1. therio- male repro review
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what is the mediastinum testis?
connective tissue in the center of testis
visible on U/S, can be a landmark when searching for a retained testicle in abdomen
what are the cell types within the testicular parenchyma?
sertoli cells: control spermatozoa development
leydig cells: produce testosterone
spermatogenic or germ cells
which part of the epididymis can potentially fertile sperm be found?
tail of the epididymis
can be collected post castration or euthanasia, but not after barbituates
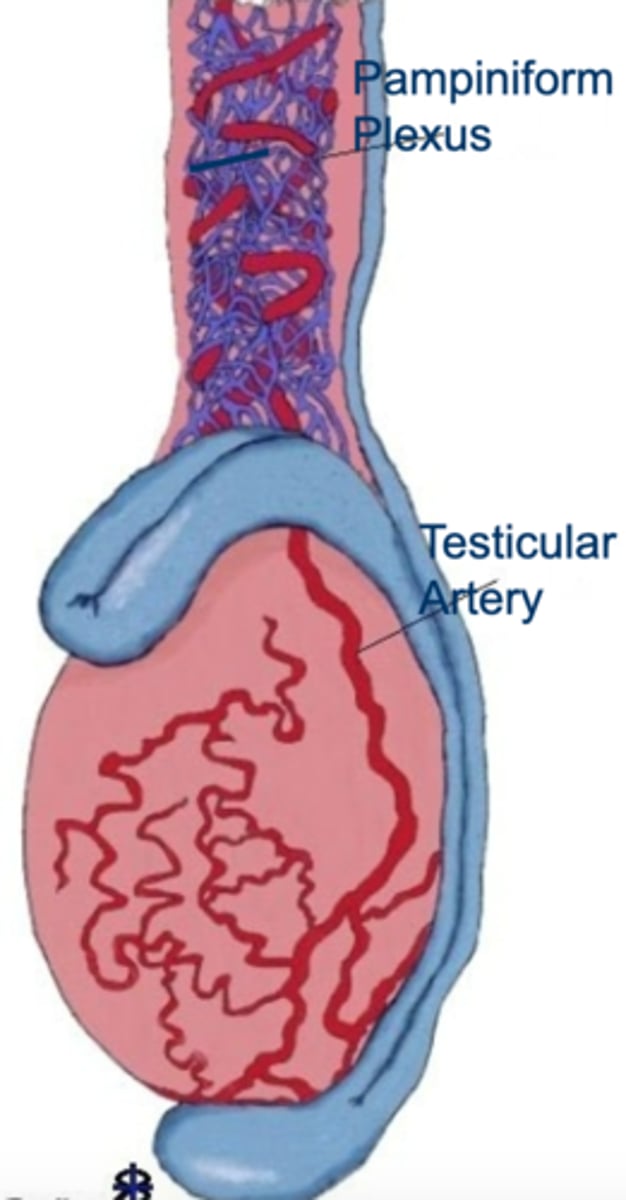
what is the function of the pampiniform plexus (aka testicular vascular cone)?
provides a counter-current heat exchange- testicular artery is surrounded by a network of veins which allows blood reaching the testes to cool down by the time it gets there
what is the gubernaculum testis?
remnant useful for finding retained testicles- responsible for testicular descent
will later shrink and degenerate turning into the proper ligament of the testis, the ligament of the tail of the epididymis, and the scrotal ligament
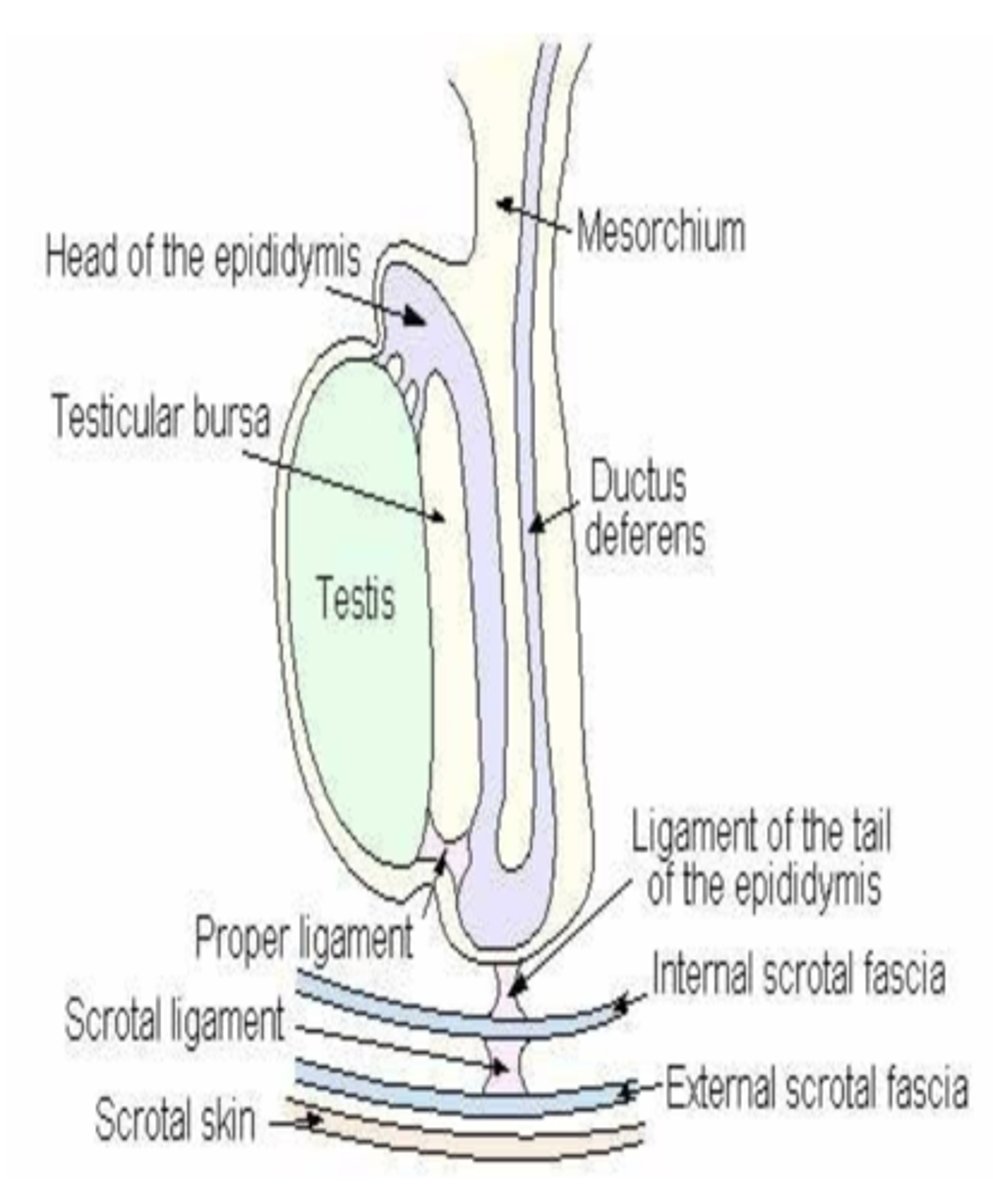
what is the purpose of the proper ligament of the testicle?
connects the tail of the epididymis to the testicle
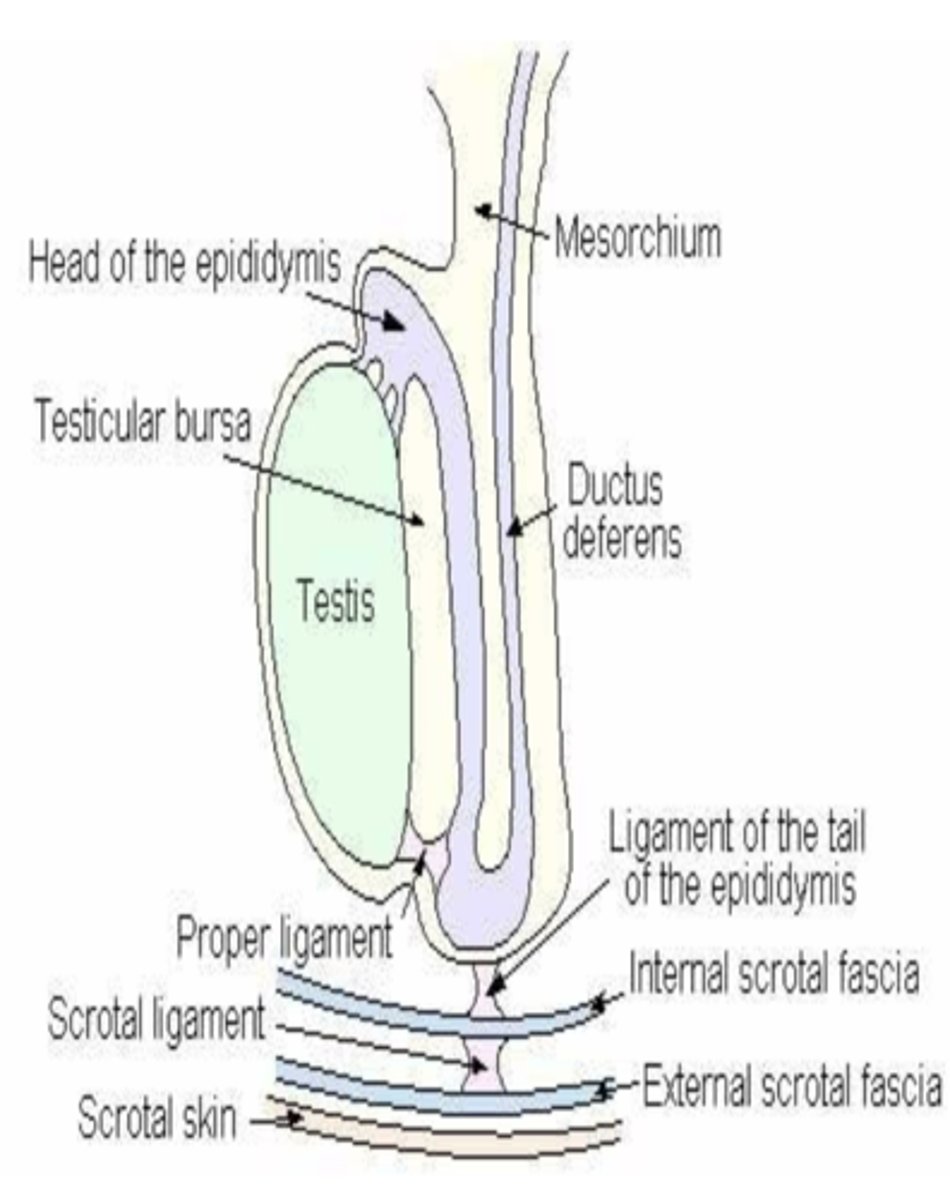
what is the function of the ligament of the tail of the epididymis (LTE)?
the LTE connects the tail of the epididymis to the parietal tunic
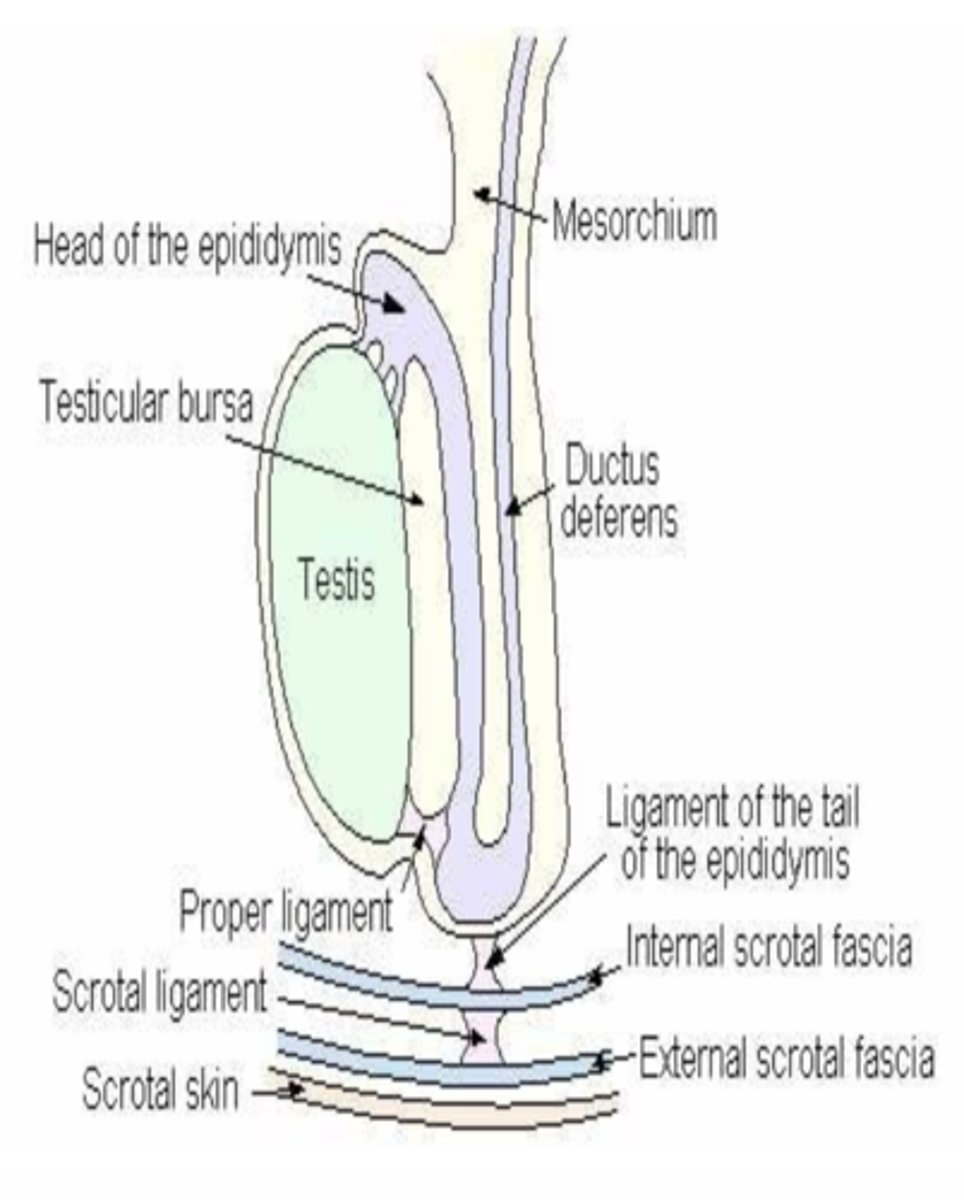
what is the function of the scrotal ligament?
