AP Unit 2 Cells Full Set
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Last updated 2:54 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
Mitochondria function
site of cellular respiration, produces ATP energy from glucose
2
New cards
cellular metabolism
chemical activities of cells, directly depends on cell size
3
New cards
high surface area to volume ratio
smaller cells: more efficient at exchanging material across the plasma membrane
4
New cards
low surface area to volume ratio
larger cells: less efficient at exchanging material across the membrane, but has more storage
5
New cards
surface area
The measurement of the outer surface of an object.
6
New cards
volume
The amount of space an object takes up
7
New cards
amphipathic
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
8
New cards
phospholipid head
polar (hydrophilic) contains a phosphate group and glycerol
9
New cards
phospholipid tail
non-polar (hydrophobic) contains fatty acid chains
10
New cards
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
11
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
12
New cards
Hydrophilic
Water loving
13
New cards
Fluidity of the cell membrane
maintained by the weak hydrophobic interactions between the tails of the phospholipids , allowing them to move/drift
14
New cards
increases fluidity of plasma membrane under cold conditions
cholesterol and more unsaturated fatty acids
15
New cards
integral proteins
embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, spanning the membrane
16
New cards
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are bound to the surface of the membrane.
17
New cards
glycolipids
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to lipids.
18
New cards
glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
19
New cards
mosaic
made of a variety of macromolecules (phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates)
20
New cards
Aquaporins
water channel proteins that speed up the rate at which water can pass through the membrane
21
New cards
channel proteins
have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel to get across the membrane
22
New cards
carrier proteins
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane buy binding to the molecules and changing shape
23
New cards
cell wall
A rigid layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and is composed of cellulose
24
New cards
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells and allow for cell-to-cell communication
25
New cards
Light microscope
microscope that uses a beam of light passing through one or more lenses to magnify an object
26
New cards
Magnification
the ratio of an object's image size to its real size
27
New cards
Resolution
the measure of the clarity of the image
28
New cards
Contrast
visible differences in parts of the sample
29
New cards
organelles
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
30
New cards
electron microscope
microscope that forms an image by focusing beams of electrons onto a specimen
31
New cards
scanning electron microscope
a microscope that produces an enlarged, three-dimensional image of an object by using a beam of electrons rather than light
32
New cards
transmission electron microscope
An electron microscope used to study the internal structure of thin sections of cells
33
New cards
cell fractionation
technique in which cells are broken into pieces and the different cell parts are separated using a centrifuge
34
New cards
prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
35
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
36
New cards
nucleus function
information center of the cell containing the chromosomes
37
New cards
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
38
New cards
nuclear pores
holes in the nuclear envelope that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus
39
New cards
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
40
New cards
ribosomes function
particles made of rRNA and proteins that carry out protein synthesis by translating the message found in mRNA
41
New cards
free ribosomes
ribosomes suspended in the cytosol
42
New cards
bound ribosomes
attached to the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope
43
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum function
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
44
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum function
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, carbohydrates are metabolized, and toxic substances are broken down.
