COMP721 Quiz 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Which one of these techniques for maintaining state information is client side and which is server side?
- Hidden form fields
- Query strings
- Cookies
- HTML5 local storage (JavaScript)
- PHP Sessions
Client Side:
- Hidden form fields
- Query strings
- Cookies
- HTML5 local storage (JavaScript)
Server Side:
- PHP Sessions
How do you create hidden form fields?
Using "hidden" type attribute in element:
How do you pass information from 1 webpage to another with a query string?
Add "?" after the URL followed by "name=value" pairs separated by "&"
What are 2 types of cookies and their definitions?
- Temporary cookies remain available only for the current browser session
- Persistent cookies remain available beyond the current browser session and are storedin a text file on a client computer
Syntax for creating cookies?
setcookie(name, value, expires, path, domain, secure)
Where must cookies be sent?
Before any HTML elements or other output are sent from the server
How to specify a cookie expiration time?
Use time() function and offset (in seconds) for the "expires" argument
setcookie("firstName", "Don", time()+3600);
Default value of "expires" is 0, which means it is available for only the current browser session
How does "path" argument in setcookie() work? What argument do you provide to allow any page? What is the default value?
Determines the availability of a cookie to other web pages on a server. (e.g. /marketing/)
- To allow any page, provide "/"
- Default value is the directory the cookie is set in
How does "domain" argument in setcookie() work?
Used to share cookies across multiple servers in the same domain:
- Includes all sub-domains
- Cookies cannot be shared outside of a domain
How does "secure" argument in setcookie() work? What is the default value?
Indicates that a cookie can only be transmitted over asecure HTTPS connection:
- Values are either true or false
- Default value is false
How do you read cookies?
Using the $_COOKIE superglobal associative array
How do you delete cookies?
Set expiration time that is in the past
What are 2 types of HTML5 Local Storage?
sessionStorage - temporary
localStorage - persistent
Where is PHP session state information stored?
In the $_SESSION superglobal as an associative array
How to set the lifetime of a PHP session? (What method do you use?)
session_set_cookie_params(3600); (sets to 1 hour)
How to delete PHP session variables?
unset($_SESSION['name'])
How to delete an entire PHP session?
session_destroy()
How do you provide redirection after manipulating PHP session variables? What’s the syntax?
header("location:URL")
What is the member selection notation in PHP classes (What do you use to access methods and properties of a PHP class?)
"->" symbol
How to define, detect and check if an object is instantiated from a given class in JS?
- Define: "class" keyword
- Detect: get_class() function
- Check instance: instance_of() function
Syntax for constructor function in PHP?
class BankAccount {
private $accountNumber;
private $customerName;
private $balance;
function __construct() {
$this->accountNumber = 0;
$this->balance = 0;
$this->customerName = "";
}
}
What is serialization in PHP and how do you serialize objects?
Serialization refers to the process of converting an object into a string that can be stored.
To serialize an object, pass an object name to the serialize() function:
$savedAccount = serialize($checking);
You can also do the opposite (converting serialized string back to an object with unserialize())
What does Ajax, DOM, and JSON stand for?
Asynchronous JavaScript and XML
Document Object Model
JavaScript Object Notation
What are the 2 ways to implement the Ajax Model?
- fetch(): fetch-then-catch code pattern. Using JS object Promise
- XMLHttpRequest Object: var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
What is the basic flow of asynchronous interation with Ajax?
User does something (clicks a button) -> event handler (onClick() calls the JS function, which creates an XHR object or fetch() -> Retrieves the data (communication with server / PHP file) with xhr.open or fetch() -> PHP echoes the result -> Does something (place text in innerHTML) | defines the function onreadystatechange then xhr.send()
How do you check if XHR communication has finished?
if (xhr.readyState == 4 && xhr.status == 200)
How do you write JS code in HTML file? How do you refer to a JS file externally?
- using script tags:"
<script type="text/javascript">...</script>To link to external file, simply add a “src” attribute:
<script type="text/javascript" src="xhr.js"></script>Difference between var and let in JS?
let has block scope
var are available throughout the entire function
How to define multi-line strings in JS?
use backticks
What does this code return?
function add1(n) {
return n+1;
}
function demo(f, p) {
return f(p);
}
alert(demo(add1, 1));Alerts 2 to the screen.
demo() is a function that takes in a function as an argument and a value. it calls add1() function with an argument "1"
Syntax for arrow functions?
const sum = (x, y) => x + y;

JSON syntax?
var person = {"name": 'Chuck', // String
"age": 29, // Integer
"college" : true, // Boolean
"offices" : [ '3350DMC', '3437NQ' ], // Array
"skills" : { // Object
"fortran": 10,
"C": 10,
"C++": 5,
"python" : 7
}
};“name” : “value”,
Remember that array definition uses square brackets
What are these browser objects (Browser Object Model (BOM)) and what do they stand for?
window
history
location
navigator
screen
document
- window: top level object in the BOM hierarchy
- history: keep track of pages the user visits
- location: contains the URL of the page
- navigator: contains information about the browser (e.g. name and version)
- screen: provides information about display characteristics
- document: belongs to both BOM and DOM
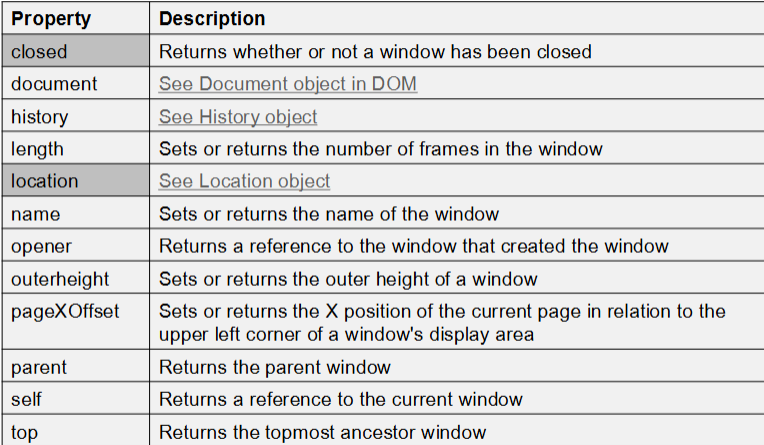
Explain these Window Object Properties:
closed
document
history
length
location
name
opener
outerheight
pageXOffset
parent
self
top
- closed: Returns whether or not a window has been closed
- document: See Document object in DOM
- history: visited URLs
- length: Sets or returns the number of frames in the window
- location: URLs
- name: Sets or returns the name of the window
- opener: Returns a reference to the window that created the window
- outerheight: Sets or returns the outer height of a window
- pageXOffset: Sets or returns the X position of the current page in relation to the upper left corner of a window's display area
- parent: Returns the parent window
- self: Returns a reference to the current window
- top: Returns the topmost ancestor window
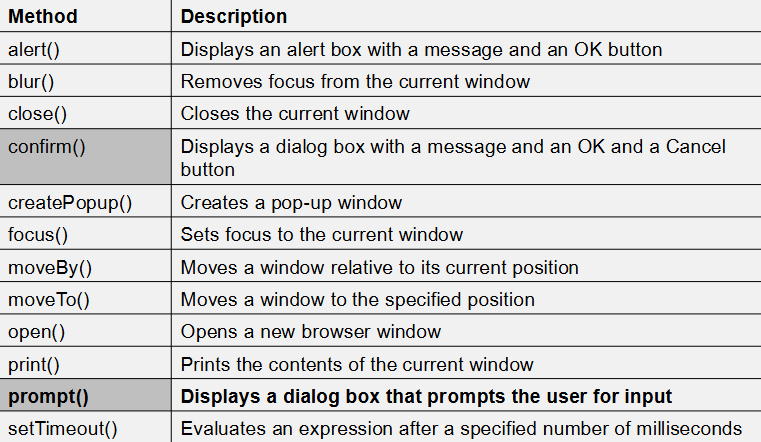
Explain these Window Object Methods:
alert()
blur()
close()
confirm()
createPopup()
focus()
moveBy()
moveTo()
open()
print()
prompt()
setTimeout()
- alert() Displays an alert box with a message and an OK button
- blur() Removes focus from the current window
- close() Closes the current window
- confirm() Displays a dialog box with a message and an OK and a Cancel button
- createPopup() Creates a pop-up window
- focus() Sets focus to the current window
- moveBy() Moves a window relative to its current position
- moveTo() Moves a window to the specified position
- open() Opens a new browser window
- print() Prints the contents of the current window
- prompt() Displays a dialog box that prompts the user for input
- setTimeout() Evaluates an expression after a specified number of milliseconds
What are the 5 ways to define an object in JS?
