Renal 1 - Intro, diffusion, tonicity, fluid movement
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Functions of kidney
1. Regulate blood volume/pressure
2. Regulate acid base balance
3. Excretion
4. Synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis)
5. Secretion of hormones
Kidney excretion function
- Excrete urea, uric acid, creatinine, bilirubin
- Remove foreign chemicals (drugs, food additives, pesticides)
Hormones secreted by the kidney
EPO, Renin, 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D
Where is uric acid fro
Nitrogenous base breakdown
Where is urea from
Protein breakdown
What % of body weight is water
60%
What percent is extracellular fluid of total body weight
20%
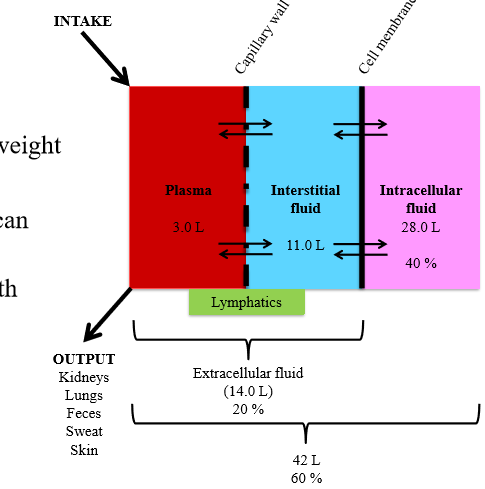
Components of extracellular fluid
Plasma, interstitial fluid
When do fluid volume changes occur in the body
- Health disorders (dehydration, diarrhea)
How does fluid volume changes occur
Osmosis - rapid movement of water
How is plasma volume altered
- Intake of water in GIT (increase plasma)
- Loss through urine, expiration, sweat, skin evaporation
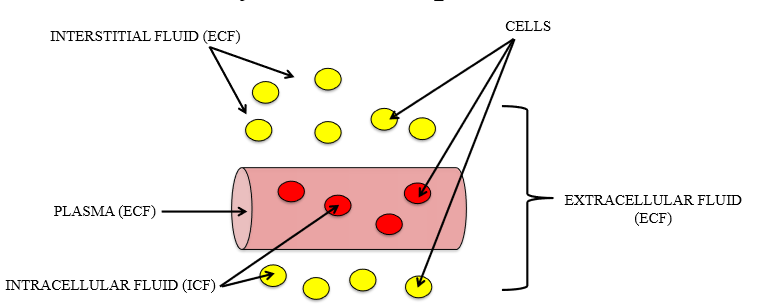
Body fluid components
intracellular and extracellular (plasma + interstitial)
Is sodium higher or lower in ECF than ICF
Higher (140 > 12 mM)
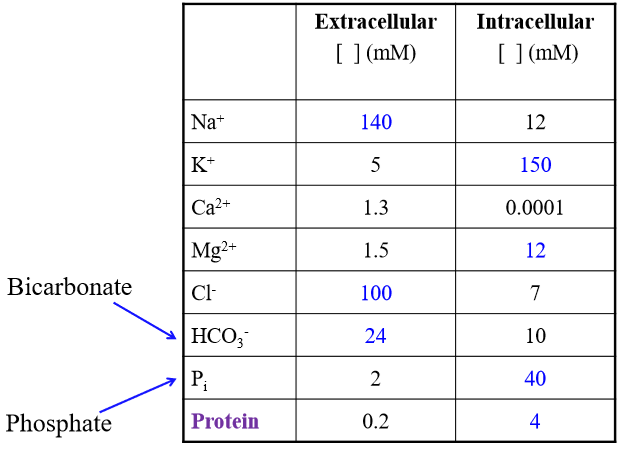
Is Potassium higher or lowe in ECF than ICF?
