AP Human Geography-Unit 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
culture
a group of belief systems, norms, and values practiced by a people EX) Makan American Indians who hunt whales
2
New cards
folk/local culture
how a group of people in a place that see themselves and share customs/traits. OR a small culture that incorporates a homogeneous population that is typically rural and cohesive in cultural traits.
3
New cards
folklore
the traditional beliefs, customs, and stories of a community, passed through generations by word of mouth
4
New cards
popular culture
large culture that incorporates heterogeneous populations, is typically urban, and experiences quick changing traits.
5
New cards
material culture
the things a group of people construct, including homes, clothing, sports, dance, and foods.
6
New cards
built environment
a material, spatial, and cultural product of human labor
7
New cards
nonmaterial culture
beliefs, practices, aesthetics, and values of a group of people. EX) Hutterites value marrying within their religion
8
New cards
cultural appropriation
the process by which other cultures adopt customs and knowledge and use them for their own benefit EX) People not of the culture getting henna tattoos
9
New cards
neolocalism
seeking out the regional culture and reinvigorating it in the response to uncertainty of the modern world. EX) In Lindsborg, Kansas, they proclaim their town Little Sweden, USA
10
New cards
ethnic neighborhoods
tight nit neighborhoods within a major city where local cultures have built a world apart to practice their customs EX) Hasidic Jews in Brooklyn, NY
11
New cards
commodification
the process through which something (a name, good, idea, or person) becomes an object that can be bought and sold in the world market, when it previously wasn't regarded so.
12
New cards
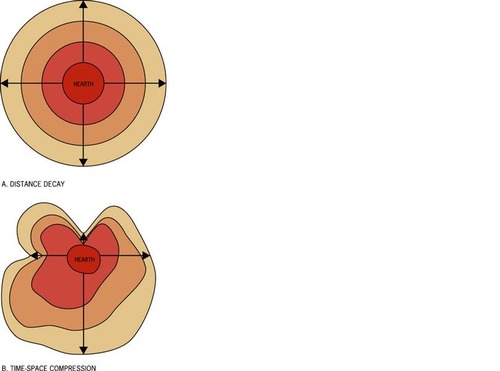
Distance Decay
How quickly innovations diffuse and refers to how interlinked two places are through transportation and communication
13
New cards
time-space compression
explains how quickly innovations diffuse and refers to how interlinked two places are through transportation and communication
14
New cards
reterritorialization
a term referring to a process in which people start to produce an aspect of popular culture themselves, doing so in the context of their local culture and place, making it their own. EX) Hip hop spread from NY and LA to major cities in Europe
15
New cards
hierarchical diffusion
can occur through a hierarchy of places. The hearth is the point of origin. Large cities to smaller ones (trickles down)
16
New cards
contagious diffusion
idea spreads from person to person EX) word of mouth
17
New cards
stimulus diffusion
when an exact idea can't be adopted in a certain area (due to cultural barriers, etc.) leading to altering of the idea. It is a stimulus for newer ideas. EX) non-meat burgers at McDonald's in India
18
New cards
relocation diffusion
when individuals who have adopted the idea move to new places and disseminate it. The hearth loses strength in the idea and the places the individuals move to gain strength in it. EX) Buddhism started in India, but now has more followers in Thailand, Cambodia, and Myanmar
19
New cards
assimilation
the process of making indigenous people adopt the dominant culture and abandon their own culture. EX) US wanted to assimilate Native Americans in the 18 and 1900s.
