MLT-MLS Hematology 2019-2020 UAMS exam 1 review
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Intramedullary Hemolysis
cell destruction inside the bone marrow
Leukocytosis
increase in the number of white blood cells
Intravascular
Within the blood vessel
Extravascular
outside the blood vascular system
RES system organs
Spleen, liver, Thymus, Bone Marrow, Lymph nodes
Where does hematopoiesis occur?
Inside the bone marrow
Where do megakaryocytes reside?
along the lining in the bone marrow
What come from magakaryocytes?
platelets
Where does erythropoietin come from?
kidneys
What is the function of the RES system?
formation and destruction of cells
What is the fast to cell ratio in an adult?
50:50
What is the location of the bone marrow in children?
in all long bones
Which cells are in bone marrow?
Plasma cells, megakaryocytes, immature red cells, macrophages, immature WBCs
Which cells are in peripheral blood?
Banded neutrophils, segmented neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lyphocytes and platelets
Which bone marrow cell is hemopoeitically active?
red marrow
Which organ is involved in red cell circulation?
spleen
How long do RBCs live?
120 days
What is the sequence of WBC maturation?
myeloblast-> promyelocyte->myelocyte->metamyelocyte, banded neutrophil-> segmented neutrophils
What cell is the most present at the dawn of neutrophilia?
Myelocyte
What cell has the ability to become any cell?
pluripotent stem cell
What can you use to tell the difference between T cells and B cells?
Flow cytometry
What cells move to the tissues and what do they become?
Basophil- mast cells
B cells- plasma cells
Monocytes- Macrophages
What is a left shift?
Increased numbers of immature neutrophils in the blood
What could be a possible reason to see many blasts in a peripheral blood smear?
a possible leukemia
What is the % of banded Neutrophils at are in peripheral blood?
5% in the peripheral blood
What reasons could there be for a left shift?
leukemia
bacterial infection
What WBC would increase during a parasitic infection and allergic reaction/infection?
