete/spirochaetes ( flexibile)
4. endospore-containing rods *(Bacillus, Clostridium)*
85
New cards
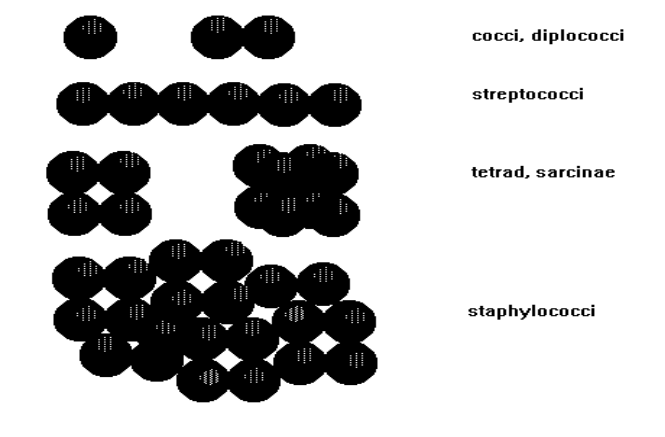
**COCCI:** Cell arrangement (groupings): arise from cells failing to separate after division
Diplococci (2), streptococci (6), tetrad, sarcinae (4, 8), staphylococci
86
New cards
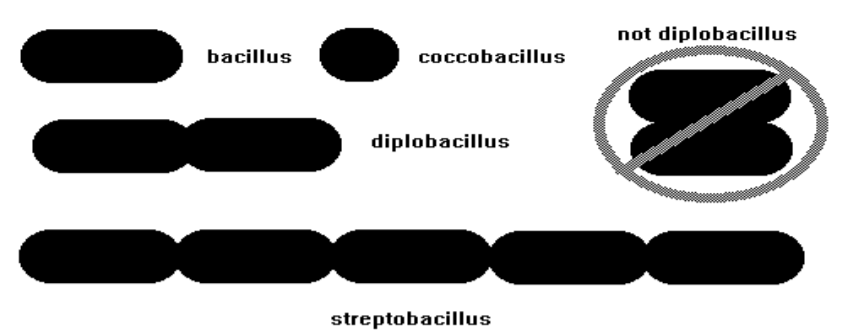
**BACILLI:** Cell arrangement (groupings): arise from cells failing to separate after division
Limited arrangements; bacillus, coccobacillus, diplobacillus, streptobacillus
87
New cards
Three domains (based on rRNA sequence)
archaea, bacteria, eukarya
88
New cards
Whittaker 5 Kingdom System
Monera (prokaryotes), Protists (formerly K. Protista), Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
89
New cards
*Saccharomyces cerevisiae* is also known as ____ yeast.
Brewer’s
90
New cards
Asexual reproduction is when?
1 mycelium produces spores via mitosis OR yeasts produce daughter cells via mitosis or budding
91
New cards
Sexual reproduction is when?
Mycelial cells of **opposite mating types** fuse → nuclei fuse → spores are produced via meiosis
92
New cards
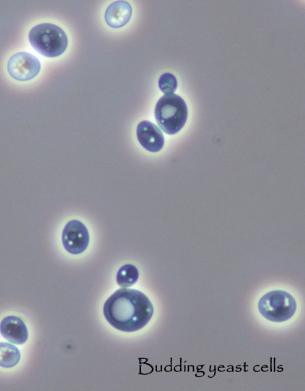
Ascomycetes: showing asexual reproduction of?
*Saccharomyces cerevisiae*
93
New cards
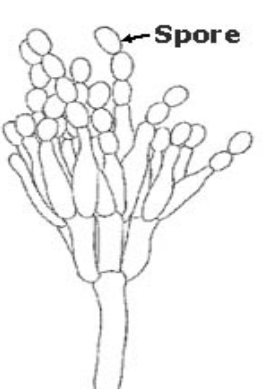
Ascomycetes: conidiophore with?
conidia
94
New cards
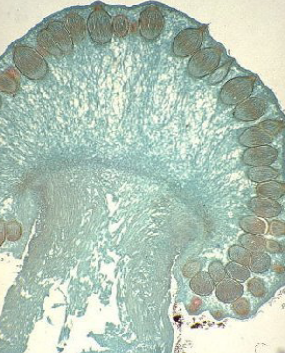
Which ascomycetes is this?
