ECON 101: Consumer Surplus, Producer Surplus, Total Surplus
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
wilingness to pay (WTP_
the maximum amount a buyer will pay for a good
demand curve from WTP
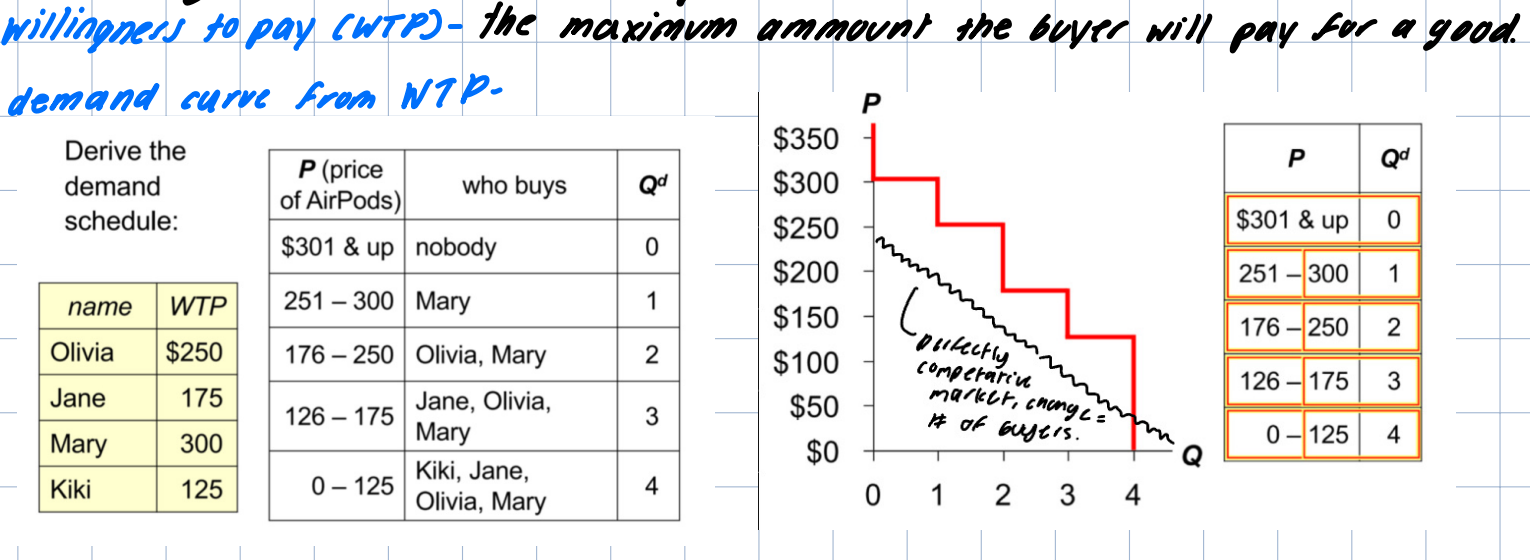
marginal buyer
at any quantity the height of the D curve is the WTP of the marginal buyer (the buyer that would leave the market if the P was any higher.
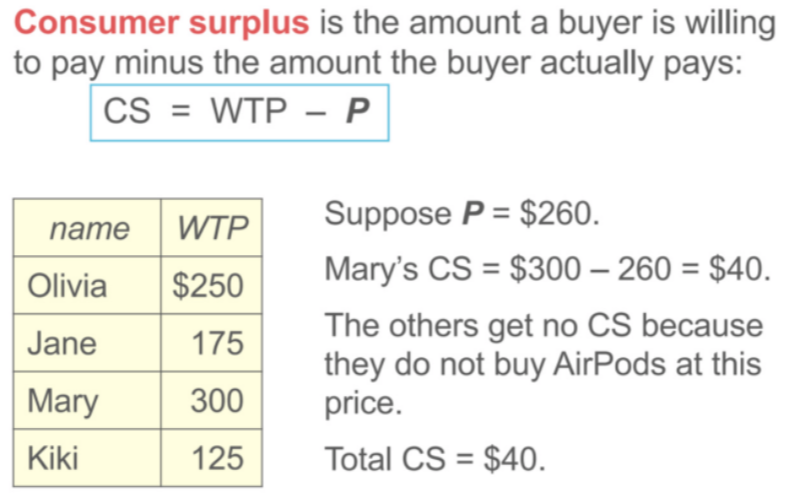
Consumer surplus (meaning and equation)
The amount a buyer is willing to pay minus the amount the buyer actually pays.
CS= WTP- P note: this only applies to people participating in the market.
