Protein Structure, Gene Expression Analysis, and Recombinant DNA Techniques
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the primary method used to study gene expression through RNA quantity?
Northern Blot Analysis
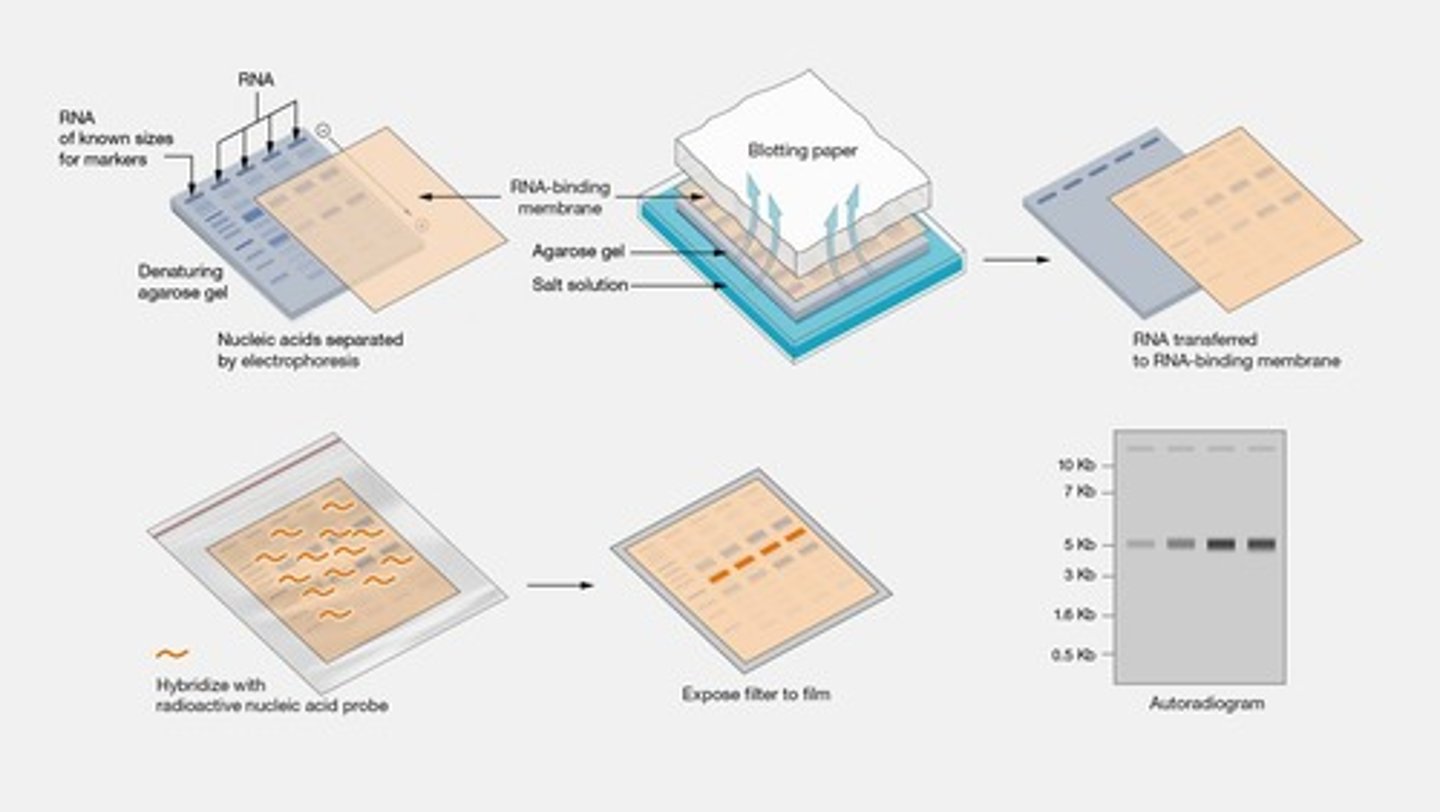
What does a probe do in Northern Blot Analysis?
