Forensic Biotechnology: DNA Fingerprinting Techniques
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is forensic science?
The intersection of law and science.
What is forensic biotechnology?
The application of biotechnology to law enforcement.
What were the early methods of identification in forensic science?
Photographs in the late 1800s, fingerprints in the early 1900s, and DNA fingerprints around 1985.
What allows DNA fingerprinting to be possible?
The genetic variability between individuals and the uniform nature of DNA in a single individual.
How much of DNA differs from person to person?
Approximately 0.1% of DNA, which is about 3 million base pairs.
What are the two types of forensic DNA profiling?
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
What is RFLP in DNA profiling?
A method that involves restriction enzyme digestion and gel electrophoresis.
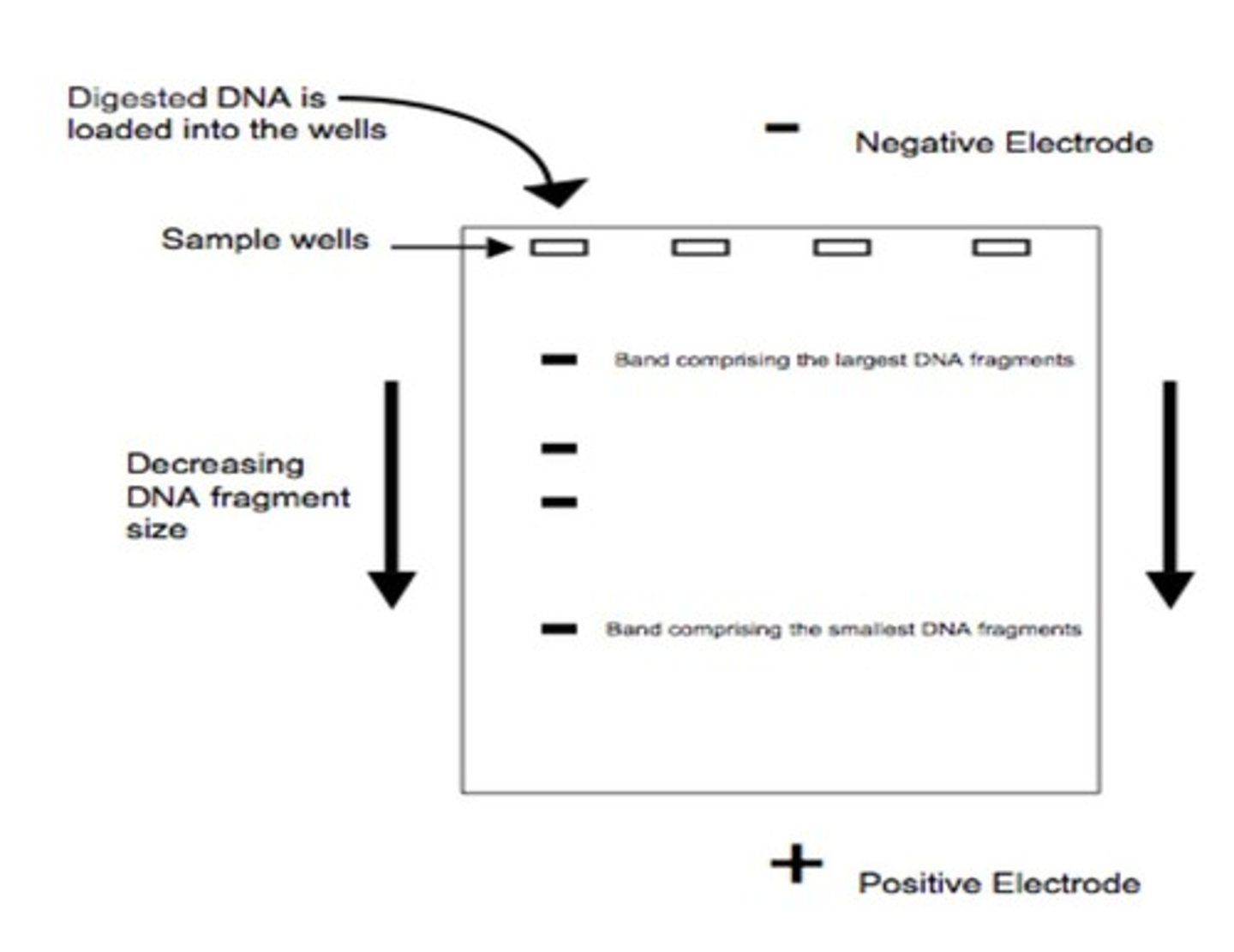
What is PCR in DNA profiling?
