Chapter 10: Liabilities
0.0(0)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/50
Last updated 7:33 AM on 12/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
liability
When a company buys goods/services, takes short term loans, and issues long term debt, this creates a(n) ________.
2
New cards
long term debt
When a company issues ________, this can create a Notes Payable or a Bonds Payable.
3
New cards
Current liabilities
________ are short term liabilities that expected to be paid off within a year OR within the companys operating cycle.
4
New cards
Non-current liabilities
________ are long term and are paid in a time frame that is longer than the operating cycle or year (paid after a year).
5
New cards
classified balance sheet
Liabilities are found on the ________.
6
New cards
cash equivalent
The ________ is how much we own or borrow, which is the initial amount of the liability.
7
New cards
creditors
When a liability increases, more is owed to ________.
8
New cards
Accounts
________ Payable: Increases when goods/services are received on credit (you owe money). Decreases when payment is made. Has a normal credit balance.
9
New cards
Accrued
________ liabilities are incurred, but not paid. They're usually used to purchase supplies or inventory. Examples are advertising, interest, and payroll.
10
New cards
Payroll deductions
________ can be required by law or voluntarily requested by employees. Both create a current liability.
11
New cards
Income tax
FICA tax
Charitable donations
FICA tax
Charitable donations
Examples of payroll deductions:
12
New cards
They pay the employees.
They pay taxes for the luxury of having their employees.
They pay taxes for the luxury of having their employees.
Two things happen when employers pay their employees:
13
New cards
One to pay employee and one to pay state or fed.
The two journal entries for when the employer gives a check to their employee.
14
New cards

\
Equation for taxable income:
15
New cards
Notes Payable
________ is a current liability with a promissory note.
16
New cards
Establish the note, incur accruing interest, record the interest paid, and record the principal paid.
The process of a Notes Payable:
17
New cards
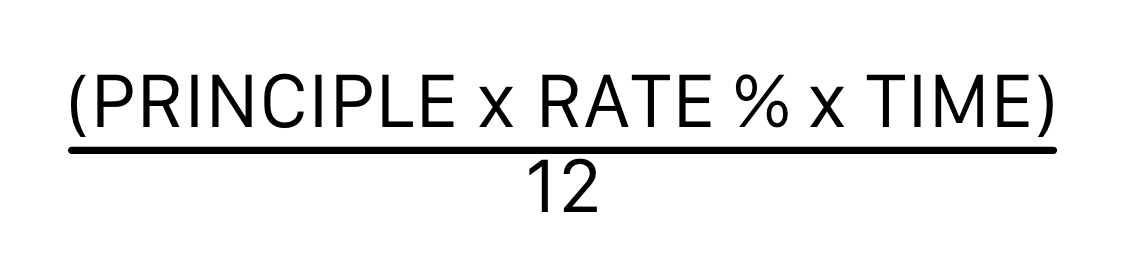
\
Equation for calculating interest:
18
New cards
Sales Tax Payable
________ are payments from customers at the time of sale of the goods/services. The liability generated is due to the state government.
19
New cards
Deferred revenue
________ means we have received cash, but we still owe the good or service to the customer. Once the good or service is delivered, the liability decreases.
20
New cards
within 12 months
The current portion of long term debt is due ________.
21
New cards
in over 12 months
Non-current portion of long term debt is due ________.
22
New cards
within a year
A long term liability must be paid ________.
23
New cards
Long term Notes Payable, Deferred income taxes, and Bonds Payable.
Examples of long term liabilities:
24
New cards
Deferred income taxes
________ are found on the balance sheet and is the amount a company will at some point pay.
25
New cards
Bonds
________ are considered a long term liability for companies and an investment for bondholders.
26
New cards
The New York Bond Exchange
Bonds are tradable on established exchanges like _________.
27
New cards
Maturity date
On the top of the bond, what is the name for the due date?
28
New cards
Face value
On the top of the bond, what is the name for the amount payable on the maturity date?
29
New cards
Stated interest rate
On the top of the bond, what is the name of the amount of interest you can expect to receive?
30
New cards
Bond pricing
________ is based on what the investors are willing to pay on the issue date.
31
New cards
$1,000
Face value is usually _____ for bonds.
32
New cards
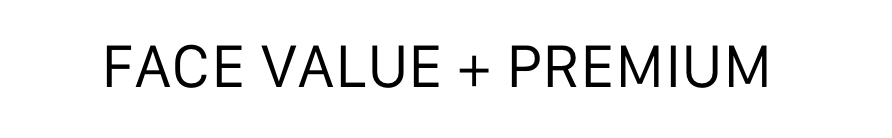
\
Equation for carrying value (premium):
33
New cards

\
Equation for carrying value (discount)
34
New cards
premium
A bond that is issued over the face value of a bond is a(n) ________.
35
New cards
discount
A bond that is issued under the face value of a bond is a(n) ________.
36
New cards
bonds premium
With a ________, the issuer receives more money on the issue date than the maturity date.
37
New cards

\
Equation to calculate premium:
38
New cards

\
Equation to calculate interest expense (premium):
39
New cards
bonds discount
With a ________, the company receives less cash on the issue date than whats received on the maturity date.
40
New cards

\
Equation to calculate discount:
41
New cards

\
Equation to calculate interest expense (discount)
42
New cards
retiring
Payment of the bond on the maturity date is ________ the bond.
43
New cards
retired early
Bonds can be ________, which decreases future interest expense and increases net income.
44
New cards
Pays cash for the bond.
Decreases the Bonds Payable.
Reports a gain or loss.
Decreases the Bonds Payable.
Reports a gain or loss.
When bonds are retired early, the company:
45
New cards
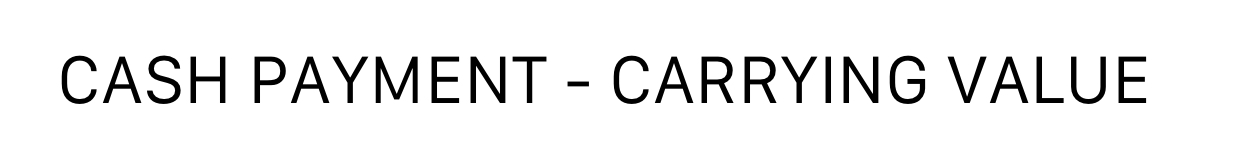
\
Equation to calculate loss or gain on the retirement:
46
New cards
Positive number means a gain.
Negative number means a loss.
Negative number means a loss.
How to determine gain or loss on retirement:
47
New cards
Contingent liabilities
________ are liabilities that came from past transactions and have an unknown future outcome.
48
New cards
debt-to-asset
The ________ shows how many assets are financed by liabilities.
49
New cards

\
Equation for the Debt-to-Assets Ratio:
50
New cards
times interest earned ratio
The ________ will tell us if resources will cover interest cost.
51
New cards

\
Equation for the Times Interest Earned ratio: