Storms & Tornadoes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
what is a front?
* boundary between two air masses w/ contrasting temperatures
2
New cards
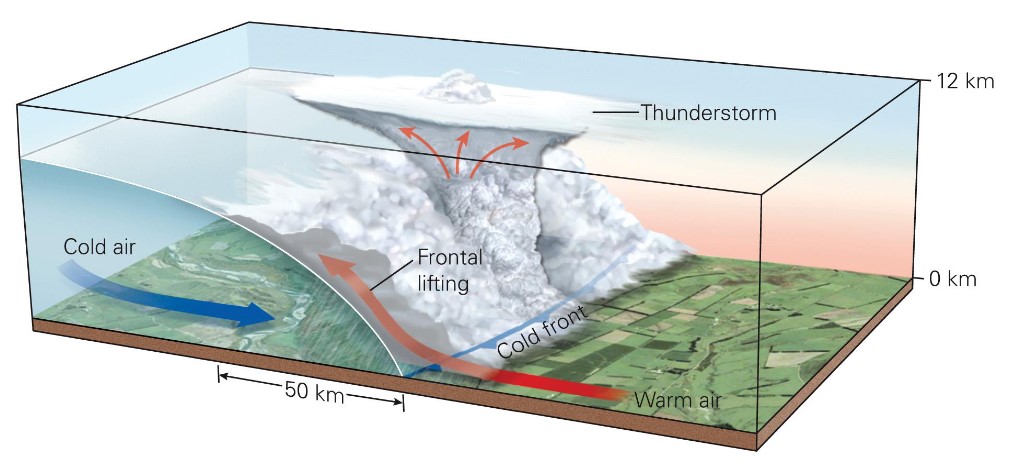
what is a cold front?
* cold air mass advances under a warm air mass
* warm air mass rises
* heavy precipitation (e.g., thunderstorms) result along a narrow band
→ tend to get storms
* warm air mass rises
* heavy precipitation (e.g., thunderstorms) result along a narrow band
→ tend to get storms
3
New cards
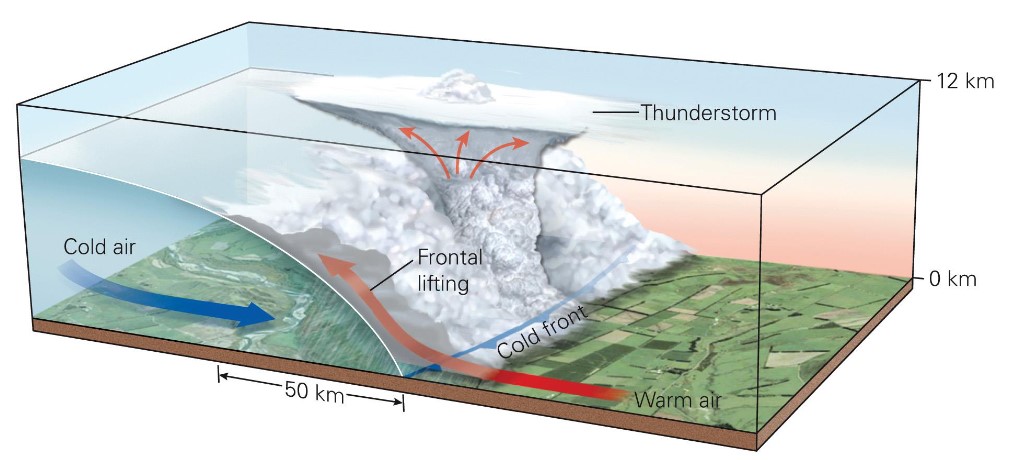
what is a water front?
* advancing warm air rises slowly over the adjacent cooler air mass
* associated w/ widespread clouds w/ moderate steady precipitation
→ gradual rise → less intense precipitation
* associated w/ widespread clouds w/ moderate steady precipitation
→ gradual rise → less intense precipitation
4
New cards
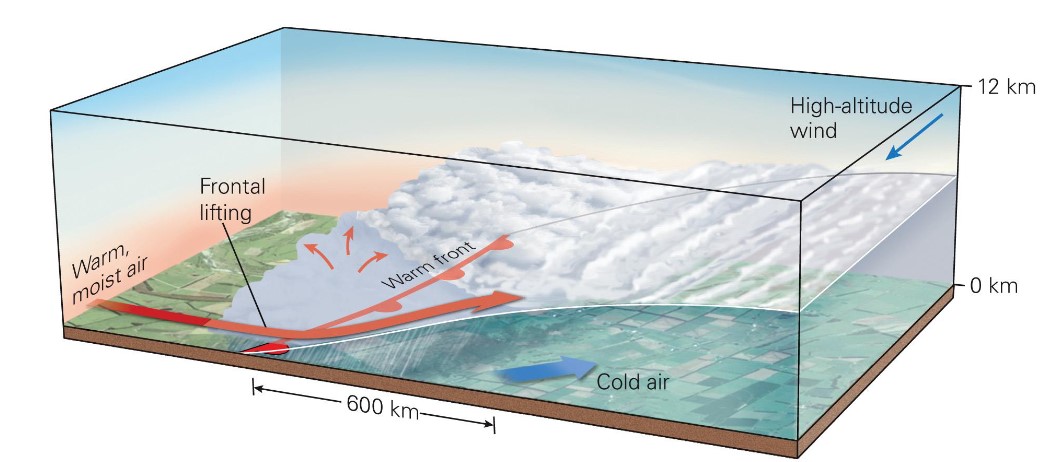
what is an occluded front?
* when advancing cold front overtakes a warm front
* warm air no longer intersect the ground surface
→ warm air not interacting w/ surface
note: cold air travels faster
* warm air no longer intersect the ground surface
→ warm air not interacting w/ surface
note: cold air travels faster
5
New cards
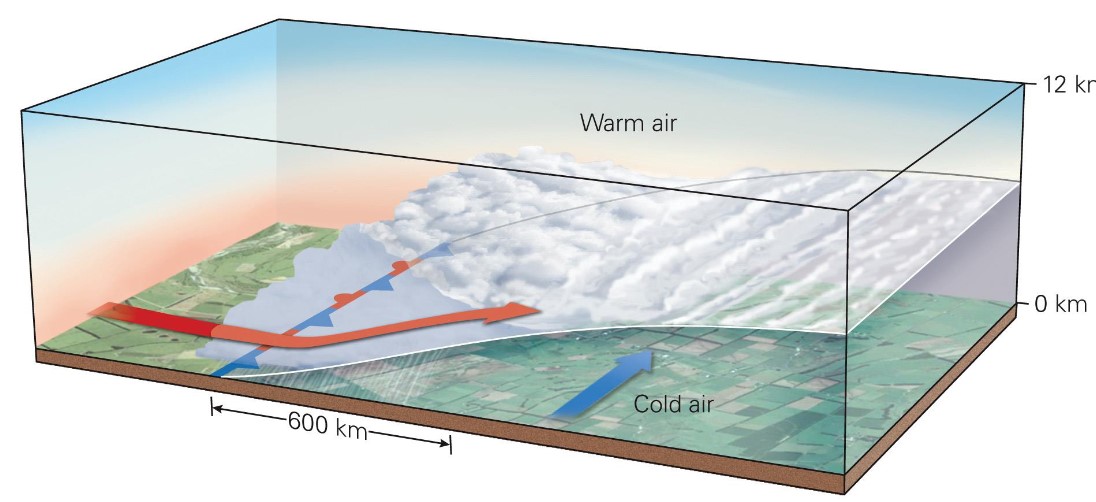
what is a stationary front?
* occurs when cold air flows nearly parrallel to the front, while warm air rises over the front
* position does not move; can lead to floods, ice storms and heavy snowfall
* warm air cant push cold air → get precipitation to same location for long period of time
* position does not move; can lead to floods, ice storms and heavy snowfall
* warm air cant push cold air → get precipitation to same location for long period of time
6
New cards
is jet stream air flow even or uneven?
* uneven
* more air flow out of a region than into it → leads to deficit in jet stream which results in low p
* more air flow out of a region than into it → leads to deficit in jet stream which results in low p
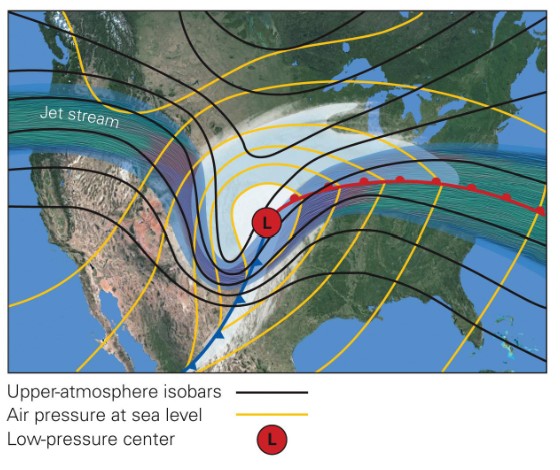
7
New cards
what is divergence in jet stream?