attaches the parietal tunic to the scrotum
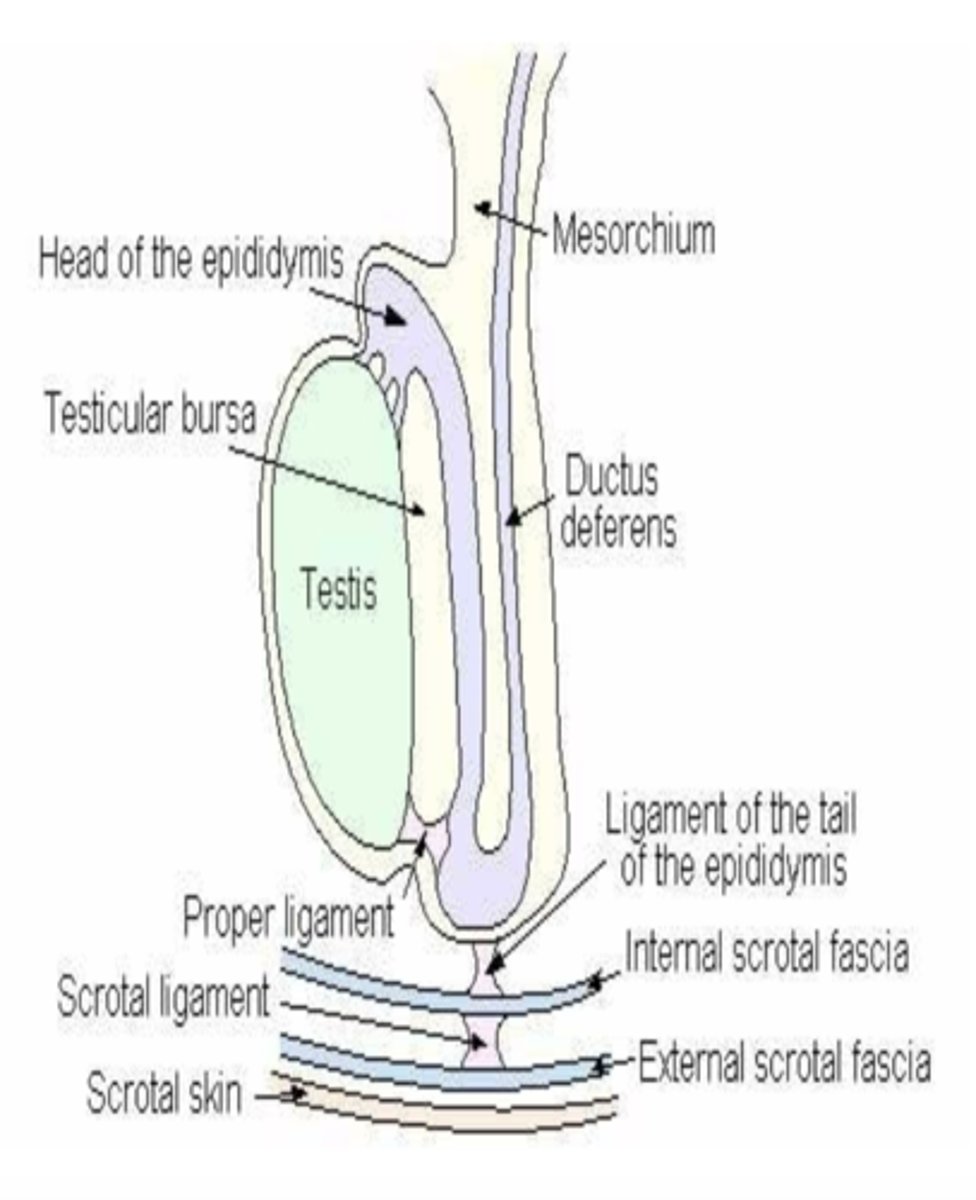
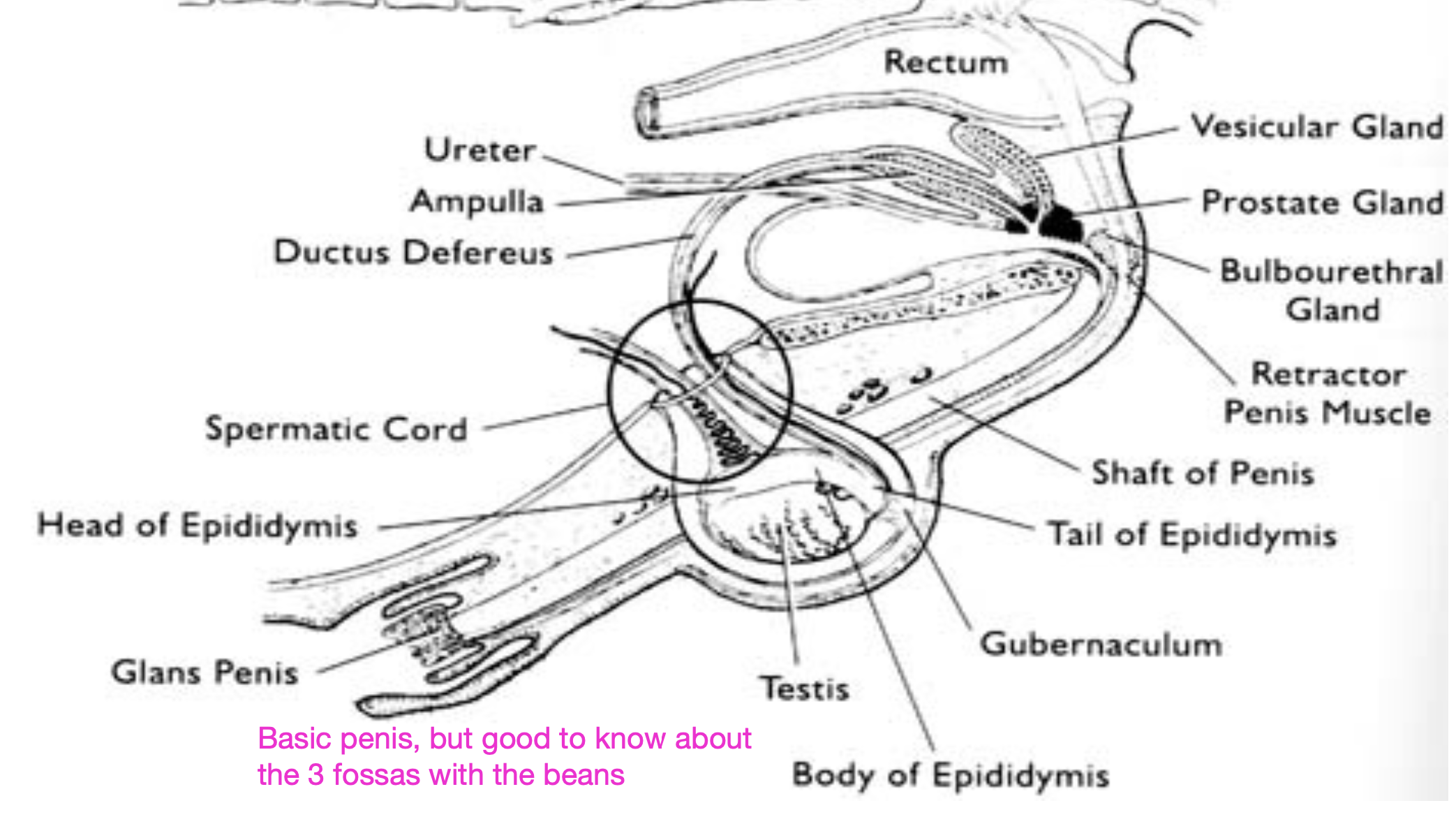
what is the function of the epididymis?
final maturation and storage of sperm
what are the 3 parts of the epididymis?
