Week II Lecture: Intro to Modern Computing Flashcards (Exam Prep)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is a bit?
A single binary digit (0 or 1)
What is a byte?
A group of 8 bits, representing a single unit of data
What are Integers (int)?
Whole numbers (positive, negative, or 0)
What are Floats (float)?
Decimal (floating-point) numbers
What are Booleans (bool)?
A data type that has two values: True or False
What are the three stages of building code components?
Data Types create Data Structures, which can create Functions
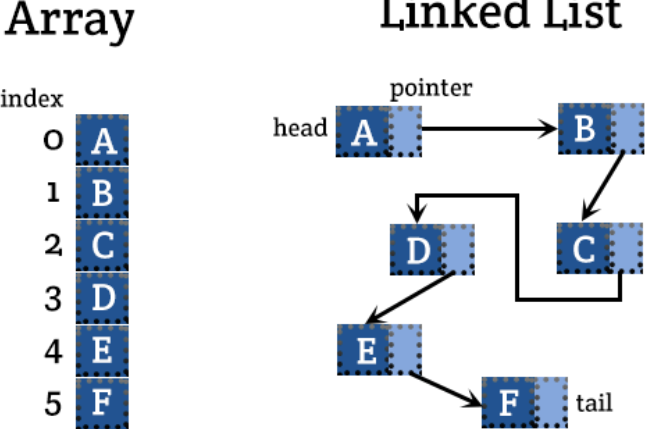
Name two types of Linear Data Structures (and what do they look like?)
Arrays and Linked Lists
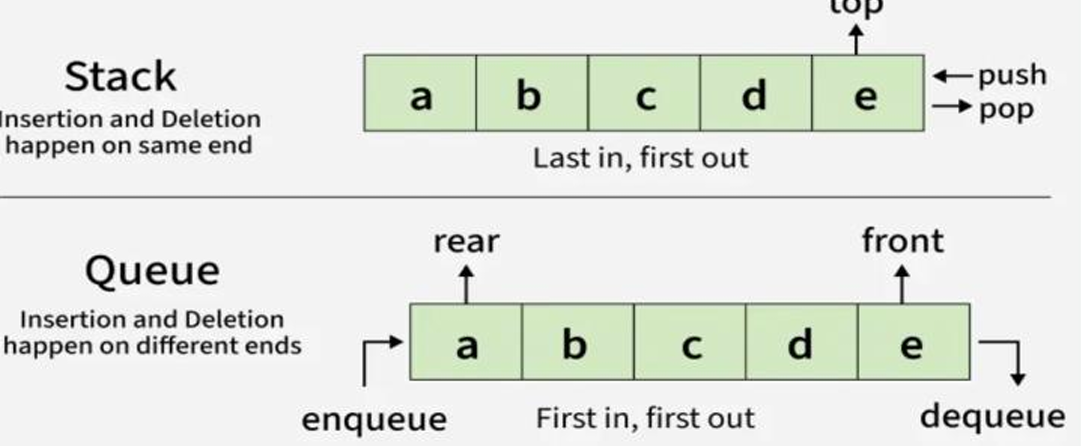
How do Stacks and Queues function
(Linear Data Structures) Stack (insertion and deletion happen on the same end (last in, first out) Queue (insertion and deletion happen on opposite end (first in, first out)
What defines a Tree structure?
A non-linear data structure with nodes that show hierarchy
Draw a Tree and label nodes
Root node, parent node, child node, leaf nodes, edges.