* an air deficit at the tropopause
* creates low p center
* surface air rises into low-p
* mid-latitude cyclones evolve → is created
* \
* creates low p center
* surface air rises into low-p
* mid-latitude cyclones evolve → is created
* \
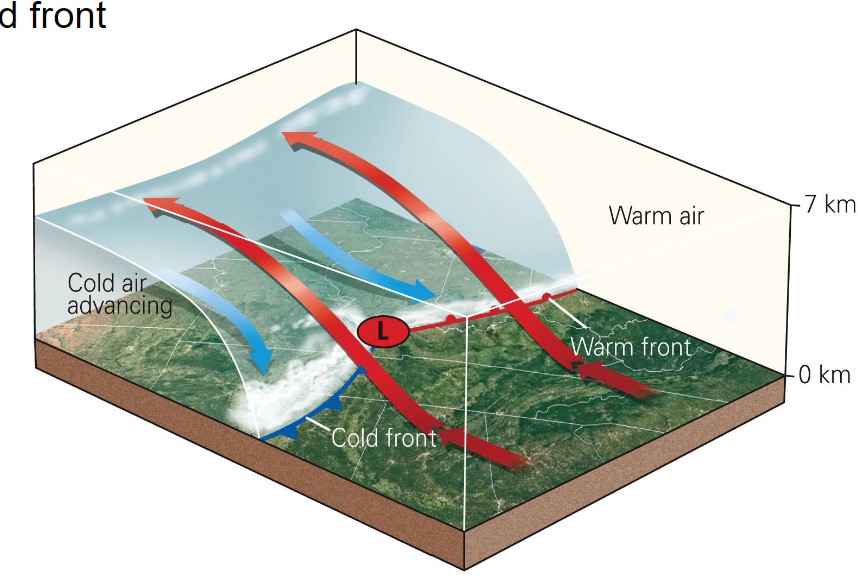
8
New cards
mid-latitude cyclone evolution 1
* warm air flows up and over the fronts
* widespread area of clouds and rain along te warm front; showers and thunderstorms along the cold front
* widespread area of clouds and rain along te warm front; showers and thunderstorms along the cold front
9
New cards
mid-latitude cyclone evolution 2
* cold front moves faster than warm front
* as air spirals counterclockwise, the cold front begins the catch up to the warm front
* warm front migrates NW
* as air spirals counterclockwise, the cold front begins the catch up to the warm front
* warm front migrates NW
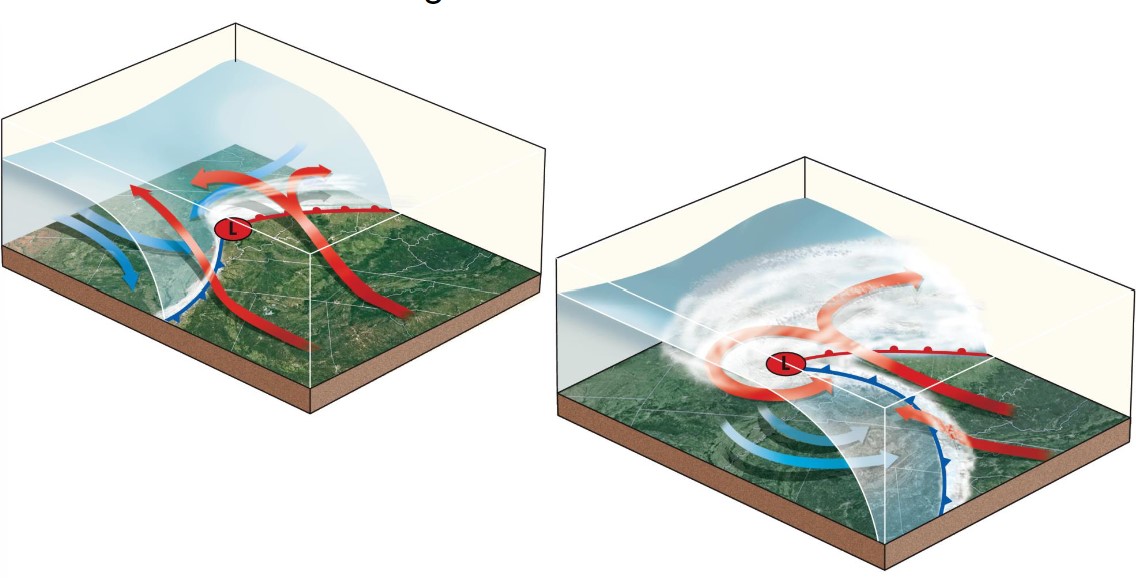
10
New cards
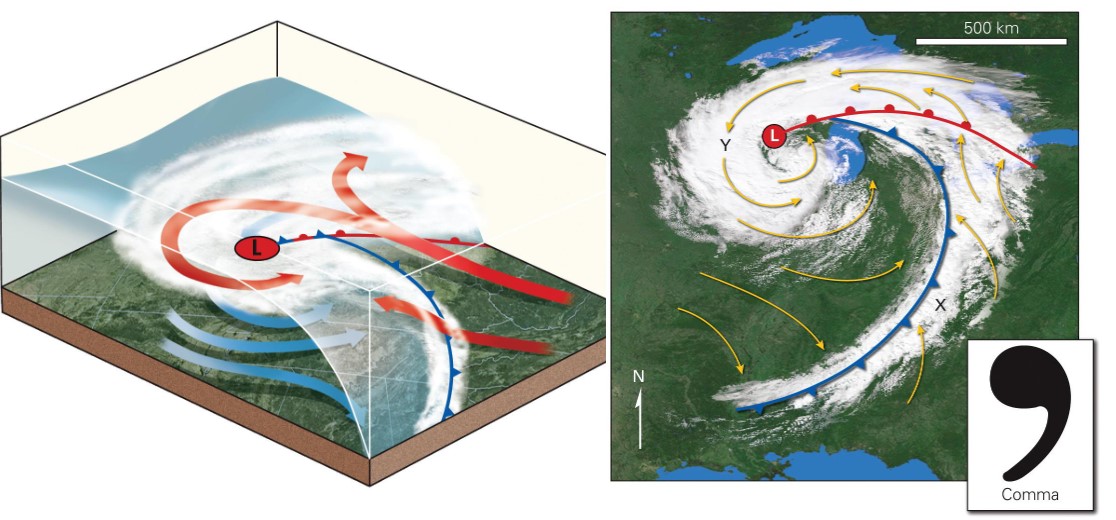
mid latitude cyclone evolution 3
* cold front catches up and overtakes the warm front; an occluded front devs
* mid-latitude cyclone has a “comma” shape
* once occluded, the sys will lose energy and dissipate ending the mid-latitude cyclone event
* mid-latitude cyclone has a “comma” shape
* once occluded, the sys will lose energy and dissipate ending the mid-latitude cyclone event
11
New cards
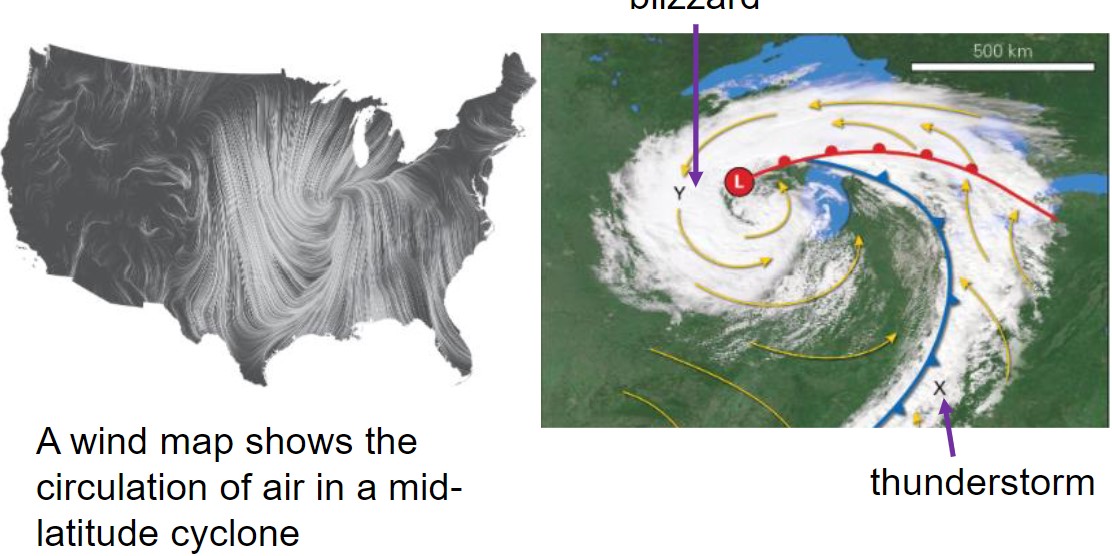
what is the head of the comma?
