The Muscular System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Last updated 2:13 PM on 10/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
tendon
strip of strong connective tissue that connects a muscle to bone.
2
New cards
define voluntary muscles
voluntary muscles are the muscles under your control.
3
New cards
3 types of muscles
The three types of muscles are skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
4
New cards
Why are skeletal muscles called striated muscles?
Skeletal muscles appear to be striped, or striated, under a microscope.
5
New cards
Explain how the bicep and tricep work together to allow you to bend your arm.
The bicep contracts and the tricep relaxes when you bend your arm toward your head. When your arm returns to the position parallel to the floor, the bicep relaxes while the tricep contracts. These muscles work together to allow you to move your arm.
6
New cards
What determines the strength or weakness of a muscle contraction? Explain how this is related to the ability to lift heavy or light objects.
The number of muscled fibers involved determines the strength or weakness of a muscle contraction. To lift a heavy object, the nervous system signals more muscle fibers to contract that a when lifting a lighter object.
7
New cards
How do muscles produce force?
Muscles produce force by contracting.
8
New cards
What two proteins does ATP interact with to produce muscle contraction?
ATP interacts with myosin and actin to produce muscle contractions.
9
New cards
Why does every movements require two muscles?
Muscle contraction can only produce a pulling motion, not a pushing motion. Therefore, muscles must work in pairs to produce movement.
10
New cards
What is myofibril?
A myofibril is a bundle of thick and thin filaments that make up muscle fibers.
11
New cards
What gives skeletal muscle is striated appearance?
The alternating thick and thin filaments in myofibrils give skeletal muscles their striped appearance.
12
New cards
What is a sarcomere? Use the term Z line in your answer?
A sarcomere is a unit of thick and thin filaments bound on Z lines
13
New cards
What is the neuromuscular junction? What occurs at a neuromuscular junction?
A neuromuscular junction is a specialized area in which a nerve fiber lies close to the end of a muscle fiber. When a nerve impulse reaches the end of a motor neuron, it triggers the release of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine diffuses across the neuromuscular junction and produces and impulse in the muscle fiber, causing the release of calcium ions within the fiber and producing a muscle contraction.
14
New cards
What causes a muscle to relax?
A muscle relaxes when acetylcholine is not longer produced and the calcium ions have been pumped back into storage.
15
New cards
Do filaments change length when a muscle contracts? Explain what happens to the filaments during a muscle contraction.
No. According to the sliding-filament model, the filaments do not change in the length. Instead, muscles shorten when the thin filaments slider over the think ones. During a muscle contraction, a cross-bridge physically links the myosin and actin filaments. With the help of ATP, the cross-bridge changes shape so that the filaments slide past each other, producing a shortening, or contraction, of the muscle fibers.
16
New cards
define involuntary muscles
muscles you cannot/do not need to control, like digestive and cardiac muscle
17
New cards
where is skeletal muscle found + voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary muscles attach to bones that allow us to move, voluntary
18
New cards
location of cardiac muscle + voluntary?
found ONLY in heart, involuntary
19
New cards
smooth muscle location + voluntary or involuntary
involuntary, found inside most body organs
20
New cards
what do muscles need to relax
ATP
21
New cards
what do your cells do when they don't have enough oxygen to produce ATP through aerobic cellular respiration?