1. head (caput): sperm not motile, and not fertile
2. body (corpus): some motility with dilution, can bind to oocytes
3. tail (cauda): normal motility after dilution, where potentially fertile sperm can be found
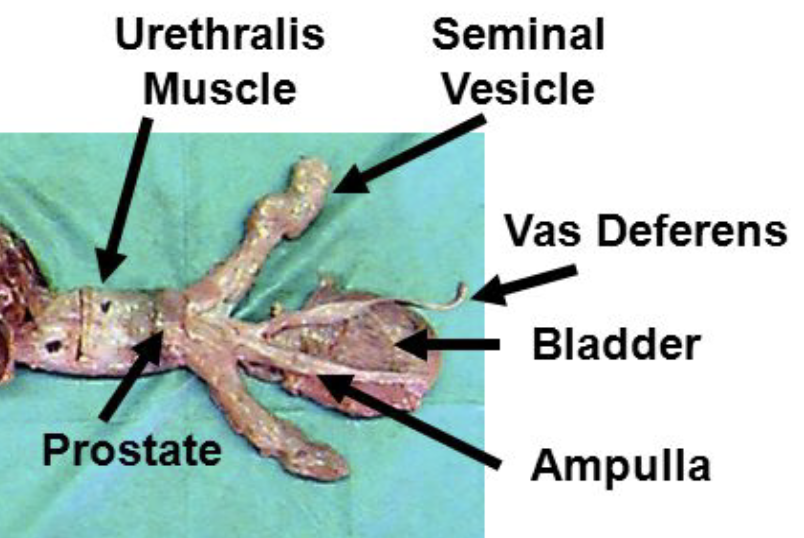
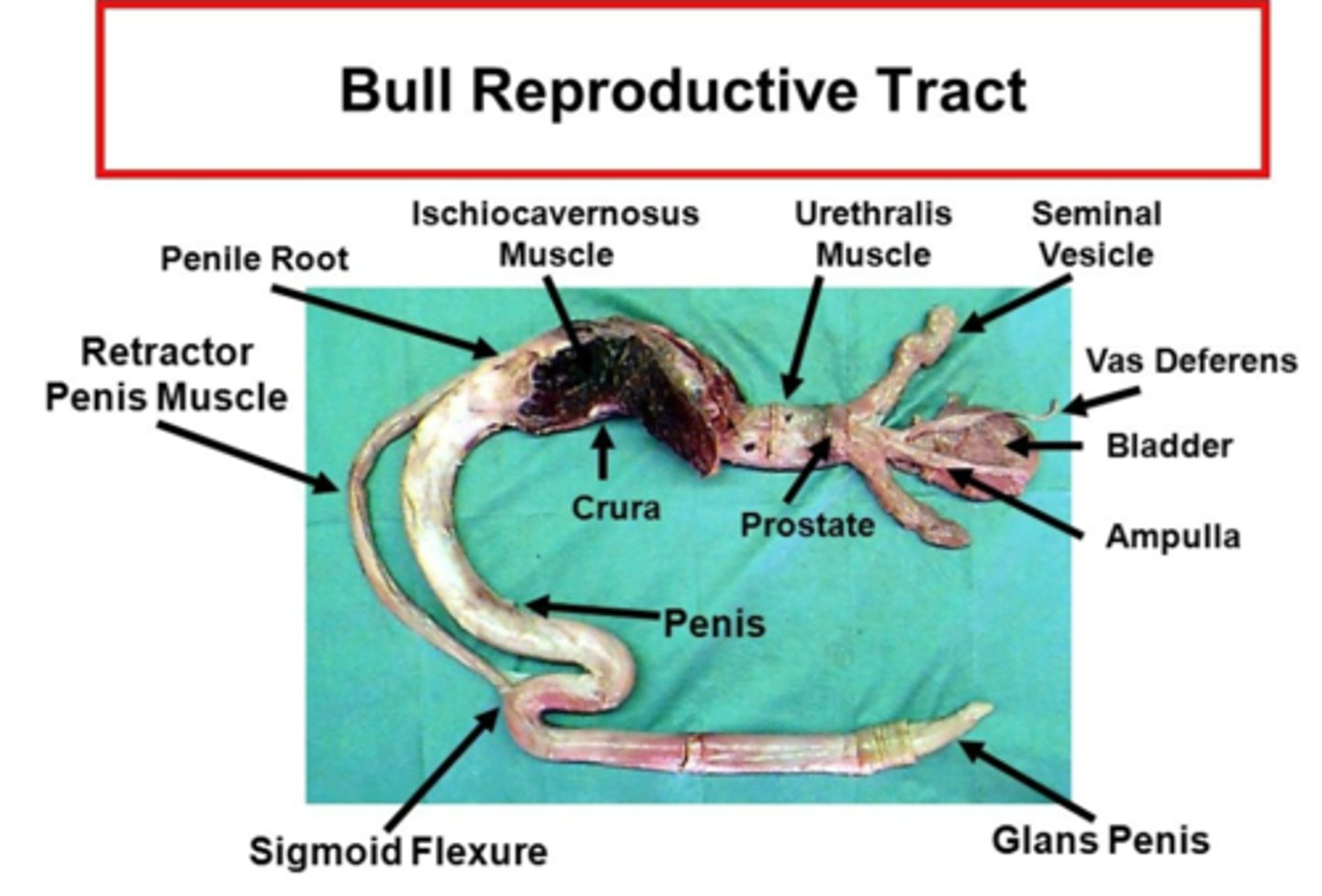
what are the 4 accessory sex glands of domestic animals?
1. ampullae
2. vesicular glands
3. prostate
4. bulbourethral gland
what are ampullae?
dilation of the terminal part of the vas deferens due to glandular thickening of the wall
considered extra-gonadal sperm storage
which domestic species have ampullae?
present in the ruminant and stallions
what are vesicular glands?
paired sacculated pouches and gland that joins the ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct
provides the ejaculate with milky and highly viscous fluid
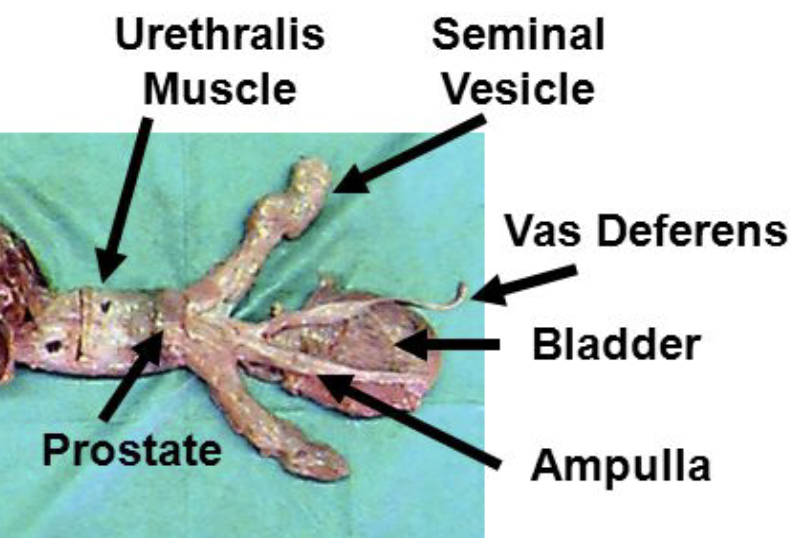
which domestic species have vesicular glands?
stallions (gel in the stallion), ruminant, boar
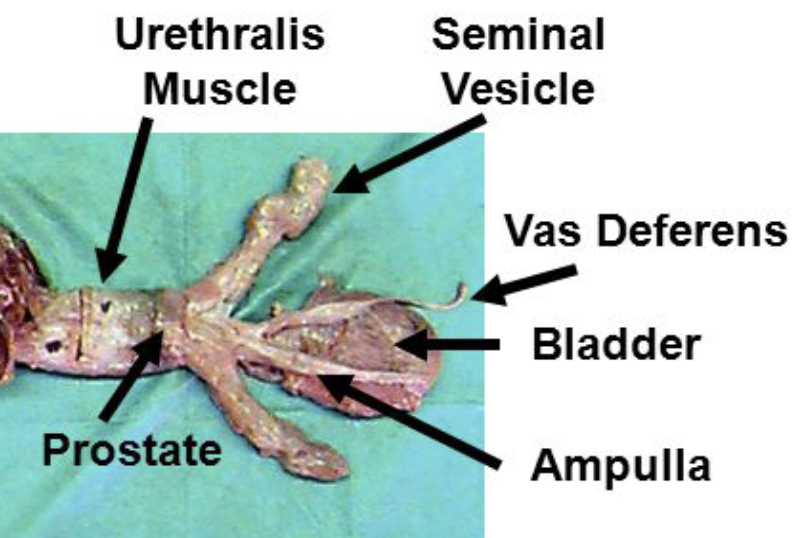
what is the prostate?
surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra. Contributes to seminal fluid with acid phosphatase and proteolytic enzymes to clean urethra during ejaculation
what are bulbourethral glands?
on either side of the urethra
alkaline pH neutralize the urethra
which domestic species have bulbourethral glands?
boar (gel in the boar- boars also have the largest), ruminants, stallions, cats, camelids
absent in the dog
which domestic species have a sigmoid flexure (fibroelastic penis)?
ruminants, boars. camelids
what is the function of the sigmoid flexure?
an s-shaped bend in the penis which permits it to be retracted completely into the body
ruminants, boars and camelids have retractor penis muscles (pair of smooth muscles which relax to permit extension of the penis and contract to draw the penis back into the body)
these retractor penis muscles arise from the coccygeal vertebrae and are fused to the ventral penis just cranial to the sigmoid flexure
which domestic species have a prostate?