Low (5 < 150 mM)
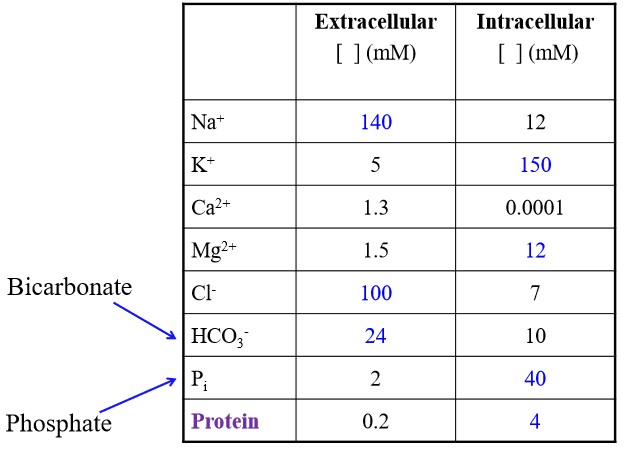
Is chloride higher or lower in ECF than ICF
Higher (follows sodium) (100 >7)
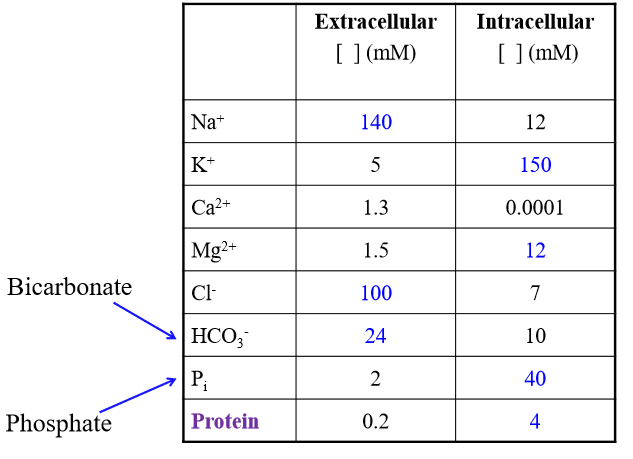
Major solutes of ECF
Na+, Cl-, HCO3-
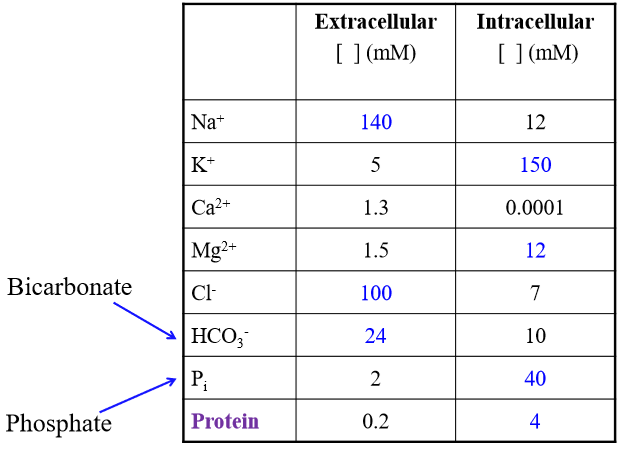
Major solutes of ICF
K+. Phosphate, Protein
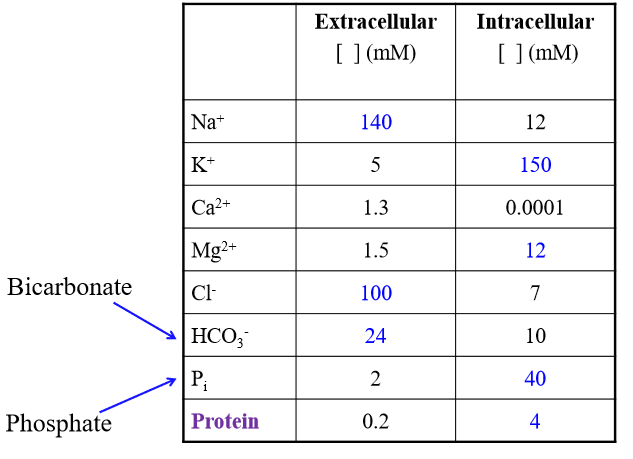
Role of aquaporins
Channels allowing for water diffusion
Osmole
1 mole of dissolved particles
Osmolarity
Number of solutes per unit volume of solution measured in mol/L
What unit is water concentration measured in?