fermentation
22
New cards
what does fermentation create
lactic acid, 2 glucose
23
New cards
function of muscles
tone and posture, movement, protection of organs, control openings, maintain body temperature,
24
New cards
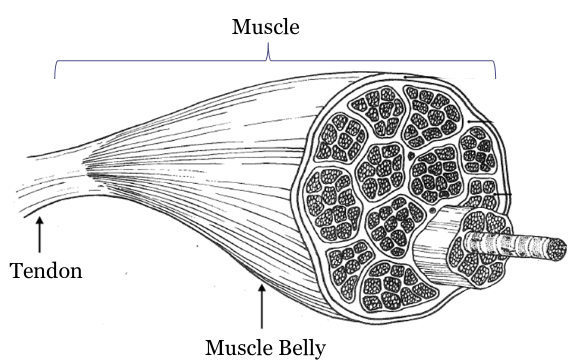
parts of a muscle
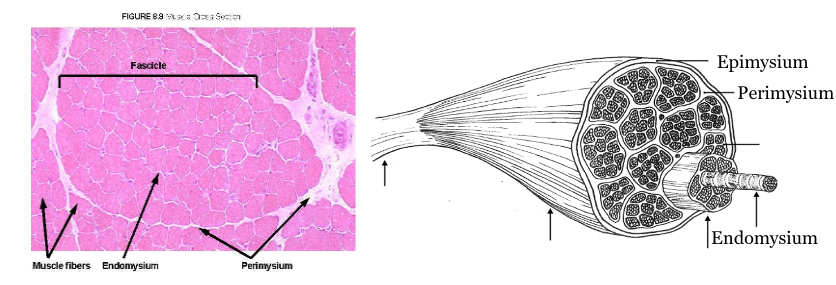
muscle itself, muscle belly, fascicle, fibers, tapers off into tendon
25
New cards
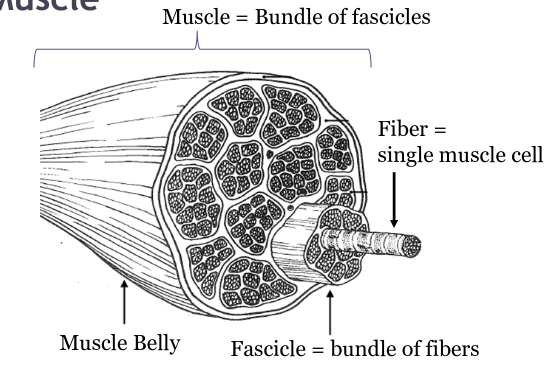
define fascicle
bundle of fibers, makes up muscles
26
New cards
muscle fiber defined
single muscle cell (longest cell in your body!), where nerves and blood vessels are found
27
New cards
muscle belly defined
middle of the muscle where fascicles bunch up
28
New cards
actin
thin, light filaments found in muscle
29
New cards
how do muscles move?
nerve cells, which receive signals from the brain and move as they're told to.
30
New cards
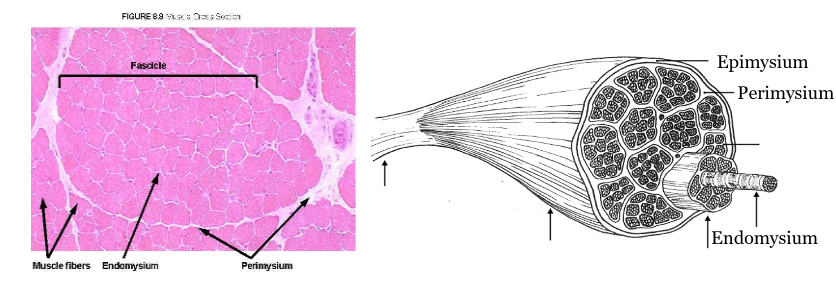
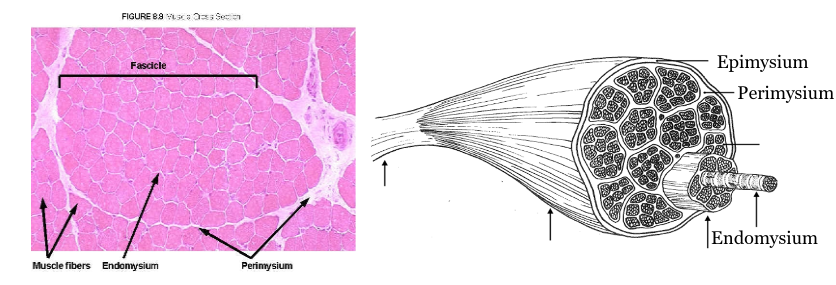
epimysium
outermost layer that covers muscles, specifically the fascicles.
31
New cards
perimysium
the sheath of connective tissue that covers a bundle of muscle fibers
32
New cards
endomysium
innermost layer that covers muscle cells
33
New cards
soreness
microtears in the muscle after exercise, that grow back stronger and bigger
34
New cards
delayed onsent muscle soreness
DOM, explains why muscles need several hours to be sore and repair themselves
35
New cards
tendon
a cord or band of inelastic tissue connecting a muscle with its bony attachment, also a bundle of collagen fibers
36
New cards
shivering
contraction of muscles to create body heat, using energy
37
New cards
aponeurosis
any of the deeper and thicker fascia that attach muscles to bones; resemble flattened tendons
38
New cards
ruptured tendon
detaches a muscle completely from one of its bones, making the muscle unusable
39
New cards
longest muscle fiber + length
sartorius muscle, 60cm
40
New cards
each fiber is ______, meaning...
multinucleate, multiple nuclei per cell
41
New cards
rectus muscles
arranged in a straight order
42
New cards
what ways are muscles named?