20
New cards
Forced assimilation
the process of making indigenous people adopt the dominant culture and abandon their own culture EX) People learning English in the US
21
New cards
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity on the landscape
22
New cards
sequent occupance
proposed by Derwent Whittlesay. Cultural imprints made over top of each other, each affect the next, have a lasting imprint EX) In N Africa, Islamic mosques have Roman influences
23
New cards
placelessness
coined by George Edward Relph to describe the loss of uniqueness in place in the cultural landscape to the point that one place looks like the next EX) subburbs
24
New cards
global-local continuum
the idea that cultural borrowing and mixing is happening all over the world. Emphasizes that what happens on one scale is not independent of what happens on another. EX) Venetian hotel is Las Vegas, Nevada
25
New cards
glocalization
people in a local place mediate and alter regional, national, and global processes. Causes global-local continuum
26
New cards
adaptive strategy
technology, ecology, demography, and economies that define human behavior EX) farming tech, air conditioning
27
New cards
folk-housing regions
Fred Kniffen researched house types and their diffusion in North America and found that 3 regions have these houses: (1)New England, (2) Mid-Atlantic, and (3) Lower Chesapeake Bay. The diffusion streams created the regions. EX) (1) Saltbox, two-chimney, Cape Cod, Front Wing, and Gable. (2) I-house, Tidewater. (3) Shotgun
28
New cards
Anglo-American landscape
the township and range patterns established by early settlers in which there were long rows of roads in square or rectangular patterns EX) prevails over US Midwest
29
New cards
traditional architecture
buildings use building materials available and reflect social/environmental customs of the people EX) log cabins
30
New cards
folk songs
traditionally sung by the common people of a region. forms part of their culture EX) May tell stories
31
New cards
folk food
traditional food EX) barbecue in South
32
New cards
gender
social differences between men and women
33
New cards
identify
how people view themselves at different scales EX) gender identity
34
New cards
identifying against
define the "other", then define ourselves in opposing terms. One of the most powerful ways to construct an identity. EX) Europeans called the Middle East and Asia the "Orient", and called it a mystical place. They also called Africans and Americans "savage". The Europeans said they weren't either of these things, so they were therefore "civil"
35
New cards
race
the product of ways of viewing minor genetic differences around the world. Excellent example fo how geographic context shapes identity.
36
New cards
racism
sense of superiority attached to race
37
New cards
residential segregation
to degree which two or more groups live separately from one another, in different parts of the urban environment. 5 statistical measurements of segregation: evenness, exposure, concentrated, centralized, and clustered. EX) In 2010 the most residentially segregated metropolitan area in the IS was Milwaukee, Wisconsin
38
New cards
sense of place
made by the emotions and memories attached to a place. Changes as we and the place change.
39
New cards
ethnicity
an identity based on being bounded or related to a certain place over time EX) Latino, Hispanic
40
New cards
ghetto
a part of a city, especially a slum area, occupied by a minority group or groups EX) ghettos in NY
41
New cards
infantcide
killing of infants EX) girls are killed in India because they are seen as a burden due to dowries
42
New cards
barrio
An urban area in a Spanish speaking country
43
New cards
language
a set of sounds and symbols that is used for communication
44
New cards
standard language
a published, widely distributed, and purposefully taught language that most technologically advanced societies have.EX) Ireland promotes the use of Celtic by requiring all government workers to pass Irish-language exam
45
New cards
dialect
a variant of a standard language along regional or ethnic liens. Made of differences in: vocab, syntax, pronunciation, cadence, and pace. EX) Southern-English
46
New cards
isogloss
a geographic boundary in which a particular linguistic feature occurs. Rarely a simple line. EX) the lines of which American dialects are fuzzy
47
New cards
mutual intelligibility
means that two people can understand each other while speaking. Has been rejected as strongly as environmental determinism. EX) mostly with two dialects of one language, but Danish and Norwegian speakers can understand each other while Mandarin and Cantonese canoot
48
New cards
dialect chains
dialects nearest to each other will be most similar. As you go farther apart, dialects become less intelligible.
49
New cards
language family
way of classifying languages at the global scale. The languages have shared by fairly distant origins. Broken into sub-families. EX) Indo-European language family includes Italian, Spanish, and French
50
New cards
language subfamily
divisions within a language family, the commonalities are more definite and origins more recent. Consists of individual languages with smaller spatial extents and dialects with even smaller spatial extents EX) Indo-European is broken into sub-families of Romance, Germanic, and Slavic
51
New cards
language groups
set of languages with a relatively recent common origin and many similar characteristics EX) Germanic, Romance, Slavic
52
New cards
Indo-European language
a language from the Indo-European family. Spoken by half of the world's people, and includes among others, the Germanic, Romance, and Slavic subfamilies
53
New cards
lingua franca
a language used among speakers of different languages for the purposes of trade and commerce. Can be one language or a mixture.