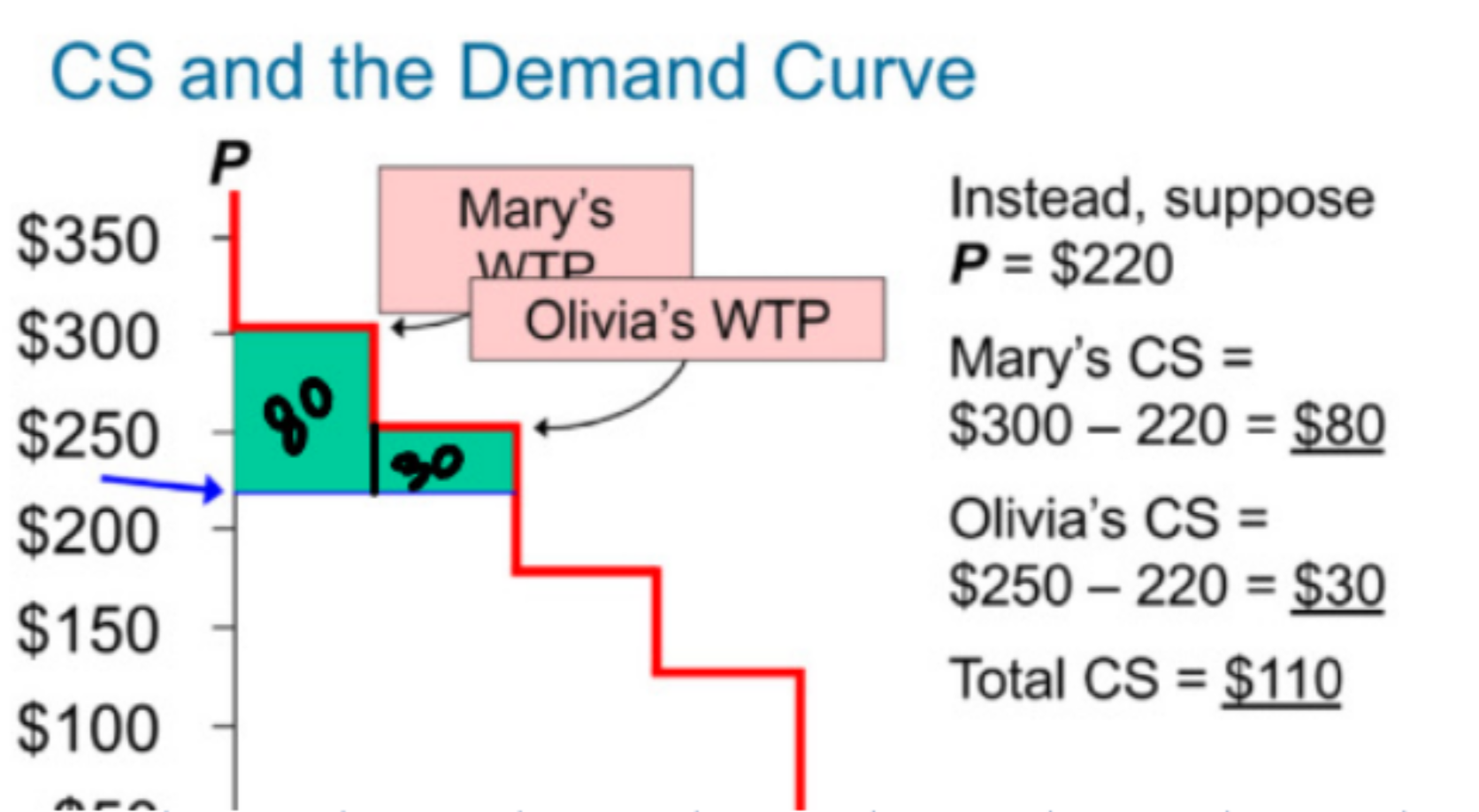
Calculating consumer surplus graphically
calculate area under the curve but above the price point, this will either be a rectangle (b x h) or a triangle (0.5 b(h))
Suppose Raymond and Victoria attend a charity benefit and participate in a silent auction. Each has in mind a maximum amount that he or she will bid for an oil painting by a locally famous artist. This maximum is called:*
1/1
a. deadweight loss.
b. willingness to pay.
c. consumer surplus.
d. producer surplus.
b
Pens are normal goods. What will happen to the equilibrium price of pens if the price of pencils rises, consumers experience an increase in income, writing in ink becomes fashionable, people expect the price of pens to rise in the near future, the population increases, fewer firms manufacture pens, and the wages of pen-makers increase?
*
1/1
a. Price will fall.
b. Price will stay exactly the same.
c. The price change will be ambiguous.
d. Price will rise.
d
What would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of lattés if the cost to produce steamed milk, which is used to make lattés, increased, and scientists discovered that lattés cause heart attacks?
*
0/1
a. Both the equilibrium price and quantity would increase.
b. The equilibrium quantity would decrease, and the effect on equilibrium price would be ambiguous.
c. Both the equilibrium price and quantity would decrease.
d. The equilibrium price would decrease, and the effect on equilibrium quantity would be ambiguous.
b
cost
is the value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good (opportunity cost). This includes the cost of all the resources used to produce a good, including the value of a sellers time.
Example: Cost of 3 sellers in the lawn cutting buisness.

