20 - Low and Stable Inflation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is inflation?
Defined as a persistent increase in APL in the economy usually measured through calculation of a consumer price index
Costs of high inflation (7)
loss of purchasing power
If price of good increase, but income doesn’t change or not enough, can no longer buy as much
effect on saving
effect on economic growth
if people want to save - may choose to buy fixed assets
fewer savings in economy for investment
effect on interest rates
commercial banks make money by changing interest
if inflation rate increases, banks increase nominal IR
effect on international competitiveness
if country has higher rate of inflation than of trading partners - exports less competitive, imports more attractive
lower export revenue and higher import expenditure, worsen trade balance
Uncertainty
firms discouraged from investing - uncertainty of inflation
labour unrest
workers feel wages are not keeping up with inflation
disputes between unions and management
Winners of inflation
people with index-linked income
people with high wage bargaining power
borrowers - real interest rate lowered by inflation - amount paid back now worth less
people who are “asset rich“
buy assets as opposed to spending
increase p of assets
importers - price of domestic increases, import demand increases
Losers of inflation
Fixed income/wages
low wage bargaining power
savers/lenders - real IR lowered by inflation, amount received worth less
people who are cash rich
value of cash decreases over time
exporters - less attractive abroad as higher P make them compare less favourably with foreign
How is inflation measured?
Consumer price index
Basket of good - when p of basket increases, APL has risen
different categories, different weights
Issues in measuring CPI
CPI - typical consumption of a household, doesn’t apply to all
variations in regional rates - national figures typically used
doesnt reflect accuracy of groups
Errors in data collection
larger the sample, more accurate, costs money and time
Due to consumption habits - items removed/added over time
if items are changed, hard to make comparisons
Further complicated by change in quality.
Countries measure differently - hard to make international comparison
Prices change for variety of reasons that are not sustained
e.g seasonal food prices
CPI measures change in consumer prices, indicates common economy health
other prices change essential for doing this
economists measure change in FOP’s
Commodity prices - change
Upward movements in price - signal of cost push pressures and may be leading indicators of inflation
Producer Price index
tracks price of goods as leave the factories before distributors, wholesalers or retailers and their profit margin
Causes of inflation - two types
demand pull and cost push
How does D inflation work - brief
Increase demand in the industry
prices up from APL1 to APL2
Change in AD can be sue to changes in the components
How does cost push inflation work - brief
increase in COP
increase in costs fall in sras
Wage -push inflation, increase in APL due to increase in labour costs
Fall in countries currency - import-push inflation
lower exchange rate makes imports more expensive, increases cost of imported FOP’s to countrys firm
Inflationary spiral
Ad keeps going up due to increased wealth, If Ad increases, demand-pull, workers demand higher wage as APL increased. Shift in SRAS due to cost push.
Inflation is a short run problem - supply side policy
supply-side policies not suitable
successful policies reduce APL over time, but time lag too great
Gov intervention for demand-pull
GOV and CB should use contractionary monetary and fiscal policy to reduce AD
Why is cost-push hard to intervene with
Caused by rising COP’s, policy makers have no control over
demand side policies needed to fight inflation
Problems with contractionary policies
Highly unpopular from a political standpoint
Fiscal
voting population not happy to accept higher taxes as it reduce disposable income
reduction in gov spending - impacts groups of people
takes time - time lag too long
Monetary
higher IR harm people in economy, especially with loan or mortgage
less borrowing, less investment, harm economy
Which policy is considered most effective
Monetary, IR considered best weapon
What is deflation
Persistent fall in average price level
“Good“ deflation - how does it work
improved in supply side of the economy, and/or increased productivity
Increase in LRAS - increase in real output, fall in price level
Bad deflation - how does it work
demand side of economy
fall in AD, decrease in APL, decrease in real output, increase unemployment
Disinflation
falling rate of inflation
prices rise, but inflation can reduce
Costs of “bad“ deflation
Unemployment
AD decreases, lay off workers, AD decreases more
deflationary spiral
Deferred consumption
put off purchase of durable goods, wait for p to drop more
fall in AD, deflationary spiral
falling consumer confidence
households become pessimistic about economic future, consumer confidence lowers
deflationary spiral
effect on investment
Business make less profit, lay off workers. Business confidence low, likely to reduce investment
costs to debtors
Anyone who has taken a loan suffers, value of their debt rises. If profits low, difficult to pay loans - bankruptcies, further lower confidence
policy ineffectiveness
Deflation make monetray ineffective. very low/negative interest rates with deflation make expansionary monetary ineffective, not possible to reduce IR to increase AD
What does the weighted price index do
Take a basket of products, which are given a different weight, based upon relatives amount people spend
Inflation rate calculation - basket
(Index for (X+1) - Index for X) / Index for X x 100
Og philips curve
inverse relationship between rate of change of money wages (wages not adjusted for inflation) in economy and unemployment
Philips curve - low unemployment
If low unemployment, firms pay higher wages to attract labour
Philips curve - high unemployment
If high unemployment, workers compete, wages could be low
Philips curve

philips curve AD/AS
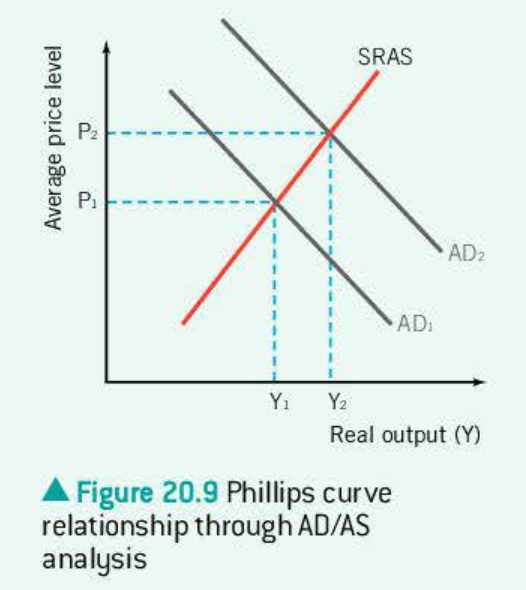
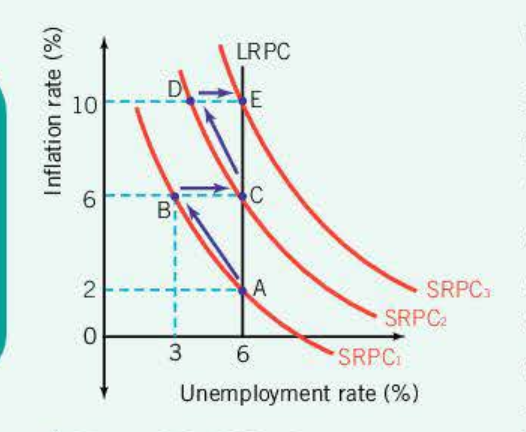
People expect inflation to be 2%, hence want higher wages
unemployment drops, people interested in higher wages
workers suffered from money illusion
workers realise wages havent risen, leave jobs, unemployment
back to natural rate, but now at a higher inflation
This is an on going cycle, resulting in higher inflation
Natural rate of unemployment
Rate that is consistent with stable rate of inflation. Economy is at full employment, labour market at eq.
if gov doesnt use expansionary policies, inflation will not accelerate at natural rate of unemployment
Difference in unemployment between countries due to dif, factors
availability of unemployment benefits
trade union power
extent of labour market regulations
wage-setting practice
Countries with more benefits and regulations of markets tend to have…
higher rate of natural unemployment