* in winter, home to blizzards and ice storms
12
New cards
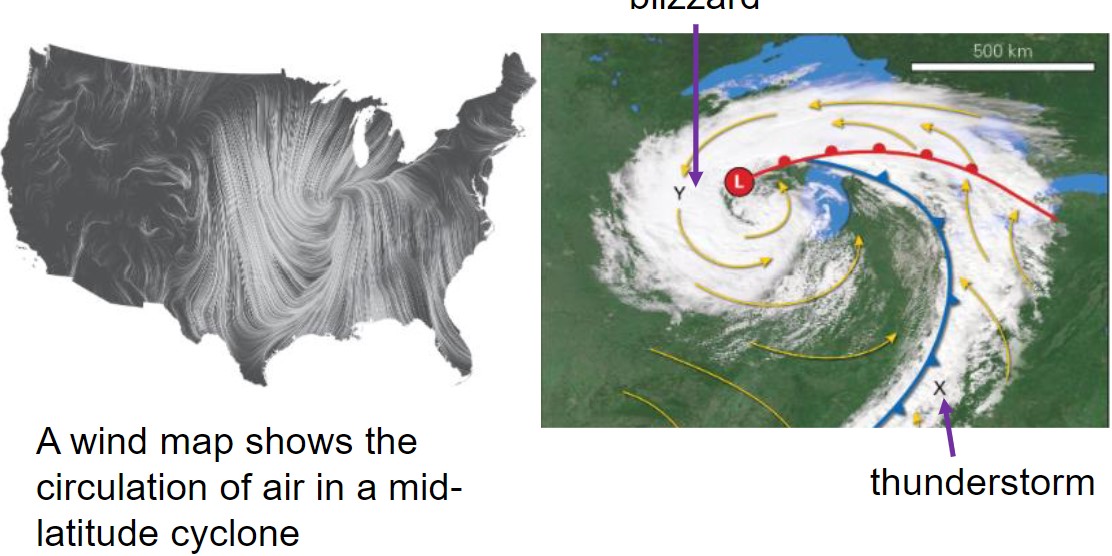
what is the tail of the comma?
* thunderstorms, tornadoes, windstorms blizzard
13
New cards
what is a thunderstorm?
* towering cloud that produces lightning and thunder
* usually have strong winds, heavy rains, and sometimes hair
* usually have strong winds, heavy rains, and sometimes hair
14
New cards
what are the conditions required to dev a thunderstorm?
1. moist air (mostly from oceans, lakes, and wetlands)
2. a lifting mecha
3. atmospheric instability
15
New cards
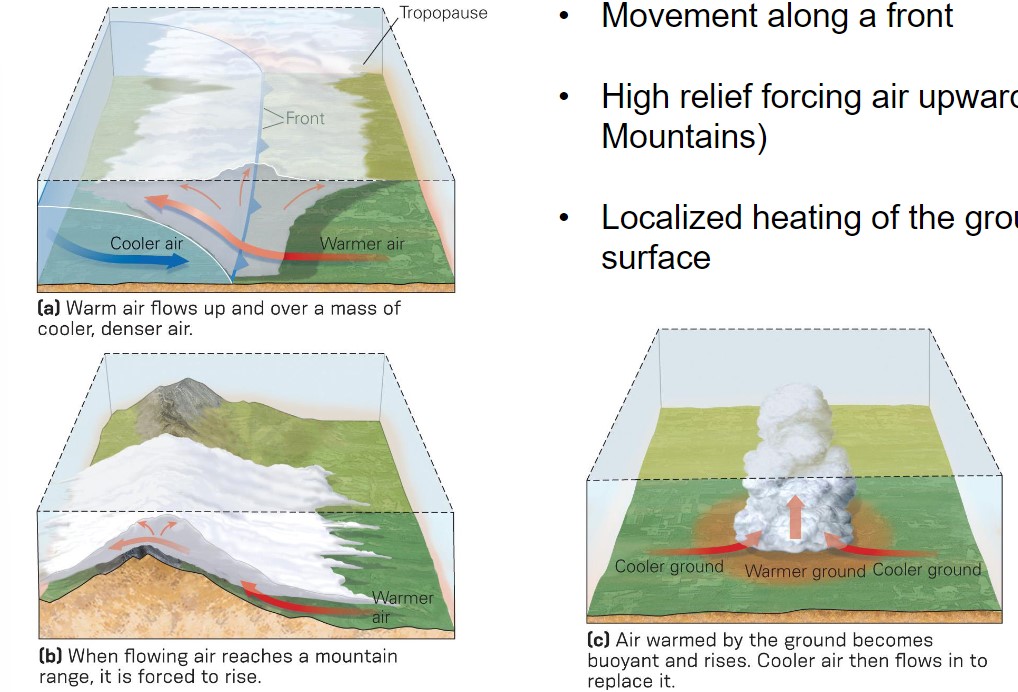
lifting mechanism
* movement along a front
* high relief fording air upwards
* e.g., mountains
* localized heating of the ground surface
* high relief fording air upwards
* e.g., mountains
* localized heating of the ground surface
16
New cards
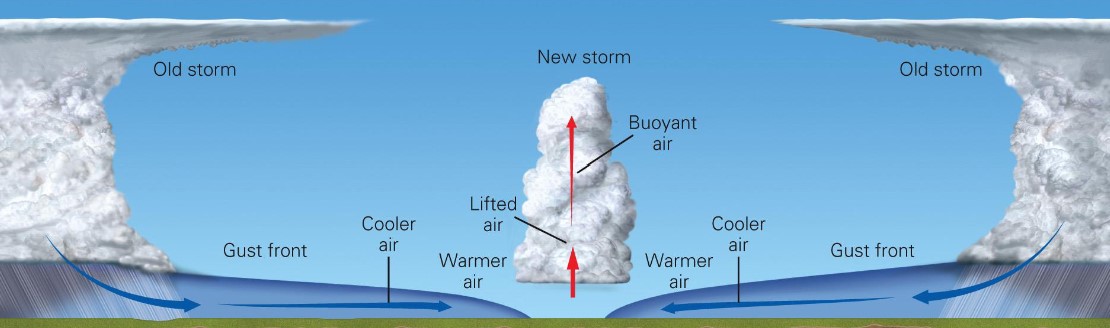
what is a gust front?
* thunderstorms create cold downdrafts
* downdrafts act like small cold fronts
* downdrafts act like small cold fronts
17
New cards
what is unstable air?
* when air parcel is less dense than its enviro
18
New cards
what is adiabatic expansion?
* air parcel expands and cools as it rises
* dry adiabatic lapse rate (\~10ºC/km)
* Saturated (moist) Adiabatic Lapse \n Rate (\~6ºC/km)
* dry adiabatic lapse rate (\~10ºC/km)
* Saturated (moist) Adiabatic Lapse \n Rate (\~6ºC/km)
19
New cards
what is environmental lapse rate?
* rate temperature drops with increasing altitude in the atmosphere.