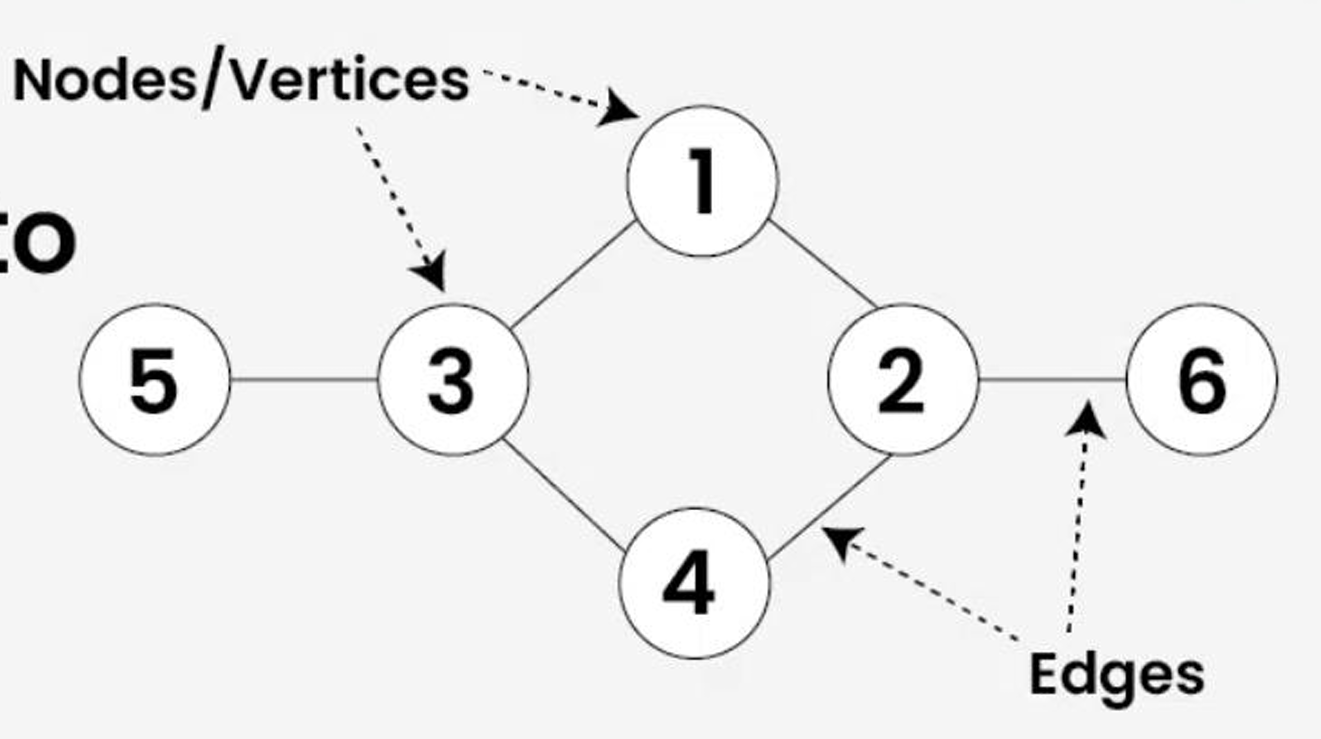
Defines a Graph structure?
A non-linear data structure that is not restricted by a strict hierarchy, It uses Nodes/Vertices and Edges.
Draw a Graph and label the nodes
Nodes/ vertices and edges
What are Control Flow Statements (with examples)
Help instruct the computer how and in what order to compute the steps of a given task or program. For example Conditional Statements or Loops.
What is a Conditional Statement (with example)
Conditional on a statement being true to execute in a certain way, otherwise execute another way.
if num > 0:
[tab] print("The number is positive.")
elif num < 0:
[tab] print("The number is negative.")
else:
[tab] print("The number is zero.")
What is a Loop (with example) p
For Loops: Repeat over finite number of times or While Loops: repeat the steps until a condition has changed.
For i in range(10)
Print (i)
If i == 10:
[tab] Break
What is a function?
A piece of code that will do its own task, so that i can be used elsewhere by just imputting one line of code (breaks larger code into sub-tasks making code cleaner and more functional)
What are Modules, Packages, Libraries?
Modules are related pieces of code in a .py file (e.g. functions, classes). For example numpy or pandas.