Osmolarity (mol/L)
Why is water measured in osmolarity
Water contains dissolved solutes - concertation of water depends on soluble substances in water
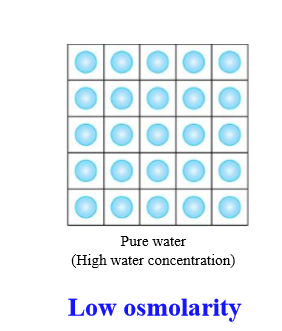
If a solution is low osmolarity, what is the water concentration
High concentration
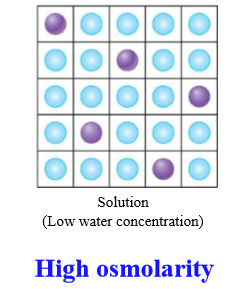
If a solution is high osmolarity, what is the water concentration
Low concentration
Effect on water concentration if you add more solute
Decreased concentration (and vice versa)
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from one location to another as result of random thermal motion
Steps of diffusion
1. Higher concentration of molecules move toward lower concentration
2. Solute molecule evenly distribute
3. Diffusional equilibrium
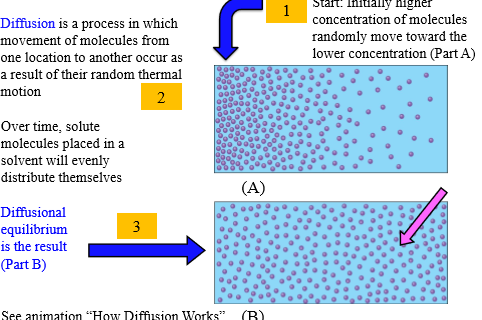
Diffusional equlibrium