A method that amplifies short tandem repeats (STRs) and also uses gel electrophoresis.
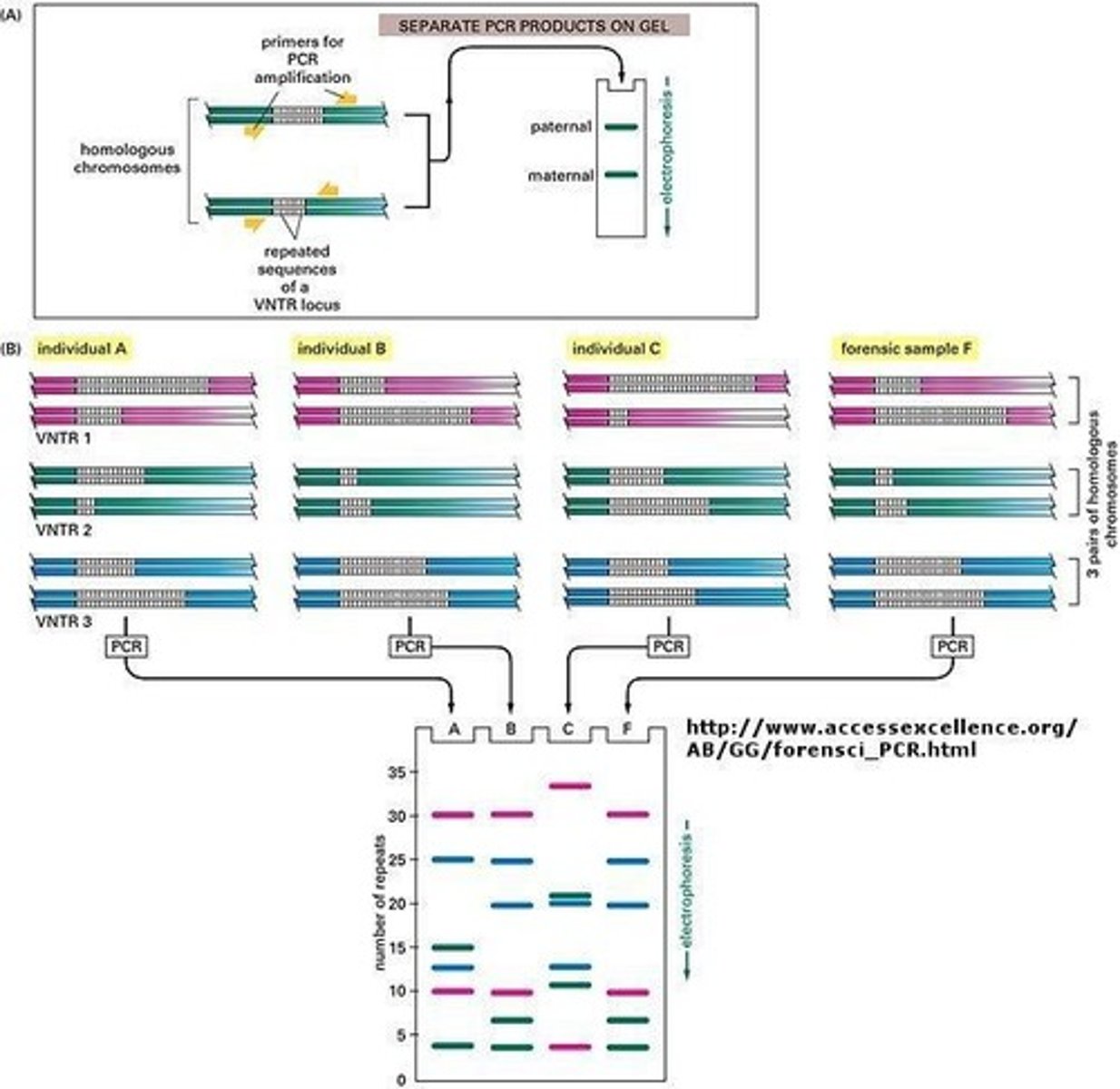
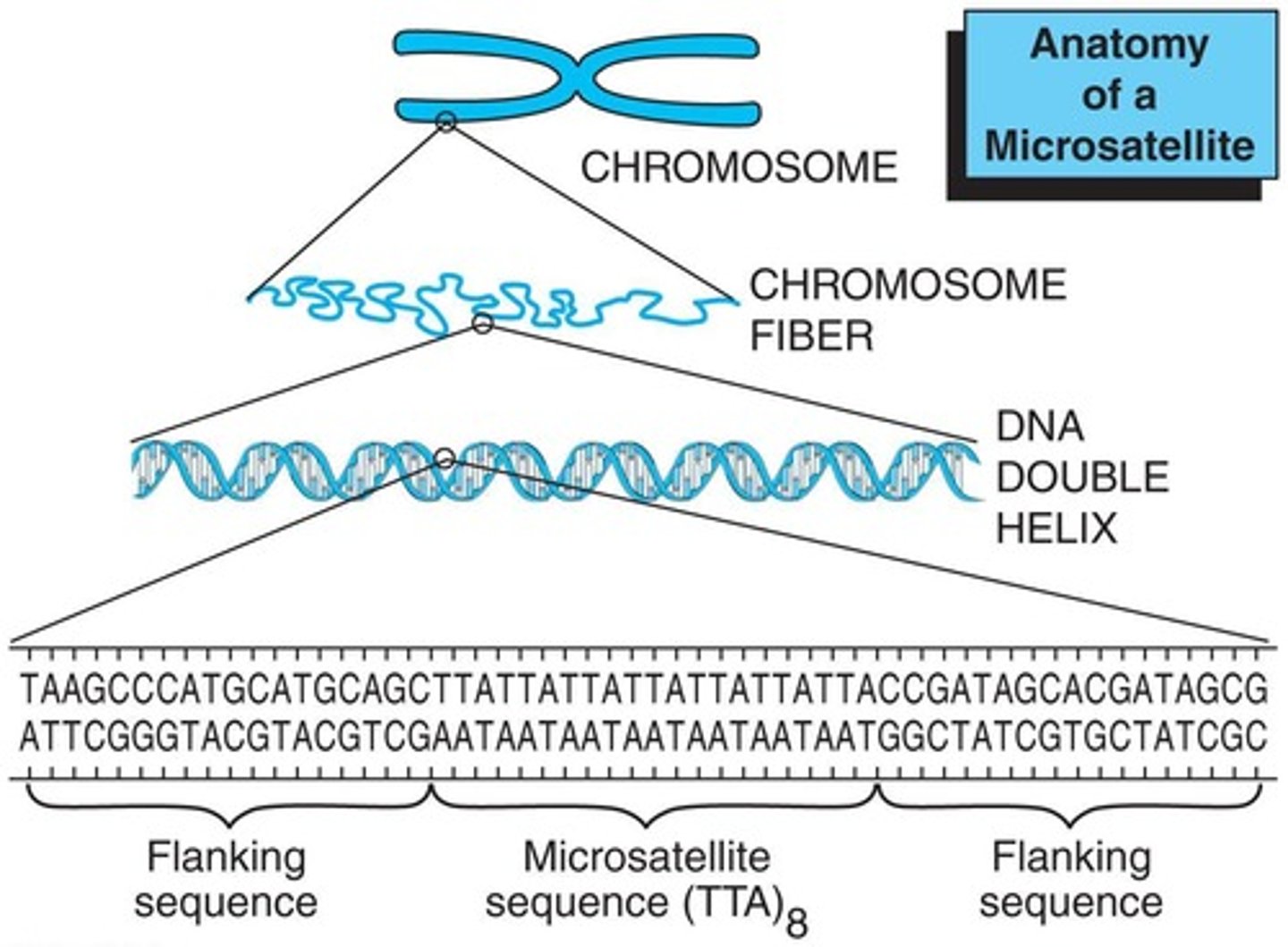
What are variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)?
Repeated sequences of DNA that vary in number between individuals, inherited from both parents.
What is the significance of STRs in DNA profiling?
STRs are short tandem repeats that are used to create DNA fingerprints, with specific primers used in PCR to amplify them.
