unit 2
1/371
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
372 Terms
what are the functions of the integument (skin)?
protection from physical damage, uv radiation, and diseases, coloration, thermoregulation, water/salt balance, respiration (ex. salamanders), secretory functions (ex. poison), feeding (ex. mammary glands), sensory functions, locomotion
what does the skin consist of?
the epidermis and dermis
describe the epidermis
the outer layer, derived from ectoderm, has an important component: keratin
describe the dermis
the underlying layer; much thicker than the epidermis, derived from mesoderm. contains glands formed by the epidermis that sink into dermis
describe the epidermis in fish
covers the scales, small amounts of keratin, has mucous glands that produce mucous or slime, constantly being sloughed off and replaced.
describe the dermis in fish
much thicker than the epidermis, produces scales, contains chromatophores
what are chromatophores?
cells that hold pigments
describe the epidermis in amphibians
thin and flexible (to allow for gas and water uptake), sheds periodically, some evidence of keratin, have mucous and granular (poison) glands.
describe the dermis in amphibians
contains chromatophores and scent glands (for reproductive and social purposes)
describe the epidermis in reptiles
more keratinized than fish and amphibians, produces scales (made of keratin), shed often
how do snakes, lizards, and crocodiles shed?
snakes: shed in one piece
lizards: shed in several smaller pieces
crocodilians: generally don’t shed
describe the dermis in reptiles
thin, few glands (mostly scent glands), dermal plates are sometimes seen (ex. carapace/plastron of turtles), chromatophores in some groups (ex. chameleons)
describe the epidermis in birds
produces feathers made of keratin; feathers are shed periodically and replaced (molting); leg scales, covering of beak, nails/claws on toes are epidermal derivatives (also keratinized); devoid of glands (except for uropygial glands used for preening)
describe the structure of feathers
main shaft (rachis) ends in a hollow quill (calamus). barbs extend laterally from rachis (forming vane), barbules branch off of barbs, hooks branch off barbules and interlock.
which vertebrate group has the most complex integument?
mammals
what are the four glands in the epidermis of mammals?
sweat glands, scent glands, sebaceous glands, mammary glands
describe sweat glands in mammals (2 aspects)
eccrine sweat glands: used for cooling (primates)
apocrine sweat glands: have sexual functions
where do non-primate mammals have eccrine sweat glands?
hands/feet, excretions are used to provide grip
describe scent glands in mammals
mainly used to mark territorial boundaries, found on the legs, near eyes, cheeks, and anal regions.
describe sebaceous glands in mammals
associated with hair follicles, produce oily material that keeps hair pliable.
describe mammary glands in mammals
paired (prominent in females, rudimentary in males), 1-12 pairs (related to maximum number of offspring), grow much with sexual maturity, produce milk
describe hair in mammals
major derivative of the epidermis, strong and pliable, thick layer is good for thermoregulation, affects coloration
hair and feathers are? (homologous/analogous)
homologous; both are derived from reptilian scales (recent embryological/developmental evidence demonstrates this)
describe the 3 types of hair in mammals
guard hair: what you generally see
under hair: shorter layer under guard hair (insulation)
vibrissae: whiskers used as sensors
describe the structure of antlers
cervids have antlers. antlers are only found in males (except for caribou/reindeer), part of the skeletal structure: outgrowth of skull. shed yearly, covered with velvet during growth which is an epidermal layer.
describe the structure of horns
bovids have horns. horns have a bony base and are covered with a thick layer of keratin, epidermal material, not shed - continue to grow throughout life, in many cases both sexes have horns.
are giraffe horns actually horns?
no, they are ossicones (ossified cartilage covered in skin).
how has trophy hunting affected horn size?
when trophy hunting is intense, horn size decreases
describe rhinoceros tusks
tusks are made of a thick keratin layer derived from dermis, tusks aren’t paired, not shed, but can regenerate.
what are the functions of the endocrine system?
controls most body functions (metabolism, growth, reproduction, behavior, color changes, etc), acts in conjunction with the nervous system, slow-acting but has long-lasting response
what are the two components of the endocrine system?
endocrine glands and hormones
describe endocrine glands
ductless glands containing secreting cells that produce hormones
describe hormones
complex chemicals that travel through the bloodstream and stimulate changes in other parts of body
what are the 9 glands of the endocrine system?
hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, pineal, ovaries, testes
describe the hypothalamus
master center of the endocrine system. located in the brain, regulates hunter, thirst, sleep, and body temperature. produces releasing hormones, which simulate the pituitary gland to produce other hormones
describe the pituitary gland
controls all endocrine glands (except hypothalamus), influences growth and metabolism, made up of the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary.
what does the anterior pituitary produce?
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), prolactin (PRL)
what does follicle stimulating hormone do?
in ovaries: egg (ovule) production
in testes: sperm production
what does luteinizing hormone do?
in ovaries: induces ovulation, estrogen and progesterone production
in testes: testosterone production
what two hormones are known as gonadotropins (hormones affecting the gonads)?