20
New cards
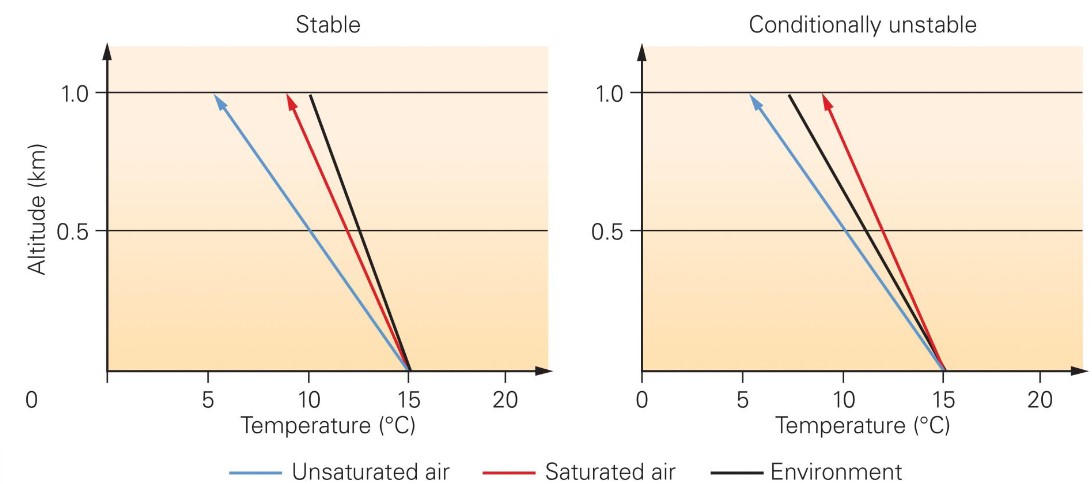
atmos instability
* if air parcel rise if warmer than enviro (atmos) → it keeps going up and creates thunderstorm
* if remains colder than atmos, stop rising, go back donw
* if remains colder than atmos, stop rising, go back donw
21
New cards
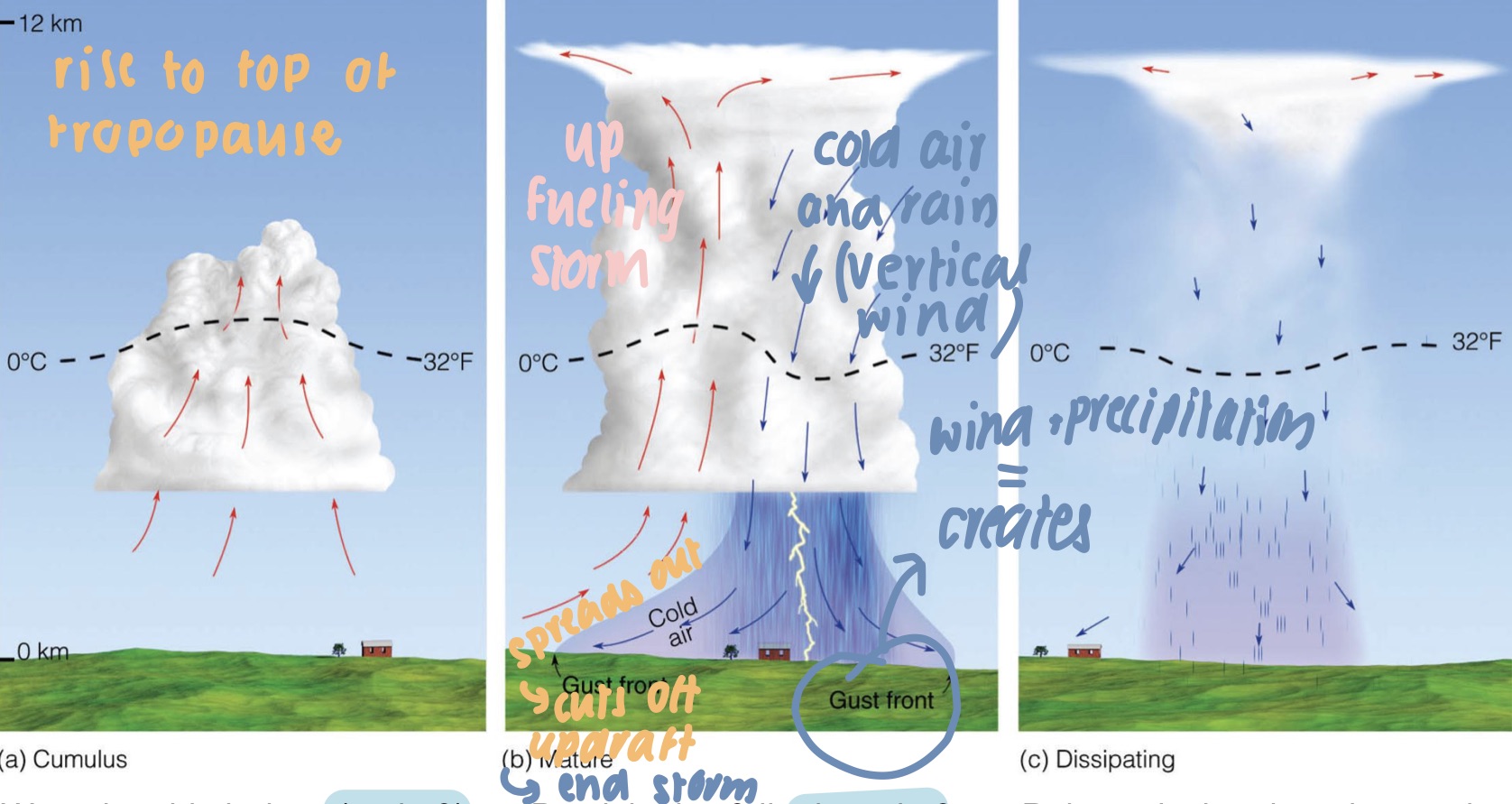
ordinary cell
* cumulus: warm humid air rises (updraft) and condenses to form a cloud
* mature: precipitation fall; downfall devs
* dissipating: rain cools the air and ground, downdraft suppresses updraft
* mature: precipitation fall; downfall devs
* dissipating: rain cools the air and ground, downdraft suppresses updraft
22
New cards
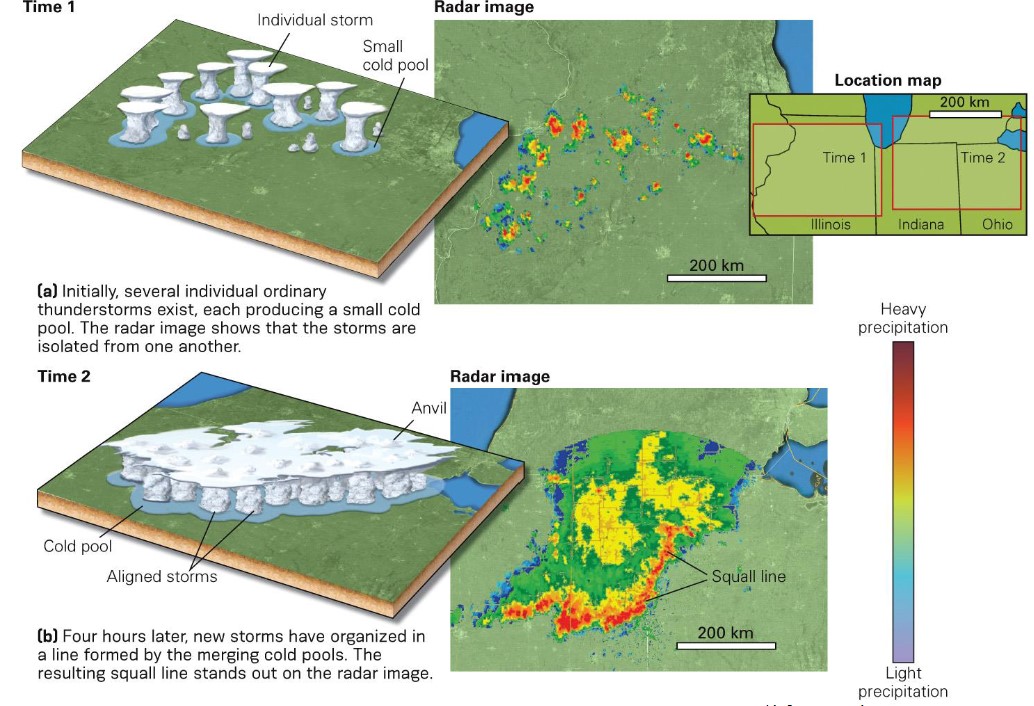
squall line thunderstorm
* acts like a giant cold front
* lifting is focused along strong, advancing cold fronts
* lifting is focused along strong, advancing cold fronts
23
New cards
what are frontal squall lines?
* thunderstorms occurring in a vv long line
* often seen along the “tail” of a mid-latitude cyclone
* associated w/ heavy rain, lightning, and straight-line winds; can damage buildings and trees
* often seen along the “tail” of a mid-latitude cyclone
* associated w/ heavy rain, lightning, and straight-line winds; can damage buildings and trees
24
New cards
what is a radar?
