Anatomy Exam 2 - Mizzou (Hill)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is the function of cartilage?
1. support soft tissues
2. model for formation of bone
3. gliding surface at articulations
What is the function of bone?
support, protection, movement, hemopoiesis (blood cell production), energy and mineral reserves
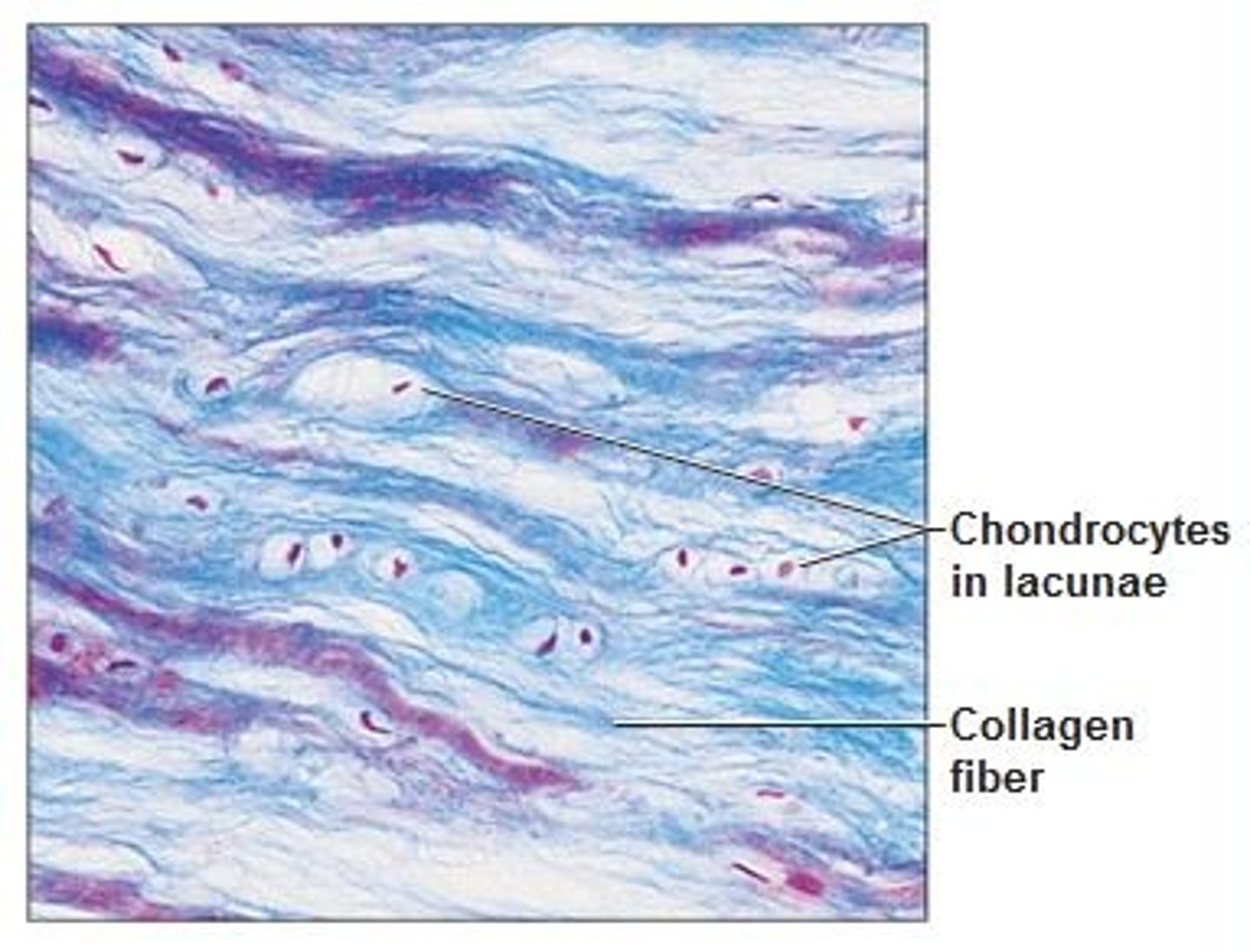