marginal
At each Q the height of the supply curve is the cost of the marginal seller who would leave the market if the price was any lower.
producer surplus
PS= P - cost ( the amount a seller paid for a food minus the sellers cost)
total ps
The area above the supply curve and below the price level
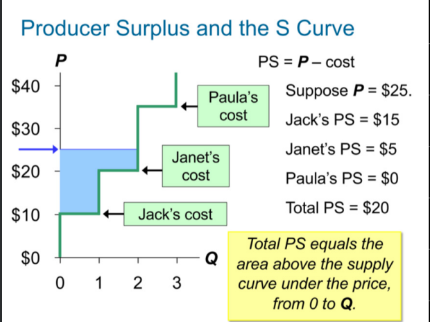
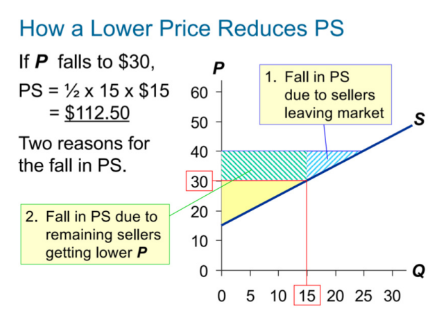
How a lower price reduces PS
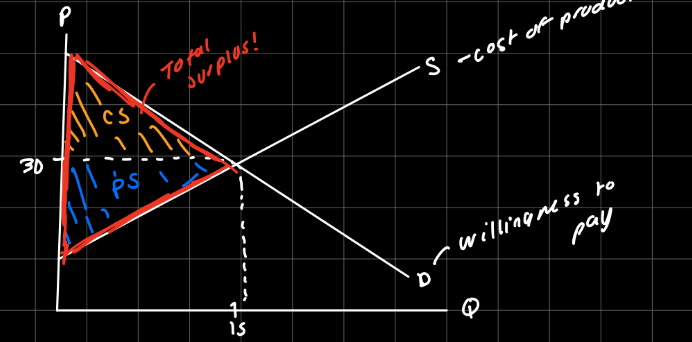
CS, PS, and total surplus (equations)
Cs= value to buyers - ammount paid by buyers
Ps= amount recieved by sellers - cost of production to sellers
Ts= value to buyers- cost of production to sellers
efficency
an allocation of resources is efficent if it maximizes total surplus by:
1) the consumers who value the product the most get the product
2) The producers with the lowest production cost produce the product
3) increasing or decreasing quantity does increaste the total surplus
where does maximum total effiencey occur?
Equilibrium point
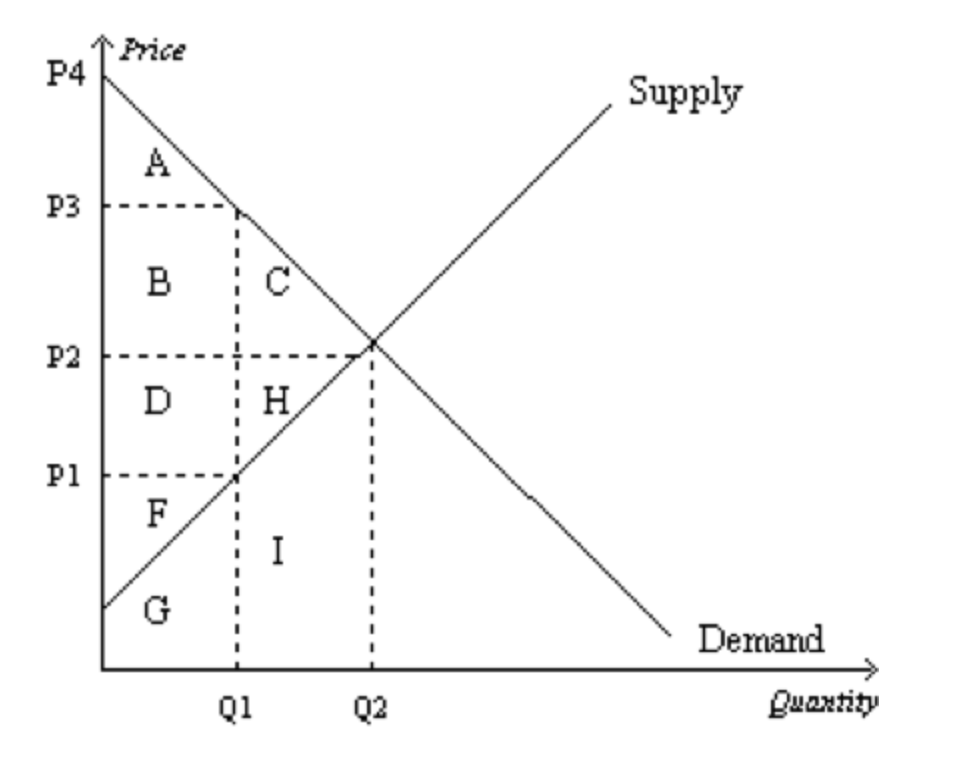
a. P1 and Q1.
b. P2 and Q2.
c. P3 and Q1.
d. P4 and 0.
b
(Refer to Figure in Question #1) At equilibrium, producer surplus is represented by the area:*
1/1
a. F
b. F+G.
c. D+H+F.
d. D+H+F+G+I.
c
(Refer to Figure in Question #1) If the price were P1, producer surplus would be represented by the area:*
1/1
a. F.
b. F+G.
c. D+H+F.
d. D+H+F+G+I.
a