- "constructor" function:
var Car = function() {
this.wheels = 4; // specifies a property "wheels"
this.start = function() {
alert("Vroom!");
}; // defines a method called "start"
};
var myVW = new Car(); // declares a new Car object
myVW.start();
alert(myVW.wheels);- "Object" constructor:
// Creates a single object, no class
var member = new Object();
// Add properties
member.name = "Donald Duck";
member.email = "dd@gmail.com";
member.isRegistered = true;
// Define methods as named functions
function showMe() {
alert("I'm here!");
}
member.present = showMe;
// Define methods as anonymous functions
member.present = function() { alert("I'm here!"); }- Object prototype
// Create the prototype function
function Member(name, emaddr, reg) {
this.name = name;
this.email = emaddr;
this.isRegistered = reg;
}
// Define methods via prototype
Member.prototype.present = function () {
alert("I'm here! ");
};
// Define properties with default values
Member.prototype.isActive = true;
m5 = new Member();
m5.isActive = false;
- object literal / JSON (preferred):
var member = {
name: "Donald Duck",
email: "dd@gmail.com",
isRegistered: true,
present: function () { alert("I'm here!"); }
};
- Class keyword (preferred):
class Member {
constructor(name, emaddr, reg) {
this.name = name;
this.email = emaddr;
this.isRegistered = reg;
}
present() {
alert("I'm here!");
}
}
var member = new Member("Donald Duck", "dd@gmail.com", true);
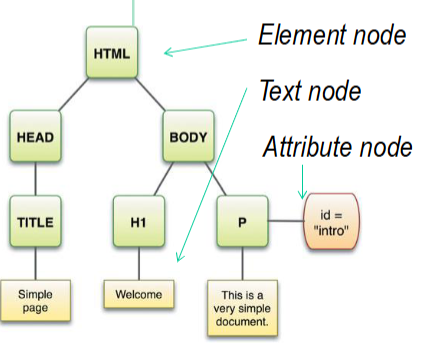
Structure of a Document Object Model?
Element → Attribute / Text
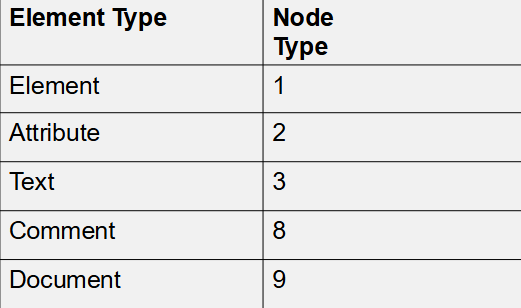
Map the Element type to node type (number) in DOM.
Element
Attribute
Text
Comment
Document
What are the 2 JS event models? Explain them.
Event capturing (default)
An event fires from the least-specific target to the most-specific target.
E.g. mouseover fires parent element (div) firs
Event Bubbling
An event fires from the most-specific target to the lease-specific target.
mouseover fires inner element (p) first
The screenshot shows the W3C DOM event registration style.

XML syntax?
remember XML declaration:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
tags are case sensitive

What is PCDATA?
parsed-character data. PCDATA is any “well-formed” text string, most text strings are “well-formed” except those that contain symbols reserved for XML, such as <, >, &
What are some common entity references in XML? what is the syntax?
