B1.1: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Carbon Bonding
Carbon can form up to 4 (single or double) covalent bonds, done by sharing electrons
covalent bonds = strongest bonds
Carbon in Organic Compounds
Carbon binds to other carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur (CHNOPS)
fully single bonded carbon forms tetrahedron structure
Carbon can form branched/unbranched chains and single/multiple rings
Metabolism and Functions (2)
Sum of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Functions: energy for cellular processes, synthesis and assimilation of new materials
Anabolism
Joining of simple molecules (monomers) to produce complex ones (polymers)
Done via Condensation Rxn
Endergonic, requires energy
Condensation Rxn
Removal of H20 to link bonds, water formed from OH (hydroxyl) from one monomer and H from another
Catabolism (digestion)
Breaking of complex molecules (polymers) to produce simple ones (monomers)
Done via hydrolysis
Exergonic, releases energy
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.
Carbohydrate Monomers/Polymers
Monomer: Monosaccharide
Disaccharide (2)
Polysaccharide (many)
Linking of Monosaccharides
Forms a glycosidic bond (covalent bond C-O-C) via a condensation rxn
Monosaccharides Function & Example
Function: Short-term energy storage (ex. glucose)
Glucose exists in both linear and ring (hexose, 6-cornered ring) formation
Glucose Characteristics
Soluble, therefore easily transported in medium like blood
Chemically Stable
Affects osmotic gradient and converted into starch or glycogen to prevent this
Yields energy when oxidized (lose electron)
Storage/Structure Polysaccharides in Plants/Animals
Plant Storage - starch, alpha
Plant Structure - Cellulose, beta
Animal Storage - Glycogen, alpha
Animal Structure - Chitin, alpha
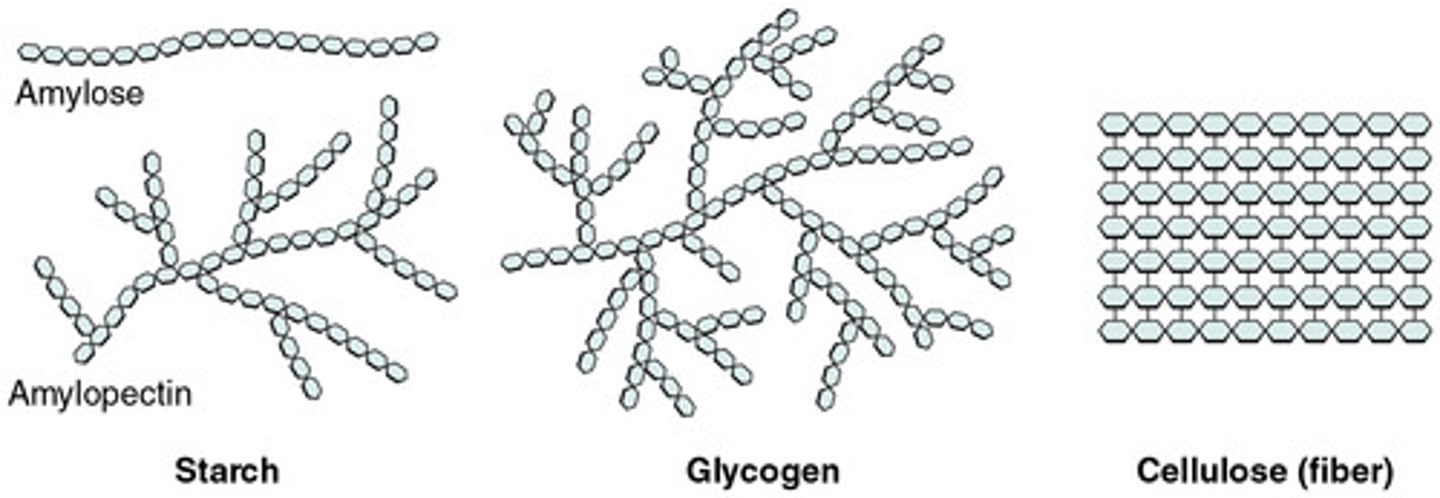
Starch
Made alpha glucose, plant energy storage, either amylose or amylopectin
Amylose
Unbranched, helical (1-4 bonds), compact, more difficult to digest, preferred storage form
Amylopectin
Branched, 1-4 and 1-6 Bonds (1-6 bonds cause branch), easier to digest bc more Surface Area
Glycogen
animal energy storage, made of alpha glucose
Unbranched (1-4) and branched (1-6) linkages
Found in liver in animals
Similar to amylopectin, but more branched, coils for good storage
Starch and Glycogen Characteristics
1-4 linkages (linear) and 1-6 linkages (branched)
Single glucose can be removed (hydrolysis) or added (condensation rxn) w/ ease
large in size, but relatively compact due to coiling and branching
