Articulation & Acoustics of Consonants
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Consonant
Speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract
Place of Articulation
Where obstruction occurs
Ex: Labial, Dental, Alveolar, Palatal, Velar, Glottal
Manner of Articulation
How airflow is modified/obstructed
Ex: Stops, Fricatives, Affricates, Nasals, Liquids, etc.
Sonorants
Periodic
All voiced
Nasals
Liquids
Glides
Obstruents
Aperiodic
Can be voiced or voiceless
Stops
Fricatives
Affricates
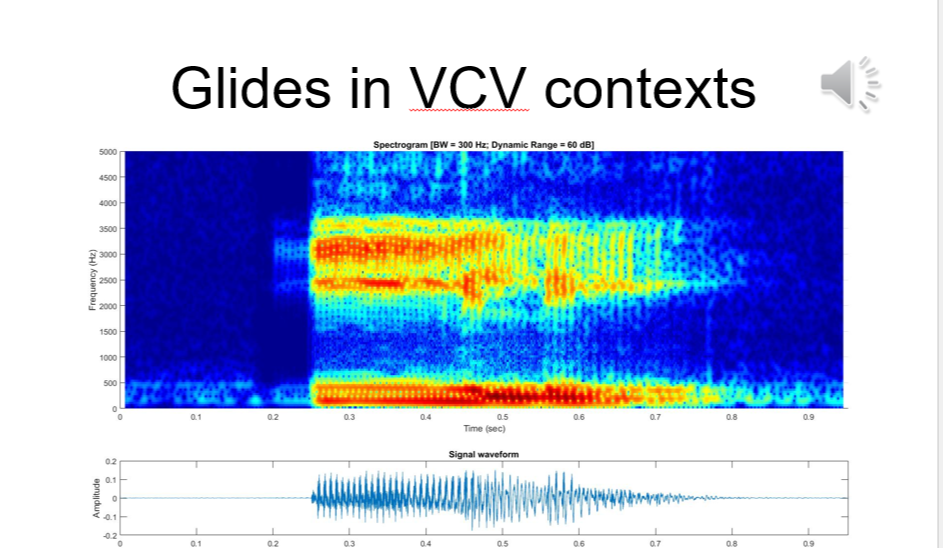
Glides [j]
High F2, Low F1
Fast formant transitions
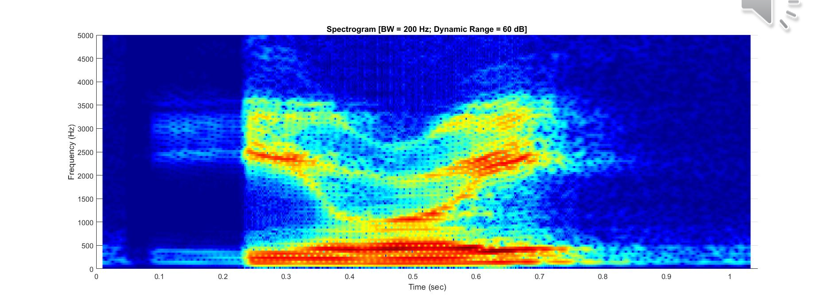
Glides [w]
Low F1, Low F2
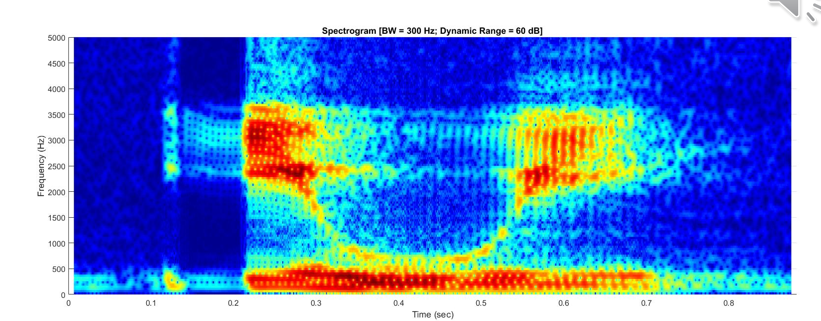
Liquid [l]
Lateral air flow
Visible formant structure
F3 = level
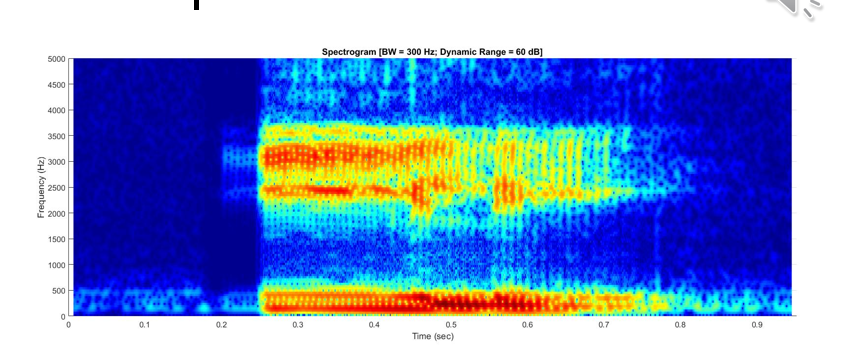
Liquid [r]
Low F3
Retroflexed and rounded
Nasals
Require an open velopharyngeal port
[m], [n], [ŋ]
Low frequency resonance (~200-300 Hz)
Damping and low amplitude due to absorption and nasal structure
![<ul><li><p>Require an open velopharyngeal port</p></li><li><p>[m], [n], [ŋ]</p></li><li><p>Low frequency resonance (~200-300 Hz)</p></li><li><p>Damping and low amplitude due to absorption and nasal structure</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7d4d014c-f224-4789-9512-4685e0e40eea.png)
Places of Articulation for Nasal
[m] = The lips
[n] = Alveolar Ridge
[ŋ] = Soft Palate
Place of Articulation for Fricative
[f, v] = Labiodental
[θ, ð] = Linguadental
[s, z] = Alveolar
[ʃ, ʒ] = Postalveolar
Fricative Non-sibilants
[f, θ, v, ð]
Low intensity, broadband noise
No strong resonance
![<p>[f, θ, v, <span>ð</span>]</p><p>Low intensity, broadband noise</p><p>No strong resonance</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6ec46df7-a11a-43f3-9dd9-124eb85fb6f2.png)
Fricative sibilant
[s, ʃ, z, ʒ]
High intensity and frequency specific
![<p>[s, ʃ, z, <span>ʒ</span>]</p><p>High intensity and frequency specific</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3566f483-9680-4052-b97e-37b245a4350c.png)
Shadle’s Model
Turbulence shaped mostly by front cavity; obstacle affects resonance
Articulation for Stops
Complete closure in the oral cavity
VP port closed = build up and release of intraoral pressure
Acoustics of Stops
Silent interval during closure
Burst of noise at release
Bilabial Stop
[p,b]
Low burst at 600 Hz
![<p>[p,b]</p><p>Low burst at 600 Hz</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f831edc3-aefc-409d-8abd-78d628ff50cf.png)
Alveolar Stop
[t,d]
High burst at 3 kHz
![<p>[t,d]</p><p>High burst at 3 kHz</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b822983b-4795-4626-b602-b87fc5cfb483.png)
Velar Stop
[k,g]
Burst dependent on vowel context
Affricates
[d͡ʒ,t͡ʃ]
Stop closure released into fricative
Features include:
Closure
Burst
Frication noise
![<p>[d͡ʒ,t͡ʃ]</p><p>Stop closure released into fricative</p><p>Features include:</p><ul><li><p>Closure</p></li><li><p>Burst</p></li><li><p>Frication noise</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dc27d61b-5ede-48b1-924e-c89aa0c0c818.png)