present in all species
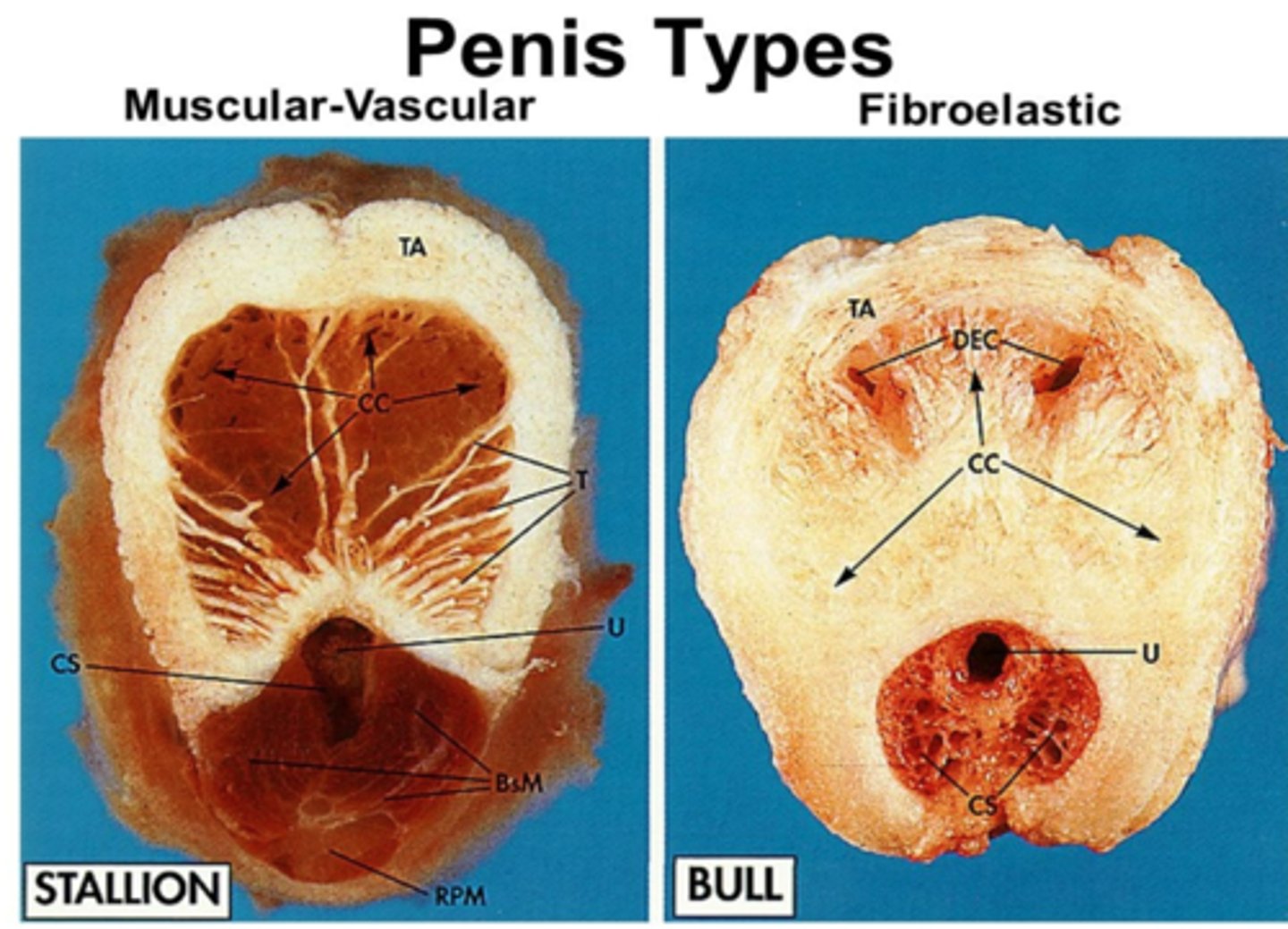
where are the corpus spongiosum and corpus cavernosum located?
spongiosum: surrounds urethra
cavernosum: above the corpus spongiosum
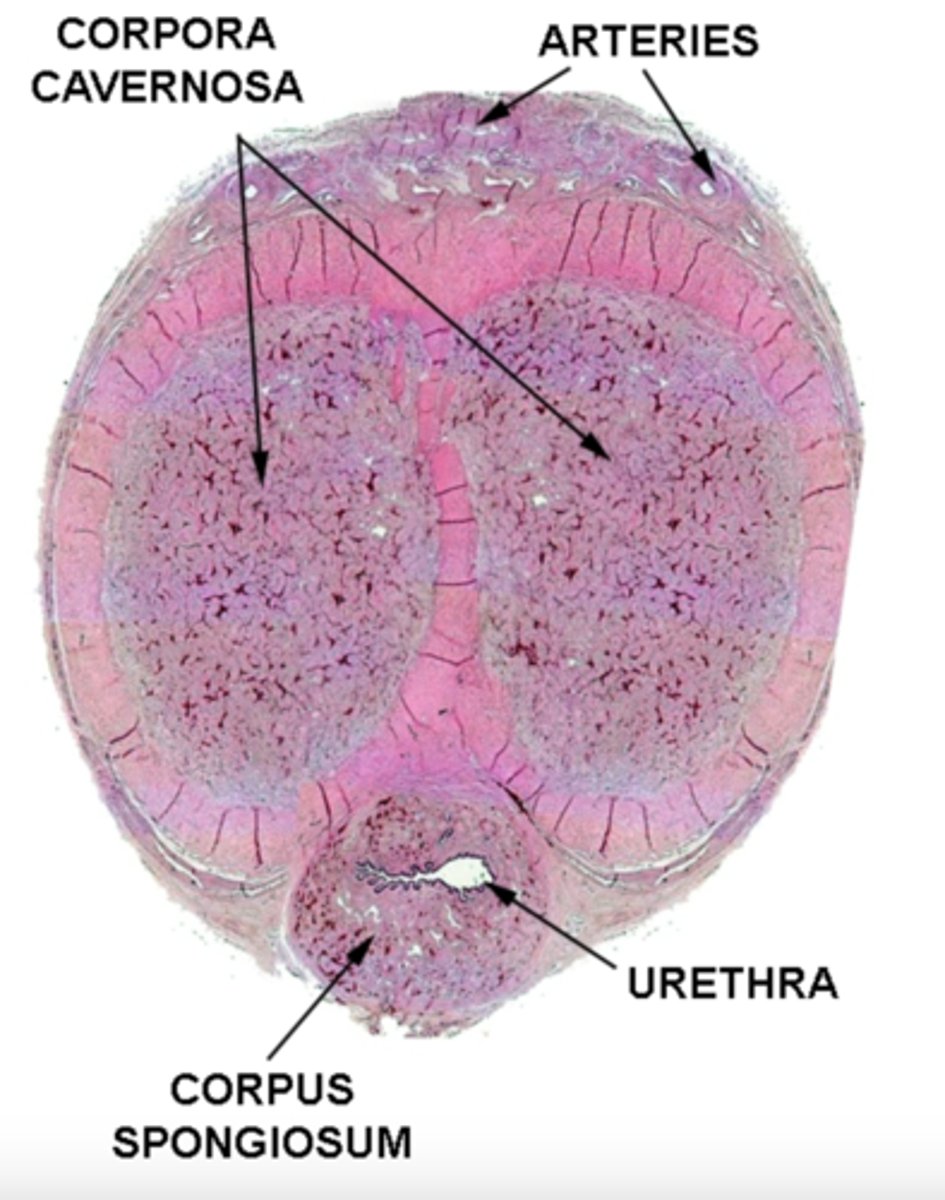
what is the function of the corpus spongiosum?
