Comprehensive Overview of Decision Making in Management for Computer Science Students
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is an integral part of being a manager?
Decision making
Why is decision making an integral part of being a manager?
Because many decisions have to be made every single day
7 Types of Decisions
1. Operational (e.g. hours of operation)
2. Budget/purchase (e.g. purchase of equipment)
3. Staffing (e.g. ratio of physical to occupational therapists)
4. Process (e.g. workflow)
5. Marketing (e.g. advertising in school newspaper)
6. Productivity (e.g. how many patients will be seen a day)
7. Contingency-based (e.g. dependent on the situation)
Data collected should be _____ and _____.
Purposeful and actionable
What should data drive?
Budgeting
Long- and short-term planning
Process implementation
Staff retention and development
What term can be defined as pieces of information used for thoughtful decision making?
Data-driven decision making
Data-Driven Decision Making
Pieces of information used for thoughtful decision making
Data-Driven Decision Making Questions
What do you want to know from the data to make decisions?
What data (KPI) would provide that information?
Do you have reliable systems in place to collect that data??
How much data is enough for you to decide?
What existing data sources can help you make a decision?
How can you minimize staff turnover?
How can you measure competencies or client satisfaction?
How will you determine evidence-based practice?
What should a manager develop/identify in order to make a data-driven decision?
Data collection plan
Steps of a Data Collection Plan
Assessment (e.g. interview, survey, poll)
Collect data (e.g. adding a parameter to existing sources)
Data sources (technology driven business intelligence tools)
Prepare and analyze data (e.g. quality control, verify data)
Make data informed decisions (e.g. present to stakeholders)
What data collection plan should a manager utilize?
Most suitable plan (e.g. be innovative, yet objective)
Examples of Data Sources
Smartphones
Wearable devices
Smart home and office technology
What should managers minimize when analyzing data?
Errors in data
Subjectivity
Missing data and outliers
What should managers avoid when analyzing data?
Sampling bias
Data entry errors
What should managers determine when analyzing data?
Suitable statistic (e.g. mean customer satisfaction by gender)
8 Steps of the Research Process
1. Identify the problem or research question
2. Scan the literature (e.g. success, failures, what's been done)
3. Make a plan (e.g. timeline, budget, communication of results)
4. Collect data (e.g. from existing or new data sources)
5. Prepare data (e.g. errors, duplicate records, outliers)
6. Analyze data (e.g. frequencies, descriptive statistics)
7. Report findings (e.g. basis from which a decision is made)
8. Assess the process (e.g. debrief with a team)
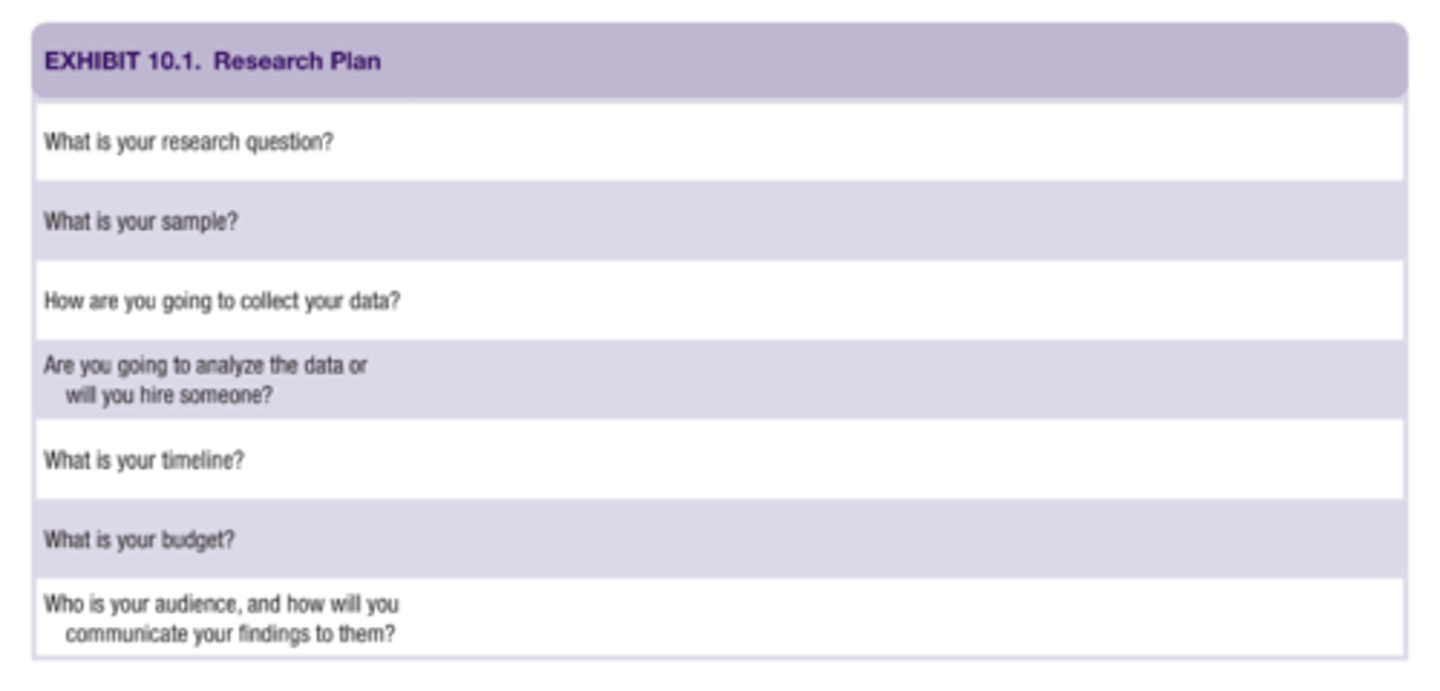
What is critical to any research process?
Proper planning (e.g. start by writing down the problem statement or research question to help frame project and limit the resources and scope)
What is the key to good planning and the first step toward being able to know what data is needed?
Asking relevant, answerable questions
What should project planning always start with?
A research question and steps for analyzing and communicating the research
