Biochemistry
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Organic Compound
Compounds ranging from simple molecules to colossal ones that mostly contain hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms, or hydrocarbons
What makes Carbon unique
This element has the ability to form complex and diverse molecules and combine with other elements because it has 4 valence electrons.
Tetravalence
The ability of an atom able to form 4 covalent bonds with 4 valence electrons
Tetrahedral Shape
A shape formed by molecules with multiple carbons
Flat Shape
A shape formed by molecules that have two carbon atoms joined by a double bond
Hydrocarbon
Organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
Functional Group
A group of atoms that are often attached to the skeletons of organic molecules. Gives each molecule its unique properties.
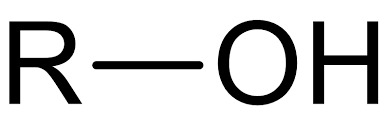
Hydroxyl Group
Found in carbohydrates and alcohol
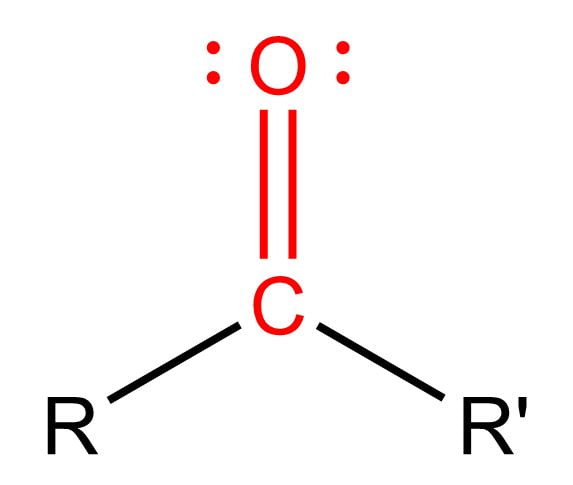
Carbonyl Group
Found in formaldehyde
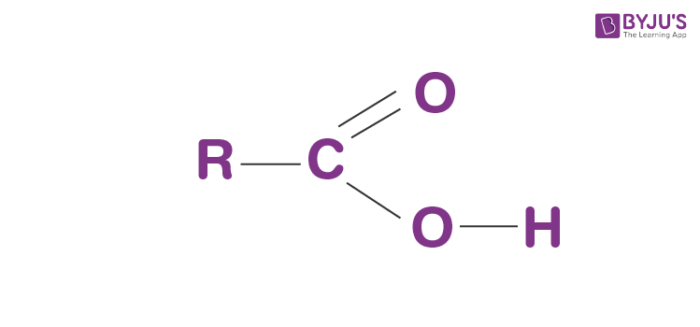
Carboxyl Group
Found in amino acids and vinegar
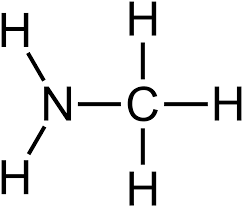
Amino Group
Found in ammonia
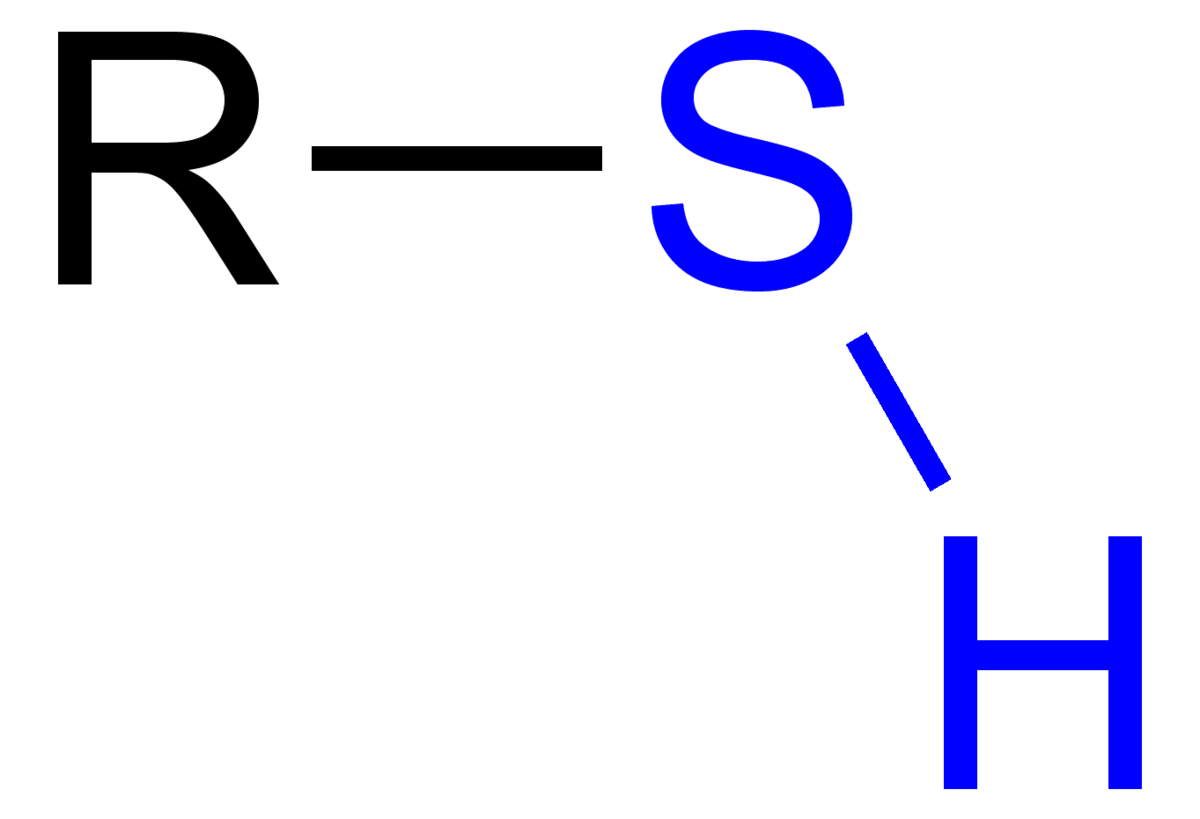
Sulfhydryl Group
Found in proteins and rubber
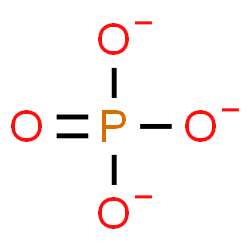
Phosphate Group
Found in phospholipids, nucleic acids, and ATP
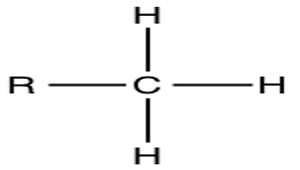
Methyl Group
Found in methane gas
Macromolecules
Large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms. Biomolecules.
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many monomers.
Monomer
An atom or small molecule that can bond together to form polymers
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
Three of four classes of life’s organic molecules that are polymers
Dehydration Reactions
The formation of a logner polymer by removing a water molecule to link together another piece
Hydrolysis
Reverse of dehydration in which polymers dissassemble by adding water molecule to break off a bond
Carbohydrate Molecule
A polysaccharide that serves as fuel and building material. Polymers of sugar. “Complex carbs”
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple sugars, or monosaccharides
Monosaccharide
Single “simple” sugars that are the structural unit of carbohydrates (polysaccharides) that contain the molecular formula of C6H12O6 in a ratio of 1:2:1 and is also used for short term energy storage.
Location of Carbonyl Group and number of carbons