*Claviceps purpurea* perithecium
95
New cards
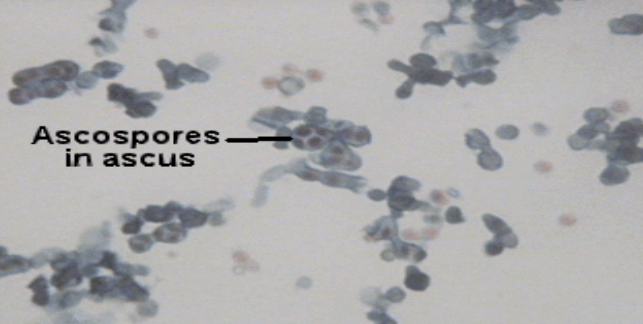
Ascomycetes: This is showing *Saccharomyces* asci with?
ascospores
96
New cards
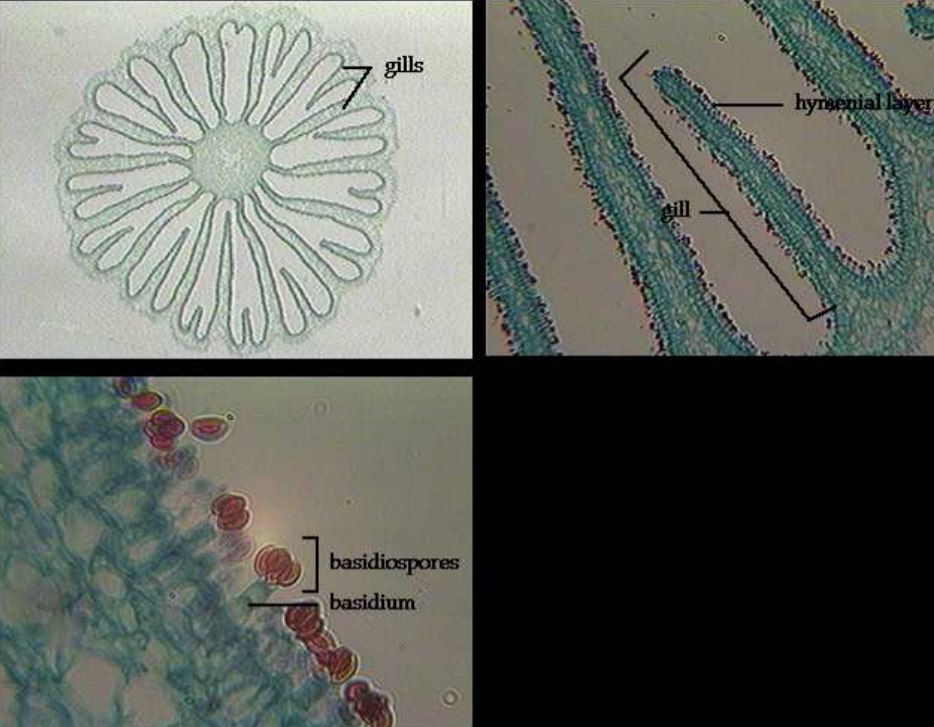
What fungi is this showing?
Basidiomycetes
97
New cards
Characteristics: Division **Ascomycota** “sac fungi” septate
1. Sexual reproduction: Ascospores in asci
2. Sexual structure: Ascocarps: morels, truffles, perithecial head (*C. purpurea*)
3. Asexual structure: Conidia
4. Disease causing member: *Claviceps purpurea, Candida albicans*
5. Disease: ergotism, thrush, vaginitis
98
New cards
Characteristics: Division **Basidiomycota** “club fungi”, septate
1. Sexual reproduction: Basidiospores in basidia
2. Sexual structure: Basidiocarps = mushrooms; *Agaricus bisporus*
3. Asexual: Conidia
4. Disease-causing member: *Amanita phalloides, Filobasidiella* (formerly *Cryptococcus neoformans*)
5. Disease: Mycotoxicosis, meningoencephalitis in HIV patients
99
New cards
Characteristics: Division **Zygomycota** “bread molds” aseptate
1. Sexual reproduction: zygospores in zygosporangia
2. Sexual structure: Zygosporangium, *Rhizopus*
3. Asexual: Sporangia
4. Disease-causing member: *Rhizopus, Mucor*
5. Diseases: bread mold, zygomycosis, mycosis in immunocompromised patients
100
New cards
Division Deuteromycota “imperfect fungi” - septate
1. Sexual reproduction: None; Ascospores or Basidiospores when found
2. Sexual structure: None found; asci or basidia when found
3. Asexual: Conidia - *Penicillium* → Ascomycota
4. No disease-causing member or disease.