Pharm- Depolarizing and non-depolarizing blockade
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
List the most common SE of Succ
Dysrhythmias- bradycardia
Myalgia from fasciculations
Hyperkalemia
Myoglobinuria- presence of an excess amount of myoglobin in the urine. It is mostly caused by muscle breakdown, releasing a high amount of myoglobin in the blood. Myoglobinuria can lead to acute kidney injury
INC Intragastric Pressure
INC IOP
INC ICP
Malignant Hyperthermia trigger
Sequence of neuromuscular blockade [1st paralyzed to last paralyzed]
Eyes and digits→trunk and abdomen→intercostal muscles and diaphragm[more junctional receptors]
discuss the SE of Bradycardia w/ Succ
mimics Ach at the M2 receptors, muscarinic receptors of SA node, and pre-ganglionic nicotinic receptors and causes:
brady, junctional rhythm or sinus arrest
More prominent in patients with high sympathetic tone, such as children
Pretreatment with NDNMB can diminish this
Discuss the SE myalgia w/ succ administration
Prominent in neck, back, & abdomen
Generalized depolarization → unsynchronized contraction (fasciculations)
PreTx with ND NMBD
(1/10 ED95 NDNMB)
If visible muscle contractions DEC , then myalgia DEC
Defasciculation
Small amount of NDP is given to bind to alpha subunits to prevent a dramatic depolarization when SCh arrives
This technique may prolong the onset time of SCh but this can be overcome by increasing the intubating dose of SCh
INC ICP w/ succ
Increased CBF & ICP with SCh not consistently observed but is due to fasciculations when it occurs
Intracranial tumors or head trauma
If increased ICP is detrimental
Pretreatment with ND is effective
Prior hyperventilation to vasoconstrict vessels in the brain
Lidocaine IV prior to intubation
hyperkalemia and Succ
pt. at risk:
Clinically unrecognized muscular dystrophy & myopathies
Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy
Burn injury > 24 hrs post injury
Denervation → skeletal muscle atrophy [in bed for long time]
Severe skeletal muscle trauma >72 hrs
Upper motor neuron lesions
Guillain-Barre
Prolonged immobilization
Crush or burn injuries have high serum potassium levels from significant muscle injury (rhabdomyolysis) which is compounded with SCh administration
PreTx with ND NMBD, NO effect on magnitude of K+ release
avoid succ in peds < _______ y/o
and especially in ____ pt b/c Hyperkalemia that results leads to cardiac arrest and death
10
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Discuss extrajunctional receptors SE seen w/ Succ
Up-regulation of extrajunctional ACh receptors
INC # of receptors→ INC depolarization
They stay open 4 X longer than normal–< Significantly INC K levels
Occurs with
muscle atrophy
Myopathies
Denervation injuries
Prolonged immobilization
discuss INC Intragastric Pressure seen w/ Succ- [not a huge issue]
GE sphincter opens > 28 cm H20 which is hard to overcome
15 cm H2O in pregnant patients
Increased intensity of fasciculations results in increased intragastric pressure
Causes in increase in lower esophageal sphincter tone.
PreTx with ND NMBD
If visible muscle contractions DEC , aspiration risk DEC esp with concomitant cricoid pressure
INC IOP SE seen w/ Succ
Striated muscle of the eye contains several motor end plates
SCh INC IOP 2 - 4 min post injection
Lasts only 5-10 minutes
Theory: SCh may cause extrusion of global contents if patient has open eye injury
Never been substantiated
pretx w/ NDNMB
Legal issue- b/c patient can go blind and sue ur ass
metabolism of Succ
how is it metabolized and what is the metabolite?
Plasma cholinesterase (pseudocholinesterase) rapidly hydrolyzes SCh
Not found in significant amounts at NM junction
Quality & quantity important
Small fraction SCh reaches NMJ
Succinylmonocholine – only active metabolite that is 1/20th to 1/80th as potent
SCh action terminated primarily by _________
Degraded via hydrolysis by plasma cholinesterase aka _____
diffusion away from NMJ
pseudocholinesterase
Phase 1 depolarizing block
general info
Sustained opening of ion channels
Depolarization occurs
Fasciculation: a small local contraction of muscles, visible through the skin, representing a spontaneous discharge of a number of fibers innervated by a single motor nerve filament
Intracellular; K+ leakage serum K+[ ] an average of 0.5 mEq/L
Phase 1 specific characteristics
Dose Related DEC in intensity of contraction in response to a single twitch
DEC Amplitude but sustained response to continuous stimulation [NO FADE]
TOF ratio > 0.7 or No fade
Absence of posttetanic facilitation
Fasciculations
Augmentation of block by anticholinesterase (AChase) drugs
![<ul><li><p><span>Dose Related DEC in intensity of contraction in response to a single twitch</span></p></li><li><p><span>DEC Amplitude but sustained response to continuous stimulation </span><strong><span>[NO FADE]</span></strong></p></li><li><p><span>TOF ratio > 0.7 or No fade</span></p></li><li><p><strong><span>Absence of posttetanic facilitation</span></strong></p></li><li><p><span>Fasciculations</span></p></li><li><p><span>Augmentation of block by anticholinesterase (AChase) drugs</span></p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/05f19a5f-f571-4ea6-8228-276140ad6218.jpeg)
phase II block w/ succ
Like Non-Depolarizing blockade
Dose related decrease in twitch height
DEC TOF twitch height with fade
Tetanus fades
Post-tetanic facilitation present
Succ characteristics
class
preparation
onset
DOA
indications
The only one in this class used in the U.S.
Di-quaternary ammonium compound
Unstable-refrigeration required
Preparation:
2% solution; 20 mg/ml in 10 ml vials
Rapid onset: 30-60 sec
Low lipid solubility
Duration: 4-8 min
Rapidly hydrolyzed in the body
Useful for rapid tracheal intubation [RSI]
Common structure in all muscle relaxants
Highly ionized at physiologic pH= lipid insoluble
Quaternary ammonium groups- in NMB
Other NMB commonalities :
Sevo can potentiate the actions of the NMB
Water soluble
Can’t cross BBB or placenta
Lipid membrane barriers
Limited lipid solubility
NOT ANESTHETICS
They do not provide amnesia, analgesia, or narcosis
Succ is CI in these conditions:
myasthenia gravis
congenital myasthenia syndromes [CMS]
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome [LAMS]
presence of extrajunctional receptors- pt w/ injuries or unuse
muscular dystrophies
low plasma cholinesterase
Examples of conditions that can cause Low PChase
Burns
Cancer
Certain neoplasms and cancer drugs
Pregnancy
Certain Drugs
Echothiophate – glaucoma eye drops – stop 4 wks prior to surgery
DEC Hepatic production of Plasma Cholinesterase (PChase)
Severe liver disease
Drug induced DEC of PChase
Neostigmine, but not edrophonium
Glaucoma/myasthenia gravis treatment
Genetic atypical PChase → slowed or absent hydrolysis of SCh
These patients usually remain intubated until further testing is done and or the Succ wears off
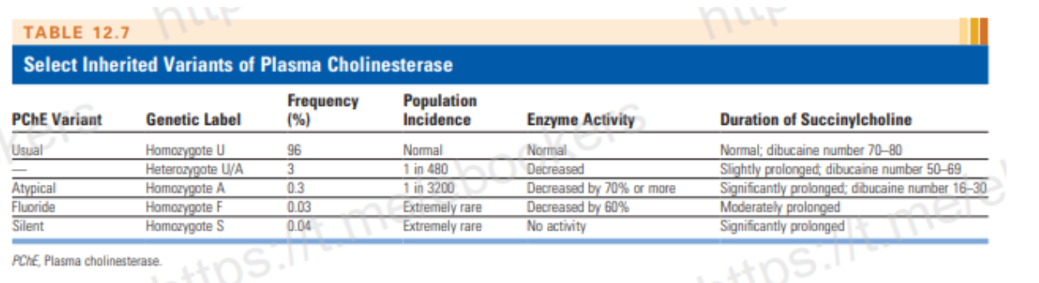
Atypical Plasma Cholinesterase
what is it and how is it dx
Genetically acquired 100 fold lower affinity for the substrate [reaction cannot occur]
Prolonged NM blockade b/c there is not enough enzyme to metabolize the drug
may require postop ventilation
Identified/Dx using Dibucaine (local anesthetic)
Amide
discuss the Dibucaine number test
Dibucaine
A local anesthetic that inhibits normal PChase by ~ 80 %, compared to ~ 20% inhibition of the activity of atypical enzyme
40-60 is considered heterozygous [U/A]
<20 atypical homozygous [A]
Dibucaine # of 80 reflects 80 % inhibition of enzyme activity
Confirms normal Pchase
Quality not quantity
Quantity DEC in liver disease
(normal Dibucaine #)
hereditary variants of PChase
Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes (CMS)
Presynaptic – Defects in ACH synthesis or release
Synaptic – Endplate ACE deficiency
Postsynaptic – Abnormal ACH receptor or Na Channels
Difficult to predict clinical effects d/t variants
Myasthenia Gravis
Postsynaptic – Autoimmune destruction of ACH receptor
Demand problem – plenty of ACH, but no ACHR to work on
Resistant to Sux, sensitive to NDMR
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LAMS)
Presynaptic – Autoimmune destruction of voltage-gated Ca++ channel that triggers release of Ach
affects the communication between nerves and muscles
Sensitive to both Succ and NDMR
LEMS can be caused by a paraneoplastic syndrome or a primary autoimmune disorder. [Most cases are associated with small-cell lung cancer]
AE of ND NMB
Anaphylactic reactions
Airway compromise (if not supported)
Respiratory arrest (if not supported)
Histamine release (mivacurium and atracurium) [Hilarious Monkey Antics]
Avoid in asthmatics
Cholinergic blockade (pancuronium and rocuronium) [Comically Performing Resuscitation]
Avoid in patients who cannot tolerate elevated HR or BP
Contraindications for NMRs
Equipment not available to manage airway/sustain ventilation
Patient is dependent on negative intrathoracic pressure to maintain airway patency or cardiac output
Ex: cardiac tamponade pt
Anaphylaxis to specific agent
Movement during surgery (conscious or evoked) is needed)
describe NDMR MOA
Competitive antagonist-affinity but no intrinsic activity
compete for Ach receptors sites on the pre-and post junctional receptors
Blocks AcH postsynaptically from binding α subunits of the α2βγδ receptor on motor endplate inhibiting depolarization→ skeletal muscle paralysis
Blocks AcH presynaptically (α3β2 type AcH receptors), decreasing mobilization down the axon or fusion with the cleft membrane of AcH vesicles.
aminosteroid NDMR include:
Intermediate Acting
Vecuronium (Norcuron)*
Rocuronium (Zemuron)*
Long Acting
Pancuronium (Pavulon)*
Pipecuronium (Arduan)
End in “-Curonium”
QUINOLINIUM NDMRs include:
BENZYLISOQUINOLINE
Intermediate Acting
Atracurium (Tracrium)*
Cisatracurium (Nimbex)*
Long Acting
d-Tubocurarine (Curare)
Doxacurium (Nuromax)
TETRAHYDROISOQUINOLINIUM
Short Acting
Mivacurium
Rapacuronium- removed from the market b/c it caused bronchospasm in 1/100 pt
characteristics of pancuronium
Bisquaternary aminosteroid drug (2 quaternary amines)
First aminosteroid in clinical use (1968)
Duration: Long (86-100 minutes)
Undergoes minimal hepatic metabolism, extensive renal excretion (prolonged duration in renal failure)
Some affinity for muscarinic receptors (anticholinergic properties) [inc HR by~35% and C.O.]
clinical uses for pancuronium
not really used anymore…but still test us on it…..