* well-defined line of thunderstorms is visible
* the well-defined line lies along advancing cold front
* the well-defined line lies along advancing cold front
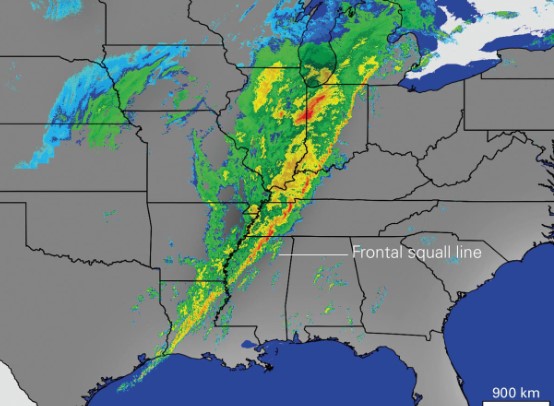
25
New cards
what is a derecho?
* spanish for “direct” or “straight”
* severed straight-line winds over a large geographic region
* may dev along squall-line thunderstorms
* severed straight-line winds over a large geographic region
* may dev along squall-line thunderstorms
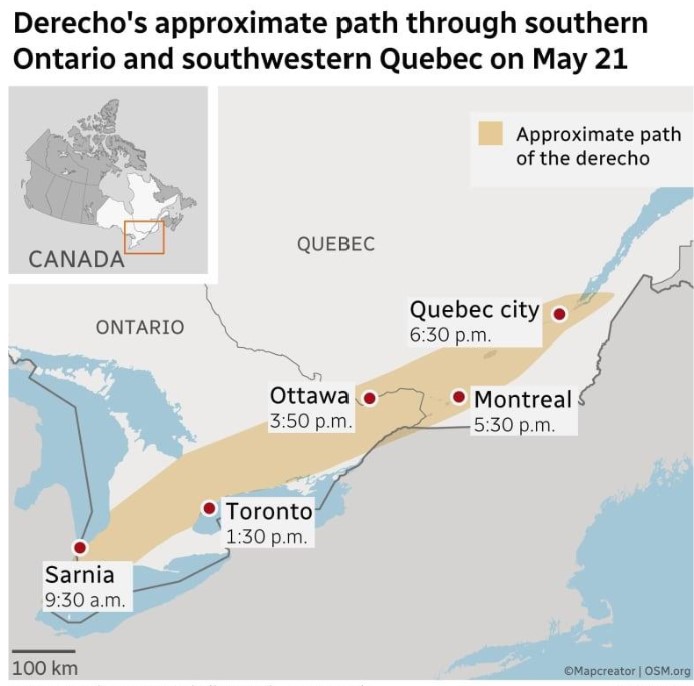
26
New cards
derecho, Ontario May 2022
* winds up to 190km/h
* impacted 15.6 million people
* power outages impacted 1.1 million people, some for over a week
* some homes were comp destroyed
* 11 people died; most from falling trees
* impacted 15.6 million people
* power outages impacted 1.1 million people, some for over a week
* some homes were comp destroyed
* 11 people died; most from falling trees
27
New cards
what is a supercell thunderstorms?
* differ from ordinary cell due to rotational motion of the upward-moving air
* they dev when wind directions near the surface are diff from conditions higher in the troposphere
* they dev when wind directions near the surface are diff from conditions higher in the troposphere
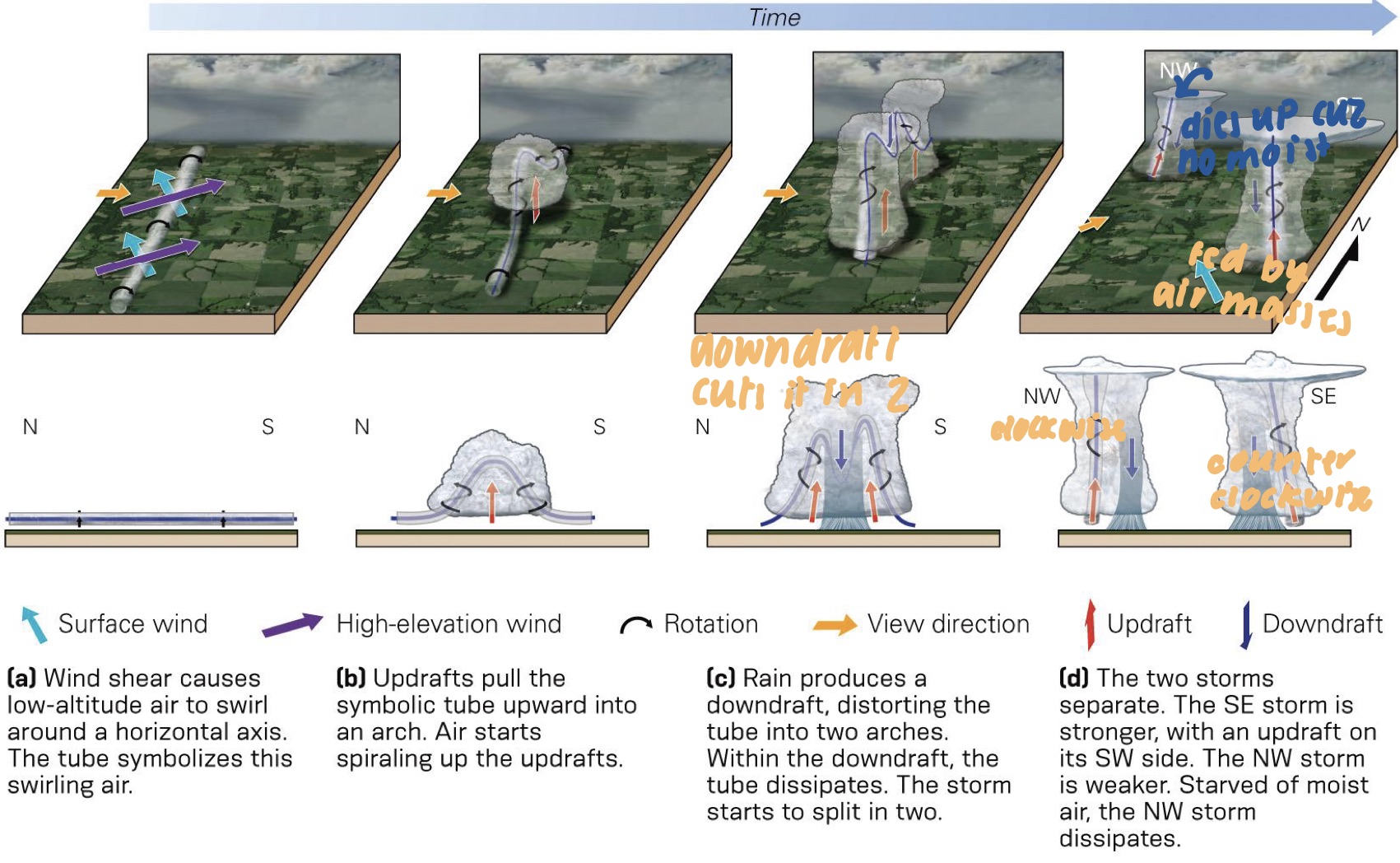
28
New cards
supercell thunderstorms?
