H Biology - Unit 3 - KA1 - Food Supply, Plant Growth, and Productivity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is food security?
Food security is the ability of human populations to access food of sufficient quality and quantity
How should food be produced?
Any food should be produced sustainably
What should food production not do?
Food production must not damage or destroy the natural resources needed for agriculture
What are the three factors affecting food production?
The three factors affecting food production are;
Photosynthesis
Plant growth
Breeding crops for particular traits
How can food production be affected through photosynthesis?
Food production can be affected through photosynthesis by;
Light intensity
CO2 concentration
Temperature
Water availability
How can food production be affected through plant growth?
Food production can be affected through plant growth by;
Higher yielding cultivars
Fertilisers
Protecting crops from diseases and pests
Protecting crops from competition
How can food production be affected through breeding crops for particular traits?
Food production can be affected through breeding crops for particular traits by breeding crops that have;
High nutritional values
Resistance to pests and disease
The ability to thrive in difficult conditions such as droughts or flooding
Physical features that are good for growing and harvesting such as big leaves or a strong stem.
What are the things farmers can influence that affect food production?
The things farmers can influence that affect food production are;
Photosynthesis
Plant growth
Why do livestock produce less food per unit area than crops?
Livestock produces less food per unit area than crops due to loss of energy between trophic levels
How many fates of light are there?
There are three fates of light
What are the three fates of light?
The three fates of light are;
Absorption
Transmission
Reflection
What are the three pigments in leaves that absorb light?
The three pigments in leaves that absorb light are;
Chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll B
Carotenoids
What do absorption spectra show?
Absorption spectra show the absorption of light by different pigments over the range of visible wavelengths of light
What do each of the pigments absorb in the absorption spectra?
Each of the pigments absorb a different range of wavelength of light
What do carotenoids do?
Carotenoids extend the range of wavelengths absorbed and pass the energy to chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
What does action spectra show?
Action spectra show the rate of photosynthesis over the range of visible wavelengths of light.
What are the stages of photosynthesis?
The stages of photosynthesis are;
Light reaction 1
Light reaction 2
Carbon fixation
What occurs in Light Reaction 1
In Light Reaction 1;
Light energy absorbed excites the electrons in the pigment molecule
The high energy electrons are transferred along the electron transport chain. This releases energy.
The energy released is used by the enzyme ATP synthase to generate ATP.
What occurs in Light Reaction 2?
In Light Reaction 2;
The energy released in Light Reaction 1 is used for photolysis
Oxygen is produced. This diffuses out of the cell.
The hydrogen produced joins coenzyme NADP to form NADPH.
What are the essential molecules for Carbon Fixation?
The essential molecules for Carbon Fixation are;
ATP from Light Reactions
NADPH from Light Reactions
CO2 from the atmosphere
RuBisCO enzyme
RuBP
How many reactions are there in Carbon Fixation
There are three reactions in Carbon Fixation
What is Reaction 1 in Carbon Fixation?
Reaction 1 in Carbon Fixation;
The enzyme RuBisCO fixes CO2 by attaching it to RuBP. This produces 3PG.