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
what does the thyroid stimulating hormone do?
causes thyroid to produce thyroid hormones
what does the growth hormone do?
stimulates body cells to grow and maintain body size once attained
what does adrenocorticotrophic hormone do?
causes adrenal cortex to produce hormones, important for molting/shedding
what does prolactin do?
maturation of mammary glands, milk production, nest building, protection of young (parental behaviors)
what does the posterior pituitary release?
oxytocin and vasopressin
both are actually produced in the hypothalamus, but are stored in the pituitary.
what does oxytocin do?
uterine contractions in mammals, release of milk. can stimulate labor.
what does vasopressin do?
also called the antidiuretic hormone, it regulates water loss by kidneys
describe the thyroid
located in the neck, produces thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (thyroxine)
describe thyroxine
under control of TSH, controls growth, some regulation of metabolic rate, and is key in metamorphosis for amphibians.
what hormone is vital to amphibian metamorphosis?
thyroxine. when given excess amounts of it, metamorphosis occurs early, and when removed, metamorphosis does not occur.
describe the parathyroid gland
it’s embedded within the thyroid, two pairs of small glands. produce parathyroid hormone (PTH).
what does parathyroid hormone do?
controls calcium levels in blood. it’s important in bone formation and egg shell formation in birds.
describe the adrenal gland
located above the kidneys, under control of ACTH. two distinct areas: the cortex and the medulla
describe the cortex (adrenal gland)
the outer part; makes several hormones that control glucose and minerals (cortisol, aldosterone)
describe the medulla (adrenal gland)
the inner part; makes the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), important components of the fight-or-flight response to stress
describe the pancreas
produces the hormones insulin and glucagon
what does insulin do?
controls glucose levels in blood (increases glucose use/storage in cells, aka reduces glucose in blood stream)
what does glucagon do?
controls glucose levels in blood (increases glucose in blood stream)
what is diabetes caused by?
lack of insulin
describe the pineal gland
also called the third eye. located in the brain, produces the hormone melatonin
what does melatonin do?
helps regulate diurnal rhythms (sleeping, feeding, etc). it is negatively light sensitive, so is only secreted in the dark. it’s responsible for daily and seasonal hypothermia in lizards preceding dormancy, and is linked to seasonal affective disorder (SAD) in humans.
describe the ovaries
under control of gonadotropins (FSH and LH), produce several female reproductive hormones; estrogen, progesterone, and relaxin.
what does estrogen do?
reproductive tract development and sexual behavior; secondary sexual characteristics
what does progesterone do?
mammary gland maturation; maternal behavior
what does relaxin do?
prepares the body for labor, cervix dilation.
describe the testes
controlled by gonadotropins (FSH and LH), produce male reproductive hormones: androgens (especially testosterone)
what do androgens do?
development of reproductive behavior, secondary sexual characteristics in males, "territory defense behavior” caused by increased testosterone
how does the endocrine system work?
receptors around the body detect changes in the environment, information is sent to the brain, which triggers the hypothalamus to make releasing hormones. releasing hormones trigger pituitary to make other hormones, which travel through the bloodstream to affect target organs.
what are the functions of the digestive system?
acquiring food, transporting food through the digestive tract, physical (mechanical) treatment, chemical treatment, absorbing nutrients and fluids into the body, ridding the body of wastes.
describe the digestive system of pre-vertebrates
filter feeders with cilia and gill slits. no true stomach, separate liver or pancreas, or gut muscles.
what are some differences between aquatic and terrestrial vertebrate feeding?
aquatic: suction is important (no equivalent in terrestrial)
terrestrial: tongue (handles food), salivary glands (moistens food), and large intestine (reabsorbs water) are important
how does the digestive system work (order)?
transportation → physical treatment → chemical treatment → absorption
what is transportation (digestive system)?
the “disassembly line” - substance is transported along the gut after collection
what is physical treatment (digestive system)?
mouth begins particle size reduction; size must be further reduced to facilitate chemical attack.
what is chemical treatment (digestive system)?
breakdown of potentially useful materials to molecules used by cells
what is absorption (digestive system)?
after breakdown, useful products are absorbed and circulated to cells and storage areas.
what are the basic parts of the digestive system?
reception (mouth parts, tongue, salivary glands), conduction (esophagus), storage (stomach (birds: crop)), grinding (birds: gizzard) and early digestion (stomach (acid)), terminal digestion and absorption (small intestine (alkaline)), water absorption and concentration of solids (large intestine), defecation
what are the teeth of fish, amphibians, and reptiles used for?
primarily used for gripping prey (homodont dentition)
what are the teeth of mammals like?
are only organisms that can chew (true mastication), heterodont dentition (incisors: biting and cutting; canines: seizing and piercing; molars & premolars: grinding and crushing)
what adaptation do birds have to pre-process food?
birds lack teeth and have beaks instead. bills are often serrated and hooked for seizing and tearing apart prey.
what adaptation do snakes have to pre-process food?
snake skull structure and jaws are highly kinetic, mandibles are only connected via a stretchy ligament
what structures are involved in transportation (digestive system)?
pharyngeal region (throat); some movement by cilia but mostly voluntary muscular activity (swallowing)
remainder of tract: sheets of smooth muscles (involuntary), longitudinal and circular layers in a spiral arrangement, active in peristalsis (waves of successive constrictions pushing the food)
describe the esophagus
anterior-most part of the digestive tract (between pharynx and stomach), made of tough material that resists scouring. sometimes ciliated in chondrichthyes, amphibians, and reptiles, but transport usually by peristalsis.
in birds, the esophagus has other functions, such as?
the crop of birds is formed by the esophagus (for storage of grain and other foods), and in pigeons, the esophagus exudes a milky substance regurgitated to young as food (pigeon milk).
describe the stomach
muscular, pouch-like expansion of the foregut anterior to the small intestine. serves in food storage, physical and chemical treatment. inside is convoluted and studded with mucous and secretory cells (produce gastric acid). found in most vertebrates, but filter feeders have no stomach. stomach is large and muscular in animals that feed on big chunks of food.
what is chyme?
food reduced to a soft, moist pulp. accomplished by muscle action, mainly by stomach
how does mucus aid in digestion?
moisture is provided by mucus producing glands along the length of the gut, facilitates passage and improve pulverization.
what is the bird and crocodilian variant of the stomach?
anterior end is a proventriculus, posterior region is gizzard
what is the ruminant variation of the stomach?
4 chambered stomach: rumen, reticulum (tripe), omasum, and abomasum
describe a bird’s “stomach”
proventriculus produces digestive juices, gizzard grinds food (muscular action and usually grit or pebbles help)
describe a ruminant’s 4-chambered stomach
new food enters the rumen and reticulum and is kneaded with liquid and fermented by bacteria and protozoa. rumen and reticulum reduce food to a workable pulp (fermentation chambers). microorganisms break down cellulose in plant materials and make amino acids, proteins, vitamins, and fatty acids (which are absorbed by the rumen). “cud" (larger solids) are regurgitated and reworked in the mouth, re-swallowed, and passed to omasum for further break-down. abomasum is the “true stomach” producing gastric juices and containing the 4 usual mammalian stomach tissues.
what are the 4 stomach epithelial tissues?
esophageal, cardiac, fundic, and pyloric
describe esophageal epithelium
anterior, non-glandular epithelium similar to esophagus
describe cardiac epithelium
only in mammals, transitional region of columnar cells secreting mucus
describe fundic epithelium
region producing mucus secretions as well as digestive enzymes (protein-breaking pepsin and fat-splitting lipase; HCl decreases pH, favoring action of pepsin)
describe pyloric epithelium
“downstream” end of the stomach containing tubular glands as in the cardiac region
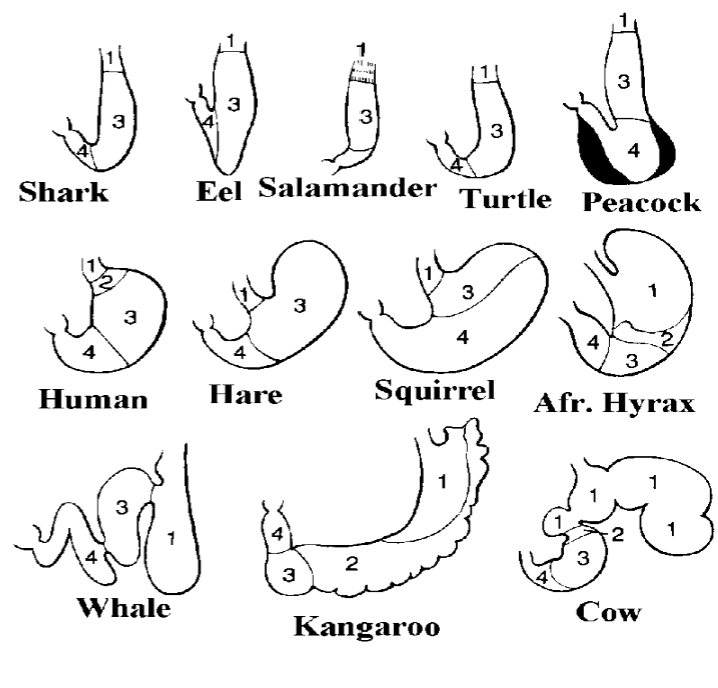
label each
1: esophageal epithelium
2: cardiac epithelium (only in mammals)
3: fundic epithelium
4: pyloric epithelium
ruminant vs non ruminant efficiency
horse (non-ruminant): food takes 30-45 hours to be digested, no control on rate of food processing regardless of cellulose and lignin content, non-selective of content, eats more food than cow
cow (ruminant): food takes 70-100 hours to be digested, more selective in food habits
describe the small intestine
starts posterior to the pylorus of the stomach. this is where most chemical digestion occurs, also major site of absorption of food material (nutrients). internal surface area of intestine enlarged by villi (digitations), or spiraling and coiling to allow increased absorption.
describe the large intestine (colon)
starts posterior to small intestine, major site of water re-absorption. compacts waste (collects unabsorbed materials into feces), most developed in terrestrial vertebrates that need to conserve water. terminates in a rectum and anus in mammals and many fish, terminates in a cloaca in sharks, amphibians, reptiles, and birds. an anus discharges feces whereas a cloaca discharges both urine and feces