Start with “&”, End with “;”
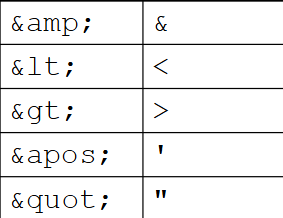
what are CDATA sections? can CDATA sections be empty?
Character Data (CDATA) sections indicate entire regions that should not be parsed. E.g. when we want to include some HTML as string and not XML markup.
CDATA sections cannot be empty

Structure of XML document?
An optional prolog:
XML declaration
Miscellaneous statements or comments
Document type declaration
A body / root element
An optional epilog – seldom used
Some notable well-formedness rules in XML?
One root element must contain all other elements
Attribute values must be in double or single quotes
E.g <book settext="no">
Element names may only begin with letters, underscores, or “:” and the remaining characters may only be alphanumeric, “_”, “-”, “:”, or “.”
Markup characters (e.g. <, >, &) do not appear directly in parsed content
<eqn>1 < 3</eqn>for showing “1 < 3”
What is XML DTD? What’s the syntax?
Document Type Definition (DTD) is a formalisation of what the data should look like.
Used to validate XML documents
What type of data can be contained in an element
What elements must be included
Order of elements
Kinda similar to regex

How do you create XML and JSON responses in PHP?
XML:
Create a structured XML Document:
new DomDocument()
Append children as required
createElement()appendChild()
Generate the text:
saveXML()
JSON
Create the data
json_encode()use
JSON_PRETTY_PRINTwill indent it nicely
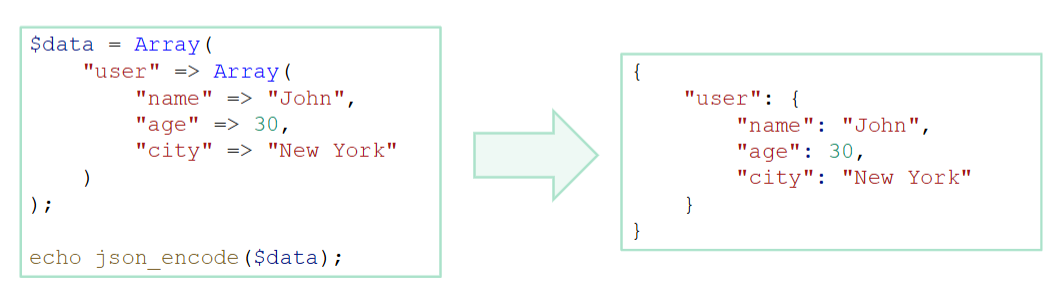
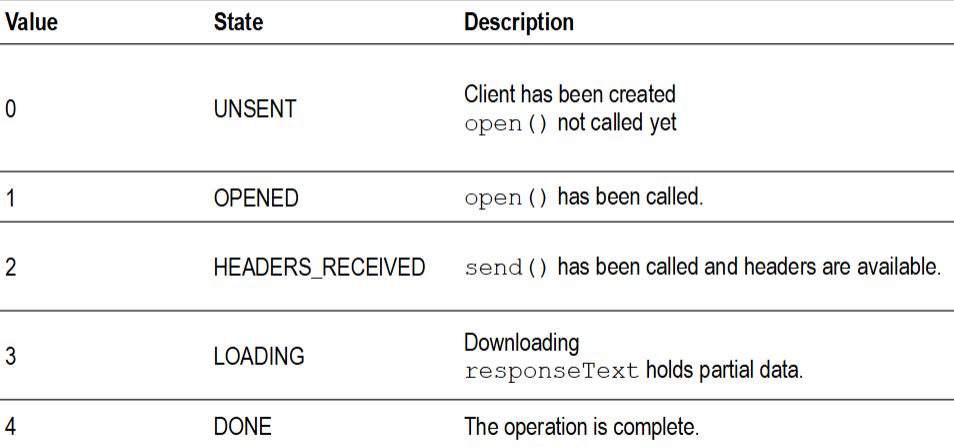
What are the different XHR readyStates? (5 of them)
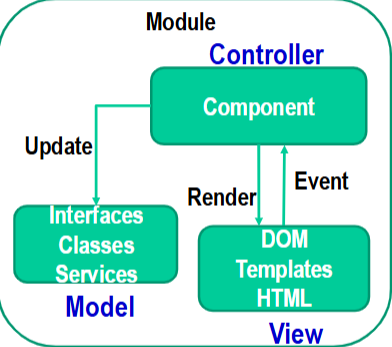
What are some Angular Key Features?