Long cases on patients with intact renal function, or who did not need to be extubated
For decades was the NDMR of choice for heart surgery (anticholinergic properties offset bradycardia in high dose opiate cases)
Also drug of choice in execution protocols
vecuronium characteristics
Quaternary aminosteroid drug (1 quaternary amine)
Like pancuronium but missing a methyl group
allowing easier hepatic metabolism via deacetylation
Duration: Intermediate (~40 minutes) until twitch back
Majority is excreted unchanged in the bile (40%) or urine (20-30%)
3 possible by-products of metabolism → 3-Desacetylvecuronium only active one [50% active]
Can build up and make it hard for the kidneys to filter and eventually regain muscle movement
17- Desacetylvecuronium and 3, 17-desacetylvecuronium are inactive
clinical uses of Vecuronium
avoid w/ _____
good b/c it has no ____release or _____ properties
Inexpensive
Good for any surgery longer than 45 minutes (adjust intubation dose)
No histamine release, no cholinergic properties (can give large doses to accelerate onset of intubating conditions)
Avoid if biliary obstruction/hepatic failure, renal failure (use atra/cisartacurium)
Rocuronium characteristics
Quaternary aminosteroid drug (1 quaternary amine)
Only nondepolarizer recommended for RSI (at 2 x ED95 intubating conditions occur in ~2 minutes)
Duration: Intermediate (~40 minutes) [esp w/ high doses]
The smaller the dose, the slower the onset
Majority is excreted unchanged in the bile (80-90%) or urine (10-20%)
Hepatic dysfunction will prolong duration of the drug [not b/c of metabolism but b/c of the fact that it is excreted in the bile]
Duration prolonged by coadministration with sevoflurane; most implicated NDMR in anaphylaxis
clinical uses for rocuronium
Inexpensive (now)
Good for any surgery longer than 20-30 minutes (adjust intubation dose)
No histamine release, mild (if any) anticholinergic properties (can give large doses to accelerate onset of intubating conditions)
Avoid if biliary obstruction/hepatic failure, renal failure (use atra/cisartacurium)
Atracurium characteristics
class
SE
DOA
metabolism
Benzylisoquinolinium (2 quaternary amines)
4 stereocenters, mixture of 10 stereoisomers d/t central plane of symmetry
Histamine release limits speed of administration [ not great for induction ]
Duration: Intermediate (30-60 minutes)
Undergoes Hoffman elimination (33%)/ester hydrolysis (66%) by nonspecific esterases (not butrylcholinesterase aka plasma cholinesterase)
Metabolites (inc. Laudanosine) renally/hepatically excreted
Degrades spontaneously at room temperature-refrigerate
Loses 10-15% of its potency each week it's not refrigerated
Cisatracurium
class
DOA
metabolism
Benzylisoquinolinium (2 quaternary amines)
Single stereoisomer version of atracurium (1 R-cis, 1’R-cis variant)
Does not release histamine
Duration: Intermediate (30-60 minutes)
Undergoes Hoffman elimination (77%)/ ester hydrolysis (~7-10%) by nonspecific esterases (not butrylcholinesterase!)
Metabolites (inc. Laudanosine) renally/hepatically excreted
Degrades spontaneously at room temperature-refrigerate
clinical uses for Cisatracurium
Inexpensive (now)
Good for any surgery longer than 40 minutes (adjust intubation dose), where rapid airway control is not needed
Cisatracurium can be safely used in asthmatics
Drugs of choice in renal/hepatic failure/obstruction (terminated by metabolism, not elimination!)