Concentration of solute in solvent is equal throughout volume
Diffusion of water through cell membrane (steps)
1. Water diffuses to side with higher osmolarity (lower water concentration), Solute moves to area with lower osmolarity
2. Diffusional equilibrium - movement of water and solute has equalized concentrations
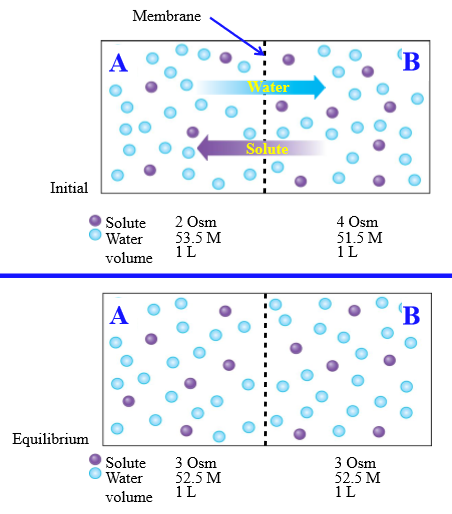
Osmosis
Net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher to lower water concentration
Osmotic pressure
Opposing pressure required to stop osmosis completely
Steps of osmosis
1. Partition between components is permeable to water only. Water moves from high to low concentration
2. Diffusional equilibrium occurs, equalizing solute concentration
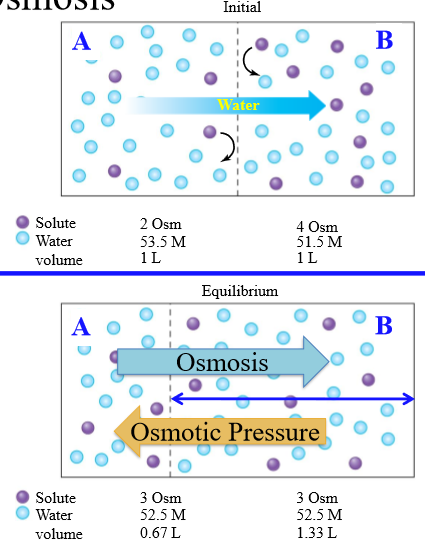
How is tonicity determiend
Concentration of non-penetrating solutes of an extracellular solution relative to the intracellular environment of the cell