spongiosum 'buffers' urethral lumen from pressure of the cavernosa during erection (prevents urethral collapse)
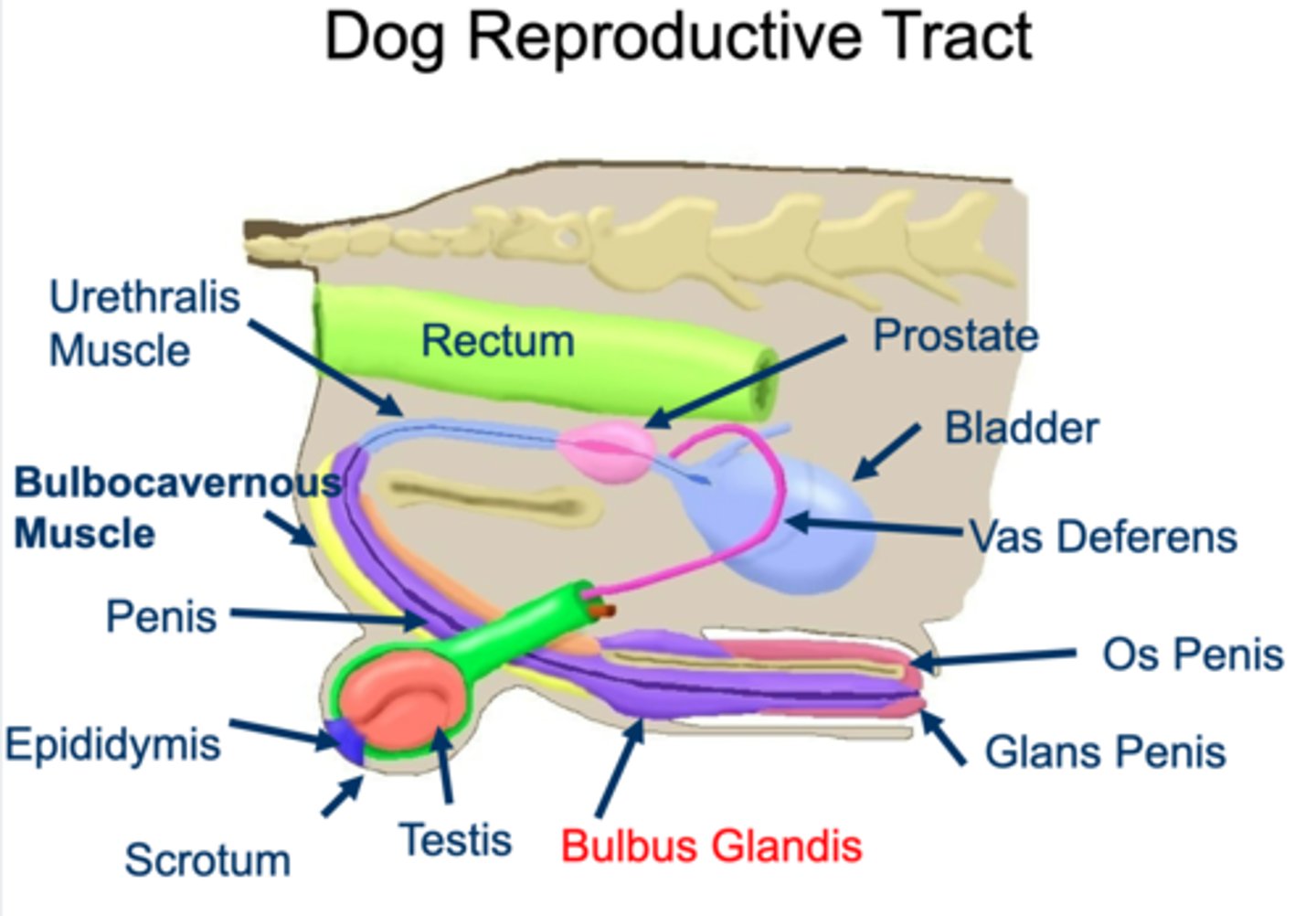
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in dogs?
dogs have an os penis and bulbus glandis
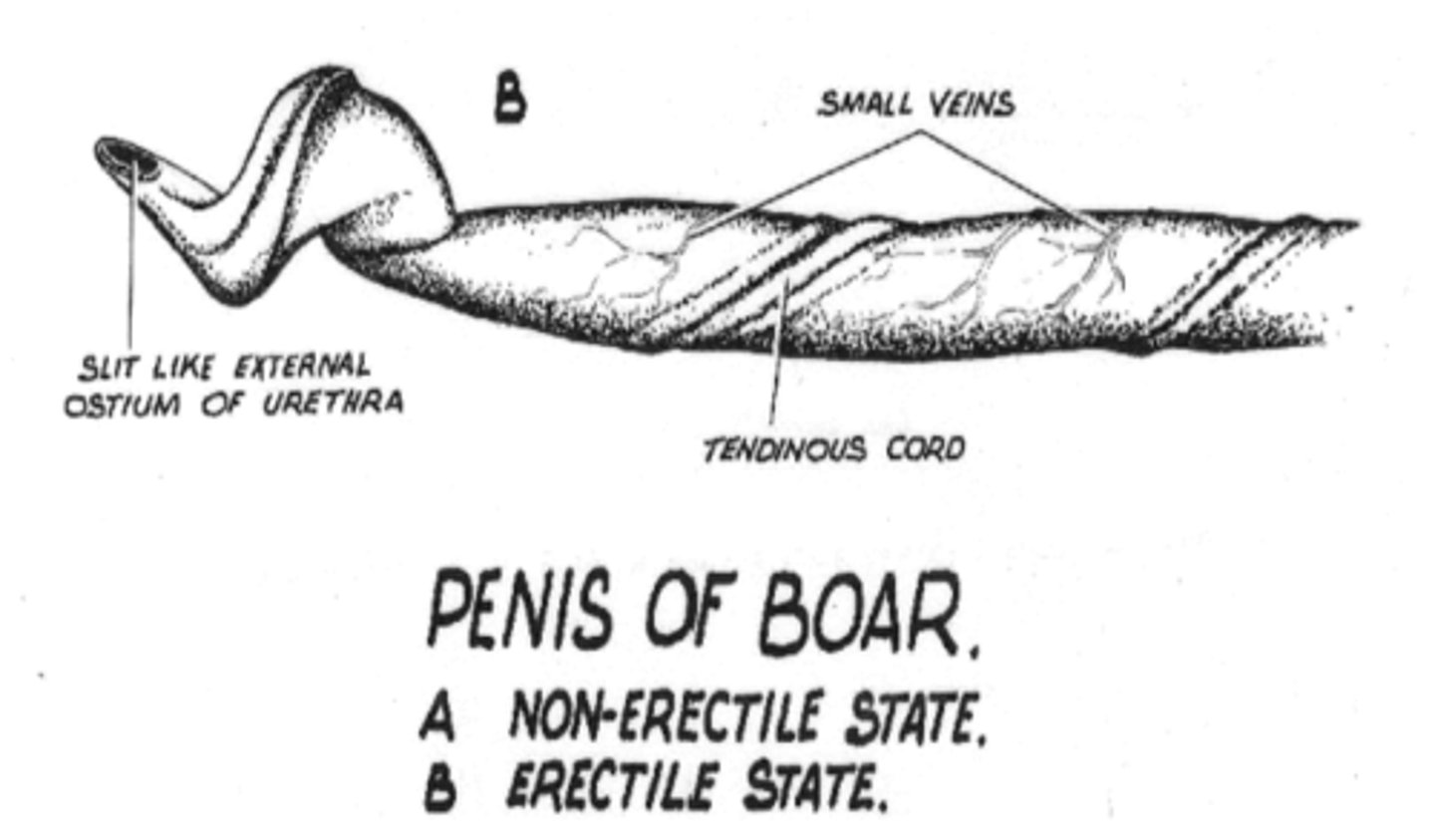
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in boars?