Written in TypeScript
Two-way data binding (NgModel)
The value of an HTML Form input element is “bound” to the property of an object
MVC architecture (“separation of concerns”)
Model, View, Controller
What are some common Angular directives? Syntax for using them?
NgModel for form control
<input [(ngModel)]="hero.name" placeholder="name">
NgIf for conditional logic
<div *ngIf="hero">(displays if “hero” is defined)
NgFor for iteration
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes">
NgClass for CSS classes
How do you launch an Angular application?
ng serve --open
What are some Angular components?
app.component.ts
The component class code, written in TypeScript
app.component.html
The component template, written in HTML
app.component.css
The component's private CSS styles
app.component.spec.ts
Unit tests for the component, written in TypeScript
What is interpolation in Angular? What is the syntax?
When you bind Class Variables to HTML Content. Change in one place apply to the other. Syntax is double curly braces:
export class AppComponent {
title = 'my-angular-app';
}Bind in HTML:
<h1>Hello, {{ title }}</h1>
What does the Input package do in Angular? Whats the syntax?
allows us to get properties as inputs:
export class HeroDetailComponent {
@Input() hero?: Hero;
}What is server side rendering? What is hydration?
SSR: A process that involves rendering pages on the server, resulting in initial HTML content which contains initial page state.
Hydration: The process that restores the SSR application on the client
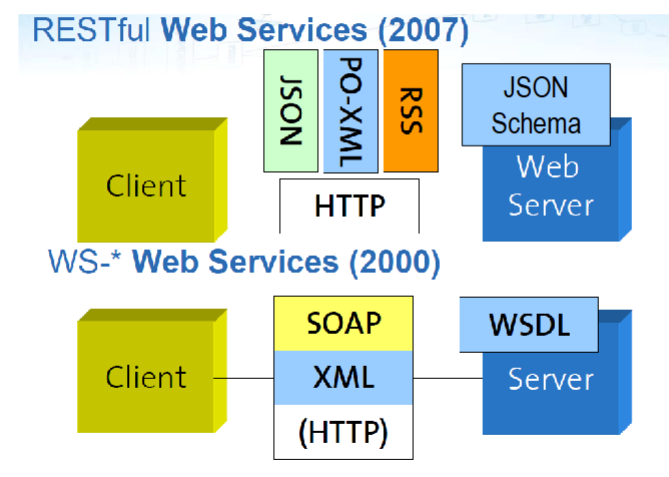
What does REST and SOAP stand for? how do they work
REST: Representational State Transfer
Uses HTTP methods to communicate intent
Send the endpoint + parameters
Receive JSON data
SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol
A SOAP XML document is used for request/response
The <SOAP:Envelope> element specifies several namespaces for the XML Schema, instance and SOAP
contains a <SOAP:Header> element (optional) and a <SOAP:Body> element
All the details about the request (method, parameters, content) are contained within <SOAP:Body>
Common characteristics of web services?
◼ Accessible over the Web
◼ Communicate using platform-independent and language-neutral protocols
◼ Provide an interface that can be called from another program
◼ Registered and located through a Web Service Registry
◼ Support loosely coupled connections between systems
◼ Promote componentization of common functions
◼ Ease the web programming effort
Difference between SOAP vs RESTful Web Services?