Eosinophil
What is diapedesis?
the passage of blood cells through the intact walls of the capillaries, typically accompanying inflammation.
What is margination?
neutrophils cling to the walls of capillaries in the injured area
How can you tell the difference between a monocyte and a banded neutrophil?
Banded neutrophil has pinker cytoplasm
What cells do NOT have granules?
myeloblasts and the RBC lineage. (sometimes monocytes and lymphocytes)
Basophils morphology
-most uncommon of granulocytes: have blue-purplish granules, and usually hidden nucleus
-release histamine
Eosinophil morphology
elongated band-shaped, bi-lobed or tri-lobed nucleus
cytoplasm has red/red-orange staining granules
feline: numerous small rod-shaped granules
canine: varying size granules in same cell
-seen during parasitic infection
banded neutrophil
contains pink cytoplasm with specific granules and a nucleus with coarse chromatin that is deeply indented more than 50% of the width of the nucleus
segmented neutrophil morphology
Monocyte morphology
largest leukocyte
nucleus is elongated & lobed or kidney bean shaped
abundant cytoplasm, may have vacuoles, phagocytosed particles
stains gray, foamy looking
Lymphocyte morphology
second most abundant leukocyte
round or slightly indented nucleus
thin rim of blue-stained cytoplasm
larger than nucleated RBC
What kind of cells have condensed nucleus clumping?
Mature cells
What are granulocytes?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What cell is most known to have vacuoles?
Monocytes
How can you tell the difference between a Myeloblast and a lympyocyte?
Myeloblast is much bigger
lymphocyte nucleus is much darker
What is the formula for a total cell count?
(cells counted X dilution factor X depth factor)/ # of squares counted
Why do you use acetic acid as a dilution?
to lyse the RBCs
What are the negatives in the coulter principle?
anything the size of a cell gets counted
What % of RBC's are removed and replaced daily?
1%
What is the corrected WBC count formula? (NRBC)
(WBC x100)/ (#NRBC +100)
What is the dominant WBC seen in peripheral blood?
Neutophils 50%-70%
What cells is the least seen in peripheral blood?
Basophils
What is erythroid hyperplasia?
Increased red cell formation
What is the first Red blood cell to not see nucleoli?
prorubricyte
What is the first White blood cell to not see nucleoli?
Myelocyte
Do RBC's have granules?
Nope
What is the approximate time a slide can be made from a purple top?
4-6 hours
What is the color of a mature RBC cytoplasm after staining?
Salmon Pink
What is the color of an immature RBC after staining?
basophilic blue
What cells can self renew?
Pluiripointent
multipoientent
What organ destroys old RBC's?
spleen
Can NRBCs be found on a newborn blood smear?
yes
Why are men's WBC count higher than women's WBC count?
Testosterone
Do RBCs become larger or smaller as they mature?
Smaller
Where are mature WBC's found?
bone marrow
peripheral blood
What cells make antibodies?
plasma/ B cells
What cell can break down old RBC's?
Macrophages
Which organ conjugates bilirubin?
Liver
What is the term that describes basophilic RBCs on wrights stain?
Polychromasia
If RCBs on a slide are too blue, what is needed to be done?
Decrease the staining time
How are WBC distinguished from platelets?
size
Which precursor cell are primary granules first observed?
Promylocyte
Which white blood cell precursor is the last cell to undergo mitosis?
Myelocyte
Which cell is the fist where secondary granules appear and the fist cell where we an visualize if the cell will mature to become a eiosinophil, basophil or neutophil?
Myelocyte
picture of monocyte
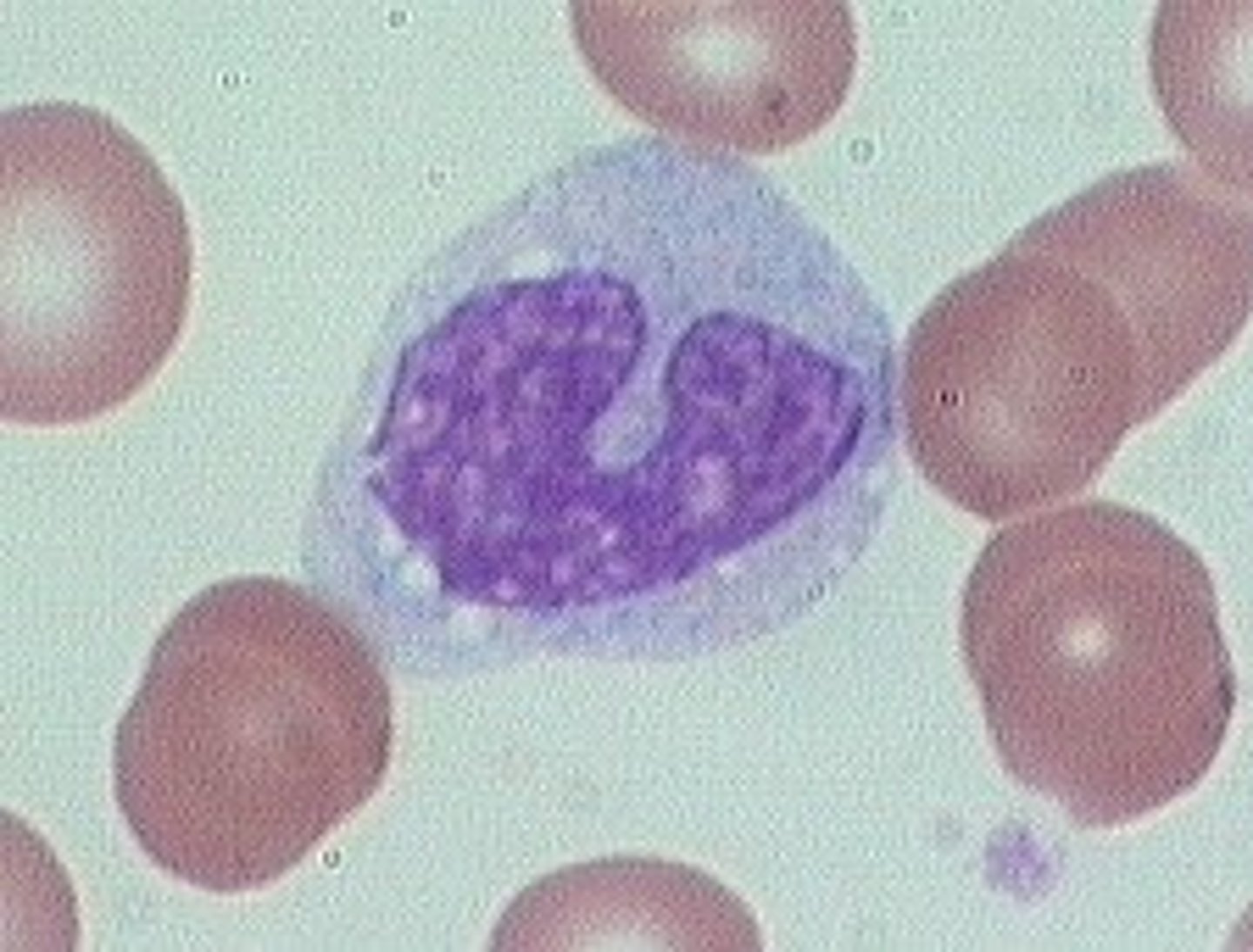
picture of a segmented neutrophil
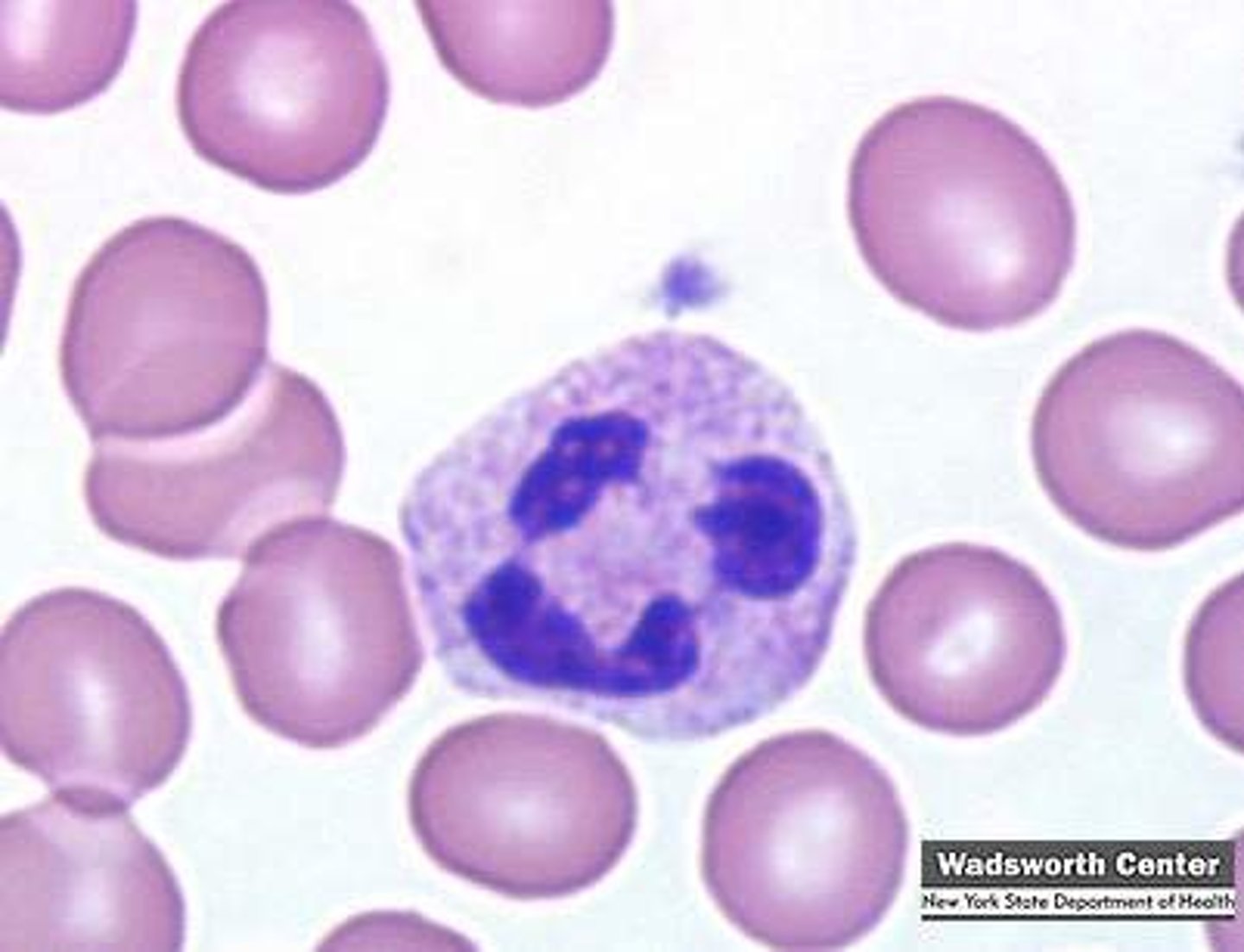
picture of eosinophil
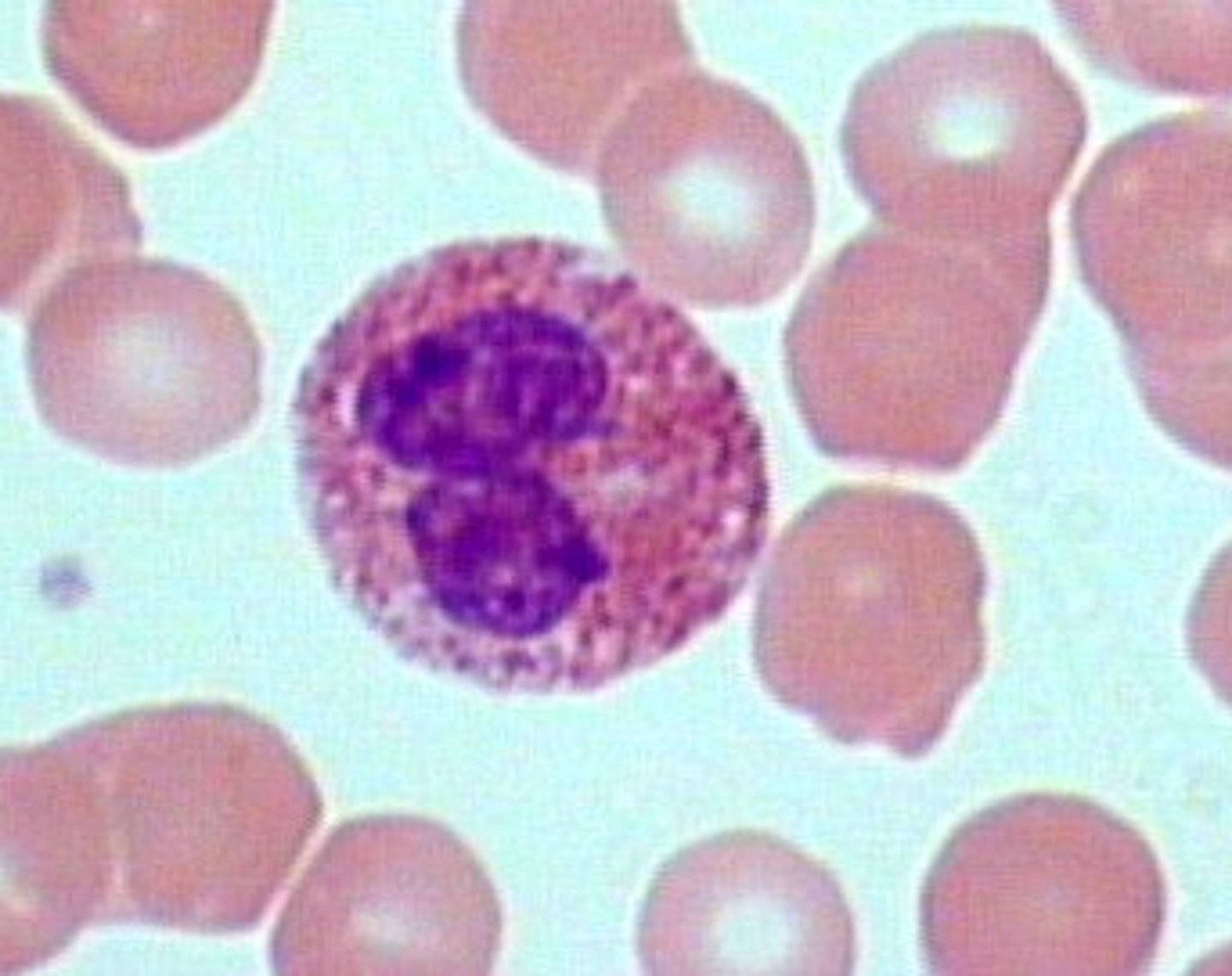
picture of banded neutrophil
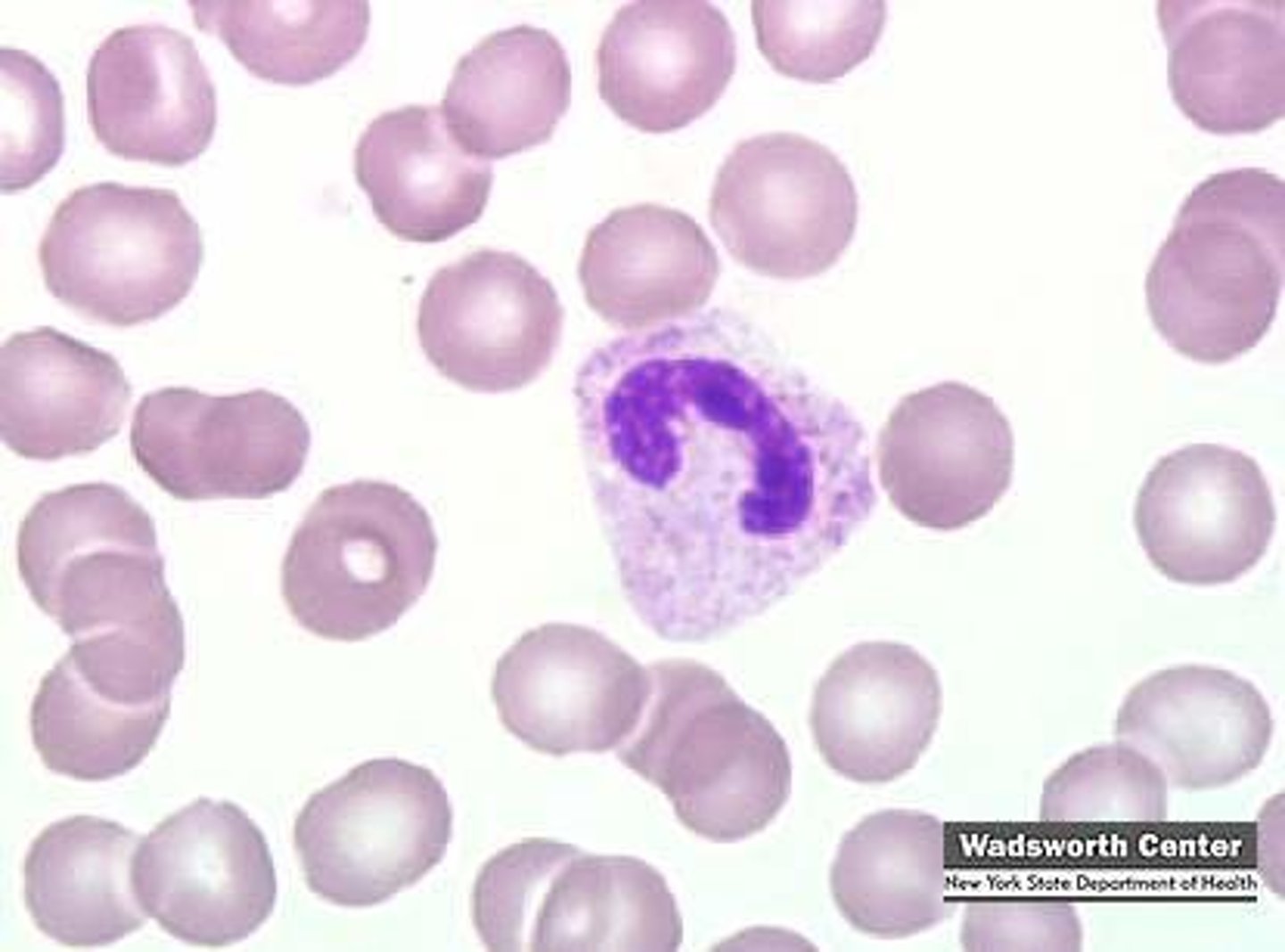
picture of lymphocyte
What is the total volume of the hemacytometer?
0.9 mm (cubed)
Within the hematopoietic cords of bone marrow, where are the megakaryocytes located?
Directly adjacent to the endothelial cell lining