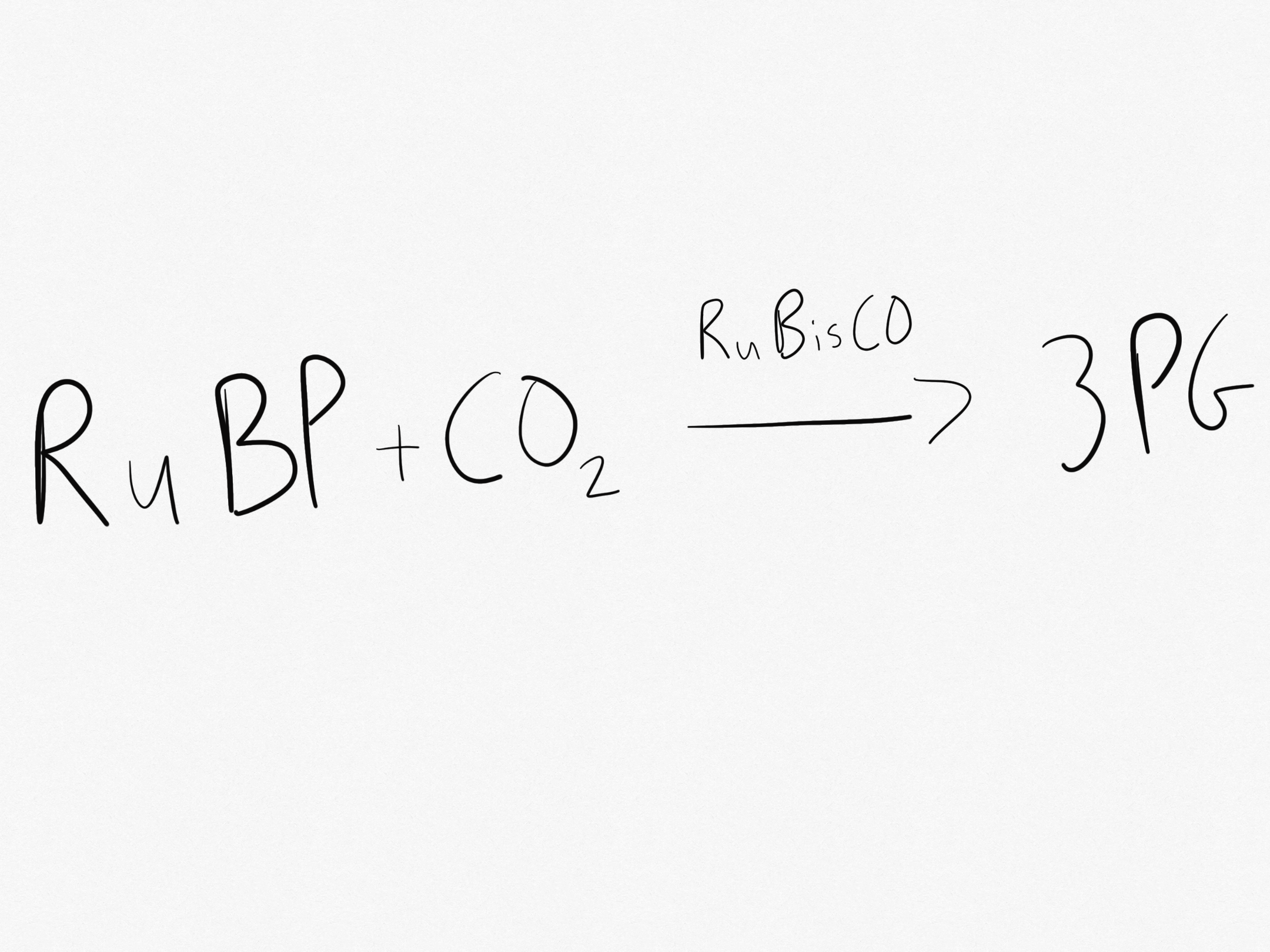
What is Reaction 2 in Carbon Fixation?
Reaction 2 in Carbon Fixation;
The 3PG produced is phosphorylated by ATP and combined with hydrogen ions from NADPH to form G3P.