What do the many people who do planning and assessment rely on?
SMART goal process
SMART Goal
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Realistic
Tangible (or Time-Bound)
What does the SMART goal process set planners up for? How?
Success, because a specific goal keeps the outcomes focused, limiting wasted time and financial resources
What term can be defined as pieces of information used as a source of thoughtful discourse, planning, and decision making?
Data
Data
Pieces of information used as a source of thoughtful discourse, planning, and decision making
What can data include?
Direct observations of opinions, attitudes, and perceptions
3 Types of Data
1. Quantitative
2. Qualitative
3. Mixed
Quantitative Data
A method of data collection that provides numerical responses to closed-ended questions, including objective measurements of data points and their analysis with mathematics or statistics
Qualitative Data
A method of data collection including open-ended questions on surveys, questions in focus groups, or interviews that gathers data by generalizing information from individuals or groups of people to explain an event
Mixed Data
A method of data collection that combines quantitative and qualitative research results
When is a mixed method data collection approach best incorporated?
In the research planning phase to help meet a timeline and budget (can also be done after 1 stage of the research has been analyzed)
What does a quantitative analysis in a mixed method data collection approach often provide?
Data point that can help guide decision making
What does a qualitative analysis in a mixed method data collection approach often provide?
Support and information about making adjustments and improvements in other areas
What can the use of different sources of data help gain a better understanding of?
A particular issue
What needs to happen before data can be analyzed?
Data needs to be prepared
What does data preparation entail?
Examining the collected data for errors (e.g. sampling, data-entry), bias, missing data, and outliers (e.g. extreme cases)
What is at the core of good research?
Objective, randomly assigned participants who provide data
How should the data be scanned in data preparation?
By running simple descriptive statistics on each variable
Descriptive Statistics
Describe the data through a frequency distribution or measures of central tendency or variability (e.g. mean, range, standard deviation)
What is key to convincing stakeholders of a manager’s or administrator’s plans as a decision maker?
Sharing data with others
What is the goal of sharing data with others?
To present findings in a clear manner and create an action plan
What is key to turning data into information that can be used to drive better decision making?
Being able to visualize data and tell stories with it
What should be created from the beginning of the research process?
Communication plan
6 Guidelines for Data Communication
1. Understand context
2. Choose an appropriate display
3. Eliminate clutter
4. Focus attention
5. Think like a designer
6. Tell a story
Examples of Data Visualization Strategies
Charts
Tables
Figures (e.g. graphs)
Dashboard report
Tables
Rows and columns of data that show exact data points
Figures
Images, maps, or diagrams that should be used to present complicated results
Graphs
A type of figure that illustrates quantitative data points
When are graphs best used?