low solubility, therefore does not interfere with the osmotic gradient of a cell
Cellulose
plant structure, made of beta glucose
Unbranched (1-4 bonds)
Found in plant cell walls
Indigestible for most (lack enzyme) therefore "fiber"
Alpha vs. Beta Glucose
structural isomers (same molecules, different structures)
Position of hydroxyl on C1 is different for alpha/beta
For beta glucose, for condensation rxn to occur, newly added one must be inverted.
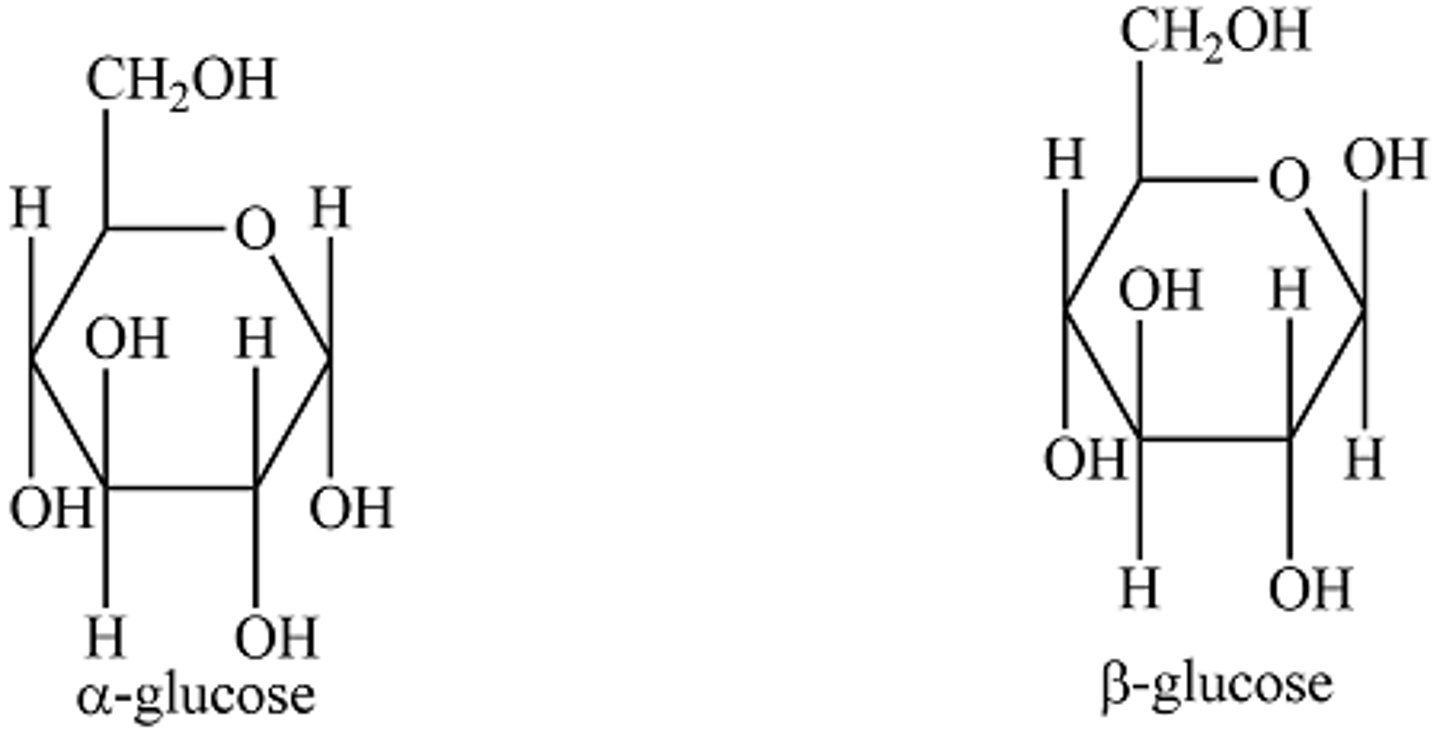
Beta-Glucose Characteristics
Bc alternating directions (bc of inversion), produces a straight chain
Forms bundles arranged in parallel, then regularly spaced OH groups allow additional hydrogen bonds with adjacent strands (forms a sheet structure)
Such Cross Link provides high tensile strength for plant cells to withstand high water pressures
Images of Glucose Polymers
Glycoproteins
Polypeptides with oligosaccharides (short sugar chain), found in plasma membrane of animal cells, facing outside
Distinctive glycoproteins allow cells to be recognized by other cells
aids in organization of tissues and identifies/destroys infected cells
ABO Glycoproteins
Red blood cells have glycoproteins that affect transfusion
Three types, A, B, O
Blood with glycoprotein A (antigen) will be rejected y someone who does not produce it (antibody)
Blood w/ glycoprotein O will not be rejected bc it is the same structure as A and B but without one monosaccharide
Blood Type A
A antigen, makes B antibodies so destroy B
Blood Type B
B antigen, makes A antibodies so destroy A
Blood Type O
Both antibodies, universal donor
Lipids
Include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
Hydrophobic, more attracted to nonpolar (not necessarily repelled by H2O
DOES NOT CONSIST OF MONOMERS AND POLYMERS
Triglycerides Formation
Condensation Rxn joins ONE glycerol and THREE fatty acids
OH (hydroxyl) of glycerol and COOH (carboxyl) of fatty acid forms ester bonds
Ester Bonds
bond between fatty acids and glycerol, 3 H2O produced when 1 triglyceride made
Hydroxyl on glycerol loses H, carboxyl on fatty acid loses OH to form H2O
Phospholipids
Polar head composed of phosphate (instead of 3rd fatty acid), 2 nonpolar fatty acid tails
Amphipathic, both hydrophilic (water-loving) and lipophilic (fat-loving)
Lipophilic
fat-loving, similar to hydrophobic
Fatty Acids Characteristics
Long hydrocarbons, consist of only C and H
CH3 (methyl) at one end and COOH (carboxyl) on the other (OH of carboxyl falls off to form H2O in condensation rxn)
Vary in number of hydrocarbons and double bonds
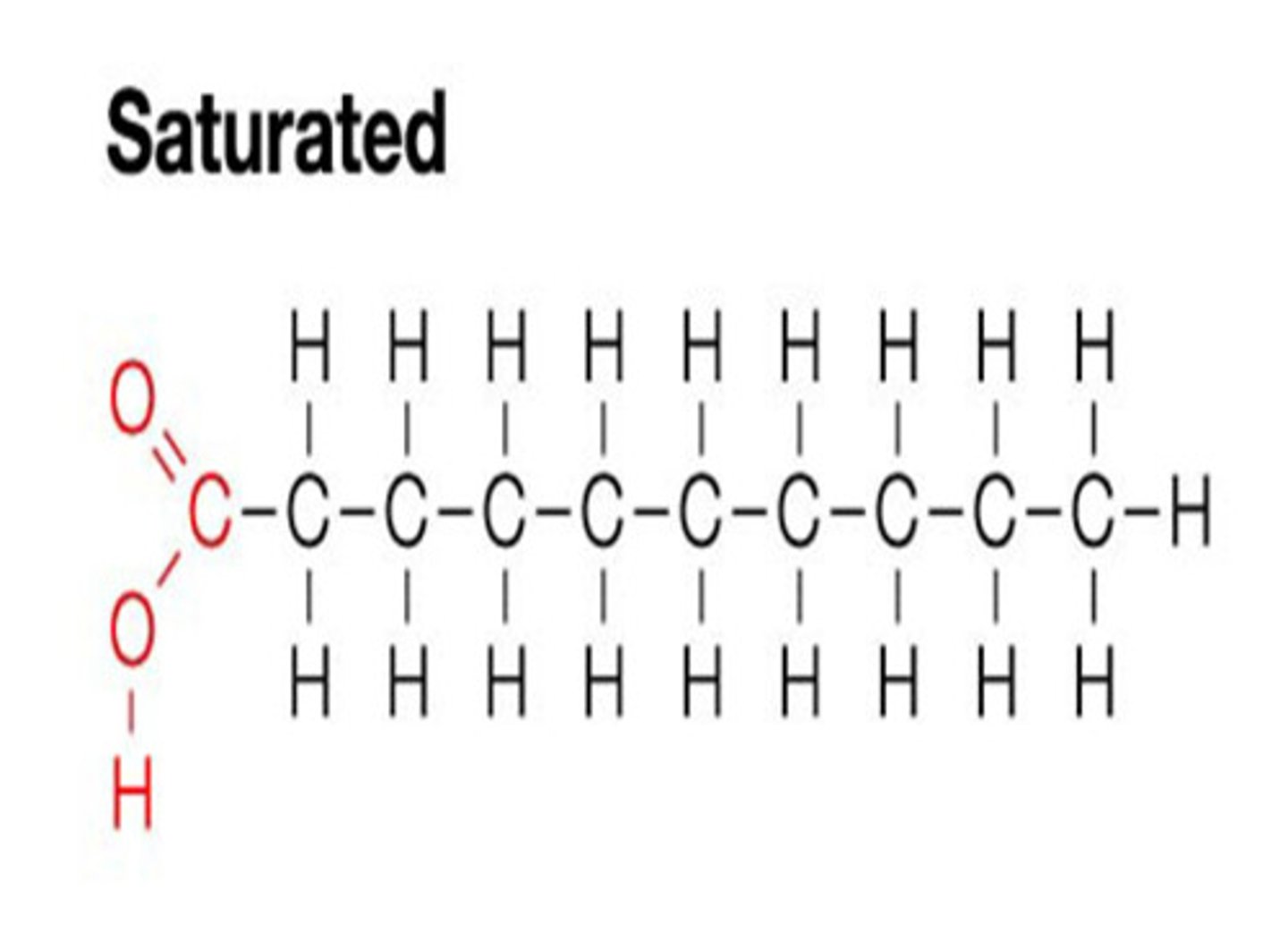