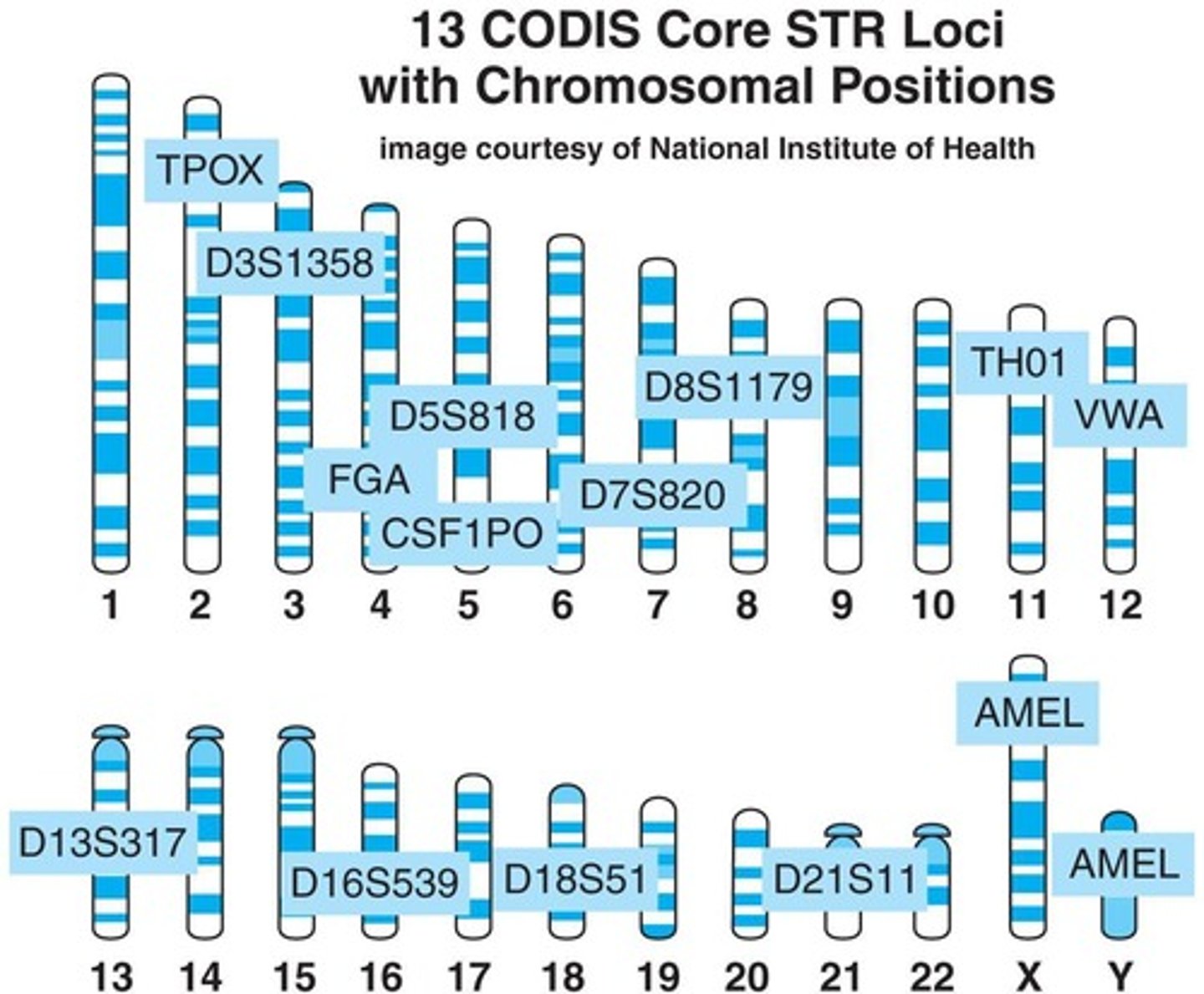
How many unique STRs does the FBI test for in DNA profiles?
13 unique STRs.
What are the differences between RFLP and PCR in DNA fingerprinting?
RFLP requires larger samples and intact DNA, while PCR can use smaller and partially degraded samples.
What is the primary concern with PCR testing?
PCR tests are extremely sensitive to contamination by foreign DNA.