boars have a spiral glans and preputial diverticulum
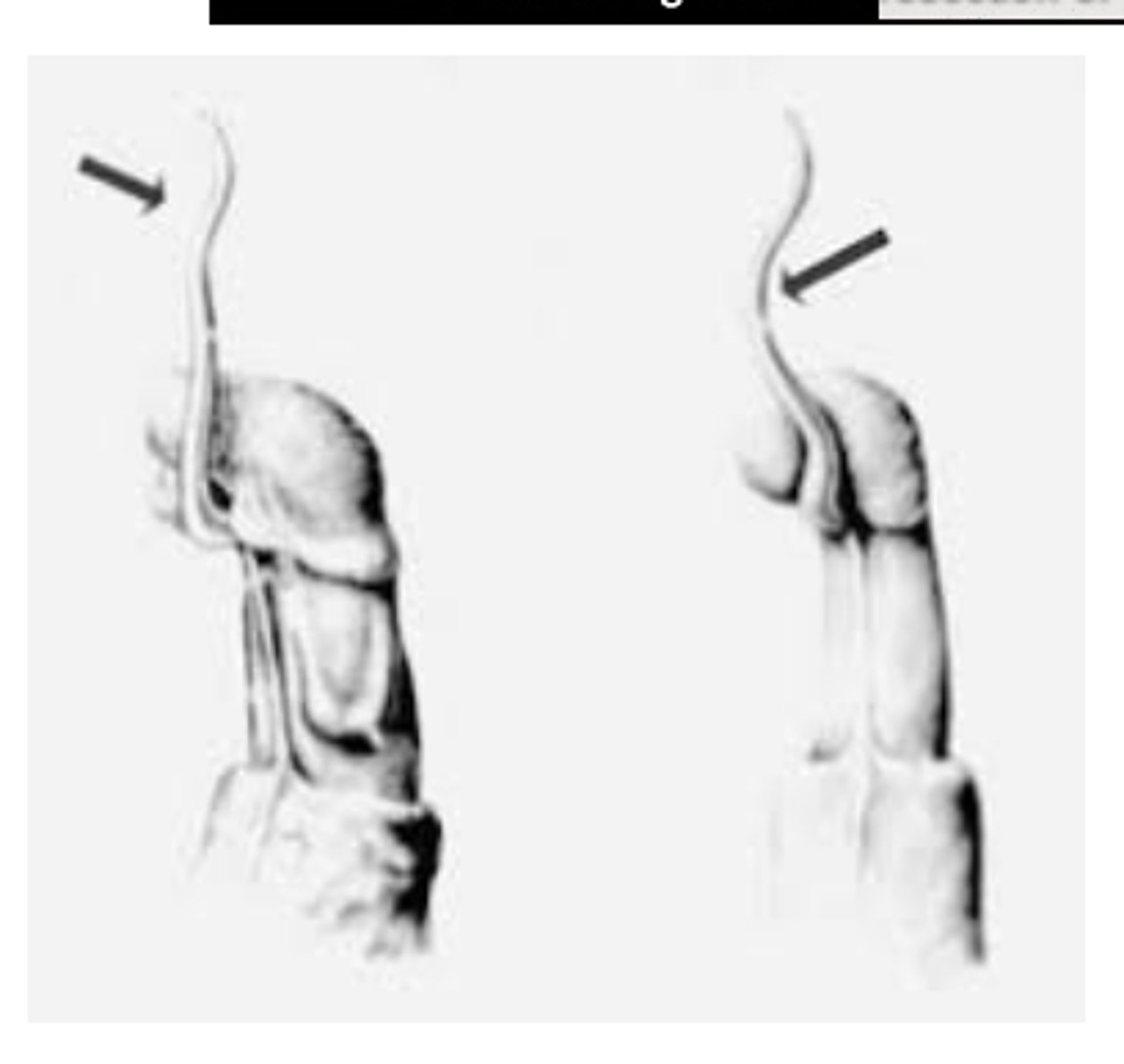
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in bucks/rams?
urethral process/vermiform appendage (common place for urolithiasis)
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in bulls?
end spirals at ejaculation (may see with EE)
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in stallions?
fossa glandis and 3 urethral sinuses
where beans collect, and where contagious equine metritis can be found
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in camelids?
protractor preputial muscle pulls prepuce forward before mating, changing direction of the opening allowing for penis to be directed forward
hook like tip of the prepuce/cartilaginous tip of penis partially contributing to ovulation induction
what are anatomical differences of the male repro tract in tom cats?
small os penis and 100-200 cornified papillae which regress after castration
what are the target cells of LH in males? what is the function of LH in males?
targets Leydig cells to stimulate androgen (testosterone) production, spermatogenesis
what are the target cells of FSH in males? what is the function of FSH in males?
targets Sertoli cells to make inhibin, androgen binding protein, and estrogens
sertoli cells control spermatozoa development by inhibin, which provides negative feedback of FSH and nourishment to developing germ cells
what is the function of androgen binding protein (ABP)?
keeps androgens high in the testes
what forms the blood-testis barrier?
tight junctions between sertoli cells
what is spermatogenesis?
spermatocytogenesis + spermiogenesis = spermatogenesis
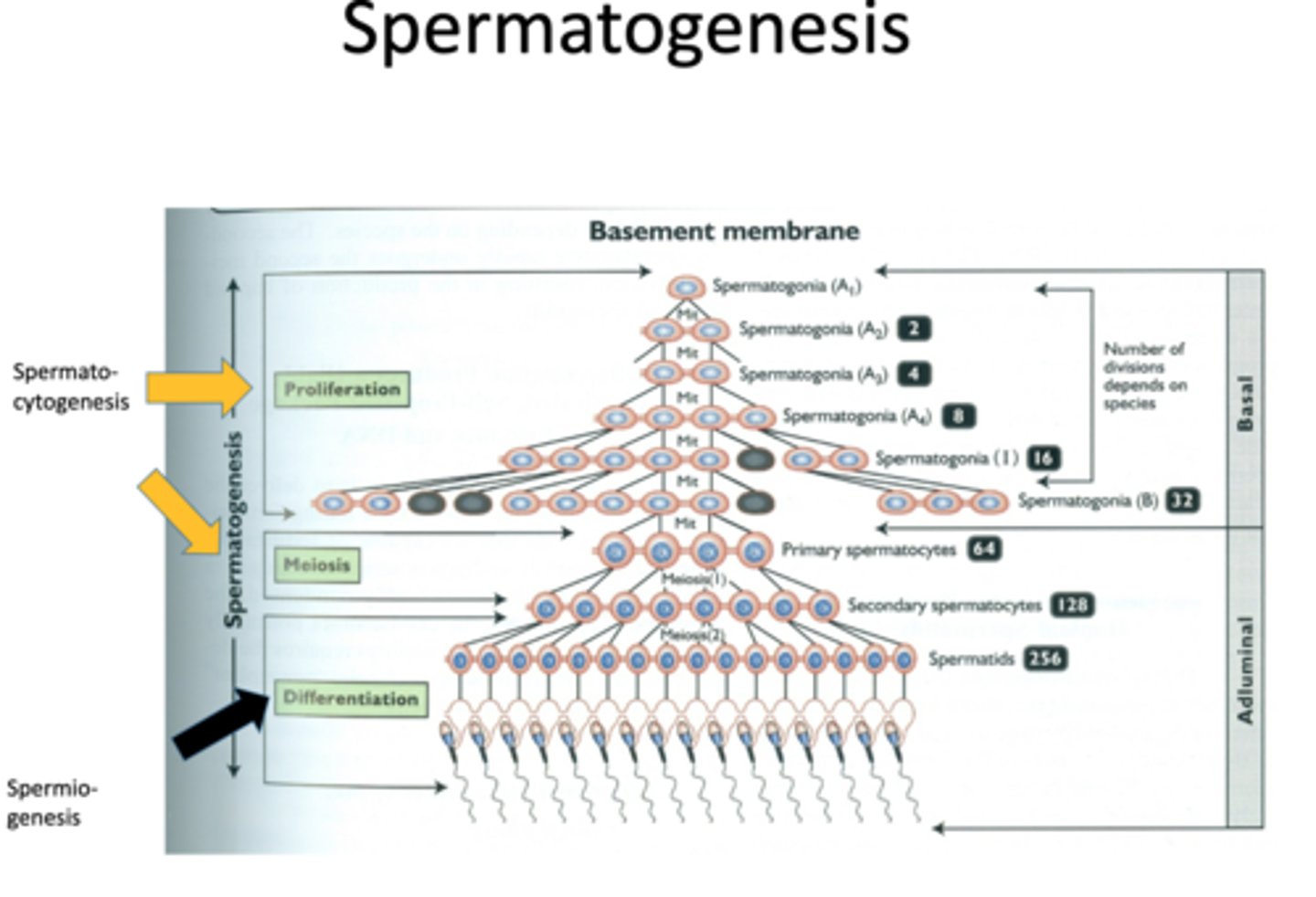
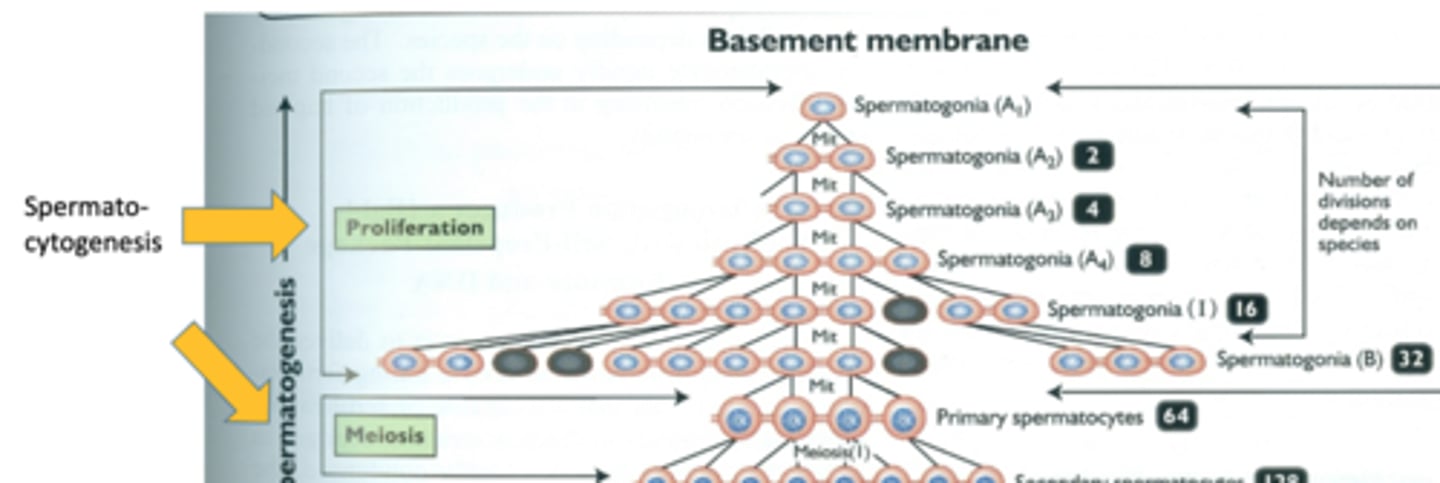
what is spermatocytogenesis?