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds, "saturated" with hydrogens
Linear, come from animal sources
High melting point - solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Has double bonds, therefore bent
Come from plant sources
Low melting point - liquid at room temp (typically)
Monounsaturated/Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Mono = 1 double bond
Poly = more than 1 double bond
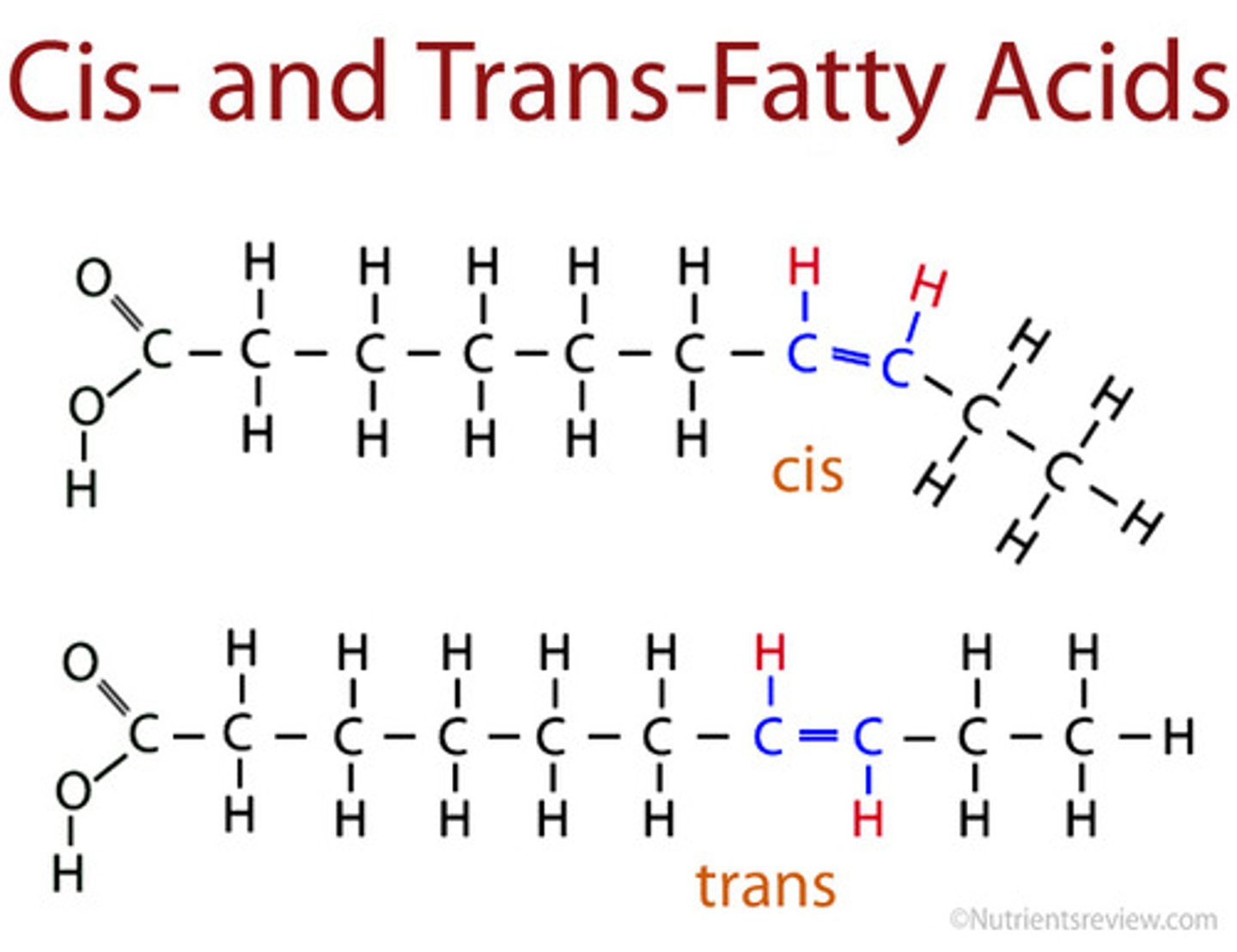
Cis Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Two H atoms adjacent to double bond are on the same side, hydrogens repel one each other, forming kinks
liquid at room temperature
Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Two H atoms adjacent to double bond are on different sides, produced in industrial process called hydrogenation (now banned)
Makes fats "spreadable" such as margarine
Linear and solid at room temp, despite double bonds
Cis vs Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Lipid Advantages (6)
Function - long-term energy storage in adipose tissue
Chemically stable, energy not lost over time
Immiscible in H2O, no effect on osmotic pressure of cell
Store 2x energy as carbs
poor heat conductors, used as thermal insulators such as blubber
Act as shock absorbers