Vibrionaceae Family and Campylobacter
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms

What 3 genera are curved GNRs that are oxidase + and ferment glucose (oxidizers in O/F)?
Vibrionaceae Family:
Vibrio species
Aeromonas
Chromobacterium
Most Vibrio species are _________, meaning they require increased amounts of NaCl to grow.
halophilic
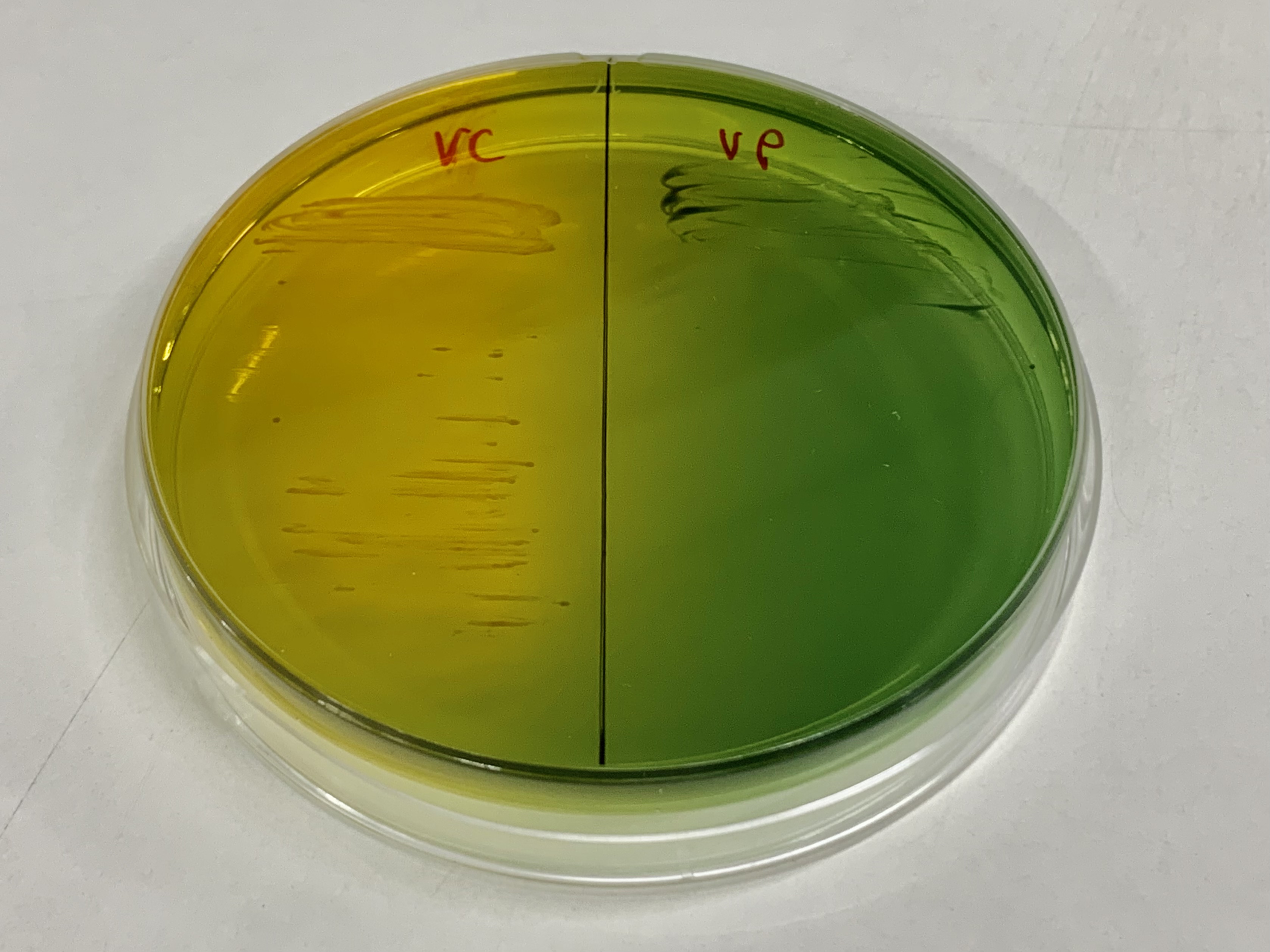
What growth media is used to isolate Vibrio species?
TCBS (thiosulfate citrate bile sucrose)
How is TCBS selective for Vibrio species?
high salt concentration inhibits normal flora
How is TCBS differential?
sucrose fermentation
yellow = Vibrio cholerae
green = Vibrio parahemolyticus
What curved GNR causes “rice water stools” after ingestion of infected shellfish?
Vibrio cholerae
What curved GNR causes seafood gastroenteritis?
Vibrio parahemolyticus
Vibrio (cholerae/parahemolyticus) REQUIRES high salt concentrations to grow.
Vibrio parahemolyticus
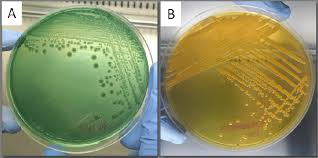
Which TCBS plate has Vibrio cholerae and which plate has Vibrio parahemolyticus?
A = Vibrio parahemolyticus (does not ferment sucrose)
B = Vibrio cholerae (ferments sucrose)
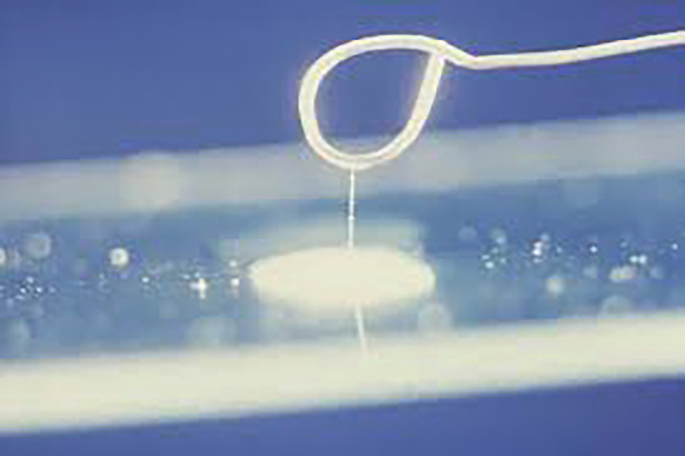
What test is used to differentiate Vibrio species from Aeromonas species? What reagent is used in this method?
string test
0.5% sodium deoxycholate