Mivacurium characteristics
class
SE
DOA
metabolism
Isoquinalone (2 quaternary amines)
Clinical drug is composed of 3 of the 20 possible stereoisomers
Histamine release limits speed of administration; must be administered over at least 30 seconds for intubation
Duration: short (~20 minutes)
Benefit: Undergoes ester hydrolysis (~100%) via butrylcholinesterase (plasma cholinesterase) → gives it a short DOA
Metabolites are physiologically inactive and renally/hepatically excreted
Mivacurium clinical uses and when to avoid use
Good for short surgery, where securing airway quickly not a concern [drug of choice for kid tonsils]
Best avoided in asthmatics [b/c of histamine release]
Good drug in renal/hepatic failure/obstruction (terminated by metabolism, not elimination!)
Avoid in atypical plasma cholinesterase, or if patient recently received neostigmine
Succinylcholine: intubation dose:
Pancuronium: intubation dose:
Vecuronium :Intubation dose:
Cisatracurium Intubation dose:
Mivacurium Intubation dose:
Atracurium Intubation dose:
Rocuronium Intubation dose:
Succinylcholine: intubation dose: 1-1.5 mg/kg
Pancuronium: intubation dose: 0.08-0.12 mg/kg
Vecuronium :Intubation dose: 0.1 mg/kg (relatively potent)
Cisatracurium Intubation dose: 0.1 mg/kg (potent)
Mivacurium Intubation dose: 0.2 mg/kg (moderate/high potency)
Atracurium Intubation dose: 0.5 mg/kg (moderate potency)
Rocuronium Intubation dose: 0.6 mg/kg (low potency)
"Silly Penguins Venture Carelessly, Making Awkward Ruckus"- increasing dose = lower potency
general comparisons of aminosteroids and quinoliniums
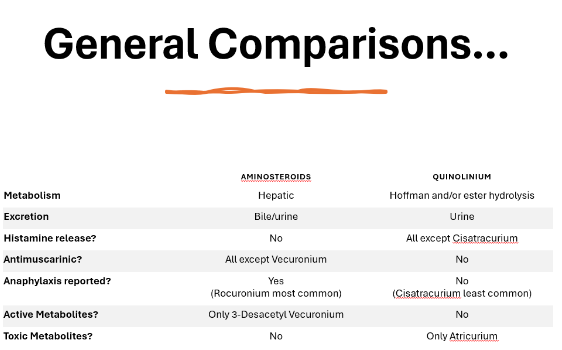
Aminosteroid metabolism
Hepatic metabolism- very minimal
Only active metabolite is vecuronium→ 3-desacetyl vecuronium
Aminosteroids are dependent on hepatic and/or renal elimination, and so will be prolonged in patients with impairment/obstruction
Quinolinium metabolism
Hoffman and/or ester hydrolysis metabolism- extensive metabolism
describe Hoffman elimination and hoffman products for cisatracurium
pH and temperature-dependent degradation [not organ dependent]
elimination reaction that breaks down an organic compound into simpler substances by removing a weak acid under the influence of a strong base
Favored by proton-poor and warm conditions
Essentially a reversal of how quaternerary ammonium ions are made.
Hoffman Products:
For cisatracurium, approximately 80% of the drug is metabolized into laudanosine (~20 excreted unchanged via hepatic/renal routes)
Laudanosine levels from cisatracurium are ~1/5 that of atracurium d/t smaller doses and differences in hydrolyzed fractions
Laudanosine is the metabolite that can cause seizures in high concentrations!
_________ is metabolized by butrylcholinesterase (like succinylcholine), so is subject to the same caveats about metabolism which include:
Mivacurium
Prolonged by atypical butrylcholinesterase
Might be prolonged by neostigmine administration (not significant once NM function has returned)
Benzylisoquinoliniums metabolism
are terminated by metabolism, not elimination, so are good choices for patients with organ impairment
more extensive metabolism than aminosteroids.
Metabolized by hoffman elimination and plasma esterases



