When the data is too complex to be reported as a table and the decision maker or audience would not be able to swiftly understand the data presented in the table
Dashboard Report
Summary that contains data points to measure performance
success in various areas
What is the first step in the research process, and why is this step important? Who would you consult in this first step?
Identify the problem or research question; this step is important because it will frame your work moving forward. You could include a team of colleagues, mentors in the field, or hire a data scientist.
What does the M in SMART goals stand for, and why is it important?
A measurable goal drives the planning process by ensuring information is based on available data. It separates the dreams of "it would be nice to know this if we had all the access, money and time in the world" from the realities "we can gauge this with our available resources."
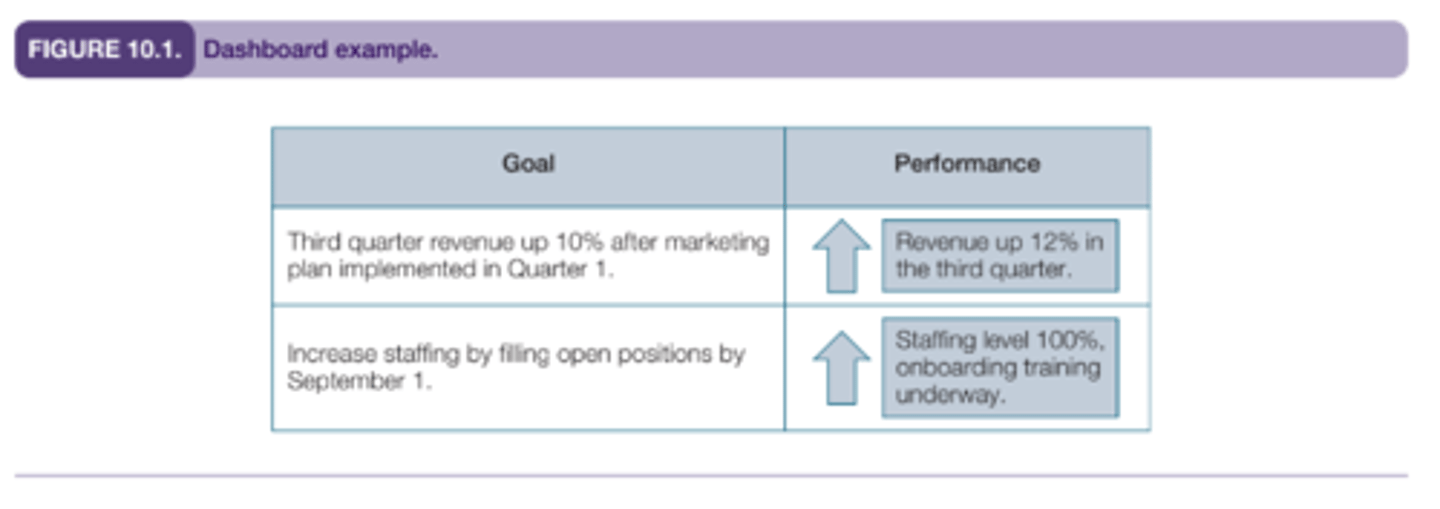
What is a dashboard report, and what types of data can you display on it? What are some limitations of dashboard reports?
A dashboard is a summary report that contains data points to measure performance success in various areas. You can display quantitative data point on it.
In what ways can outcome identification, client satisfaction, and practitioner productivity be assessed?
Alone
With a team
Data Scientist
Someone who is knowledgeable about data and statistics

What should be considered when using data for marketing and research purposes without employee or client consent?
Ethics
How do you think clients may react when they learn that you may be using technology to track encounters and interactions?
Answers may include discussion of recent news reports that highlighted data tracking and sharing without consent using common social media platforms
Where can you find information about emerging cyber technology standards?
Information on cybertechnology standards can be found when reviewing the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 privacy and security rules regularly, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2018) website that lists HIPAA-covered entities that are subject to following cybersecurity rules
As documented in the AOTA (2015) Occupational Therapy Code of Ethics (2015), the standard for Nonmaleficence states that “Occupational therapy personnel shall refrain from actions that cause harm.” Describe what harm may come from collecting data from clients using technology without their consent.
Collecting data on clients without their consent can result in mistrust if this information is discovered. Additionally, there are also rights issues with who owns what data, and issues surrounding what researchers are allowed to do with that data once it is collected without consent
2 Types of Action Plans
1. Client (e.g. safety, success, and timeliness of services)
2. Internal-business (e.g. employee performance, finances)