It binds to the specific RNA you want to study.
What indicates more gene expression in a Northern Blot?
More probe signal means more gene expression.
What is cDNA?
Complementary DNA synthesized from mRNA.
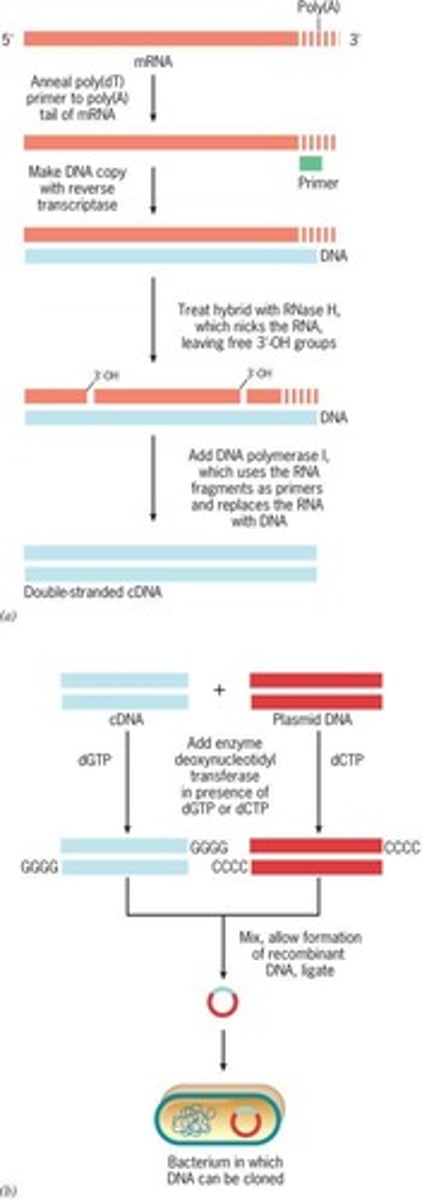
What is the role of reverse transcriptase in cDNA synthesis?
It synthesizes DNA from the RNA template.
What is the purpose of PCR in studying mRNA transcripts?
To amplify specific DNA fragments derived from cDNA.
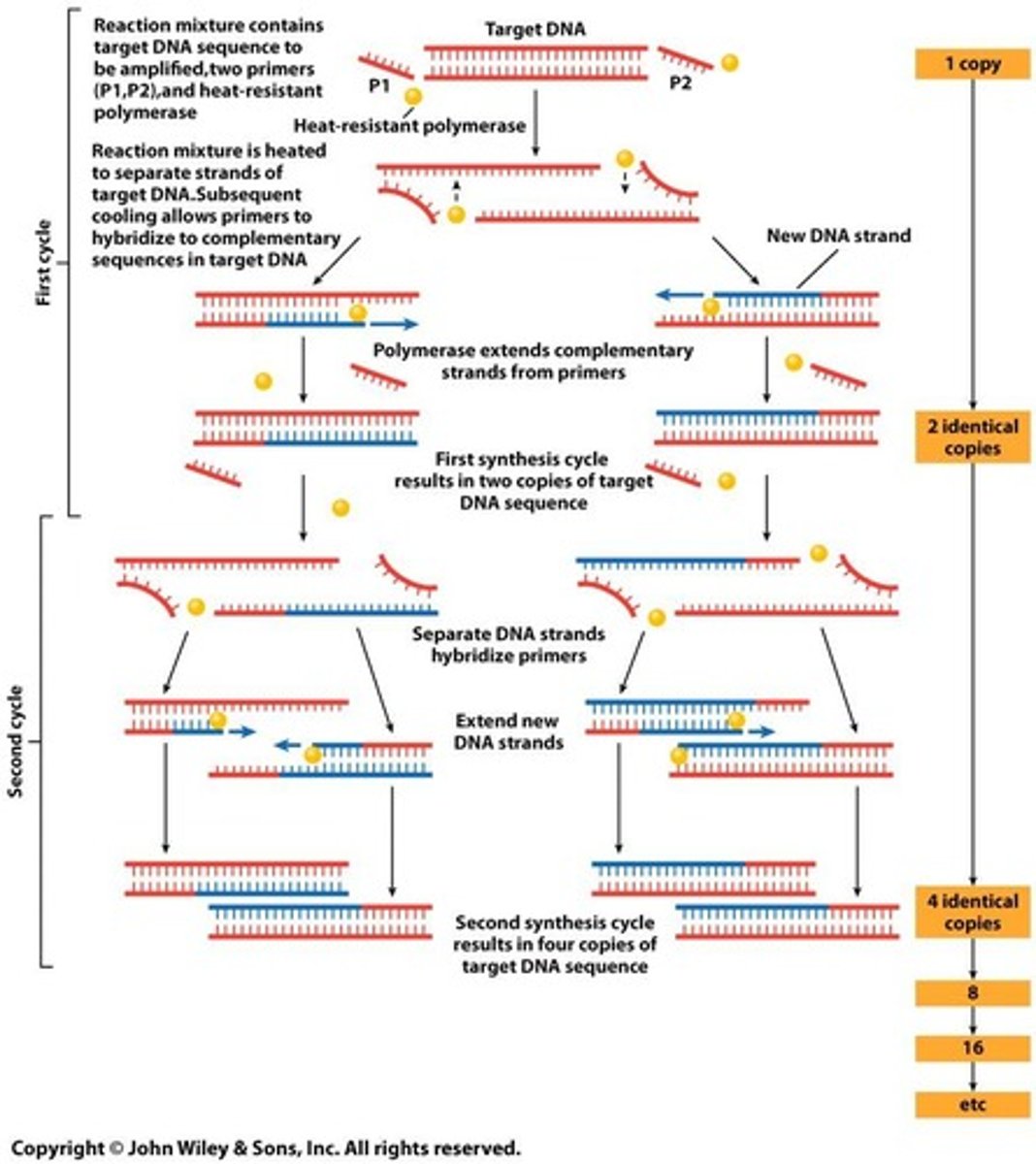
What does semiquantitative PCR measure?
It analyzes mRNA expression levels.
What is the significance of band intensity in PCR results?
It corresponds to the relative abundance of mRNA.
What are the two major secondary structures of proteins?
Alpha helices and beta sheets.
What drives the formation of tertiary protein structures?
The hydrophobic effect.
What are quaternary structures of proteins composed of?
Two or more polypeptide subunits.
What is the primary structure of proteins?
The order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
How are peptide bonds formed?
Through a condensation reaction between amino acids.
What is the role of DNA ligase in recombinant DNA technology?
It joins DNA fragments together.
What is a recombinant plasmid?
A plasmid that contains DNA sequences from multiple sources.
What is the purpose of using antibiotic resistance genes in plasmids?
To select for bacteria that have taken up the plasmid.
What is site-directed mutagenesis?
A technique to introduce specific mutations into a DNA sequence.
What can changes in protein primary structure affect?
Protein function and stability.
What is the difference between homodimers and heterodimers?
Homodimers consist of identical subunits, while heterodimers consist of different subunits.
What is the significance of the N-terminus and C-terminus in proteins?
They indicate the directionality of the polypeptide chain.
What are the two phases of generating a protein expression vector?
Obtain the coding sequence and ligate it into an expression vector.
What is the purpose of a sham reaction in PCR?
To ensure that PCR amplification is not due to genomic DNA contamination.