* strong winds in upper atmos cause the storm tilt, so updraft isn’t vertical
* there are 2 downdrafts
* downdraft cant cut off updraft cuz lower so last longer
* there are 2 downdrafts
* downdraft cant cut off updraft cuz lower so last longer
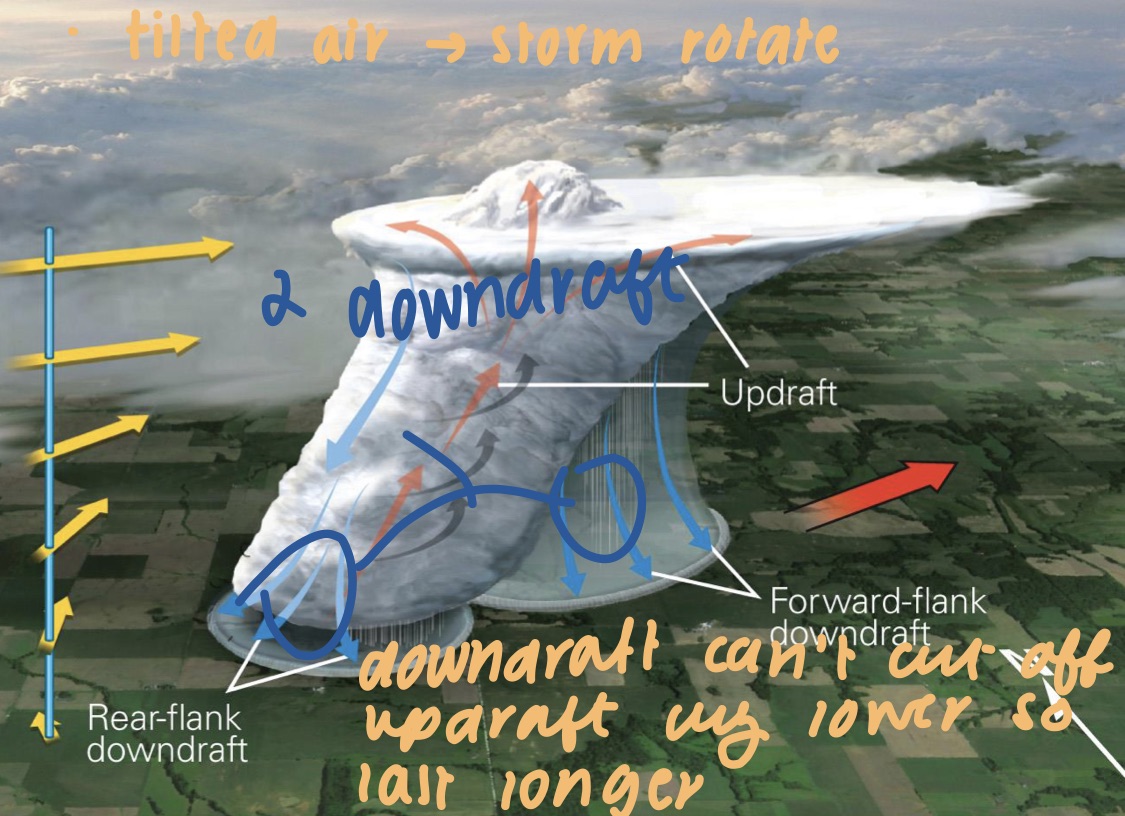
29
New cards
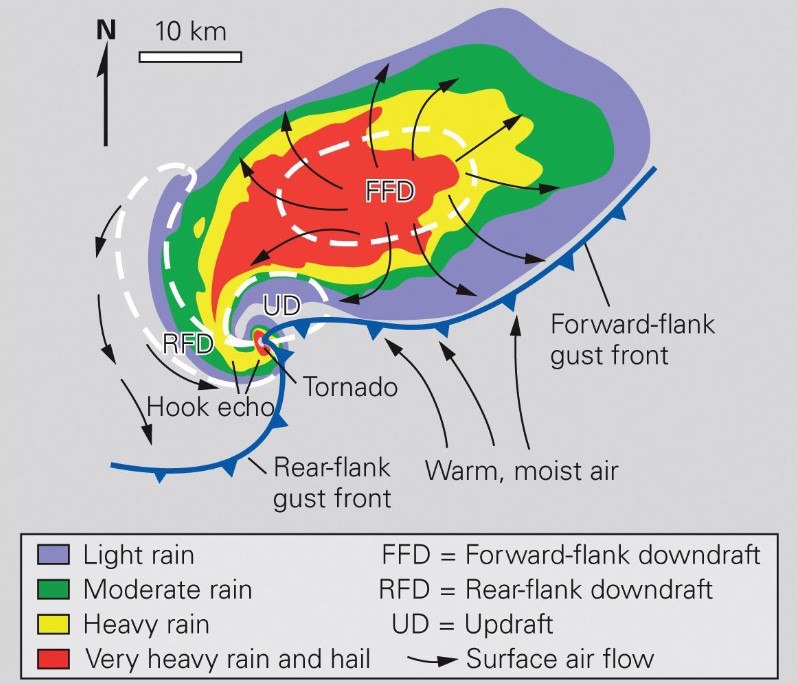
supercell thunderstorms
* forward flank: NE side of NE-moving supercell
* strong wind at forward flank downdraft (FFD)
* rear flank: SW side of NE-moving supercell
* rear flank downdraft (RFD)
* can produce tornadoes
* strong wind at forward flank downdraft (FFD)
* rear flank: SW side of NE-moving supercell
* rear flank downdraft (RFD)
* can produce tornadoes
30
New cards
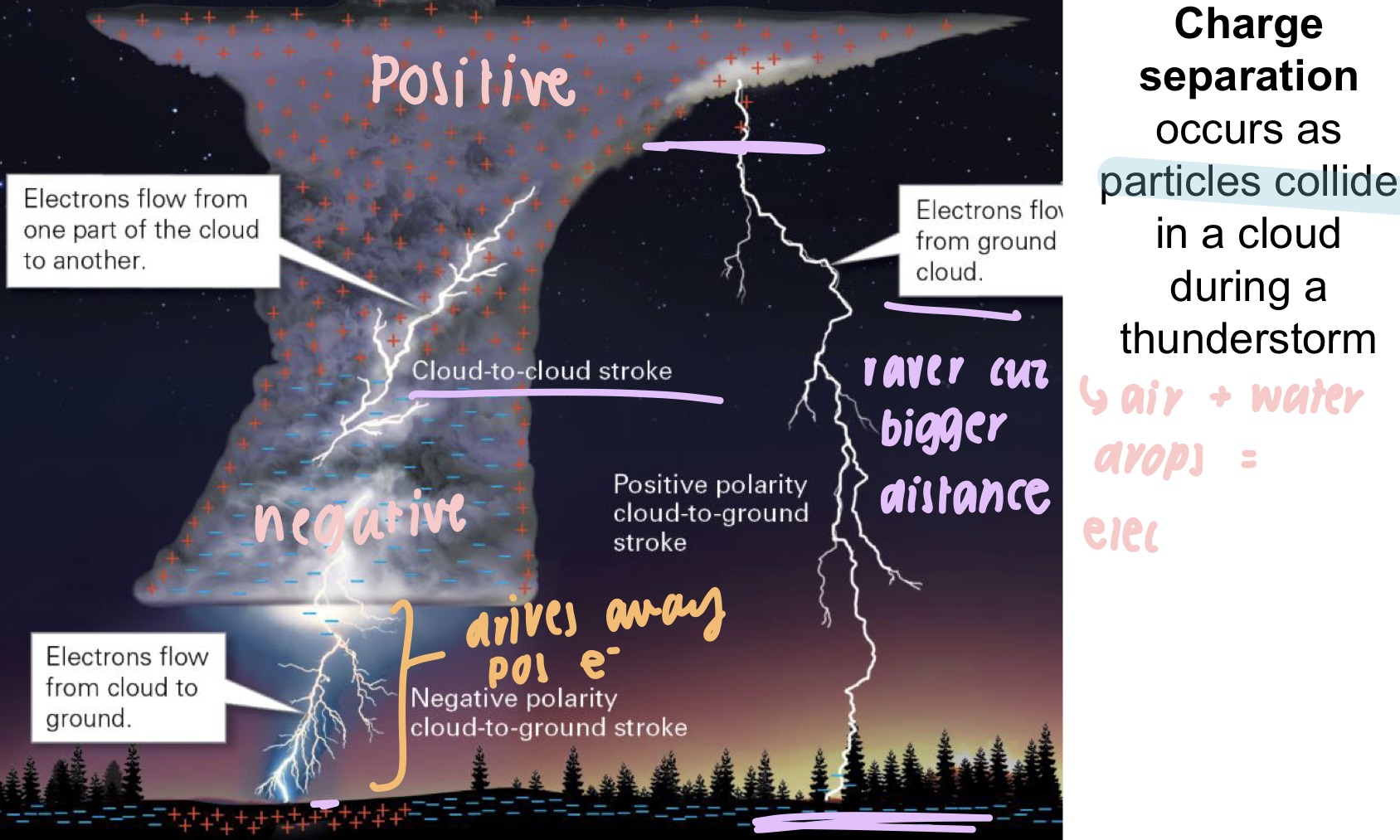
what is lightning?
* an electrostatic discharge in the atmos that occurs when negatively and positively charged particles become separated
31
New cards
when can charge separation occur in lightening?
* as particles collide in a cloud during a thunderstorm
32
New cards
hazards of lightning?
* damage to trees and homes
* start forest fires
* power outages
* can injure or kill humans that are struck; can cause burns, paralysis, organ damage
* kills approx 7 canadians each each (global \~2,000
\- 6,000)
* start forest fires
* power outages
* can injure or kill humans that are struck; can cause burns, paralysis, organ damage
* kills approx 7 canadians each each (global \~2,000
\- 6,000)
33
New cards
what is thunder?
* the sound generated by lightning
34
New cards
what can lightning temp reach?
30,000ºC
35
New cards
how is thunder generated?
* lightning stroke instantly heats the air around it, \n causing it to expand explosively.
* When the lightning stroke ends, air contracts violently.
* contracts = collapse
* The sudden expansion and contraction of air generates thunder.
* When the lightning stroke ends, air contracts violently.
* contracts = collapse
* The sudden expansion and contraction of air generates thunder.
36
New cards
what are downbursts?