This determines how a monosaccharide is classified. In example, glucose is a tetrose as it has 4 carbons.
Isomer
Molecules with the same molecular formula but arranged differently, such as glucose and fructose. Typically drawn as a linear skeleton, but form rings in Aqueous solutions.
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides that are joined through dehydration synthesis.
Lactose
Common disaccharide made of glucose and galactose
Maltose
Common disaccharide made of glucose and glucose
Sucrose
Common disaccharide made of glucose and fructose, table sugar.
Polysaccharide
Polymers of monosaccharides, or complex carbohydrates, that have storage and structural roles determined by sugar monomers and position of glycosidic linkages
Starch
A storage polysaccharide of plants consisting entirely of glucose monomers
Glycogen
A storage polysaccharide of animals that humans (and other vertebrates) store in the liver and muscle cells
Cellulose
A structural polysaccharide that is a major component of the wall of plant cells. Enzymes cannot digest the beta links in this, so cellulose in human food are nondigestable, being digested as soluble fiber.
Lipids
Fats, utilized for energy storage, membranes, insulation, and protection. This is the one class of macromolecules that do not form polymers. Hydrophobic due to being made of mostly hydrocarbons.
Fats, phospholipids, and steroids
The most important lipids
Acid
A molecule that donates/gives up a hydrogen ion, or a molecule that will break off in water.
Fatty Acid
A long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group attached to it, which is what makes it an acid. Can be saturated or unsaturated.
Saturated Fat
Fatty acid that comes from animals and has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. Does not have any double bonds and is solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated Fat
Fatty acid that comes from plants that has one or more double bonds (monounsaturated or polyunsaturated). Liquid at room temperature, seen as oils. Has bent shape.
Hydrogenation
The process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated fatty acids. Turns them from a liquid to a solid at room temperature.
Triglyceride/Triacylglycerol
Three fatty acids joined together with glycerol.
Phospholipid
A lipid that has two hydroxyl groups on glycerol joined to fatty acids, and the third one joined to a phosphate group that’s joined to a polar group of atoms.
Polar Head
The hydrophilic phosphate and polar groups at the head of a phospholipid.