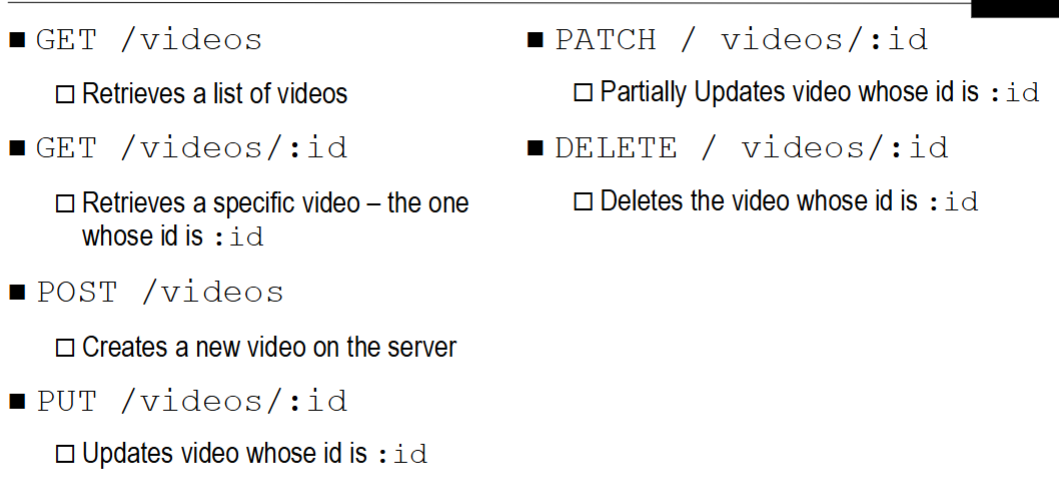
Map HTTP methods with CRUD operations
POST – Create
GET – Retrieve
PUT – Update
PATCH – partial update
DELETE – delete
What is the 4 step process of a web service?

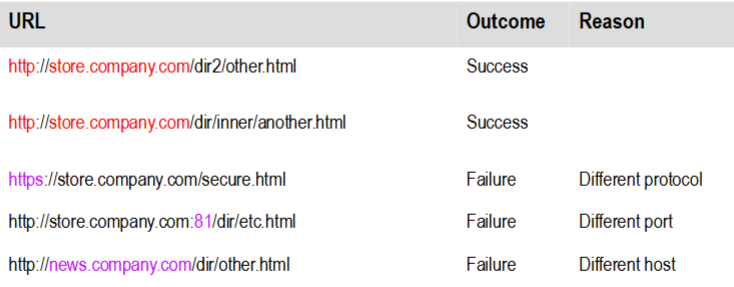
What is the same origin policy in web services?
API must be called from the same origin.
Two pages have the same origin if the protocol (https), port (default 80), and host (domain) are the same
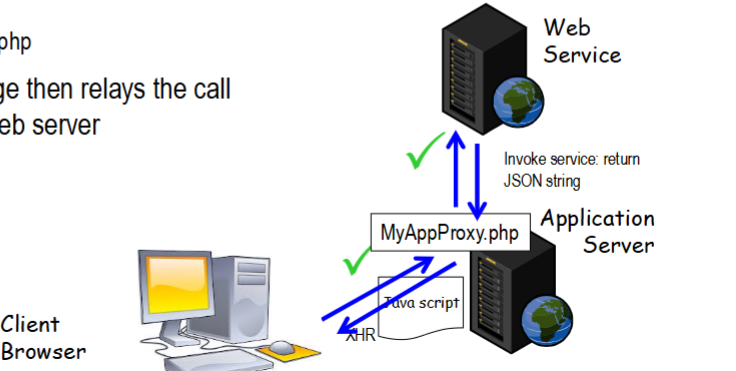
What is a solution to the same origin policy?
Create an “appliation proxy”, a proxy page on the server since the same origin policy only applies to client side, not the server side.
Call the page on the server → relay the call to the external web server
However, application servers can still be subject to firewalls
What is Curl?
Curl is a multi-protocol file transfer library
Library that allows you to connect and communicate to many different types of servers with many different types of protocols
What is Routing in RESTful API design?
Routing refers to how an application’s endpoints (URIs) respond to client requests
A route associate an URI/URL with one or more functions defined in the backend
Mapping the URL and method to a function