Effect of tonicity
Changes in cell volume
Three conditions of tonicity
Isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic
Isotonic
Same osmolarity inside and outside of the cell
Hyper tonic
Higher osmolality outside the cell than inside the cell
Hypotonic
Lower osmolarity outside the cell than inside the cell
Normal osmolarity inside a cell
300 mOsm/L
Difference between isotonic and isosmotic
Isosmotic = solutes are penetrating membrane
Why is isotonic saline given to patients
Prevents RBC explosion or shrinking
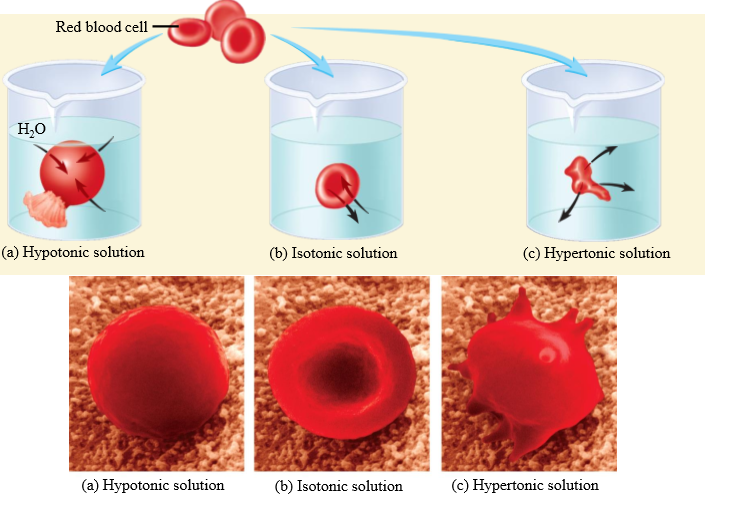
Effect of hypotonic solution on RBC
Cell swells
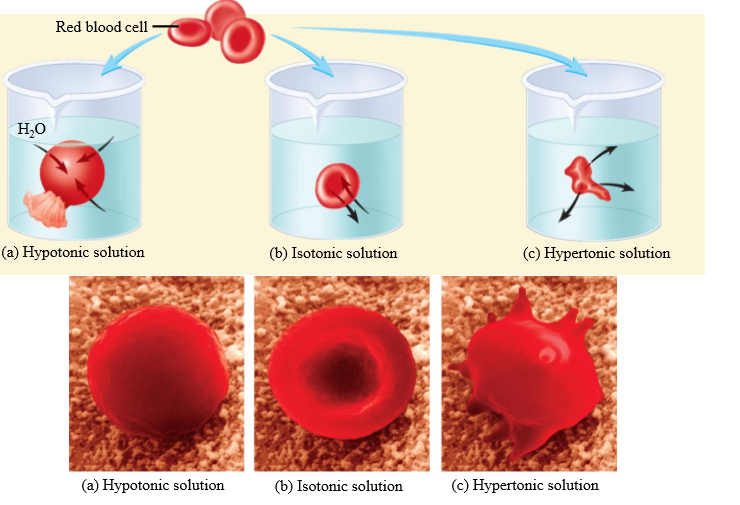
Effect of isotonic solution on RBC
No change in cell volume
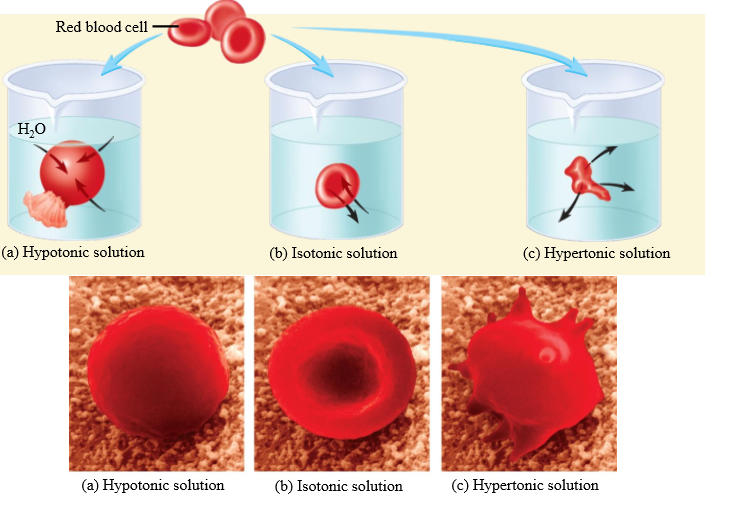
Effect of hypertonic solution on RBC
Cell shrinks
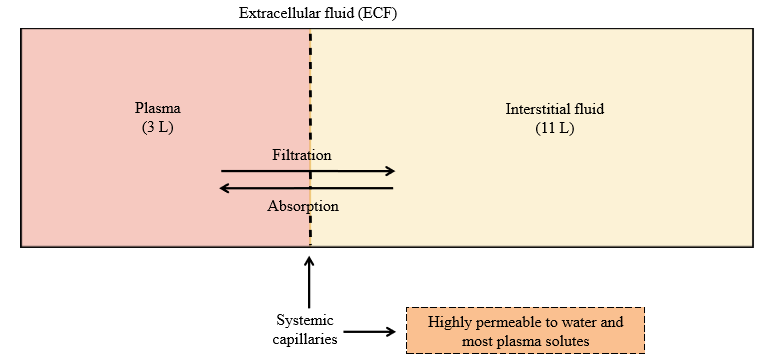
Systemic capillary permeability
Highly permeable to water and most plasma solutes (exchange between plasma and interstitial fluid)
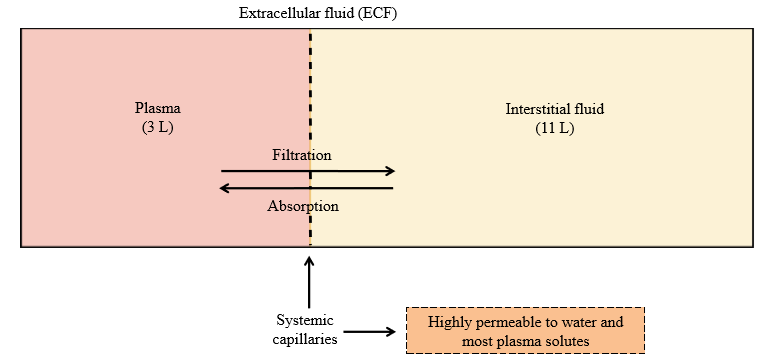
Absorption
Movement of solute/water into the blood (plasma) from interstitial fluid
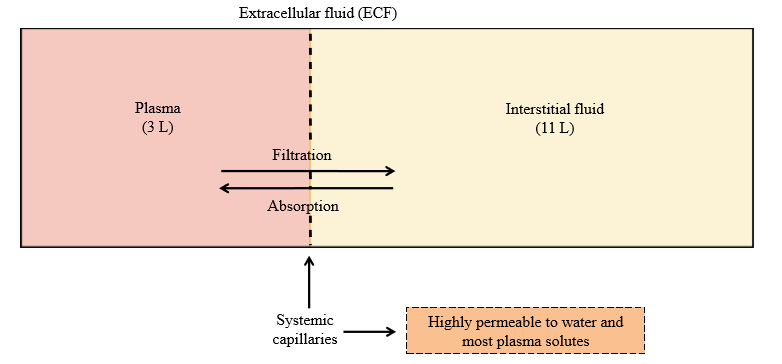
Filtration
Movement of solute/water out of the blood (plasma) into the interstitial fluid
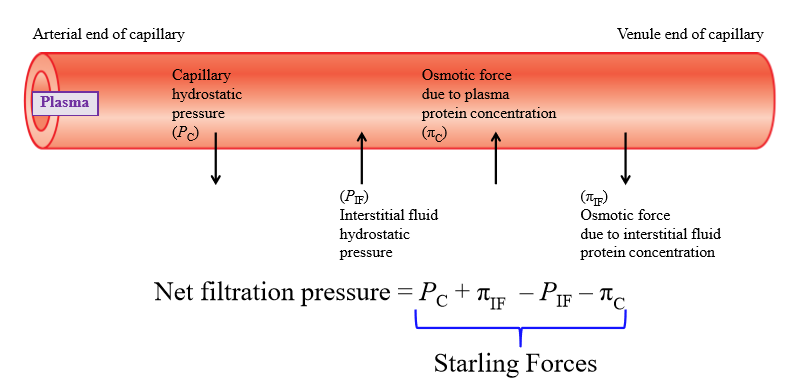
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by fluid inside capillary walls (pushes fluid out of capillary into interstitial fluid)
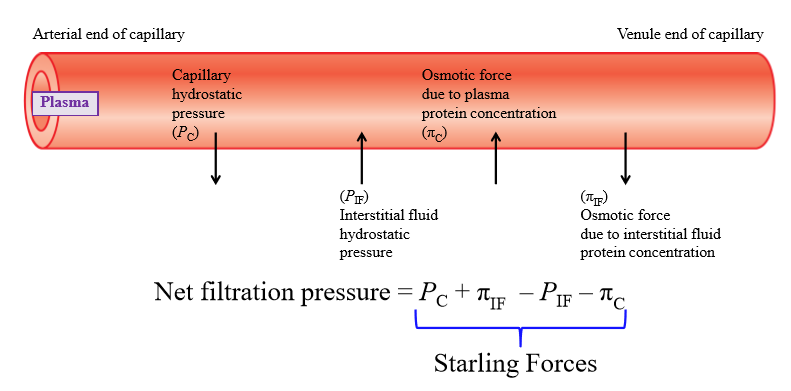
Interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by IF onto capillary wall (exterior)
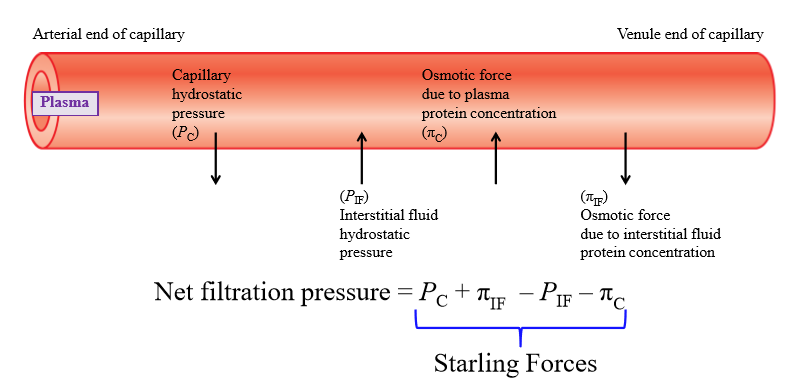
Osmotic force due to plasma concentration
Negatively charged plasma proteins cause water to move into capillary
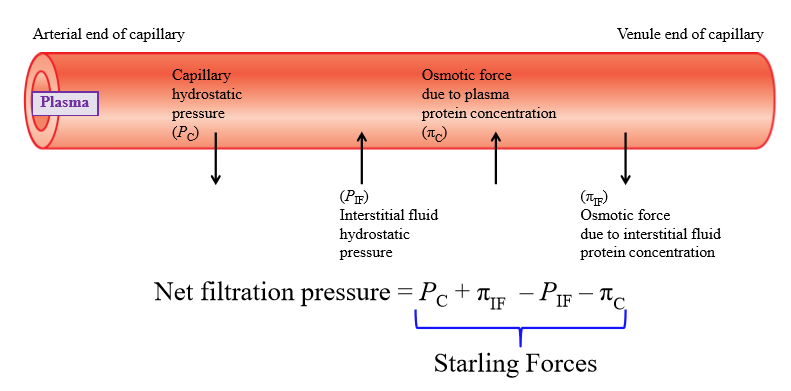
Osmotic force due to interstitial fluid protein concentration
Some plasma proteins escape capillary and end up in IF - proteins pull water with them
Is filtration or absorption favored at arterial end of capillary
Filtration favored
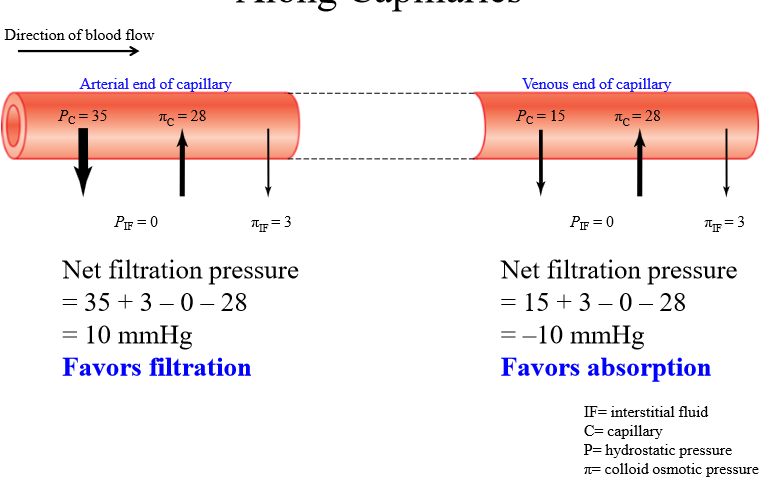
Is filtration or absorption favored at venous end of capillary
Absorption favored
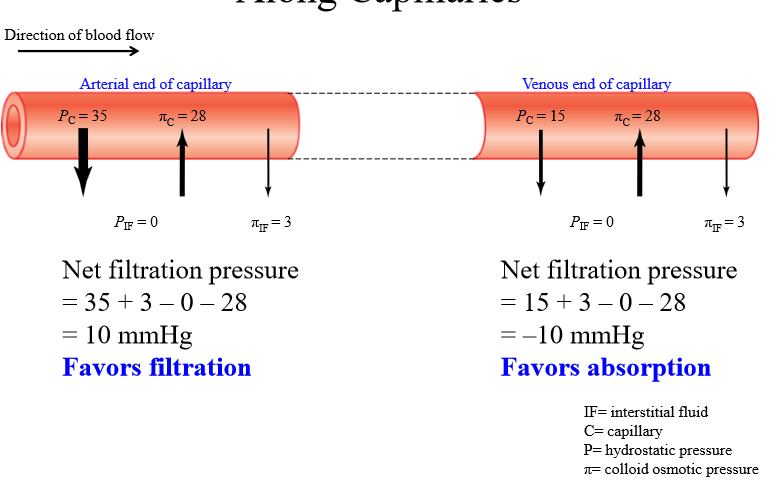
Change in starling forces across capillary
Capillary hydrostatic pressure decreases from arterial to venous end. Other pressures stays the same
Homeostasis
Total body balance of any substance
- Gain via ingestion/metabolism balanced with loss via excretion/metabolism
What do kidneys do with excess water
Excrete in urine
What do kidneys do if dehydrated
Keep water in plasma