Hematopoiesis
formation and development of blood cells occurring primarily in the bone marrow and peripheral lymphatic tissues
Margination
accumulation and adhesion of leukocytes to the epithelial cells of blood vessel walls at the site of injury in the early stages of inflammation.
Maturation sequence of RBC
1. Pronormoblast
2. Basophilic normoblast
3. Polychromatophilic normoblast
4. Orthochromic normoblast
5. polychoromatophilic Red Cell
6. Erythrocyte
Rubriblastic nomenclature of pronormoblast
Rubriblast
Rubriblastic nomenclature of Basophilic Normoblast
Prorubricyte
Rubriblastic nomenclature of Polychromatic Normoblast
Rubricyte
Rubriblastic nomenclature of Orhtochromic Normoblast
Metarubricyte
Rubriblastic nomenclature of Polychromatic Erythrocyte
Polychromatic Erythrocyte
Rubriblastic nomenclature of Eythrocyte
Erythrocyte
picture of Rubriblast
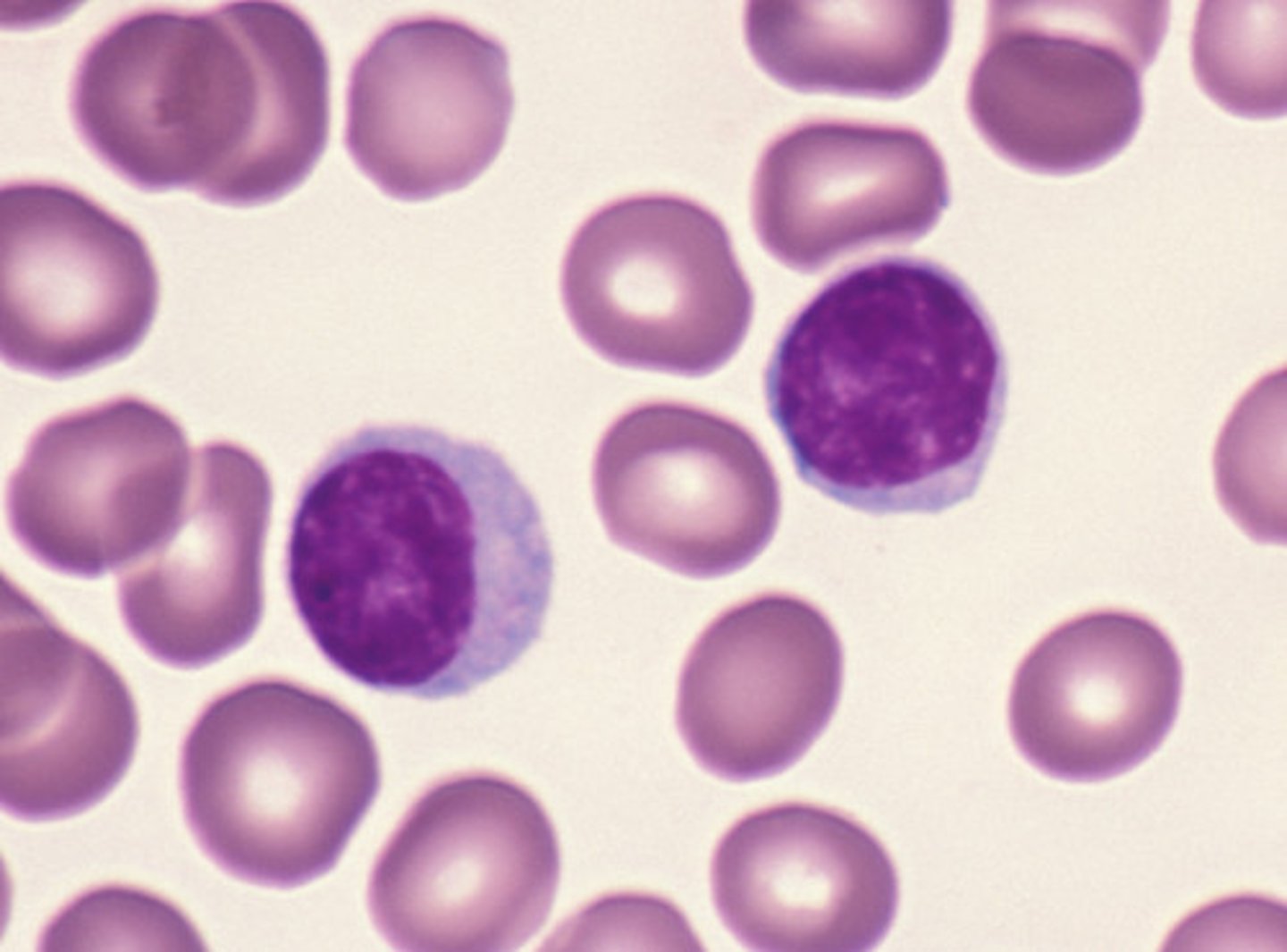
picture of Myeloblast
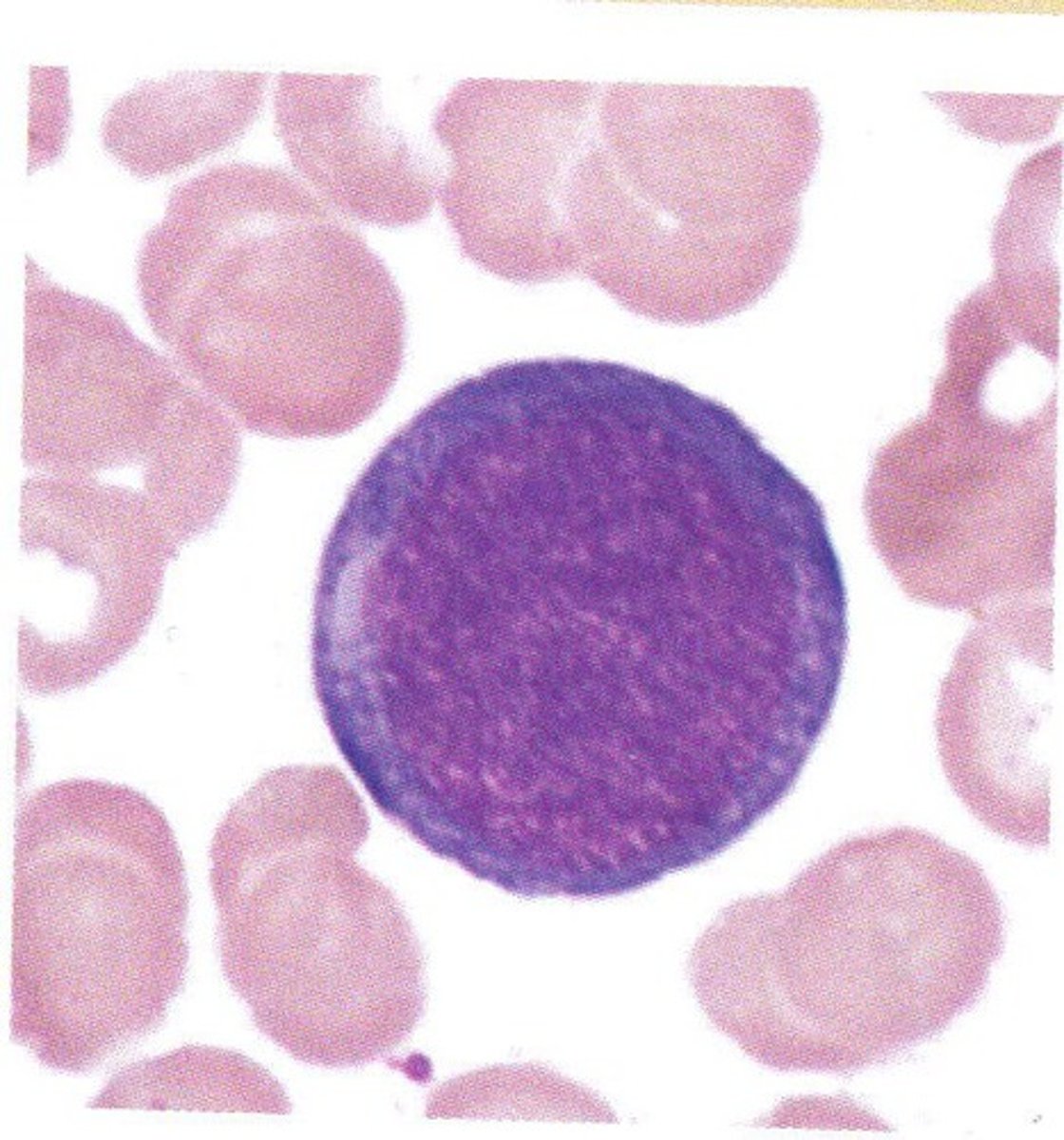
picture of Prorubricyte
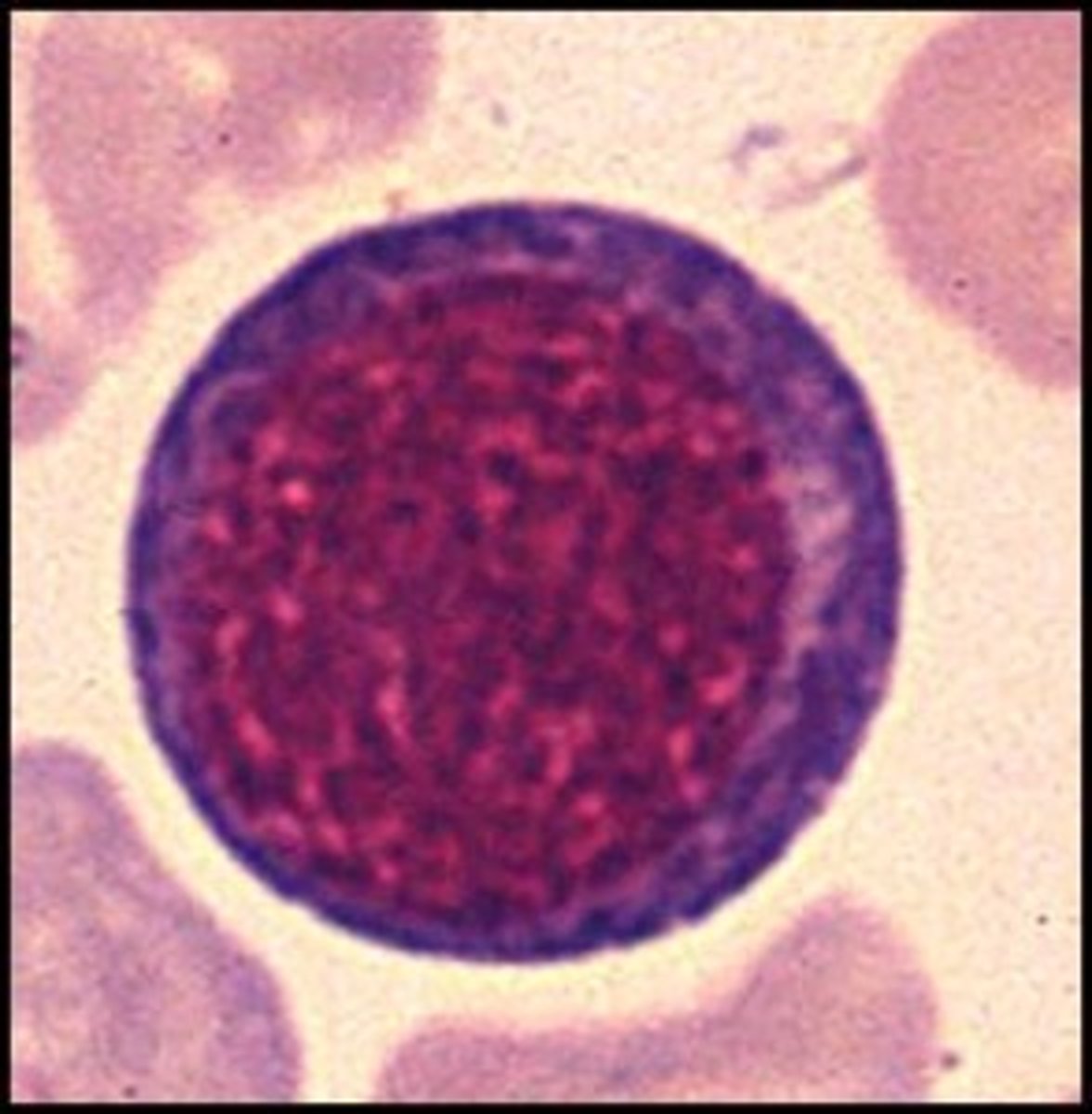