Nonpolar Tails
The hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains at the end of a phospholipid
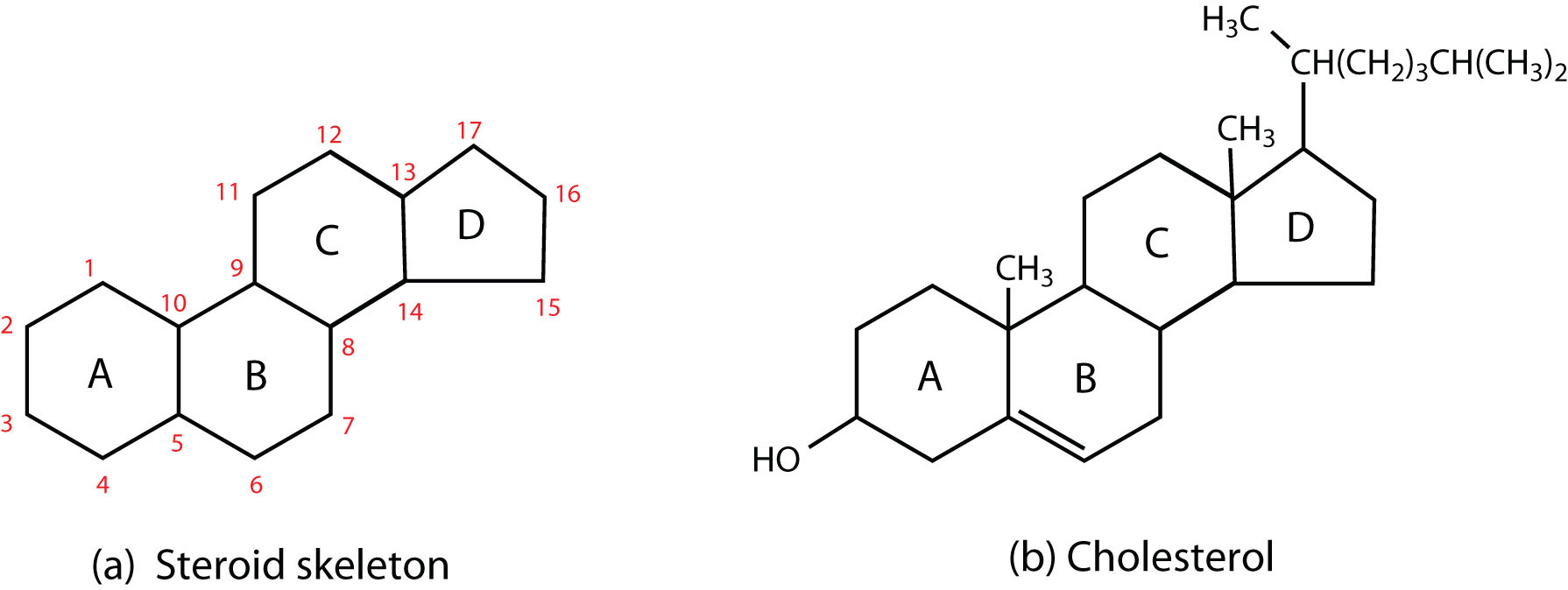
Steroids
Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.
Protein
A large macromolecule that have many structures resulting in many functions. Account of 50% of dry mass of most cells.
Protein function in which they act as messengers
for cellular communications through hormones
Protein function in which they transport globins
Through the membrane
Antibody Protein Function
Immunoglobin proteins defend against foreign substances
Structural support, storage, and movement of fiber
Common protein functions
The shape
What determines the function of a protein.
Amino Acid
Monomer of protein or polypeptides that are composed of a carboxyl group, amino group, and an R group. The building blocks of protein. A single peptide.
Peptide Bond
A bond between two amino acids
Primary Structure of Protein
The unique sequence of amino acids including the number of amino acids and the length.
The amount of amino acids in the human body
20 amino acids
Secondary Structure of Protein
Consists of coils and folds in the polypeptide chain. Depicted as a helix shape or a pleated sheet form.
Tertiary Structure of Protein
Structure of protein that creates a 3D arrangement of the polypeptide chain.
Quaternary Structure of Protein
Several protein chains packed together in a 3D shape.
Catalyst function
Increases reaction rates in the body byt reducing the energy needed to reach activation state without being changed.
Enzyme
Proteins that function as catalysts. Lowers the energy of activation. Speeds up one or few select chemical reactions, and can be reused as it is not consumed during reactions
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Formed by a reactant (substrate) binding to the active site on an enzyme. The thing the enzyme acts on. Such as sucrase, which breaks apart sucrose into glucose and fructose.
Denaturation
The loss of a protein’s native conformation due to changes in external factors, causing the protein to be biologically inactive.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecule composed of nucleotides. The body contains two types: deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Known as [ ]NA. Uses Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine.
Ribonucleic Acid
Known as [ ]NA. Uses Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The primary energy transferring molecule in the cell. Consists of adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups.