TOPIC 6- Immunity and Host Defense
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
innate immune response

adaptive immune response
needs exposure to pathogens first before immunity is built
leukocytes
white blood cells involved in both innate and adaptive immune response
granulocytes
a type of white blood cell in which its granules are filled with reactive chemicals that can kill microbes and signal other components of immunity. examples include:
basophils and mast cells
eosinophils
neutrophiles
basophils and mast cells
a type of granulocyte that is:
not strongly phagocytotic
involved in allergic reactions because they release histamines
eosinophiles
a type of granulocyte that:
non-phagocytotis
attack large parasites by attempting to eat them
neutrophiles
type of granulocytes that:
strongly phagocytotic bcuz the granules contain digestive enzymes
they die after phagocytosis
monocyte
type of white blood cell that differentiates into either macrophages or dendritic cells
macrophage
a type of monocyte:
have specific surface receptors that recognized pathogen
detects elements specific to prokaryotes
LPS, peptidoglycan, fungal cell wall
strongly phagocytotic
dendritic cell
a type of monocyte that:

lymphocyte
natural killer cell
type of lymphocyte:

pathogen-associated molecular patterns
____ may include things like lipopolysaccharides, lipoteichoic acids, flagellin, peptidoglycan etc.
things specific to bacteria, not our own cells
pattern recognition receptor
acceptors on the surface of phagocytic cells that allows them to recognize pathogenic microbes
defensins

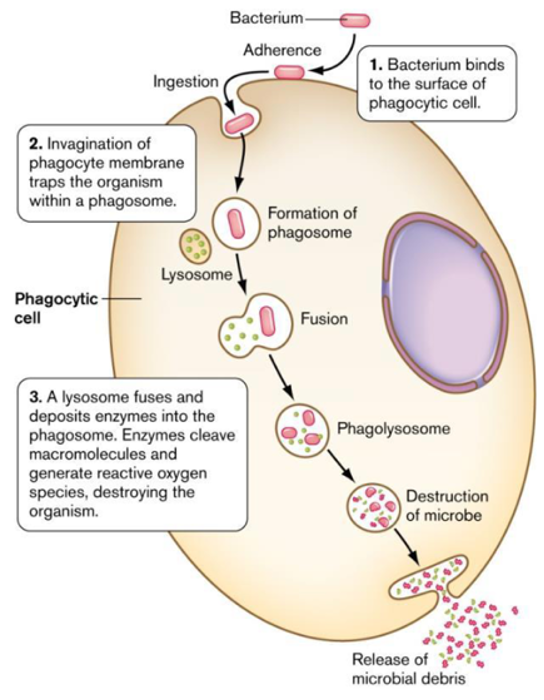
steps for phagocytosis

humoral immunity
branch of adaptive immunity that is antibody mediated
cellular immunity
branch of adaptive immune systems byt it is cell mediated
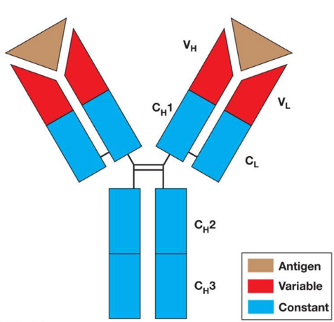
antibody
protein made by the immune system that can bind, and inactivate foreign antigens
sometimes called immunoglobulin

IgG
Monomer |
-most common -circulates through blood -most important for fighting pathogens |
-most common -circulates through blood
|
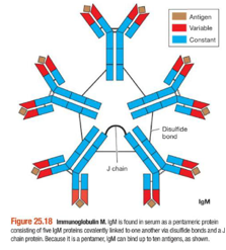
IgM
Pentamer -made of 5 antibodies |
agglutination- the process of sticking multiple identical pathogens together
|
first antibody made when a new antigen is encountered -loves blood
|
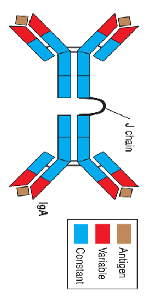
IgA
Dimer |
-protects mucosal surfaces -protects against reproductive and digestive tract infections |
Secreted into saliva, tears, and mucous |
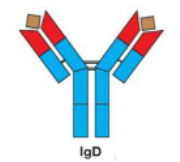
IgD
Monomer |
-b cell activator |
Found on the surface of B cells |
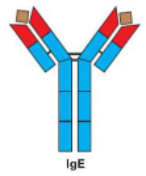
IgE
Monomer |
-causes mast cells and basophiles to release granules of histamine |
Extra bit on the ends helps them stick better on parasites |
major function of antibodies
neutralization, opsonization, agglutination, antibody mediated cytotoxicity and complement activation
neutralization

opsonization
agglutination
function of antibody in which it they stick multiple identical pathogens together
antibody mediated cytotoxicity
IgE helping eosinophils to eat parasites
Fc attaches to the eosinophils
complement
b cells
adaptive immunity cells that produce antibodies
involved in humoral immune responsw
t-cytotoxic cells

t-helper cells

antigen presenting cells
macrophages, dendritic cells and b cells
they eat foreign material and presents its antigens on their surface after phagocytosis
MHC I

MHC II

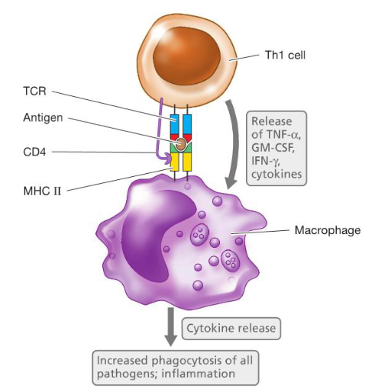
humoral response
b cell receptor (IgD) attaches to the pathogen
B cell eats the pathogen
B cell presents the pathogen’s antigen on its MHC II
T helper cells bind to the MHC II of the B cell
if the antigen matches with the T-cell’s receptor, then the T helper cell will secrete cytokines to activate the B cell into releasing antibodies
plasma cells
short lived B cell that makes a LOT of antibody
makes IgA to prevent pathogens from entering the body
memory B cells
long lived B cell that targets a specific pathogen
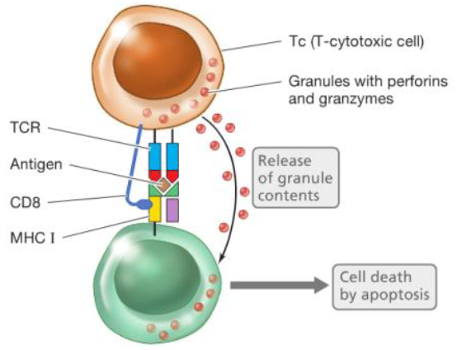
t-cytotoxic cells

t-helper cells

perforins
contained in the granules of effector Tc cells
they poke holes in the infected cell’'s membranes so they die
granzymes
enzyme from the granules of infector Tc cells that promote apoptosis (cell death)
primary response
live attenuated vaccine

whole agent inactivated vaccine

subunit vaccine

toxiod vaccine