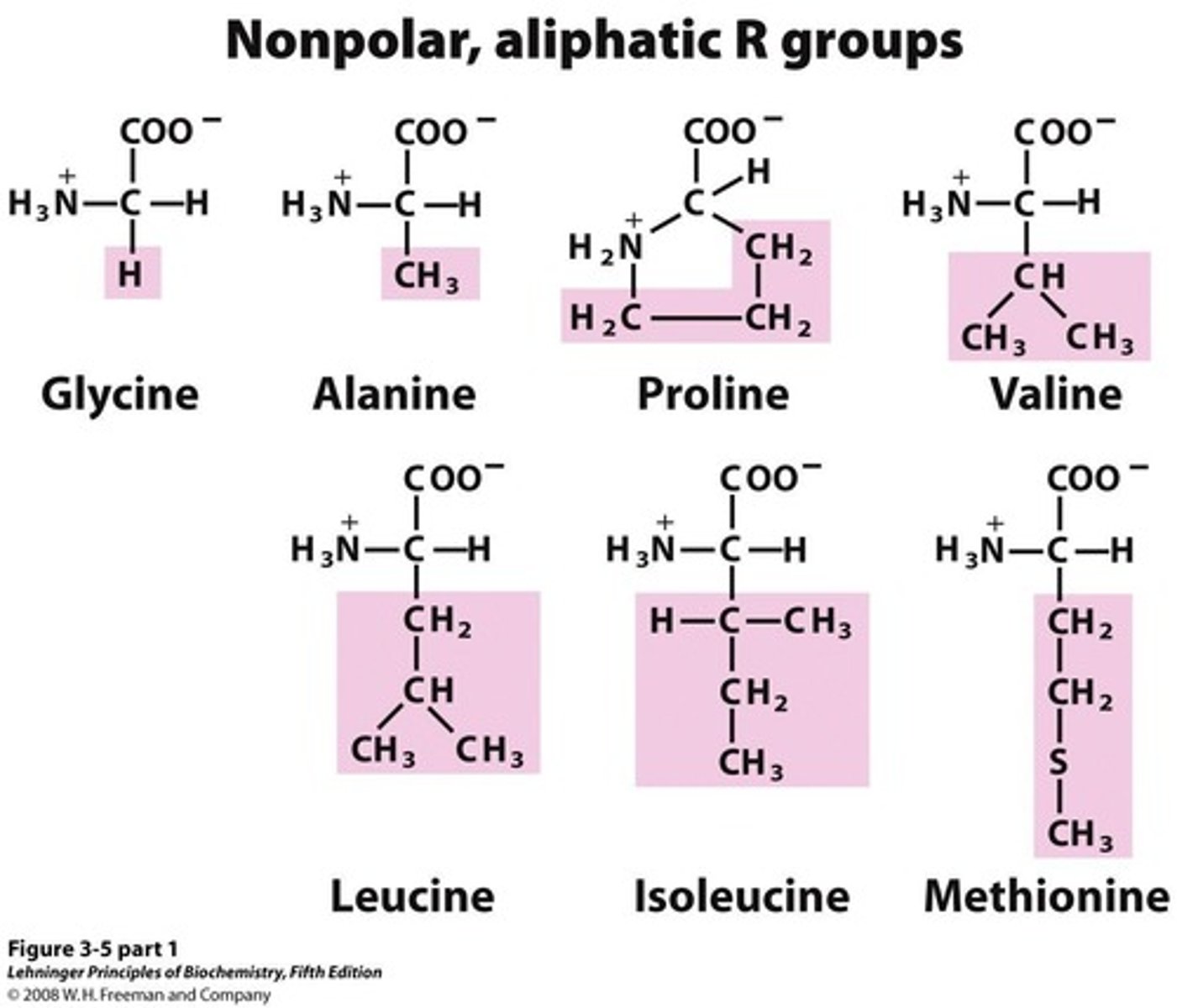
What are the three types of amino acids based on their R groups?
Nonpolar, polar but uncharged, and charged (positively or negatively).
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in secondary protein structures?
They stabilize the folding of the polypeptide chain.
What type of RNA is used as a template for synthesizing cDNA?
mRNA (messenger RNA).
What is the primary driving force for quaternary protein structure formation?
The hydrophobic effect.
What are prions and how are they related to protein structure?
Infectious proteins that misfold and aggregate, causing diseases.