What is an allele in the context of STR analysis?
The number of repeats within an STR.
How is the interpretation of DNA profiling results conducted?
Results from the suspect are compared to evidence from the crime scene; if the patterns match, the samples are likely from the same person.
What was a significant case involving DNA evidence in court?
The O. J. Simpson trial in 1994.
What can lead to the loss of DNA evidence value in court?
Breaking the chain of evidence or not following the rules of evidence.
What are some sources of human error in DNA evidence collection?
Improper storage, failure to label samples, contaminating the crime scene, and disregarding the chain of evidence.
What is the role of accreditation in forensic laboratories?
To ensure the reliability of DNA collection, processing, and analysis.
What is the purpose of paternity testing in forensic biotechnology?
To resolve child support and custody disputes.
What is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) analysis used for?
To analyze older samples that lack nucleated cellular material, such as hair, bones, and teeth.
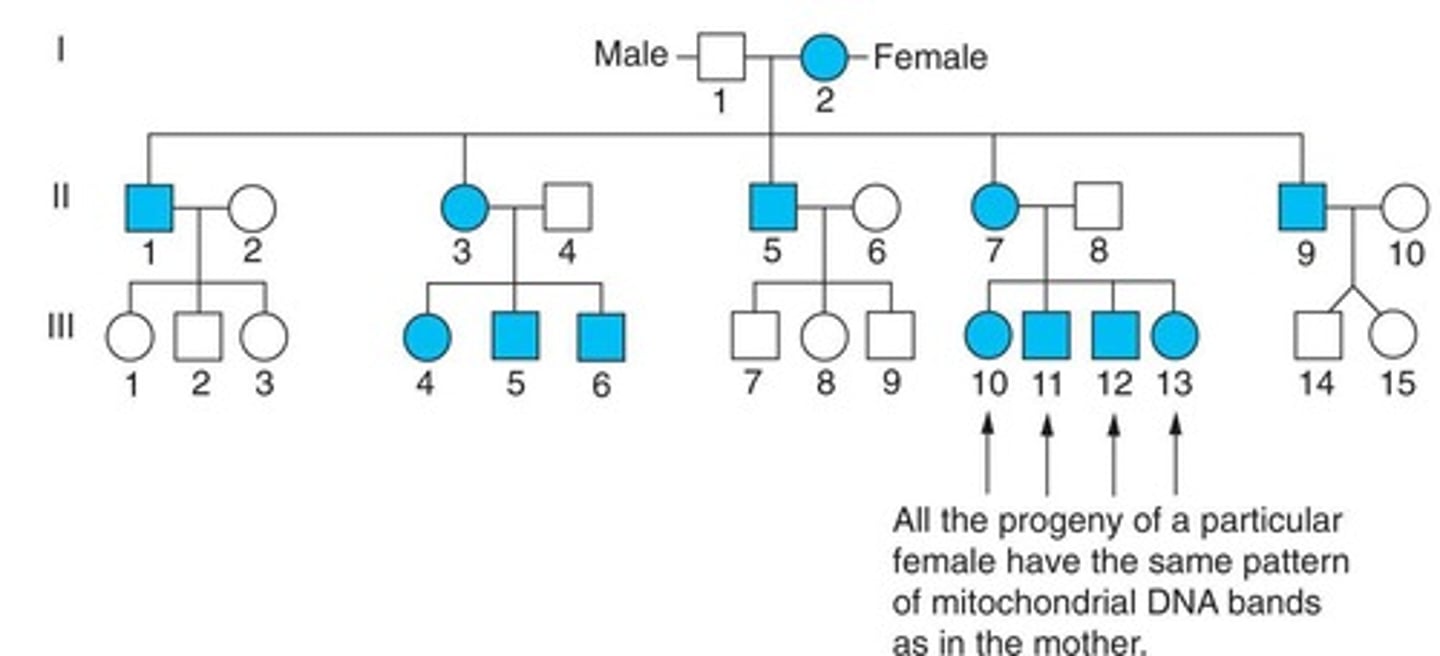
How is mtDNA inherited?
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother.
What is Y-chromosome analysis used for?
To trace relationships among males.
