Micro - Ch. 6 - metabolism: fueling cell growth
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
metabolism
all chemical reactions necessary to maintain life
catabolism
breakdown of molecules
“cats break stuff”
anabolism
building molecules
coenzymes/cofactors
compound that helps enzymes
vitamins or minerals
Enzyme classes
oxidoreductases
transferases
lyases
hydrolases
isomerases
ligases
Oxidoreductases
causes losses or gains of oxygen and hydrogen
Transferases
transfers functional groups
lysases
removes atoms without use of water
Hydrolases
split bonds with water
isomerases
rearrange molecules
ligases
joins molecules
What is the effect of temperature on enzymes?
high temperature speeds enzymes to a point of denaturation occurs and that then that causes a decrease in temperature which slows enzymes
What is the effect of pH on enzymes?
high or low disrupts structure and function
inhibitors of enzymes
slows or stop enzyme activity
Types of inhibitors
1 competitive
2 noncompetitive
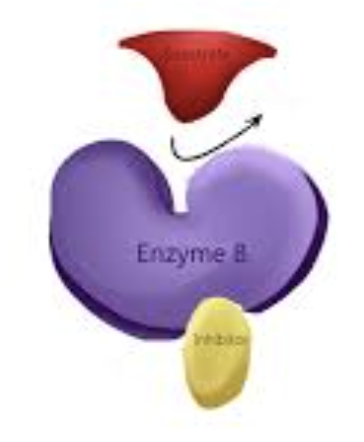
Competitive inhibitors
bind reversibly to enzymes active site
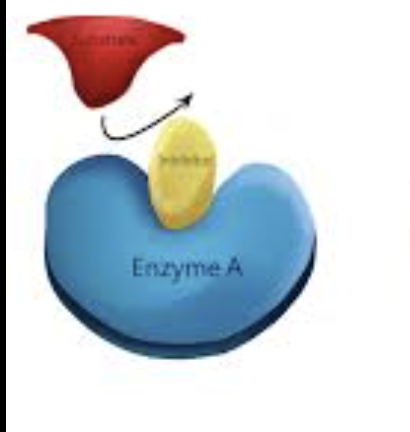
Noncompetitive inhibitors
bind to a raondom spot on enzyme called “allosteric site” - can be reversible or not
What does ATP do?
stored energy
a nucleic acid thats broken to release stored energy energy
What does ATP mean?
adenosine triphosphate
What are the ways ATP is made
1 photosynthesis
2 aerobic respiration
3 anaerobic respiration (fermentation)
4 transferring a phosphate group to ATP
photosynthesis
uses sunlight and water
aerobic respiration
breakdown of glucose with oxygen
anaerobic respiration (fermentation)
breakdown of glucose WITHOUT or with LITTLE oxygen
transferring a phosphate group to ATP
phosphorylation (P)
ADP + P = ATP
parts of the chloroplast
thylakoid membrane (green pancakes)
stroma
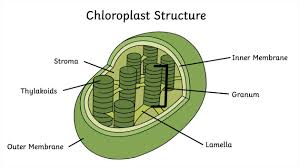
What is the stroma in a chloroplast?
the fluid-filled space inside the chloropla that surrounds the thylakoid membranes
What happens in step 1 of photosynthesis?
light excites electrons locates in the thylakoid membrane and leaves chlorophyll and passes along electron transport chain
What happens in step 2 of photosynthesis?
high energy electrons move through the ETC releasing energy to pump hydrogen across thylakoid membrane
What happens in step 3 of photosynthesis?
water split to replace lost electrons, releasing oxygen (O2) into the air plus reducing hydrogen (H+)
What happens in step 4 of photosynthesis?
Hydrogen proton gradient of high concentration in thylakoid space drives ATP synthesis as H+ flow back into stroma through ATP synthesis (facilitated diffusion)
Recall: what is facilitated diffusion?
concentration of substance from high to low
What happens in step 5 of photosynthesis?
Electrons (e-) continue through the membrane to photosystem 1 where NADH+ accepts electrons and hydrogen to form NADPH
Step 5 for photosynthesis cheat
NADP+ + e- & H+ = NADPH
For steps 1-5 for photosynthesis they are:
light dependent
ATP and NADPH were critical products
What happens in step 6 in photosynthesis?
CO2 enters the Calvin cycle from air and binds to sugars to for a 6 carbon atom
What happens in step 7 in photosynthesis?
the 6 carbon atoms split into two 3-carbon molecules (3PGA)
What happens in step 8 in photosynthesis?
ATP and NADPH converts the pair 3-carbon into G3P (high energy sugar)
From step 8 of photosythesis, what happens with the high energy sugar (G3P)?
Part of the G3P becomes glucose or carbohydrates
other half becomes RuBP to continue the cycle
What does step 8 of photosynthesis require more of?
requires more ATP
What is the oxidation of glucose equation (cellular respiration)?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
What are the reactants of the oxidation of glucose equation?