Packages collect a bunch of related modules together.
Libraries collect related packages and modules together.
What is an Algorithm?
Text-based instructions to achieve a specific task, with a defined input and output.
What are the 4 important parts of an Algorithm?
Input, Processing, Output, and Termination.
What is Time Complexity?
A measure of how efficiently an algorithm runs in computer time, described with Big O notation.
Explain the Pen Example for Time Complexity.
O(n²) Quadratic: worst (slow): ask first person about all other people and repear for all (use when only one student knows where the pen is hidden).
O(n) Linear: fair: ask each student individually: if one studnet has the pen and only they know they have it.
O(logn) Logartihmic: best: divide class in two ask which side etc. (all sutdent know but only tell if guess the correct side)
What is Space Complexity?
Space complexity is a measure of how efficiently an algorithm runs in terms of the memory or storage space it requires, also usually annotated using Big O notation.
Name different categories of an algorithm?
1. Sorting (data that isn’t in order) 2. Search (data in order) 3. Graph Algorithm (work through data in graphs)
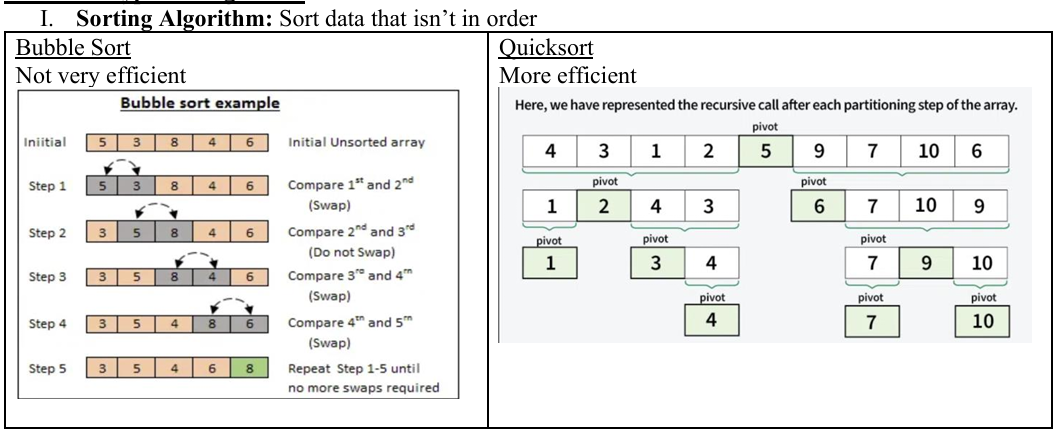
What are sorting algorithms? Explain the efficieny differences
Sort data that isn’t in order.
Bubble sort (swap each piece of data one by one through comparing two at a time) - not time efficient.
Quicksort (pivots around data points until in order) - more efficient.
What are search algorithms? (two different types)
Can be used for finding numbers E.g. for numbers games, finding a number higher or lower. Common Types: 1. Linear Search 2. Binary Search.
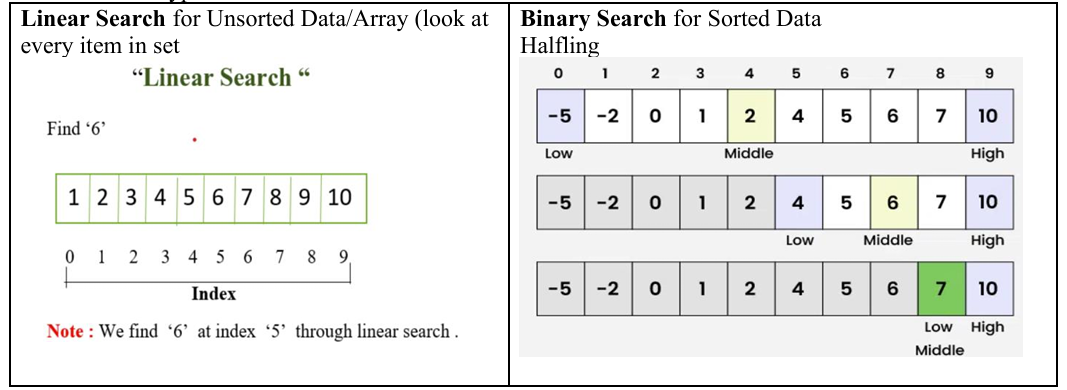
What is the difference between Linear Search and Binary Search?