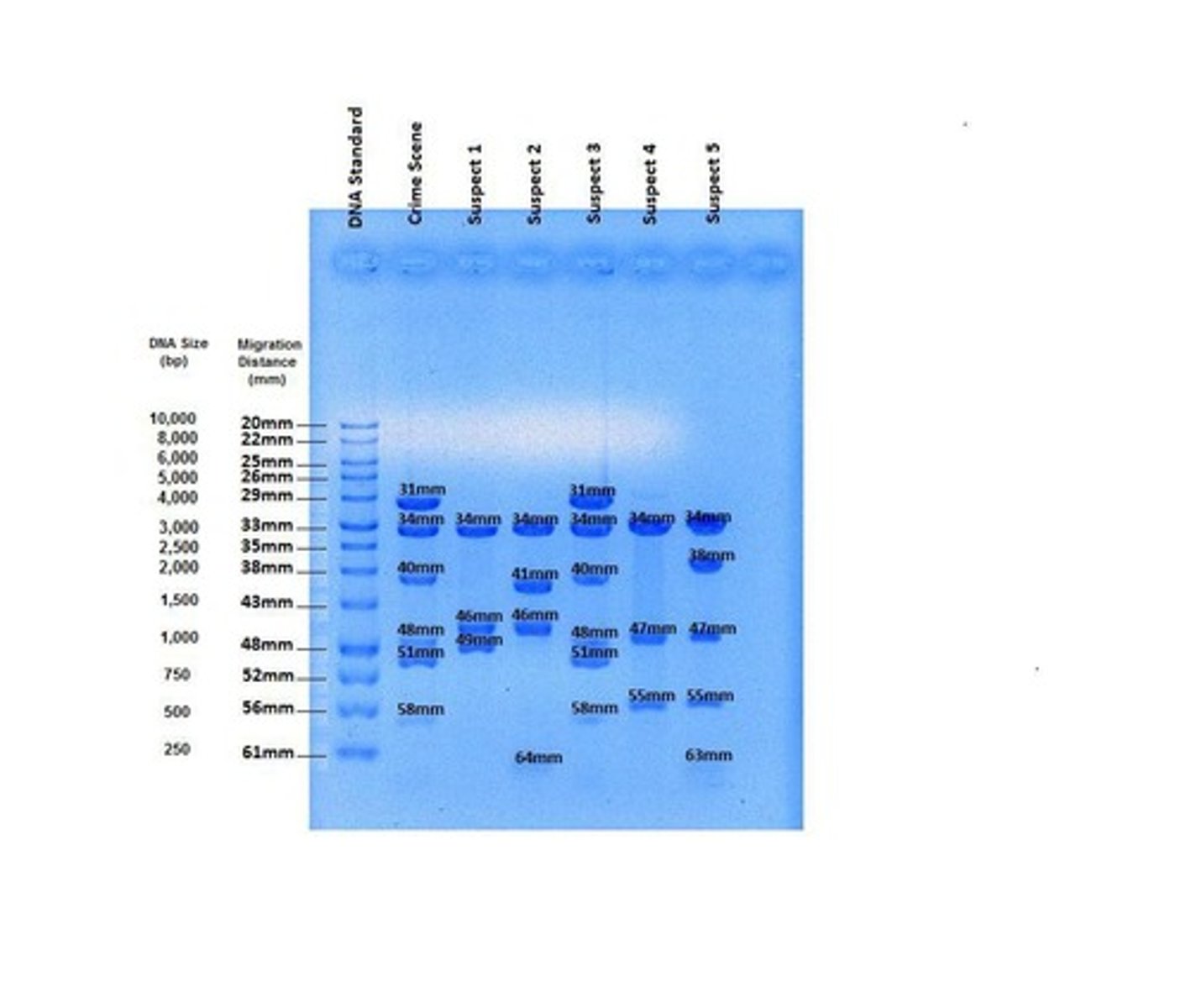
What are some applications of DNA profiling?
Determining guilt or innocence in crimes, settling paternity questions, identifying victims, and analyzing nonhuman materials.
What is the likelihood of a random member of an ethnic group matching a specific DNA profile?
Approximately 1 in 1.5 billion.
What is the significance of STR allele variations?
They create multiple possible genotypes for DNA profiling.
What happens if no difference is found in DNA testing after a statistically acceptable amount of testing?
The probability of a match is considered high.