* formed by a rapidly descending mass of cold air from a thunderstorm
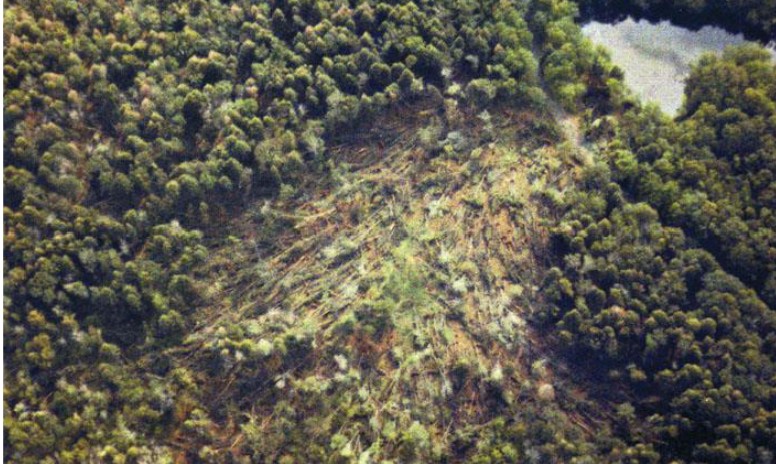

37
New cards
what is hail?
* associated w/ intense thunderstorm activity
* dev of large hailstones (golf ball-size) requires strong updrafts so snow can’t fall
* longer it stays in atmos → bigger it grows
* dev of large hailstones (golf ball-size) requires strong updrafts so snow can’t fall
* longer it stays in atmos → bigger it grows
38
New cards
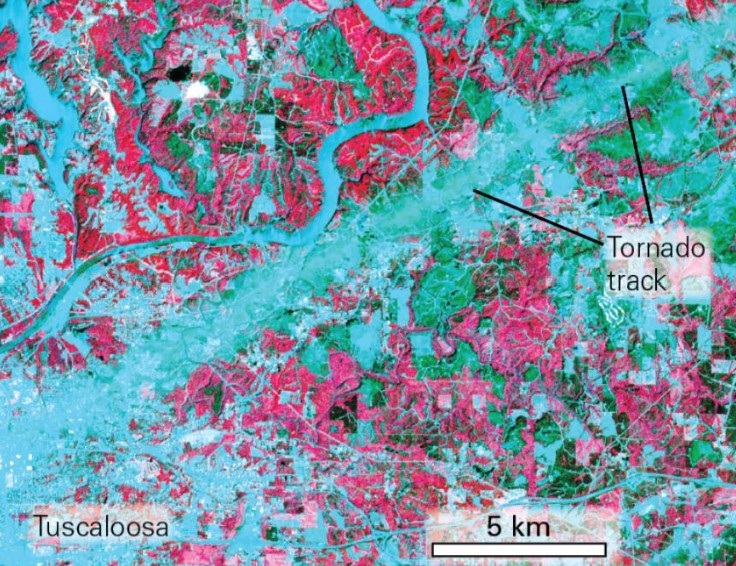
what is a tornado?
* a violently rotating column of air extending downward from the base of a severe thunderstorm to the groud
→ leaves scars → tornado track
→ leaves scars → tornado track
39
New cards
what is a tornado track?
* the path a tornado takes across the ground
40
New cards
what is a tornado outbreak?
* when multiple tornadoes are produced from storms
41
New cards
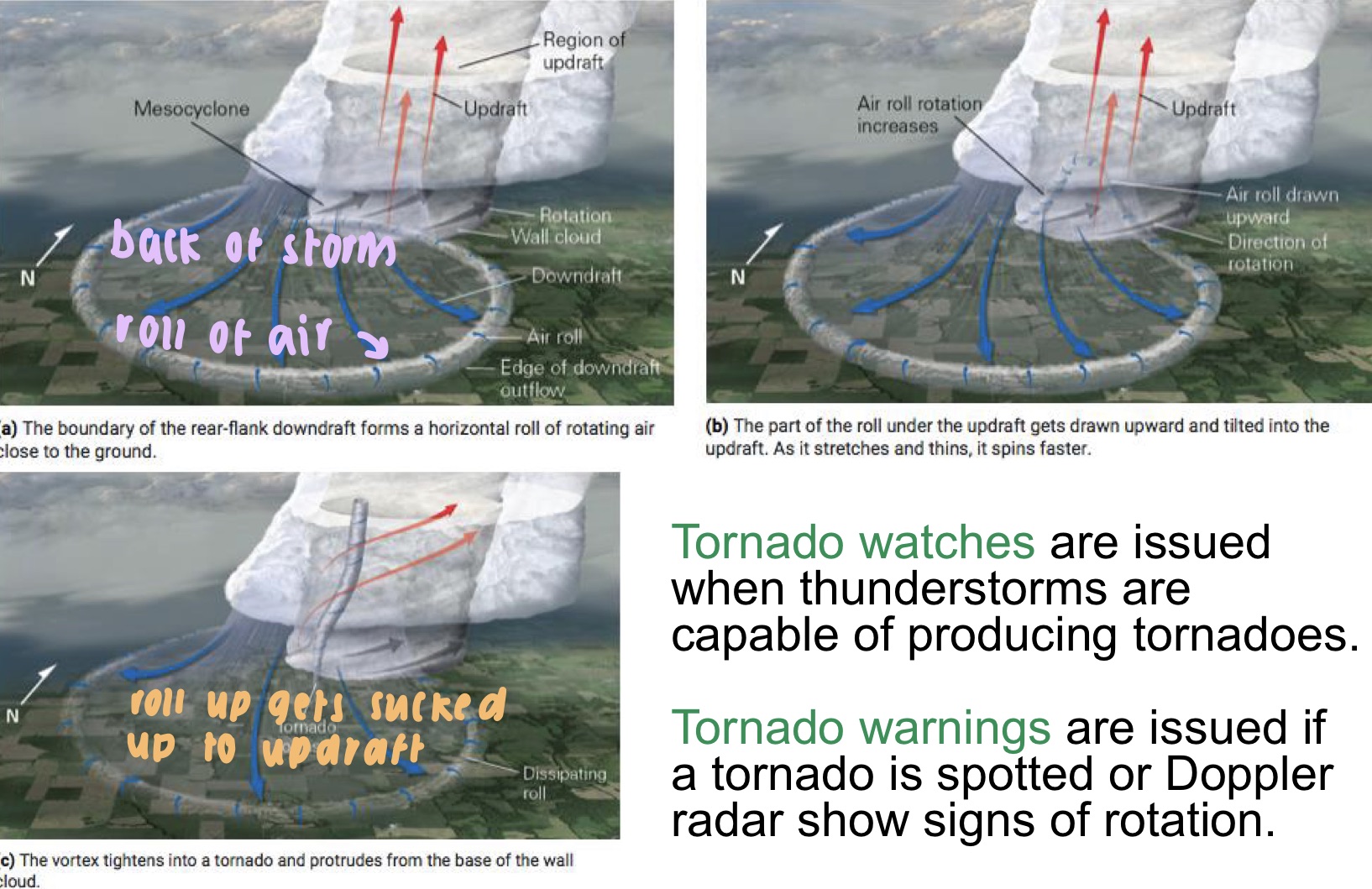
supercell tornado formation
* is most devastating
* there is a rear-flank downdraft
* forward-flank downdraft
* and updraft
* there is a rear-flank downdraft
* forward-flank downdraft
* and updraft
42
New cards
when are tornado watches issues?
* when thunderstorms are capable of producing tornadoes
43
New cards
when are tornado warmings issues?