45
New cards
Golgi apparatus function
modifies, packages, sorts, and transports materials made by the endoplasmic reticulum
46
New cards
nucleus location
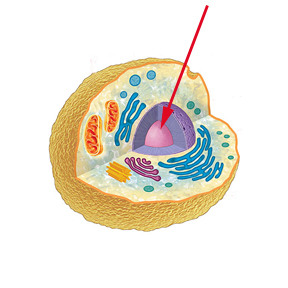
47
New cards
ribosomes location
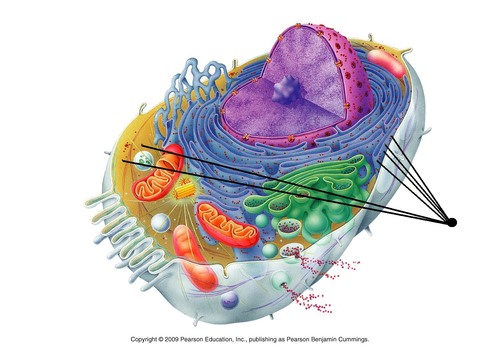
48
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Location
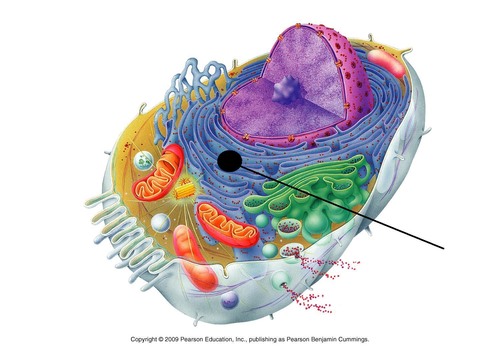
49
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Location
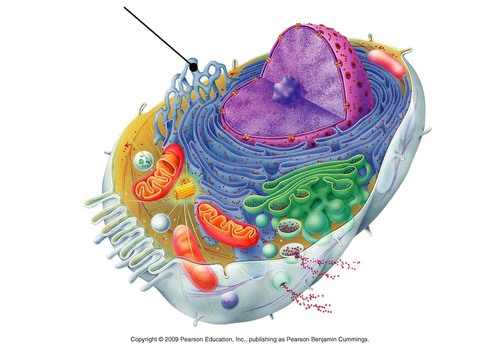
50
New cards
Golgi apparatus location
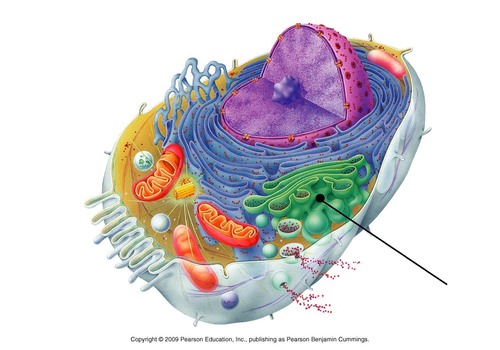
51
New cards
cis face of golgi apparatus
located near ER. Receiving side of golgi apparatus. Vesicle buds from ER can add its membrane and contents of lumen to this by fusing with golgi membrane.
52
New cards
trans face of the golgi apparatus
gives rise to vesicles, which pinch off and travel to other sites. Shipping side.
53
New cards
lysosome function
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down macromolecules (carbs, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins) as well as old cell parts through autophagy
54
New cards
lysosome location
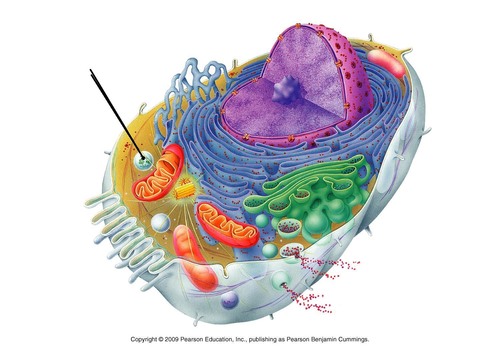
55
New cards
autophagy
lysosomes break down damaged organelles (self-eating)
56
New cards
peroxisomes
membranous sacs containing hydrolytic enzymes used to catalyze reactions that produce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
57
New cards
food vacuole
A membranous sac formed by phagocytosis of microorganisms or particles to be used as food by the cell.