Linear Search is used for Unsorted Data/Array (must look at every item, while Binary Search is faster and can be used for Sorted Data.
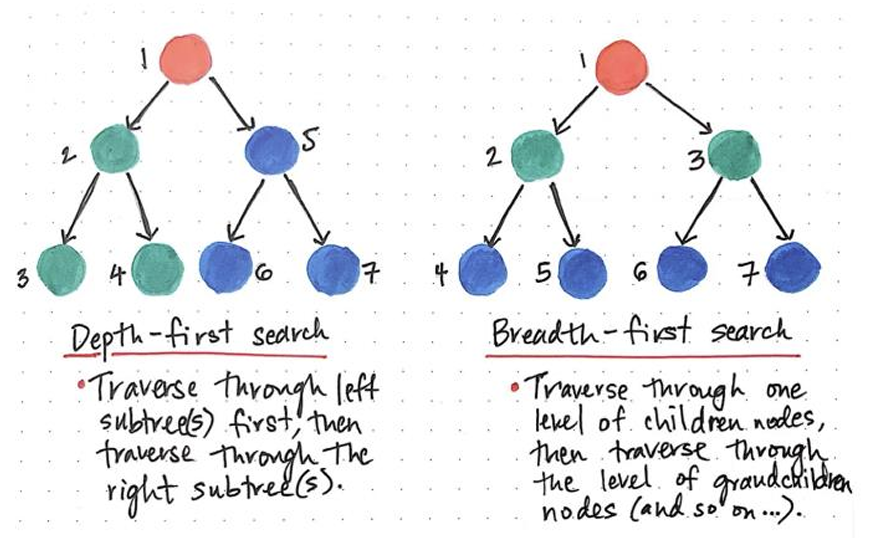
How does Depth-first search work in Graphs? How does Breadth-first search work in Graphs?
It traverses through the left subtrees first, then traverses through the right subtrees. It traverses through one level of children nodes, then traverses through the level of grandchildren nodes (and so on).
What is a non-useful algorithm?
Bogosort (like throwing a deck of cards on floor and trying to pick up in order).
Why do we use programming langauges?
As source code looks more like English syntax and easier to work with that binary.
What is the difference between a Compiled and an Interpreted language?
Compiled languages fully translate code into machine code first, then run it.
Interpreted languages (e.g., Python) translate instructions line by line as they run.
Different Uses of Languages?
For example, JavaScript (used for web) v Python (for data science and Machine Learning)
Where to wrtie code?
Colab/ Jupyter Notebooks (relies on someone else computational resources.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE): purpose built for software development.
Text editors (lightweight but no testing/ debugging features)
What is a Lower-Level Language?
A language closer to the hardware/ metal (e.g., Assembly) v Higher Level like Python.
What are the two main types of software that can be built?
System Software (underlying systems that make computers work) and Application Software (for a variety of purposes, typically for end users).
Who develops software with what tools
Programmers
Software Engineers (SWE)
Software Developers
What are the 5 phases of the Software Development Cycle (SDLC)?
Planning,
Analysis,
Design,
Implementation
Testing/Maintenance.
How is security considered in software development?
Security is considered at all stages of the lifecycle,SSDLC (Secure Software Development Life Cycle).
What is a tech stack?
Set of technologies or modular tools used to build/ run software (tools and libraries used by developers/ engineers)
What is Cloud Computing?