* if a tornado is spotted or Doppler radar show signs of rotation
44
New cards
multiple-vortex tornadoes
* top right → blue shows that air sucks down in middle
* bottom left → downwards air helps widen it and can split tornado
* bottom left → downwards air helps widen it and can split tornado
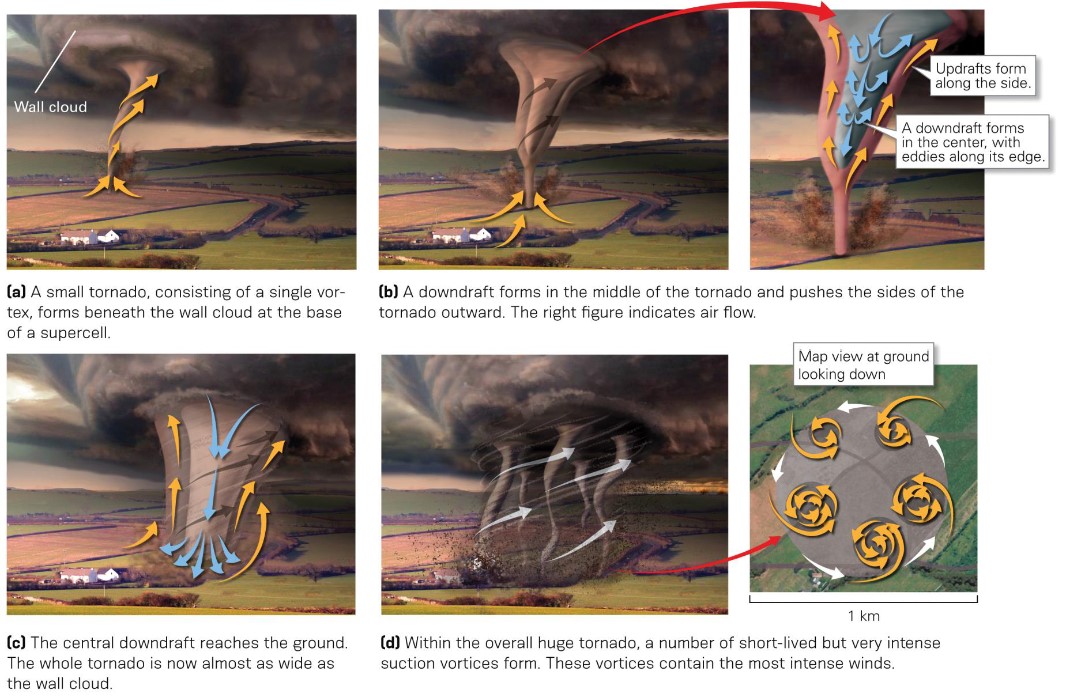
45
New cards
non-supercell tornadoes
* dev along squall lines and in hurricanes
* sig horizontal wind shear is needed for vortices to dev
* updrafts may lift and stretch vortices into tornadoes
* hurricane rain band shear may also cause tornadoes
* generally weaker than supercell tornadoes
* this is vertical air movement
* sig horizontal wind shear is needed for vortices to dev
* updrafts may lift and stretch vortices into tornadoes
* hurricane rain band shear may also cause tornadoes
* generally weaker than supercell tornadoes
* this is vertical air movement
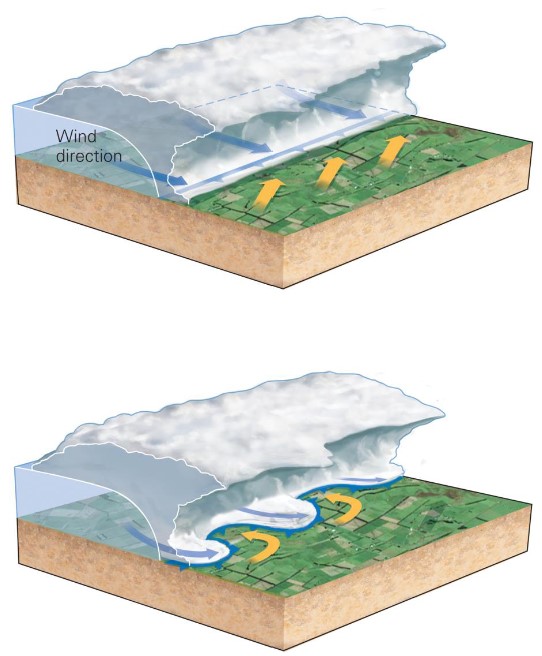
46
New cards
what is the enhanced Fujita Scale?
* is used to classify the intensity of a tornado
* based on wind speed thresholds and linked to their associated damage
* a tornado is classified on the Enhanced Fujita Scale based on the max damage it causes along its path, they evolve over time
* they first grow in strength, then dies
* can be one rating at some point, or another
* based on wind speed thresholds and linked to their associated damage
* a tornado is classified on the Enhanced Fujita Scale based on the max damage it causes along its path, they evolve over time
* they first grow in strength, then dies
* can be one rating at some point, or another
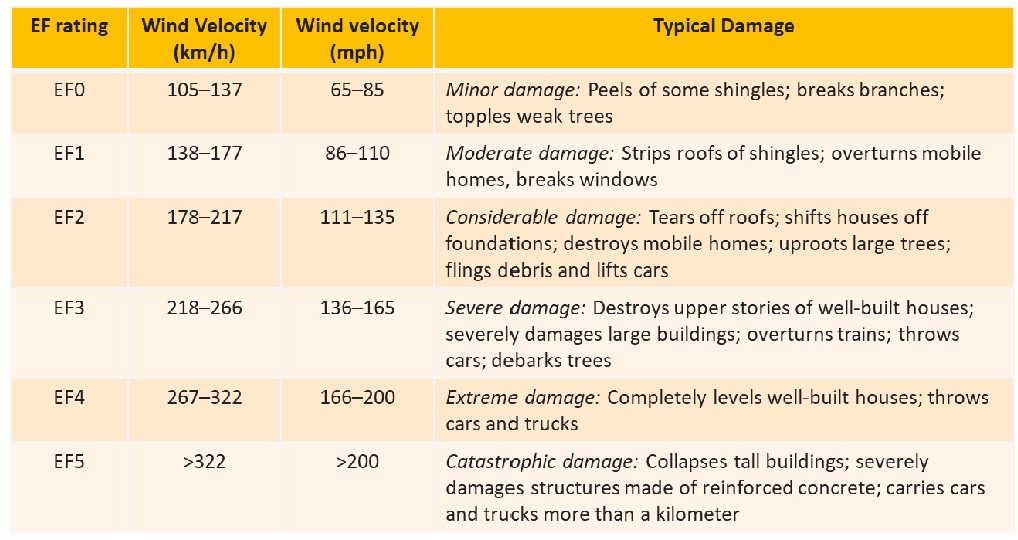
47
New cards
Jopling, Missouri tornado
* 158 deaths
* $3 billion of damage
* homes wiped off foundation
* medical center sustained so much damage it had to be demolished
* $3 billion of damage
* homes wiped off foundation
* medical center sustained so much damage it had to be demolished
48
New cards
Canada tornado geography
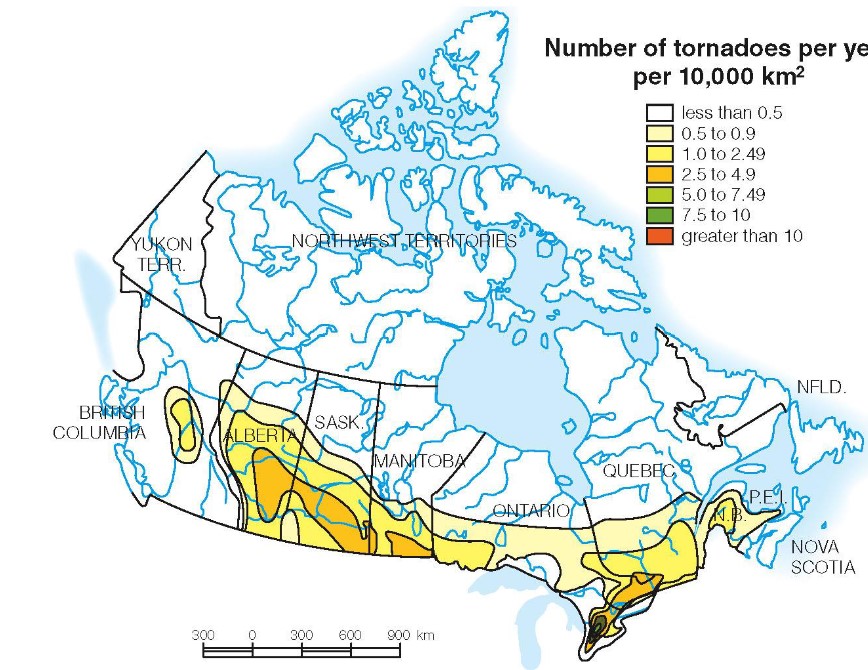
49
New cards
Barrie, Ontario tornado
* cluster of 2 EF2 tornadoes
* $75 million in damage
* 110 homes damaged
* $75 million in damage
* 110 homes damaged
50
New cards
how to survive a tornado?
* move to a tornado shelter, basement or interior room
* protect your head using a helmet is available
* highway overpasses are not safe locations. wind speeds can be amplified
* cars provide only modest protection
* protect your head using a helmet is available
* highway overpasses are not safe locations. wind speeds can be amplified
* cars provide only modest protection
51
New cards
what can mid-latitude cyclones cause?
* blizzards, thunderstorms, nor’easters (storms called in Atlantic Canada)