58
New cards
contractile vacuole
pump excess water out of protist cells
59
New cards
central vacuole
A membranous sac in a mature plant cell that holds water and ions
60
New cards
plasma membrane function
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
61
New cards
cell wall function
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to plant cells
62
New cards
plasma membrane location
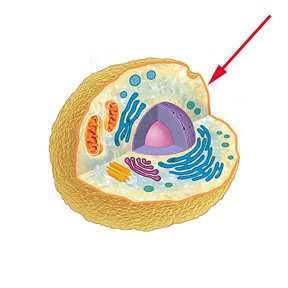
63
New cards
cell wall location
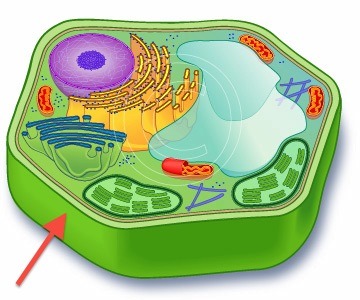
64
New cards
Endosymbiont Theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts were formerly small prokaryotes that began living with larger cells (early eukaryotic cell engulfed a prokaryotic cell)
65
New cards
mitochondria location
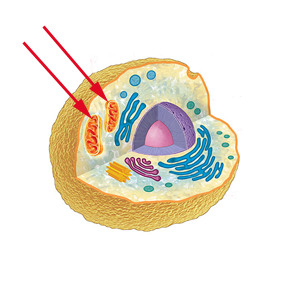
66
New cards
Cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
67
New cards
mitochondrial matrix
the space inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion where the Krebs cycle occurs
68
New cards
chloroplast function
Site of photosynthesis (makes glucose for plant cells)
69
New cards
chloroplast location
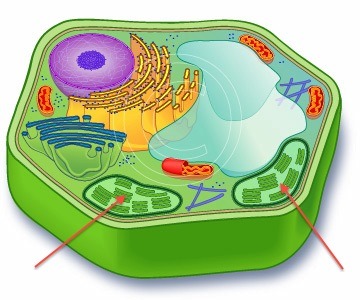
70
New cards
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
71
New cards
thylakoids
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast where the light dependent reactions occur
72
New cards
granum
stack of thylakoids
73
New cards
stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane where the Calvin cycle occurs
74
New cards
Compartmentalization
prevents interfering reactions from occurring in the same location, increases surface area for reactions to occur
75
New cards
cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
76
New cards
Microtubules definition
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells
77
New cards
Microtubule function
Motility (conveyor belt, cilia, flagella), cell shape, assist in the separating of chromosomes in cell division
78
New cards
centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only (grow out of centrosome)
79
New cards
cilia and flagella
hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement with their beating patterns
80
New cards
basal body
anchors the cilium or flagellum to the cell
81
New cards
dynein
motor protein that drives the bending movements of a cilium or flagellum
82
New cards
Microfilaments definition
thin, solid rods built as double chain of actin subunits
83
New cards
microfiliments functions
maintain cell shape (bear tension and form crotex), assist in muscle contraction, create the contractile ring during cell division
84
New cards
pseudopodia
A cellular extension extended and contracted through microfilaments
85
New cards
cytoplasmic streaming
The motion of cytoplasm in a cell that results in a coordinated movement of the cell's contents.
86
New cards
intermediate filaments definition
Threadlike proteins in the cell's cytoskeleton that are larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules
87
New cards
intermediate filaments function
support cell shape, anchors organelles in place, and forms the nuclear lamina
88
New cards
exocytosis
The process by which the vacuole surrounding particles fuses with the cell membrane, forcing the contents out of the cell.
89
New cards
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
90
New cards
endomembrane system
A network of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles.
91
New cards
cisternae
flattened membranous sacs that make up the golgi apparatus
92
New cards
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
93
New cards
small, nonpolar molecules
molecules that pass through the plasma membrane easily
94
New cards
large polar molecules and ions
molecules that can only go through the plasma membrane by active transport, proteins pumps, or facilitated transport
95
New cards
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell (high to low concentration)
96
New cards
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy (low to high concentration)
97
New cards
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (to spread out evenly into the available space)
98
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
condition of continuous, random movement of particles but no overall change in concentration of materials (roughly equal concentrations on either side of the membrane)
99
New cards
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
100
New cards
support for endosymbiotic theory
chloroplasts and mitochondria are similar to prokaryotes in that they have circular DNA,
double membranes, can self-replicate, have ribosomes, and can produce ATP
double membranes, can self-replicate, have ribosomes, and can produce ATP