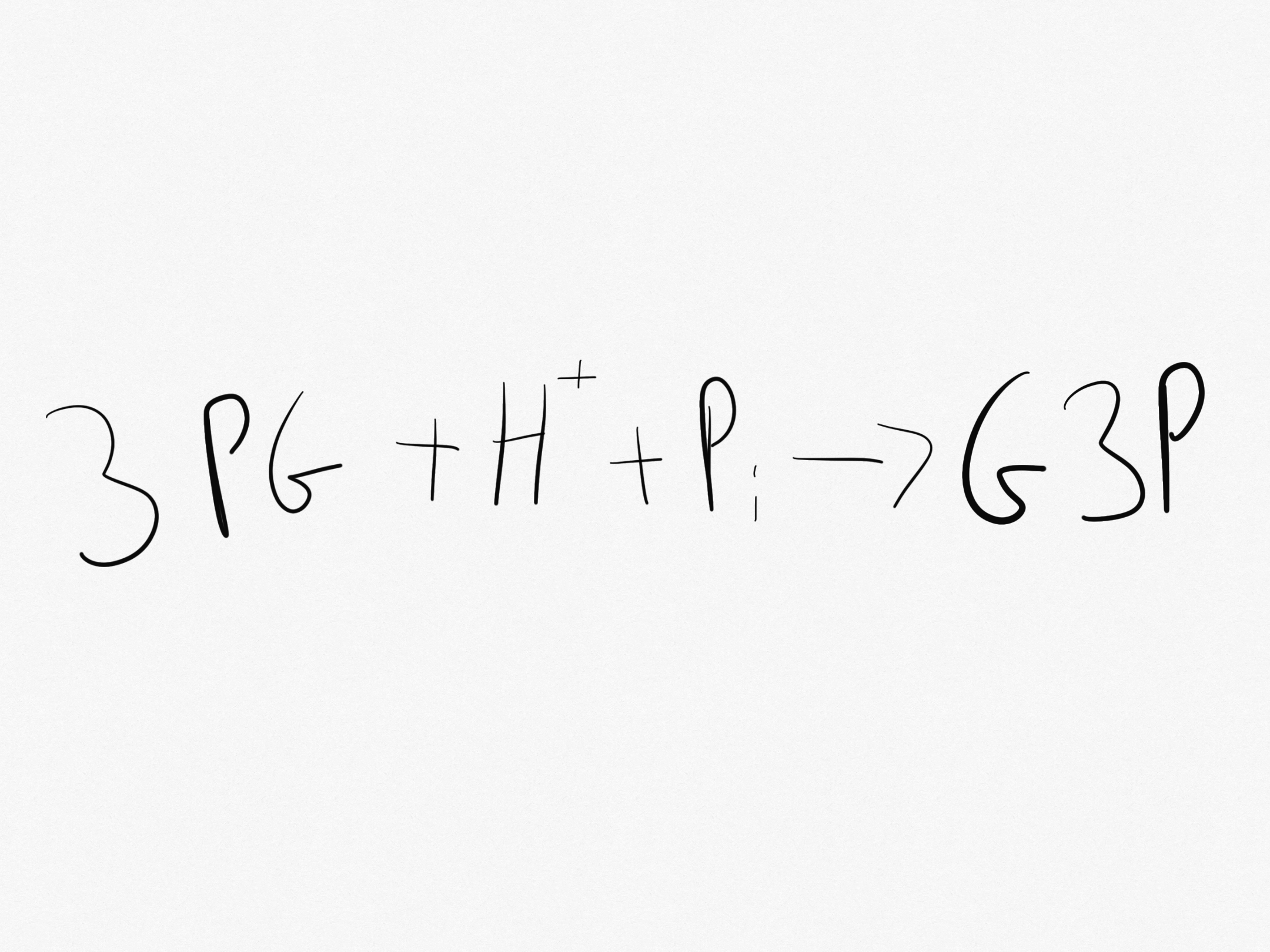
What is Reaction 3 in Carbon Fixation?