54
New cards
pidgin language
when people speaking 2 or more languages are in contact and they combine parts of their languages in a simplified structure and vocabulary EX) the first widely known pidgin language is the Frankish language, a mix of Frank tongue with Italian, Greek, Spanish, and Arabic for trade on eastern Mediterranean with Southern Franks.
55
New cards
trade language
a simplified language that develops as a means of communication between two or more groups that do not have a language in common. EX) in SE Asia, Bazaar Malay is Myanmar (Burma) to Indonesia and from the Philippines to Malaysia. It is a lingua franca and simplified form of Chinese
56
New cards
creole language
a pidgin language that has developed a more complex structure and a vocabulary and has become a native language of a group of people EX) Swahili
57
New cards
monolingual states
countries in which everyone speaks the same language EX) Japan, Uruguay, Iceland, Denmark, Portugal, Poland, and Lesotho
58
New cards
multilingual states
countries in which more than one language is in use EX) US
59
New cards
official language
adopted by countries with linguistic fragmentation to tie the people together. Or in colonies, one that ties them to their colonizer.
60
New cards
global language
a common language of trade and commerce used around the world. EX) like lingua franca
61
New cards
linguistic diversity
there are more than 7000 languages spoken today that are created by economic, technological, and ideological globalization. EX) more than 1500 languages are spoken in Sub-Saharan Africa
62
New cards
toponyms
place names. often refer to social progress in the area. May impact how people view the lace. Dominated by 10 themes: descriptive, commendatory, possession, commemorative, associative, incidents, possession, folk, manufactured, mistakes, shift. EX) "Mount Prospect" and "Mount Misery"
63
New cards
religion
a system of beliefs and practices that attempts to order life in terms of culturally perceived ultimate priorities. EX) Baha'i
64
New cards
monotheistic religion
worship a singly deity, God or Allah EX) Islam grew in Northern Africa from 11 to 234 million in 1900 to 2010
65
New cards
Zoroastrianism
monotheistic religion that developed about 3500 years ago in SW Asia. Some believe it was the first monotheistic religion, others say Judaism. EX) The Parsi are Zoroastrianists who moved to India
66
New cards
polytheistic religion
worship more than one deity, even 1000s EX) Hinduism, Vodum/Voodoo
67
New cards
animistic religion
centered on the belief that inanimate objects, such as mts., trees, rivers, and boulders. posses spirits and should be revered. EX) Shamanism
68
New cards
universalizing religions
actively seek converts because they view themselves as offering belief systems and universal appropriateness and appeal. Few in number and of recent origin. EX) Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam
69
New cards
ethnic religion
Adherents are born into the faith and converts are not actively sought. Spatially concentrated, except for Judaism. EX) traditional religions in Africa and SA. Judaism, Hinduism, Confucianism, Shintoism
70
New cards
Hinduism
3rd biggest religion, DID NOT originate in Pakistan, given name by Aryans, no founder, based on ancient practices of Indus River Valley city of Mohenjo Daro and Harappa, sacred river is the Ganges, and their main god is Brahman. Other gods are expressions of Brahman. Not a polytheistic or monotheistic religion, or even both. Vedas is it's 4 sacred texts. Defined as an ethnic religion to SE Asia.
71
New cards
Reincarnation
A soul is reborn and in Hinduism you are moved up and down in the caste system based off your behavior. The goal is to escape reincarnation through union with Brahman. EX) Hinduism
72
New cards
caste system
locks people into particular social classes and imposes many restrictions, especially to those in lower castes
73
New cards
Sikhism
created by interaction of Hinduism and Islam. Didn't like worship of idols and caste system in Hinduism. EX) wear turbans and forbid hair-cutting
74
New cards
Buddhism
came from Hinduism as a question to its teachings (caste system). 2 branches: Mahayan (salvation comes by appeal to holy sources of merit) and Theravada (Salvation is personal matter achieved by good behavoir and being monk or nun). EX) Theravada- Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia. Mahayana- Vietnam Korea, Japan, and China
75
New cards
Shintoism
ethnic religion, related to Buddhism, focuses on nature and ancestor worship EX) Japan
76
New cards
Taoism
traced to older contemporary of Confucius, Lao-Tsu, who published Tao-te-Ching or "Book of Way". EX) China. Avoid competition possession pursuit of knowledge. Evils= war, punishment, takes, and ceremonial ostentation.
