Global economic history lecture 5
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Name five things that inequality is linked to
Place
Social status and rank
Class
Gender
Ethnicity
What is intra-national inequality?
Intra-national inequality refers to the disparities in wealth, income, education, and access to resources within a single country.
What is inter-national inequality?
Distribution of wealth between countries
What is global inequality?
Intra-national and inter-national combined
What is the gini coefficient?
The gini coefficient is a measure of income inequality within a population, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality).
What are the issues with the gini coefficient?
The gini coefficient does not account for regional disparities, ignores demographic differences, can be sensitive to high-income outliers, and may not reflect overall wealth distribution accurately.
What does the maximum gini mean? (IDK IF ITS CORRECT)
The maximum gini refers to a scenario where income or wealth is distributed in the most unequal manner possible, resulting in a gini coefficient of 1.
What is Kuznets curve?
The Kuznets curve is an economic theory suggesting that as an economy develops, market forces first increase and then decrease economic inequality.
What are the historical trends of poverty?

What were the problems of industrialisation and intranational inequality?
Proletarization of workers (females and kids)
Le chapelier: no labour associations
Little or no protection on the work floor (sickness, accidents)
Poor living conditions (rapid urbanization)
What are the differences of trade unions between Europe and US/Japan?
Corporatist bargaining model in Europe
Collective bargaining at national sectoral and firm level
Embeddedness of union in social economic institutions (wages, working conditions, board representation, enforced by the state)
Liberal model in US and Japan
Restricted role in the management of economy
Power at the level of the firm
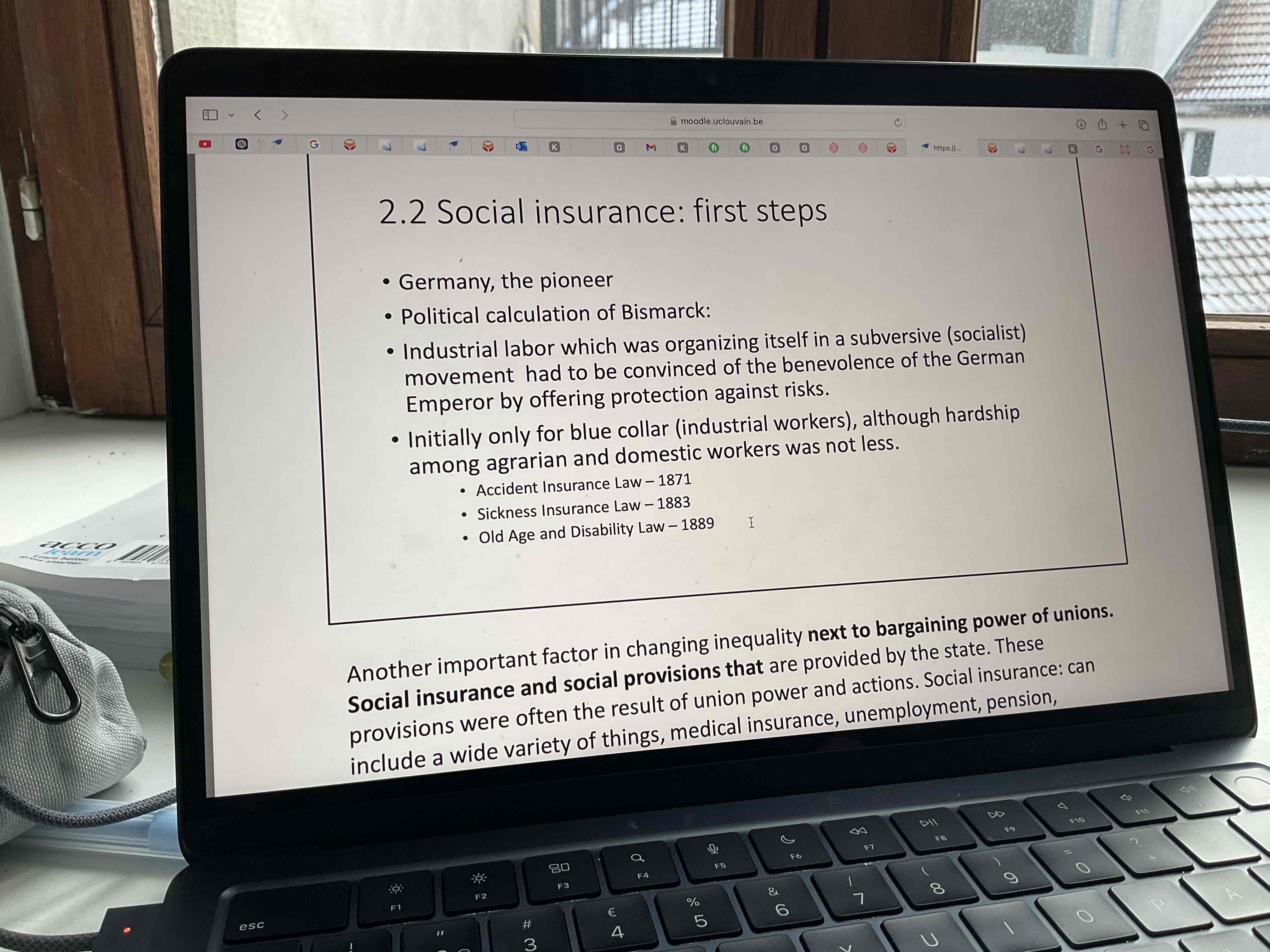
Why was Germany the first to get social insurance?
What are the three reasons that global inequality has remained high in the last centuries?
The great divergence in the 19th century although there is convergence international inequality today is far higher than it was in 1820 today it is roughly the same as in 1900.
The 20th century saw decrease in intra-national inequality with countries due to spending yet international inequality continued to climb. This was caused by countries unable to catch up or fixed in the colonial system so the effects of the welfare state on global inequality for a globally ambiguous
The pattern has reversed international inequality clearly declines but these beneficial effects on global inequality are undone by rising intra-national inequality. Rising intra-national inequality seems to be a global phenomenon.
What is rising intro national inequality linked to?
Stagnating social spending
Weak Labour bargaining power
Oil crisis of 1970s that was triggered by OPECs 1973 boycott which led to high inflation rising unemployment and the end of the economic boom.
Progressive taxes lowered
What is trickle-down economics?
Trickle-down economics is an economic theory that suggests that benefits provided to the wealthy or businesses will eventually trickle down to the rest of the population through job creation and investment.