first stage of spermatogenesis
spermatogonia >> spermatocytes >> spermatids
what is spermiogenesis?
second stage of spermatogenesis (golgi phase, cap phase, acrosomal phase, maturation phase)
spermatid >> spermatozoon
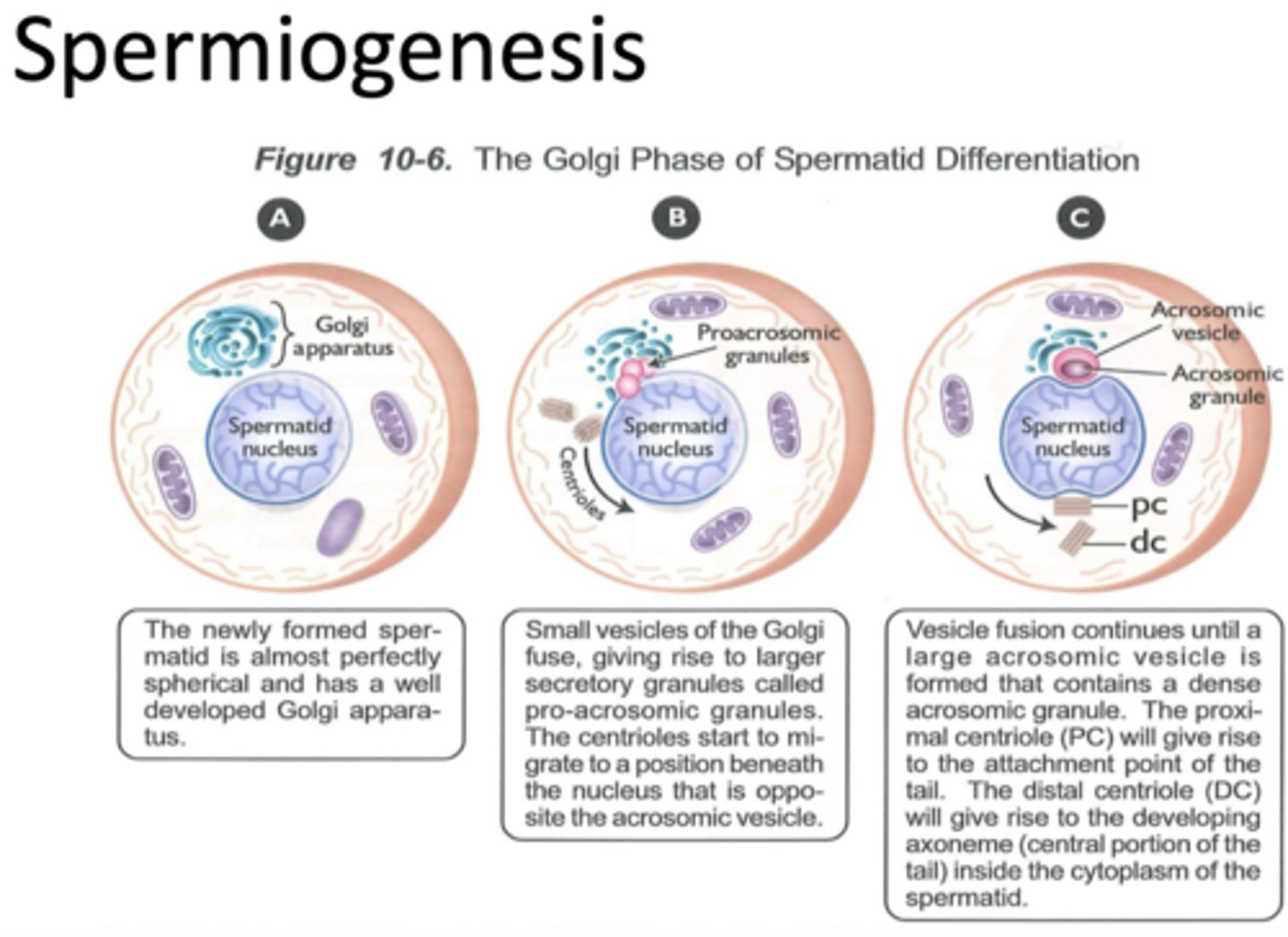
what is spermiation?
release of spermatozoa from sertoli cells
how long does normal spermatogenesis in most species take to complete?
varies with species, but in general 6-8 weeks
when does testicular descent occur in the majority of domestic species?
testes should decent in majority of domestic species through the internal inguinal rings by 2 weeks after birth
at which age should stallions have descended testes?
testes in stallions should be down within 16 months
testes are below the inguinal ring after birth in most animals (and are large)
when does testicular descent occur in dogs? when should they be palpable?
dogs testis should descend by 5-14 days post birth
should be palpable by 6-8 weeks of age (some say less than 6 months)
what nervous system controls erections?
parasympathetic NS controls erection
corpus cavernosum fills with blood, ischiocavernosus muscle pumps blood
what nervous system controls sperm emission?
sympathetic stimulation
alpha-2 sedatives can induce emission
what nervous system controls ejaculation?
combination of sympathetic, parasympathetic, and spinal nervous systems
which species can alkaline phosphatase-containing sperm be found in?
dogs and stallions
in dogs and stallions, what does a high alkaline phosphatase concentration in sperm indicate?
if very high (5000 or above) indicates sperm came from epididymis= indicates job completed (ALP only found in epididymis)
what generates the pre-sperm ejaculate fraction?
generated by the bulbourethral gland and prostate
what generates the sperm-rich ejaculate fraction?
generated by the epididymis and ampullae
what generates the post-sperm ejaculate fraction?
generated by the prostate and then the gel producing glands in the gel producing species (bulbourethral gland in boar, vesicular gland in stallion)
how is the sperm count for dogs calculated?
10 million sperm per pound
Still learning (21)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!