Reaction 3 in Carbon Fixation;
G3P is used to regenerate RuBP and for the synthesis of glucose
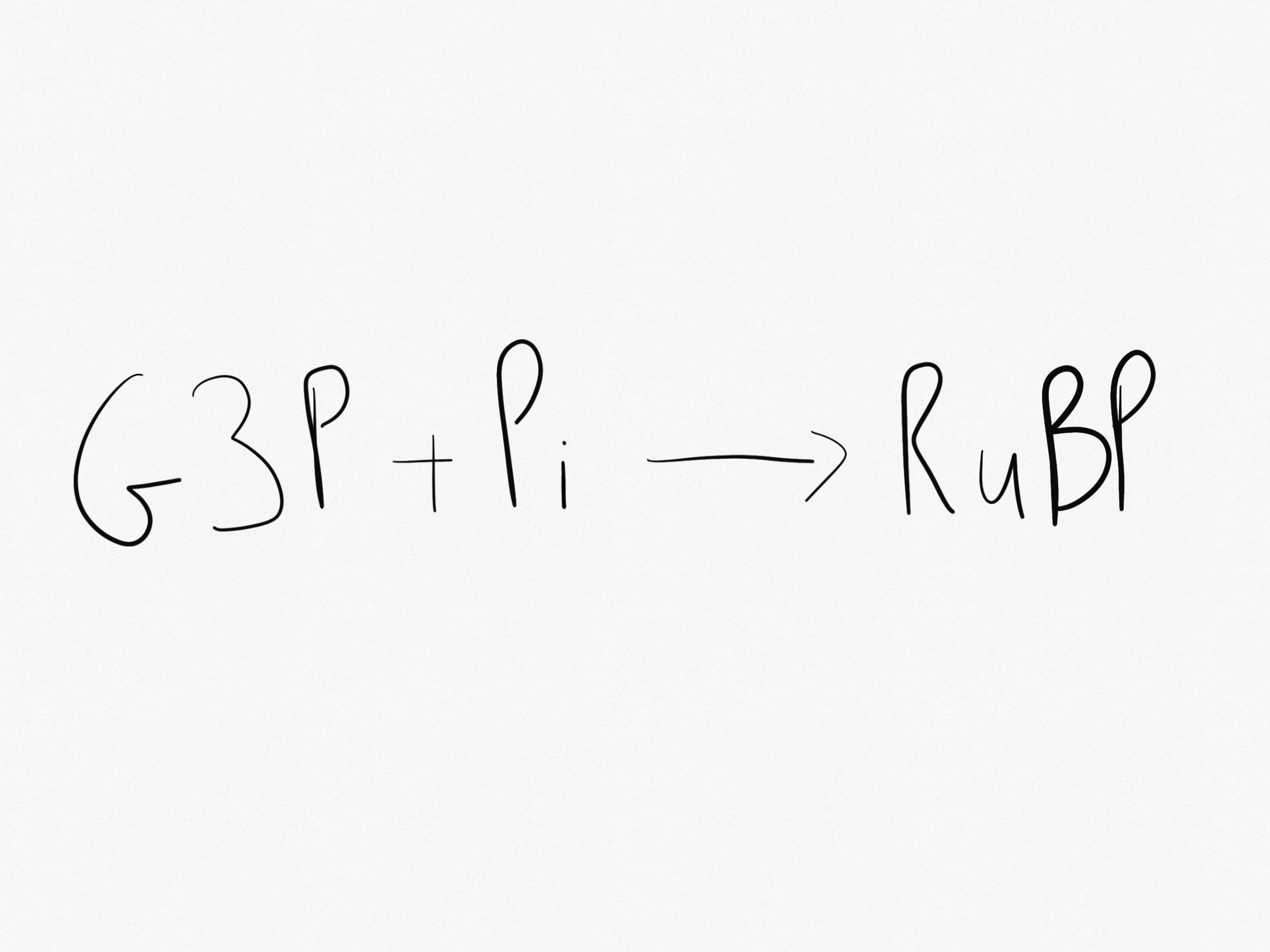
Carbon fixation
Carbon fixation:
The enzyme RuBisCO fixes CO2 by attaching it to RuBP. This produces 3PG.
The 3PG produced is phosphorylated by ATP and combined with hydrogen ions from NADPH to form G3P.
G3P is used to regenerate RuBP and for the synthesis of glucose
What are the fates of sugar in photosynthesis?
The fates of sugar in photosynthesis are being used;
As respiratory substrate
To synthesise carbohydrates
As starch for storage
As cellulose for cell walls
In biosynthetic pathways which make DNA, proteins, and fat.
When answering photosynthesis questions what coenzyme must you say?
When answering photosynthesis questions you must say NADP