Fetal Circulation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
point of fetal circulation
-delivering oxygen and nutrients
-clearing waste products and CO2
high priority v. low priority fetal organs
-high: brain and heart
-low: lungs (babies don’t breathe as they grow- get oxygen from maternal placenta, fetal circulation set up to bypass lungs)
placenta
-grows with developing fetus
-basic function: bring fetal and maternal blood together for exchange of gas and nutrients
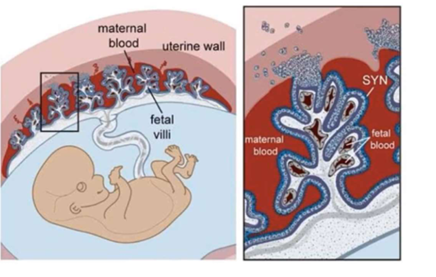
interface of placenta and uterus
-maternal blood enters into spaces in the placenta
-fetal blood meets in capillaries for exchange via diffusion
-fetal and maternal blood never actually touch
fetal circulation- umbilical vessels
-2 arteries, 1 vein
-arteries: carry blood away from the heart
-veins: carry blood towards the heart
umbilical vessels connected to
-placenta
-umbilical vein carries freshly oxygenated blood from placenta back towards the fetal heart
-umbilical arteries bring deoxygenated blood back to the placenta to pick up more oxygen
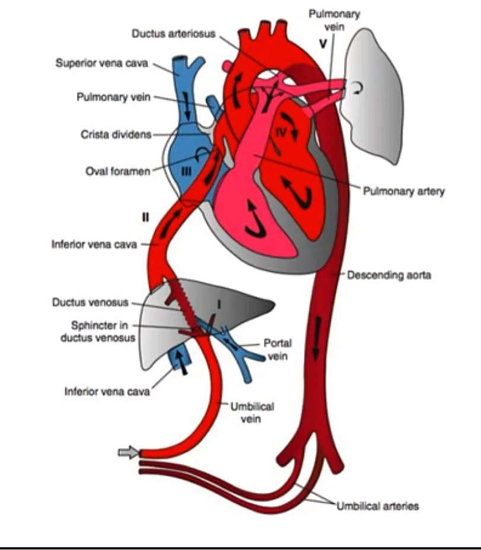
3 main shunts of fetal circulation
-ductus venosus
-formane ovale
-ductus arteriosus
ductus venosus
-first stop of oxygenated blood in umbilical vein is fetal liver
-ductus venosus allows blood to bypass the liver entirely and continue making its way to the heart
-allows blood to pass directly into the inferior vena cava
-connects umbilical vein to IVC
post-natal v. fetal heart
-post-natal: deoxygenated blood from RA to RV, then to lungs, then comes to LA and LV, then out to the body
-fetal heart: RA to LA to body without going through the lungs; IVC to RA, then through foramen ovale to the LA, then to the body
-”streaming” effect: oxygenated blood not mixing with deoyxgenated blood in the right atrium from the superior vena cava
ductus arteriosus
-pulmonary artery to aorta without passing through the lungs
-connects pulmonary artery and aorta, favors shunting of blood from pulmonary artery to aorta- oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mixed
-high priority organs still get oxygenated blood- brain from aortic arch, heart from coronary arteries
-aortic arch and coronary arteries both from aortic root, so oxygenated blood travels in them
fetal pulmonary vessels
-filled with fluid
-very resistant
-very little flow
transition to postnatal life- 2 major events following birth
-crying
-cutting of umbilical cord
when baby cries
-lungs go from squeezed down to full of air
-once lungs get full of air, vessels open up and resistance goes down
-flow to lungs goes way up, right ventricle now pumping against much less resistance, so RV pressure goes way down (and RA pressure goes down)
umbilical cord clamping and cutting
-fetal aorta now no longer connected to placenta
-when cord is clamped, fetal aorta seeing higher resistance and the pressure in the aorta goes up
-increase in pressure felt back to the heart where LA and LV pressure rises
what closes the 3 shunts post-birth?
-foramen ovale: pressure changes in atria (LA > RA now)
-ductus arteriosus: kept patent in utero by prostaglandins mostly produced by the placenta (a little produced by ductus arteriosus itself), so when placenta is clamped the prostaglandins go down, which closes the ductus arteriosus; permanent closure after a few weeks
-ductus venosus: decreased flow; umbilical vein no longer has blood flow after clamping, so ductus venosus also has no blood flow; ductus venosus narrows and eventually closes, permanent closure days post-partum and eventually become ligamentum venosum (ligament)