direction of fibers, size, shape, location, attachment sites, origin, function
43
New cards
oblique muscles
diagonally arranged
44
New cards
larger muscles may be called
maximus, longus
45
New cards
smaller muscles may be called
minimus, brevis
46
New cards
medial muscles are found where
middle of the body, median
47
New cards
lateral muscles are found where
towards the sides of the body
48
New cards
attachment site/muscle head prefixes
bi/two, tri/three
49
New cards
the origin is a muscle attachment to what type of bone
immovable
50
New cards
insertion is a muscle attachment to what type of bone
movable
51
New cards
flex meaning
bend a joint
52
New cards
extend
straighten a joint
53
New cards
involuntary muscles are connected to what
nervous system, heart, brain
54
New cards
first step of muscle contraction
a signal is passed through a motor neuron to a muscle.
55
New cards
what happens to bones when muscles contract?
they pull closer together
56
New cards
contracted muscles create definition, which is called
muscle belly
57
New cards
what do the amount and force of muscle tension depend on:
frequency of stimulation (from central nervous system), number of skeleton muscle fibers involved, size of muscle fibers (larger fibers contain more myofibrils)
58
New cards
summation
process of recruiting more muscle fibers to generate a greater force, begins with a single muscle twitch and results in a single stimulus-contraction-relaxation sequence in the muscle
59
New cards
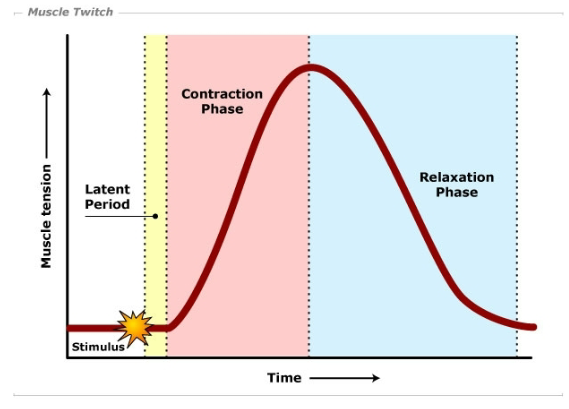
three parts of a twitch
latent period, contraction phase, relaxation phase
60
New cards
latent period of a muscle twitch
stimulus spreads through the muscle, first part
61
New cards
contraction phase of a muscle twitch
actin and myosin create tension, second part of the twitch
62
New cards
relaxation phase
last part of a muscle twitch, defined by actin and myosin uncoupling and the muscle relaxing (uses ATP)
63
New cards
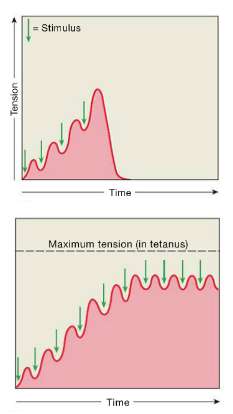
tetanus
continuous simulation in your muscles, when twitches overlap. defined by a PROLONGED CONTRACTION.
64
New cards
creatine phosphate
can be broken down to release high-energy phosphates, quickly recharging ATP (8-10 seconds worth of contraction)
65
New cards
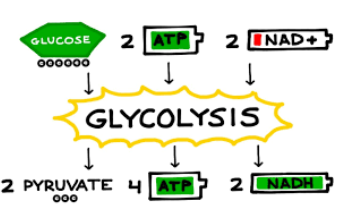
glycolysis
breaking down of glucose, releases 2 molecules of pyruvate and 2 molecules of ATP, takes place in cytoplasm. next step changes based on amount of oxygen
66
New cards
cellular respiration (aerobic)
breaks down 34 molecules of ATP for every molecule of glucose, takes place in mitochondria, oxygen-needing
67
New cards
post-glycolysis, anaerobic
usage of fermentation reactions, recycles unused products of glycolysis into 2 ATP, happens in cytoplasm without oxygen, produces LACTIC ACID which causes fatigue and soreness
68
New cards
causes of muscle fatigue
running out of glucose ("hitting the wall"), insufficient oxygen levels (forces muscles to rely on fermentation)
69
New cards
why are smooth muscles called smooth muscles
smooth muscles do not have these stripes and appear smooth.
70
New cards
second step of muscle contraction
the signal is sent through every fiber in the muscle through t-tubes
71
New cards
third step of muscle contraction
the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions that initiate muscle contraction.
72
New cards
fourth step of muscle contraction
the calcium influx stimulates the myosin filaments to form connections to actin filaments
73
New cards
fifth step of muscle contraction, final step
the myosin filaments pull the actin filaments inward which causes the muscle to contract.