77
New cards
Feng-Shui/geomancy
given rise to by "Book of Way". the art and science of organized living spaces in order to channel the life forces that exist in nature in favorable days, done by consulting geomancers- know desires of spirits of ancestors and beings of natural world EX) Shamanism uses geomancers
78
New cards
Confucianism
philosophy of life. Like Taoism, great impacts of Chinese Life. Confucius was appalled by the poor and suffering and urged them to assert themselves. Said virtues and abilities, not heritage, should determine position in society. Altered by emperors over time
79
New cards
Judaism
grew out of the beliefs of Jews, a nomadic semetic tribe in SW Asia. Based off teachings of Abraham. In Middle East, N Africa, Russia, Ukraine, Europe, and N and S America. Monotheistic.
80
New cards
Christianity
single founder (Jesus), split from Judaism, monotheistic, first split: between Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox. Emperor Diocletian split empire eventually leading to separate denominations. Last branch- Protestant (came from Catholic)
81
New cards
Islam
founded by Muhammad, Qu'ran, Allah, monotheistic, 5 pillars, pilgrimage to Mecca/hajj. EX) Most Muslims are in Indonesia
82
New cards
Sunni
majority accept rulers who aren't descendants of Muhammad/Ali. EX) many in US and Europe
83
New cards
Shia/Shi'ite
don't accept rulers who aren't descendants of Muhammad. More centralized hierarchical clergy than Sunni. Imams are the source of knowledge. EX) Iran, Iraq, Palestine, Afghanistan
84
New cards
Shamanism
community faith in which people follow their shaman (religious leader) . small, isolated religion. EX) Africa, Native America, SE Asia, and E Asia.
85
New cards
secularism
the indifference to or rejection of formal religion. EX) 57% of US said religion isn't super important in their lives while 98% of Senegal said the opposite.
86
New cards
Mormonism
Church of the Latter day Saints. Created by Joseph Smith, has similar beliefs to Christianity. Began in NY, then moved to Utah due to persecution.
87
New cards
sacred sites/sacred space
places people infuse with religious meaning (reverence or fear). If infused with reverence, a pilgrimage may be made to the place.
88
New cards
religious toponym
the origins and meanings of the names of religions EX) St. Peter's Basilica- burial site for Catholic tradition
89
New cards
interfaith boundaries
the boundaries between the world's major faiths. subject to potentially divisive cultural forces. EX) several countries in Africa that straddle the Christian- Muslim boundary EX) Israel, Palestine, Nigeria, former Yugoslavia
90
New cards
intrafaith boundaries
the boundaries within a single major faith. Divisions between: Catholics and Protestants (especially in N Ireland), Muslim Sunni and Shia
91
New cards
enclave
when a community or group is trapped and surrounded by unfriendly population or government. EX) the Gaza strip in Israel where Muslims are surrounded by the Jewish population and government
92
New cards
exclave
a portion of a country not connected to the main part physically EX) Alaska
93
New cards
genocide
A mass killing of people EX) Holocaust
94
New cards
ethnic cleansing
a mass killing of a specific group of people EX) Serbian campaign for ethnic cleansing of Kosovo Albanians (Muslims) who demanded autonomy.
95
New cards
theocracy
a government in which religion rules Ex) Taliban
96
New cards
religious fundamentalism
born over perceived breakdown of society's morals and values. hold to religious beliefs. EX) Traditionalism Catholic Movement- preach in Latin and don't recognize the Pope and the Vatican
97
New cards
religious extremeism
religious fundamentalism carried to the point of violence EX) 9-11, extremist Jews who are for anti-Arabism (Kahane Chai), and Taliban
98
New cards
Shari'a Law
the legal framework within public and some private aspects of life are regulated for those living in a legal system based on Muslim principles
99
New cards
jihad
Islamic holy way against West, US in particular. Promoted by Taliban in Afghanistan because provided haven for Islamic extremeists EX) 9-11
100
New cards
Zoroastrianism
world's oldest monotheistic religion