What are the expected results for Vibrio species and Aeromonas species when performing a string test?
Vibrio species = + (string)
Aeromonas species = - (no string)
What curved GNR that is similar to Aeromonas causes gastroenteritis?
Pleisiomonas shigelloides

What curved GNR has a characteristic purple pigment on SBA and MAC and has an almond-like odor?
Chromobacterium violaceum

What 2 genera are curved GNRs that are oxidase + and do NOT ferment glucose (non-oxidizers in O/F media)?
Campylobacter species
Helicobacter species
What is the atmospheric and temperature requirements for Campylobacter species?
microaerophilic (5% O2 and 10% CO2)
42C

What curved GNR has runny tan/pink colonies on selective media?
Campylobacter jejuni
What 2 types of media are used to isolate Campylobacter jejuni?
Campy blood agar
Skirrow’s blood agar
How are campy blood agar and Skirrow’s blood agar selective for Campylobacter jejuni?
antibiotics inhibit growth of natural flora
What curved GNR causes infection my ingesting raw chicken and is the most common cause of gastroenteritis?
Campylobacter jejuni
What organism causes gastritis and peptic ulcers?
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is able to neutralize stomach acidity because it possesses the enzyme _______.
urease
The CLO test and the urea breath test can both be used to detect what curved GNR?
Helicobacter pylori