A model that shifted software interaction from buying a copy to installing locally to using a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model.
Is standalone software a product or service?
Matters for product liability. Don’t necessarily have a specific way to handle modern software and intangible services. In many cases, the definition provided by law may not fit some software we want to regulate. (something to consider/ keep in mind)
What is a network.
Essentially one computer talking to another.
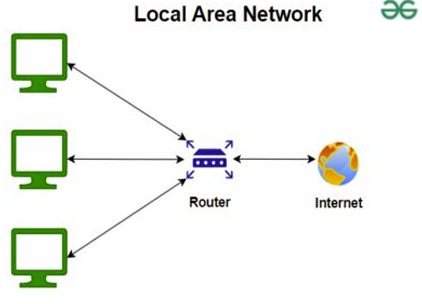
What is LAN? What is a Router?
A local network that can connect to the internet. A LAN (Local Area Network) is essentially more than one computer talking to another in a confined area. A Router is a device used within a LAN to manage the network and connect it to the Internet.
What is the Internet?
A network of other networks that all talk to each other using TCP/IP (the Internet Protocol suite).
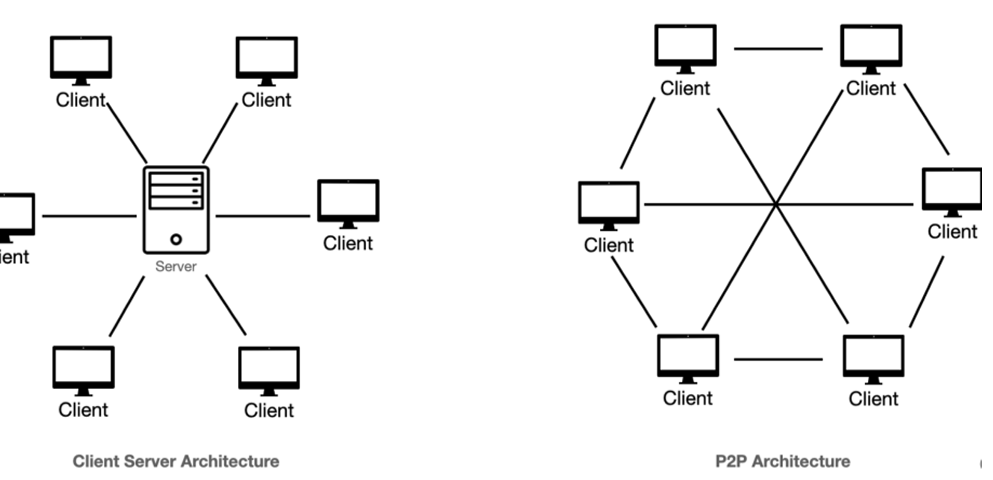
Name the two main network architectures.
Client Server Architecture and Peer to Peer (P2P) Architecture.
Who created the World Wide Web (WWW), when, why and what is it?
The World Wide Web (WWW) was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 , out of frustration with accessing information across different computers. It is a system that linked information together in a unified, worldwide system.
Name the different layers of the Open System Interconnect Model? (and briefly what is each levels function).
Physical (basically “the metal” - bit streams on the hardware
Data Link - connect to directly connected nodes in a local network
Network - figure out where to send data
Transport actually send data with specific protocols
Session - keep connections alive for sessions
Presentation - convert data to make useable
Application (furthest from the metal) - where human interact
Which layer of the OSI Model is the "furthest from the metal"?
Layer 7: Application layer (Where humans interact and use data). [HTTP/ DNS] - basically layers 5-7 are application layers.
Which layer of the OSI Model handles sending the data with specific protocols (TCP/UDP)?
Layer 4: Transport layer.
Which layer of the OSI Model figures out where to send data (IP)?
Layer 3: Network layer (Internet Layer - IP).
What layer is the Network Access Layer (Ethernet)
Layers 2 -1: Data link and Physical layer.