picture of rubricyte
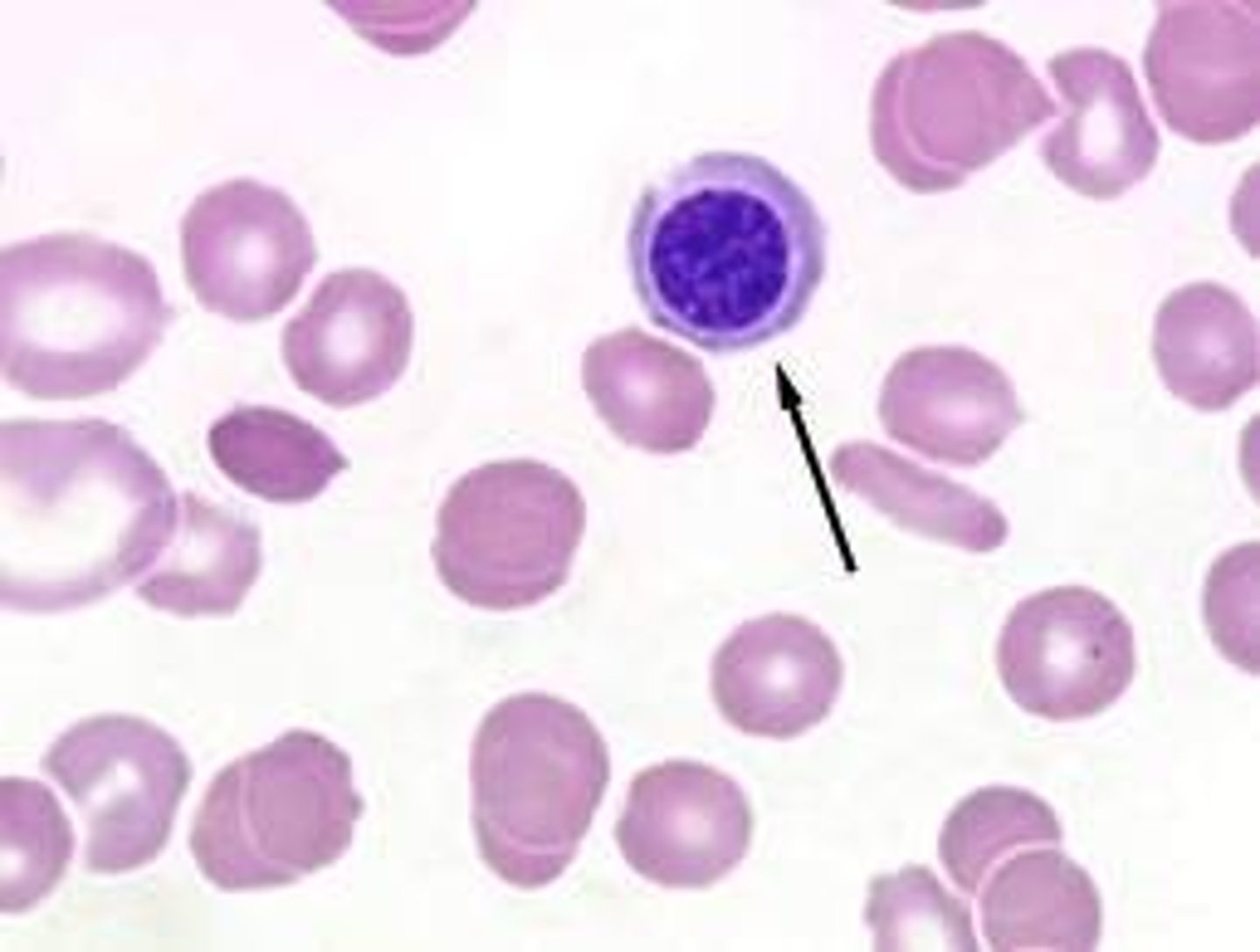
picture of Metarubricyte
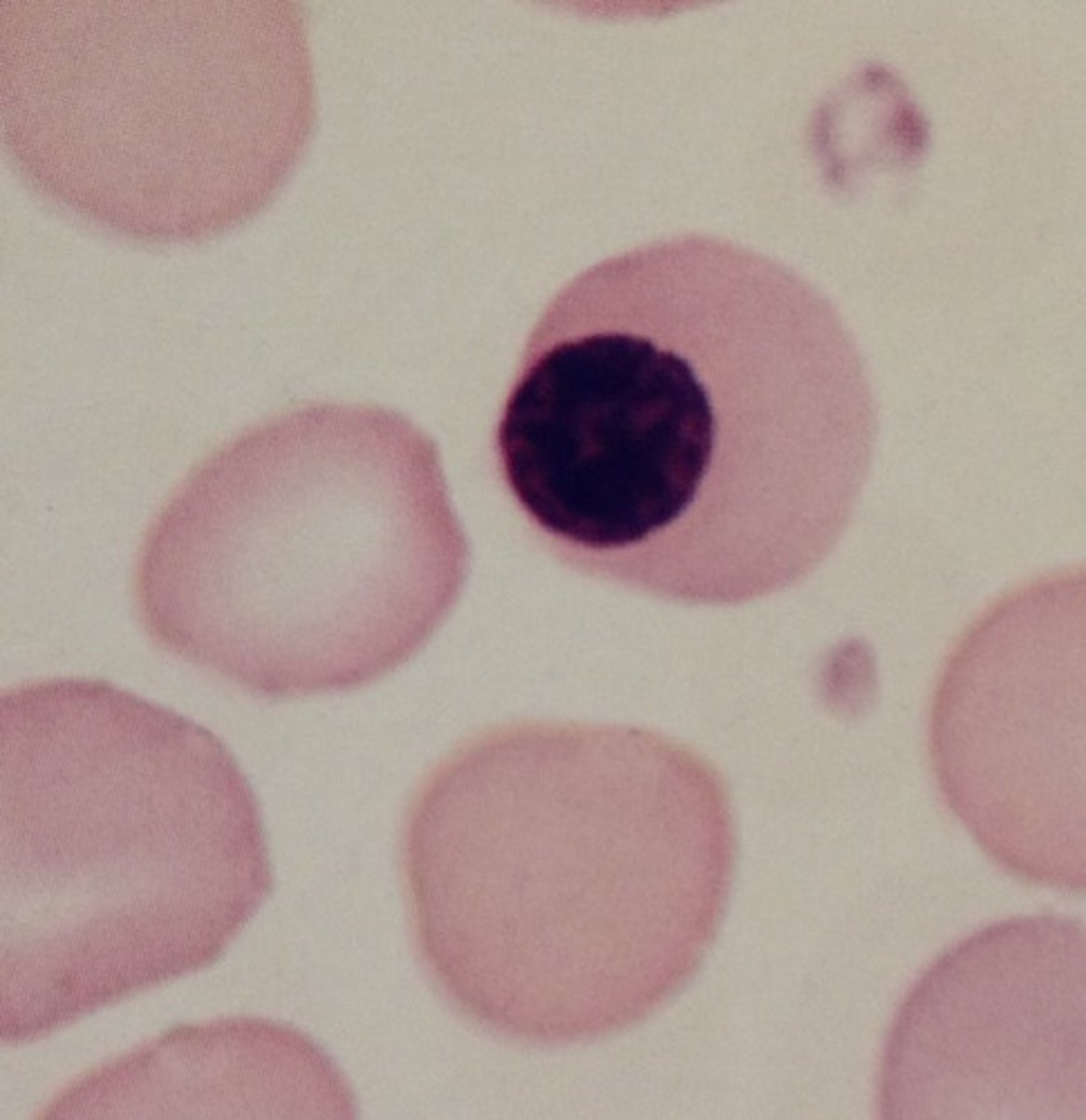
picture of Reticulocyte
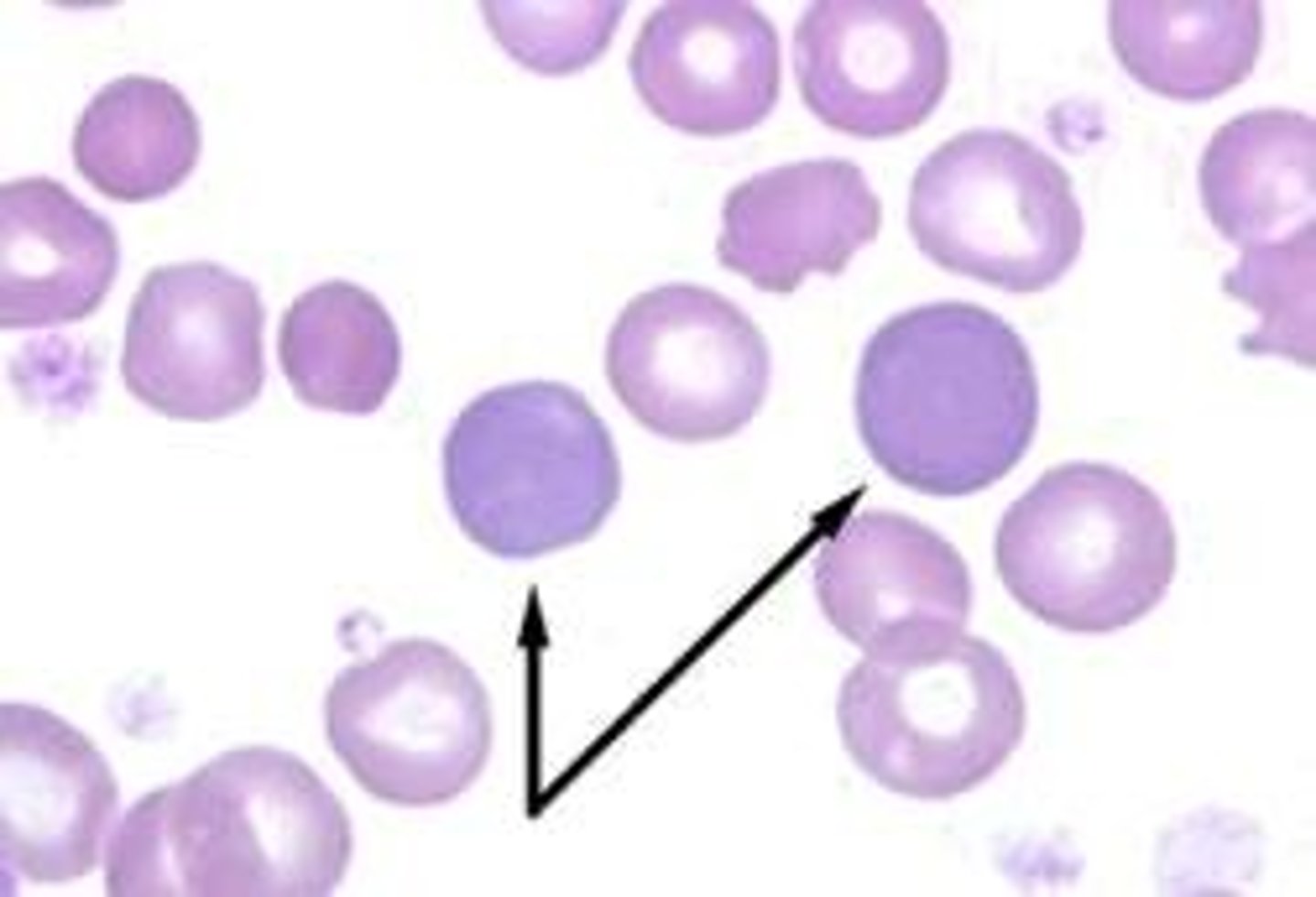
picture of Promyelocyte
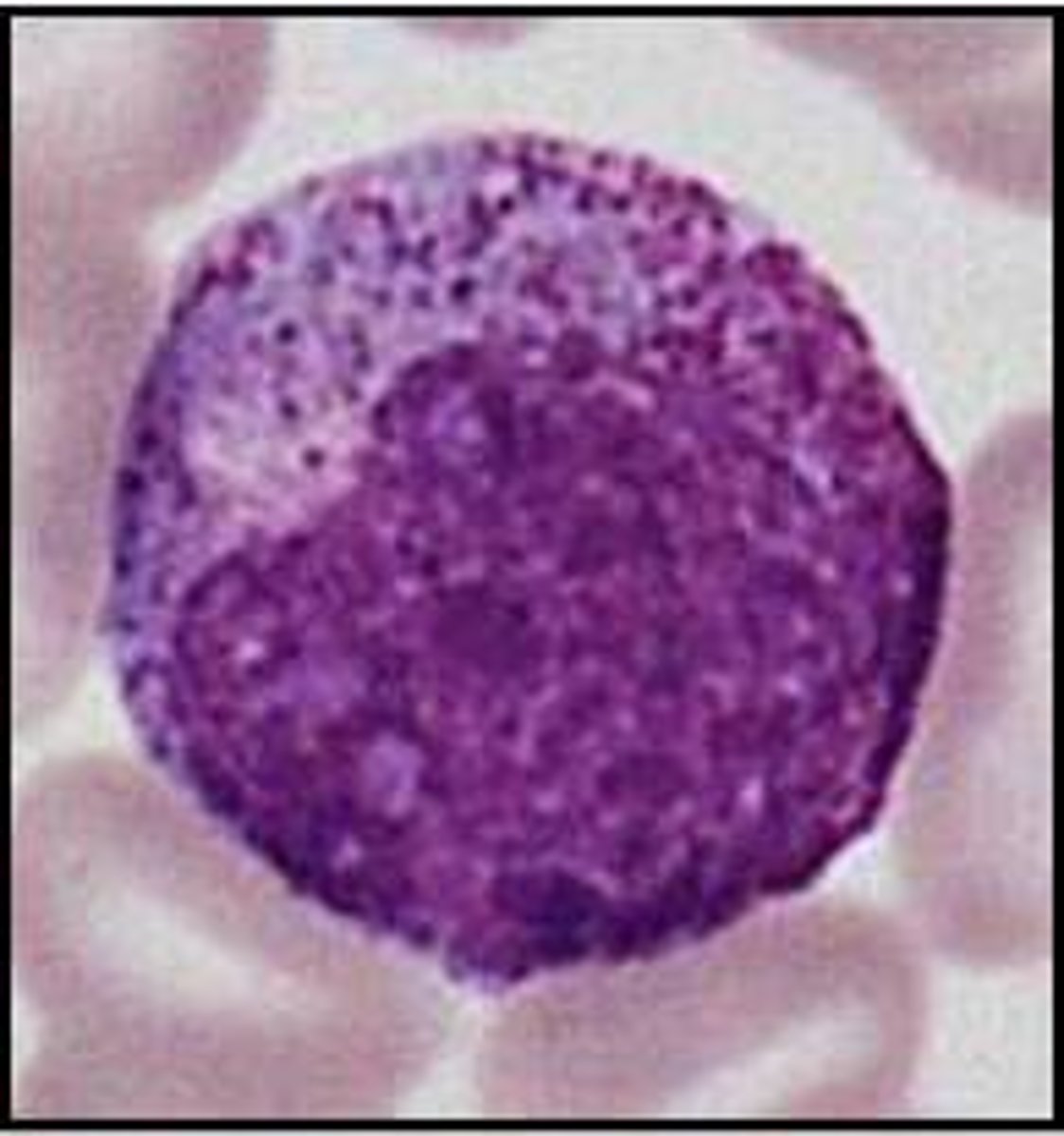
picture of Myelocyte
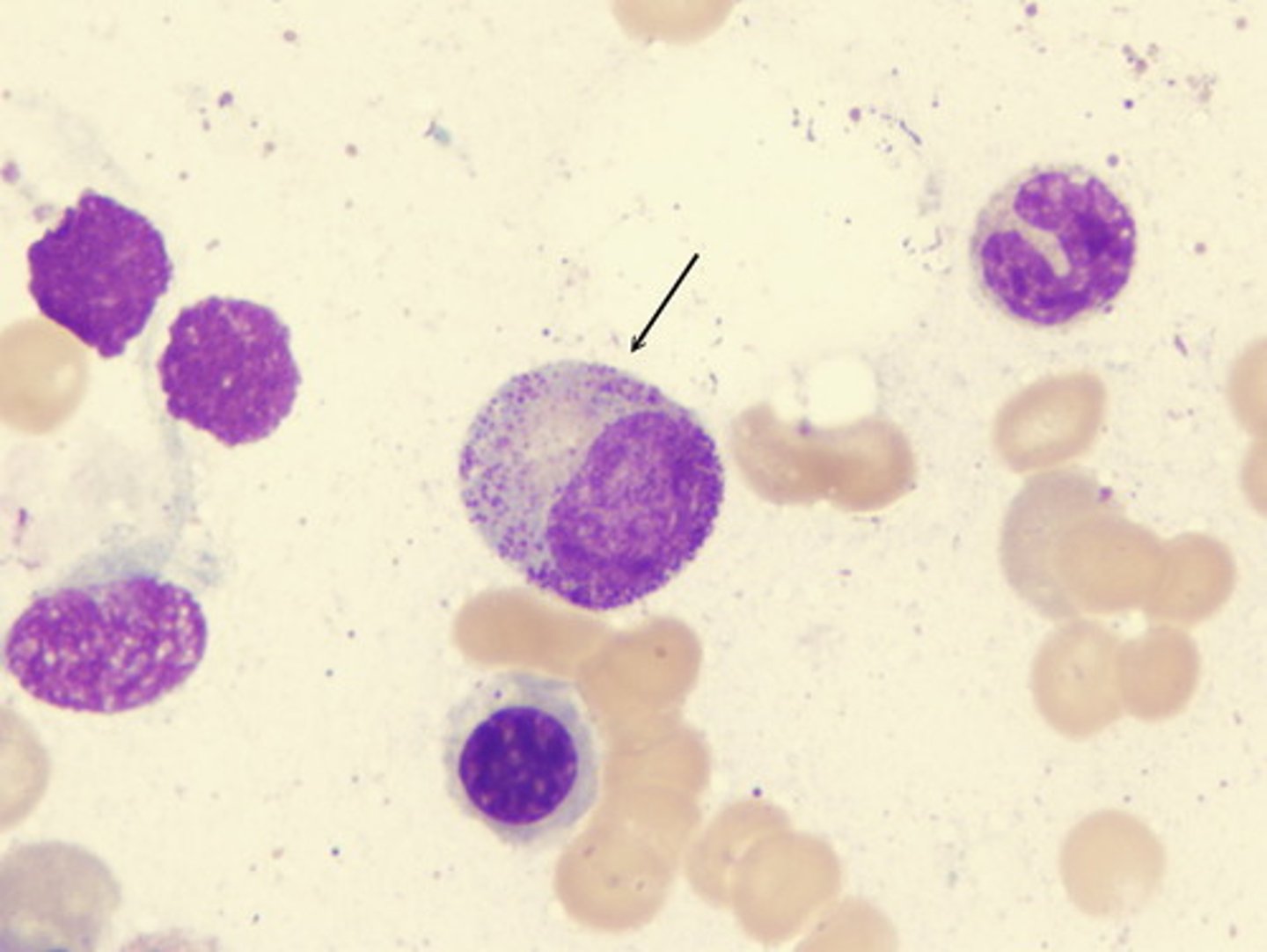
picture of Banded neutrophil
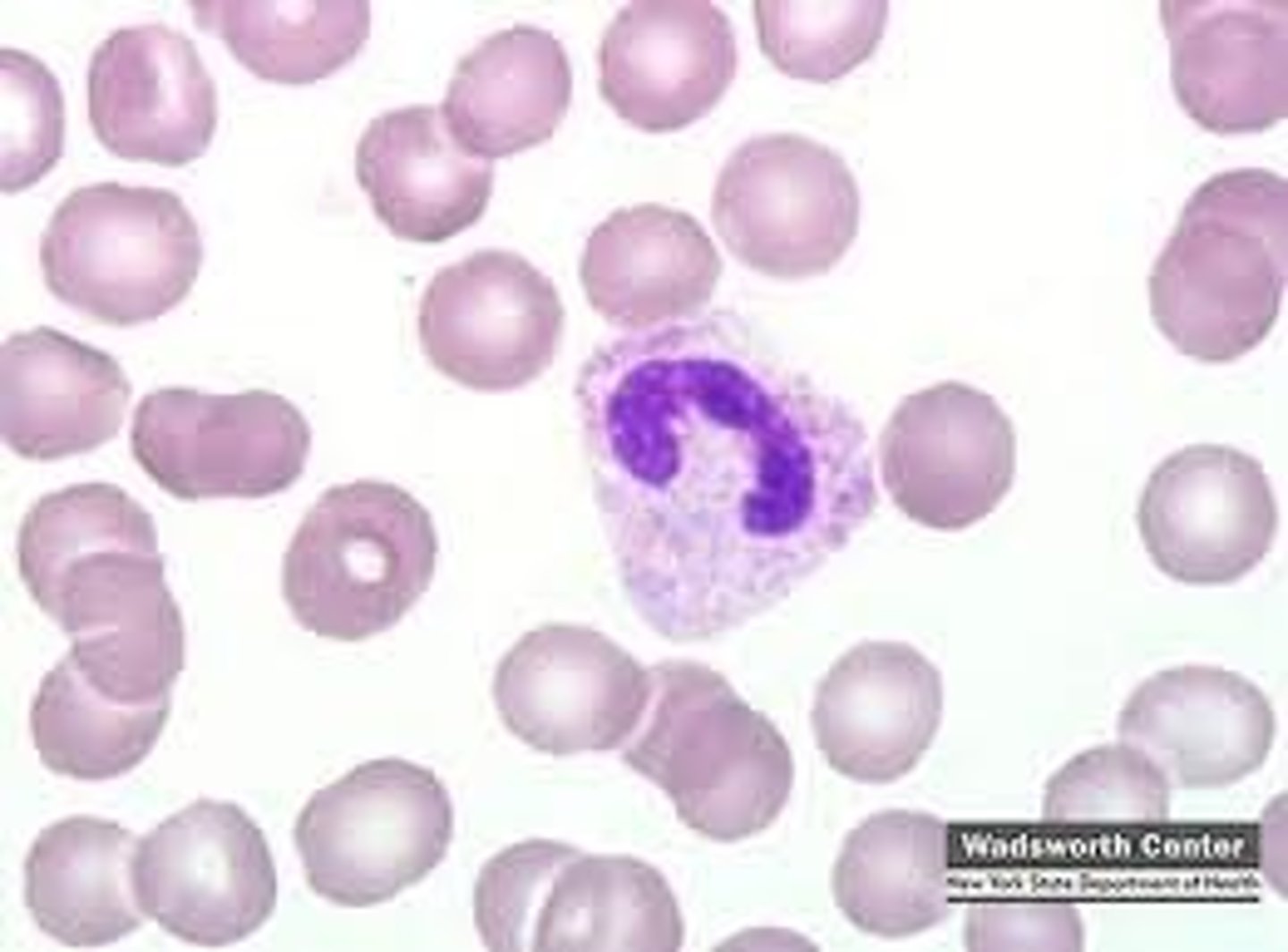
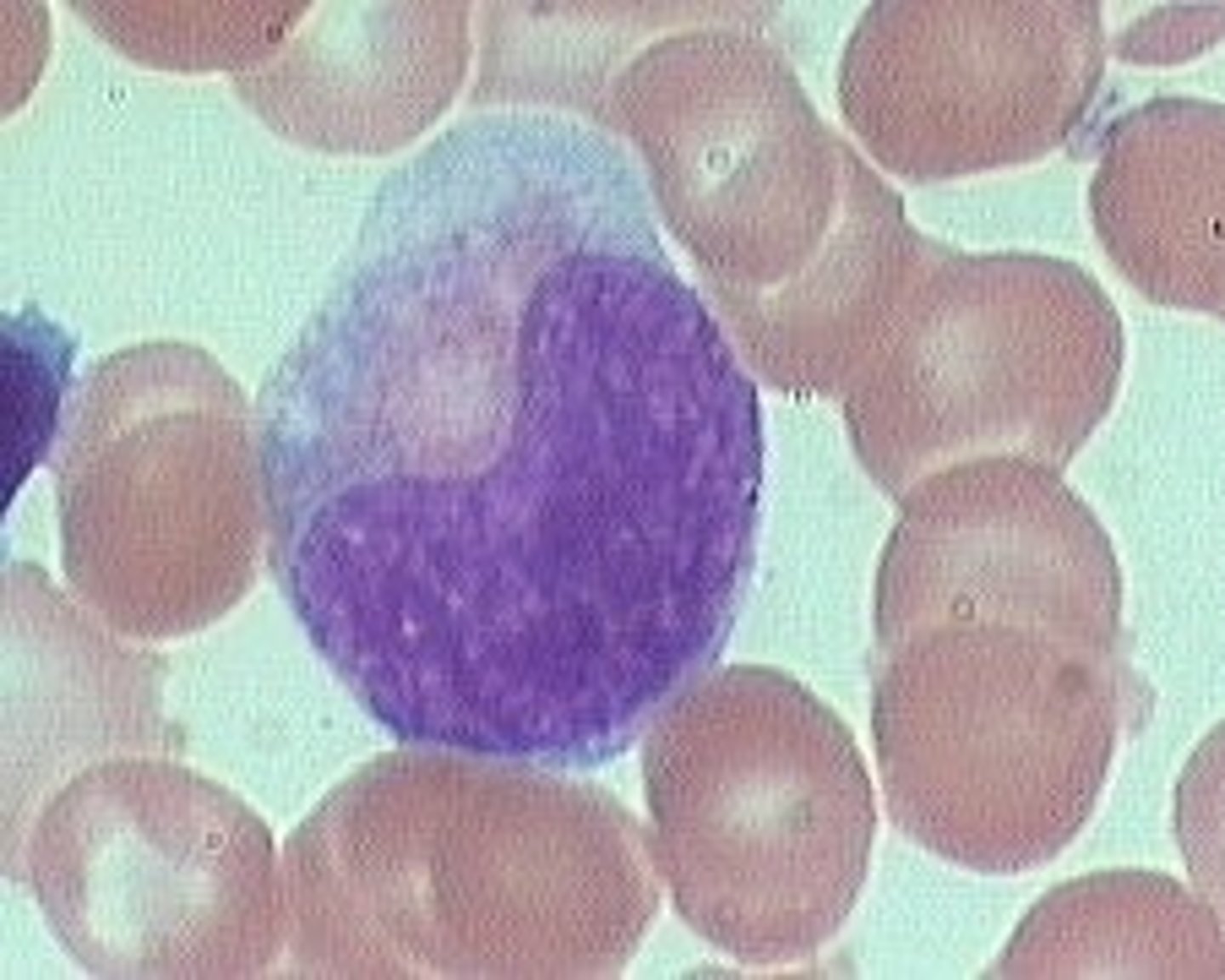
picture of metamyelocyte
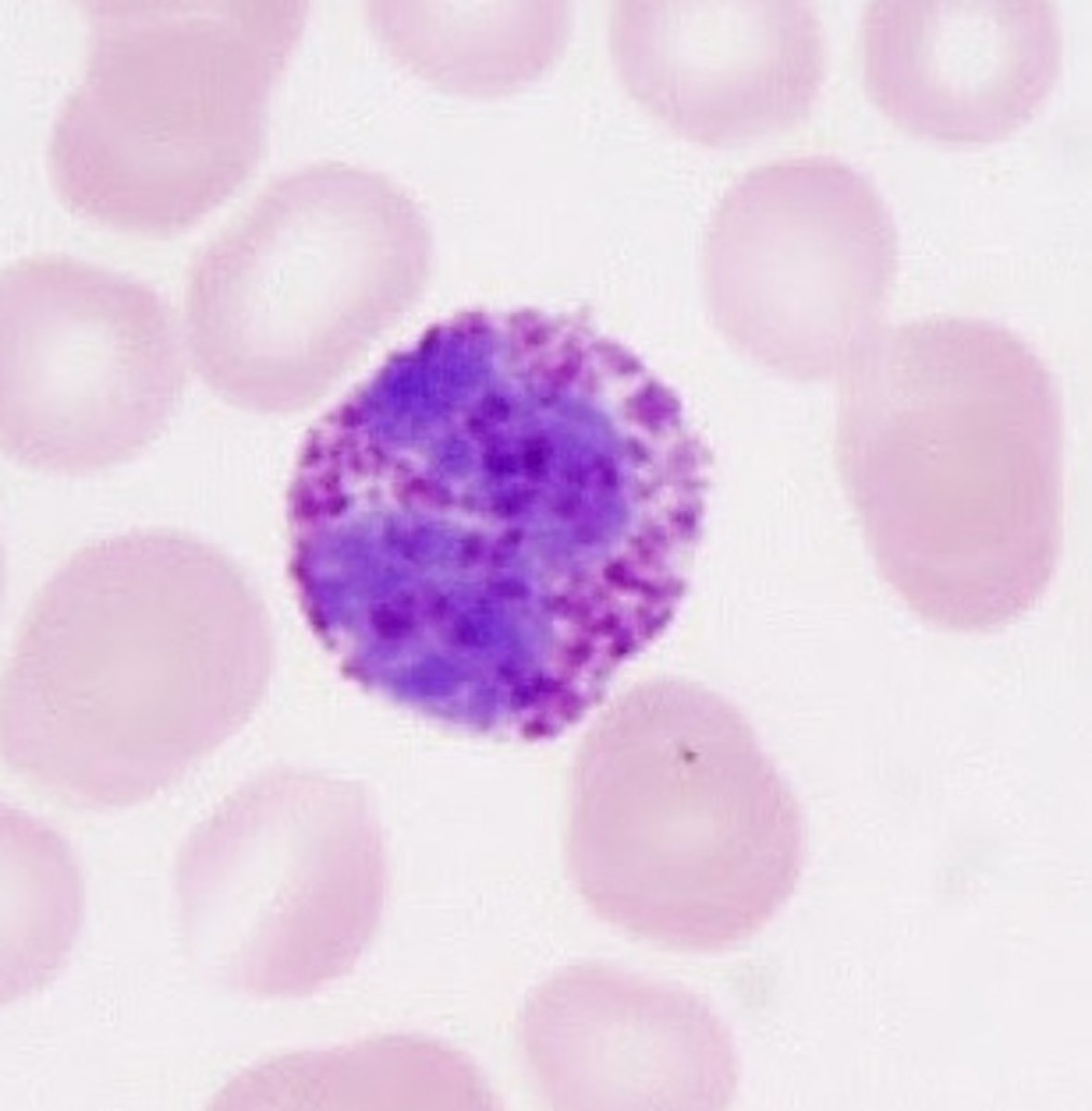
picture of basophil
Polychromasia
term used to describe a RBC as diffusely basophilic cell seen on the Wright stained peripheral smear
Reticulocyte
Term used to describe an anucleated RBC that shows mesh like pattern of dark blue treads and particles, vestiges of endoplasmic reticulum, when stained with New Methylene blue superavital stain
While performing a manual differential on an adult peripheral smear, 25 nucleated red blood cells are noted per 100 white blood cells. What corrective action must be taken?
Preform a corrected WBC count