C6H12O6 + 6O2
glucose and oxygen
What are the products of oxidation of glucose equation?
6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
carbon dioxide, water, ATP
How much ATP is produced from glucose being oxidized?
38 ATP
What does cellular respiration do?
“reverses” photosynthesis
How does cellular respiration reverse photosynthesis?
breaks down sugar using oxygen to make energy, water, and carbon dioxide
What are the basic steps of cellular respiration?
glycolysis → citric acid cycle/Krebs cycle → electron transport chain
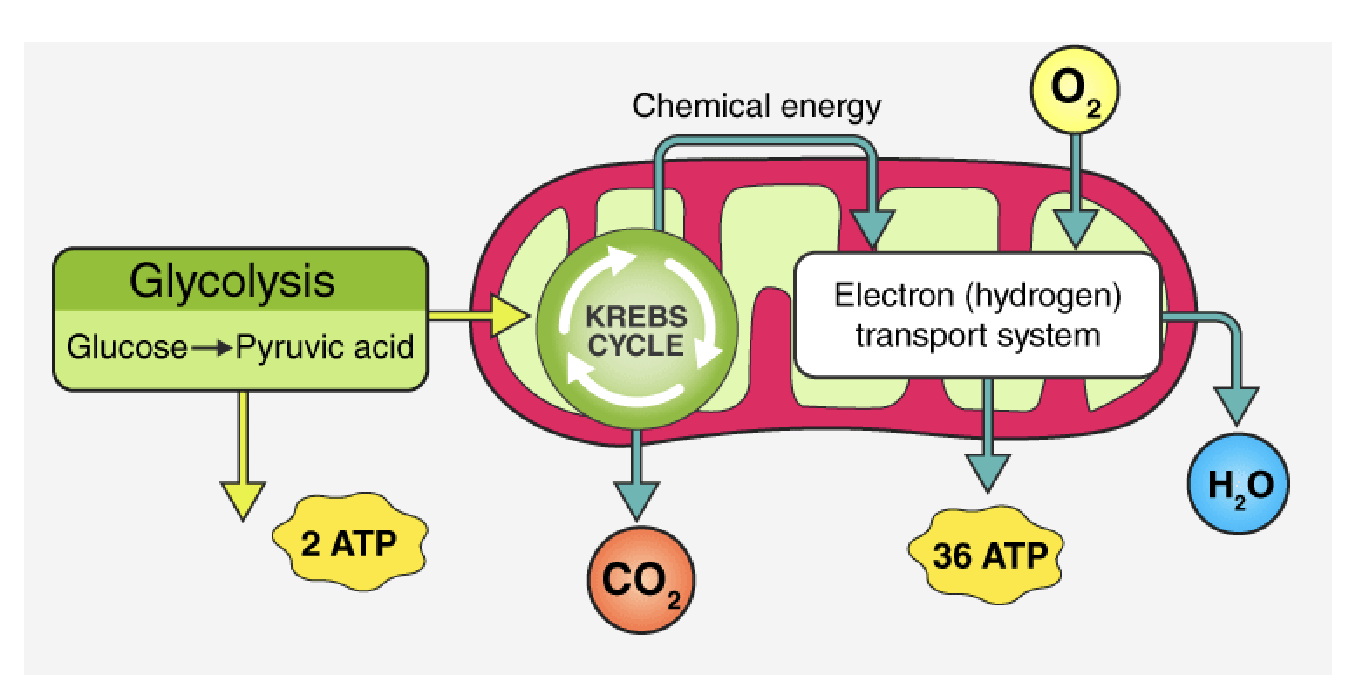
Describe glycolysis
process of breaking down glucose
What happens in glycolysis?
glucose breaks into 2 pyruvate, 4 ATP (uses 2), 2 NADPH
What molecule begins the Krebs cycle?
the pyruvate acid we just made in glycolysis
How is acetyl CoA formed through the Krebs cycle?
pyruvic acid and coenzyme A joins
What forms citric acid?
oxaloacetic acid joins with acetyl CoA
What are the products of Kreb’s cycle?
CO2, NADH+, FADH2
What molecules are used with the electron transport chain?
NADH+ and FADH2
What happens in the ETC with NADH+ and FADH2?
they split to make H+ (protons) and electrons (e-)
What do the electrons pass through when released?
they pass through proteins that are the transport chains
What happens to the hydrogens (protons) in the ETC?
pumped into membrane to create a proton gradient
How is ATP made in the ETC?
uses the energy while the H’s & electrons join with oxygen to form water
fermentation
microorganism convert to pyruvate without oxygen to make acid, gases, and alcohol for bacteria and yeast
lipid breakdown
triglycerides are broken into glycerol and fatty acids
What do fatty acids go through?
beta oxidation
What does beta oxidation do to fatty acids?
breaks long fatty acid chain into smaller 2 carbon units (acetyl CoA)
Protein breakdown
broken into individual amino acids called “carbon skeletons” to join the Kreb’s cycle