Hyaline Cartilage
-Most common type
-Has tiny nearly invisible collagen fivers called fibrils
Found: Ends of long bones, costal cartilages, respiratory structures, fetal skeleton
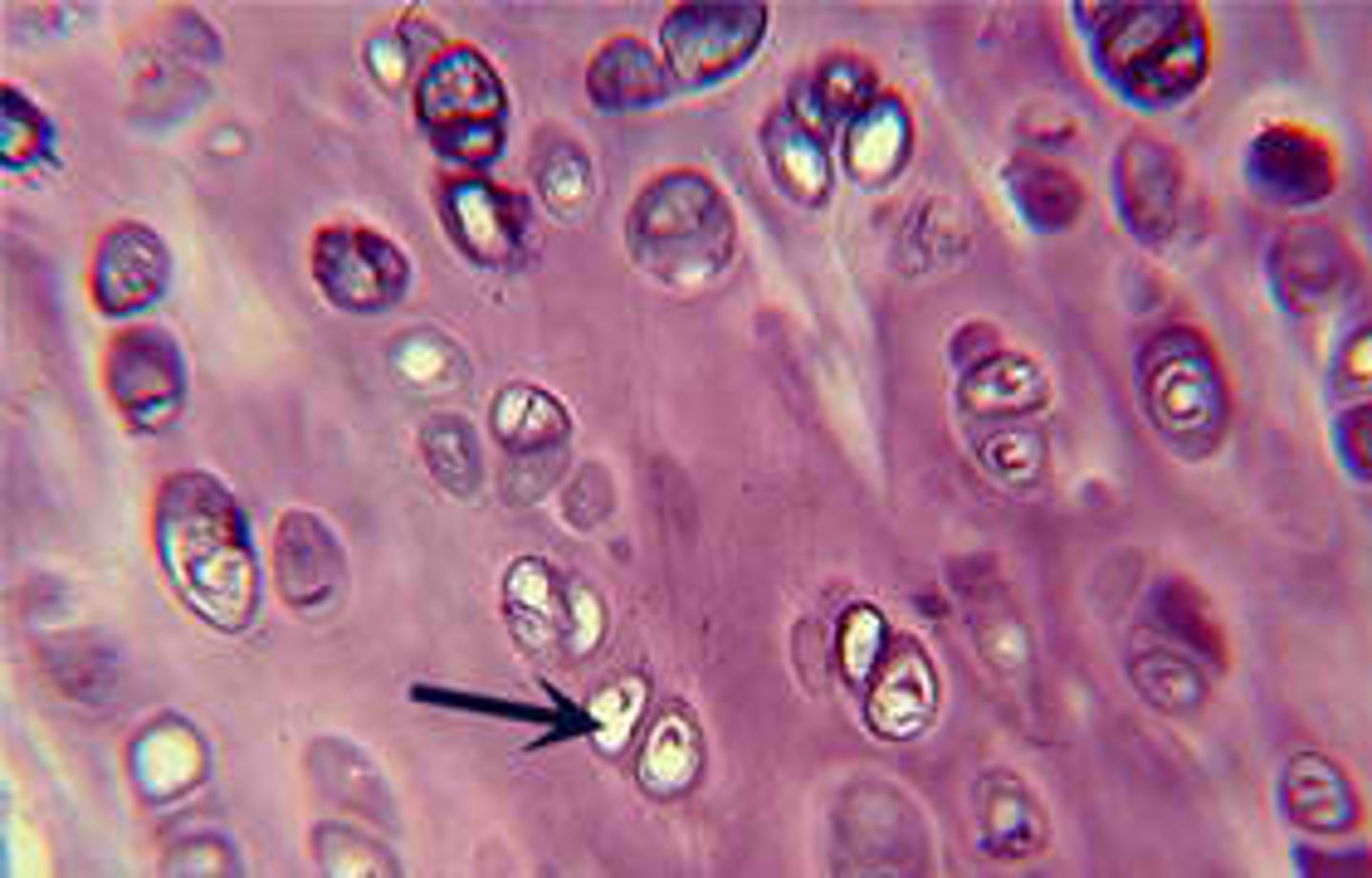
Elastic Cartilage
- VERY similar to hyaline but los of elastic fibers
- Very resilient/flexible, tolerates bending
Found: in pinna (outer ear) and epiglottis
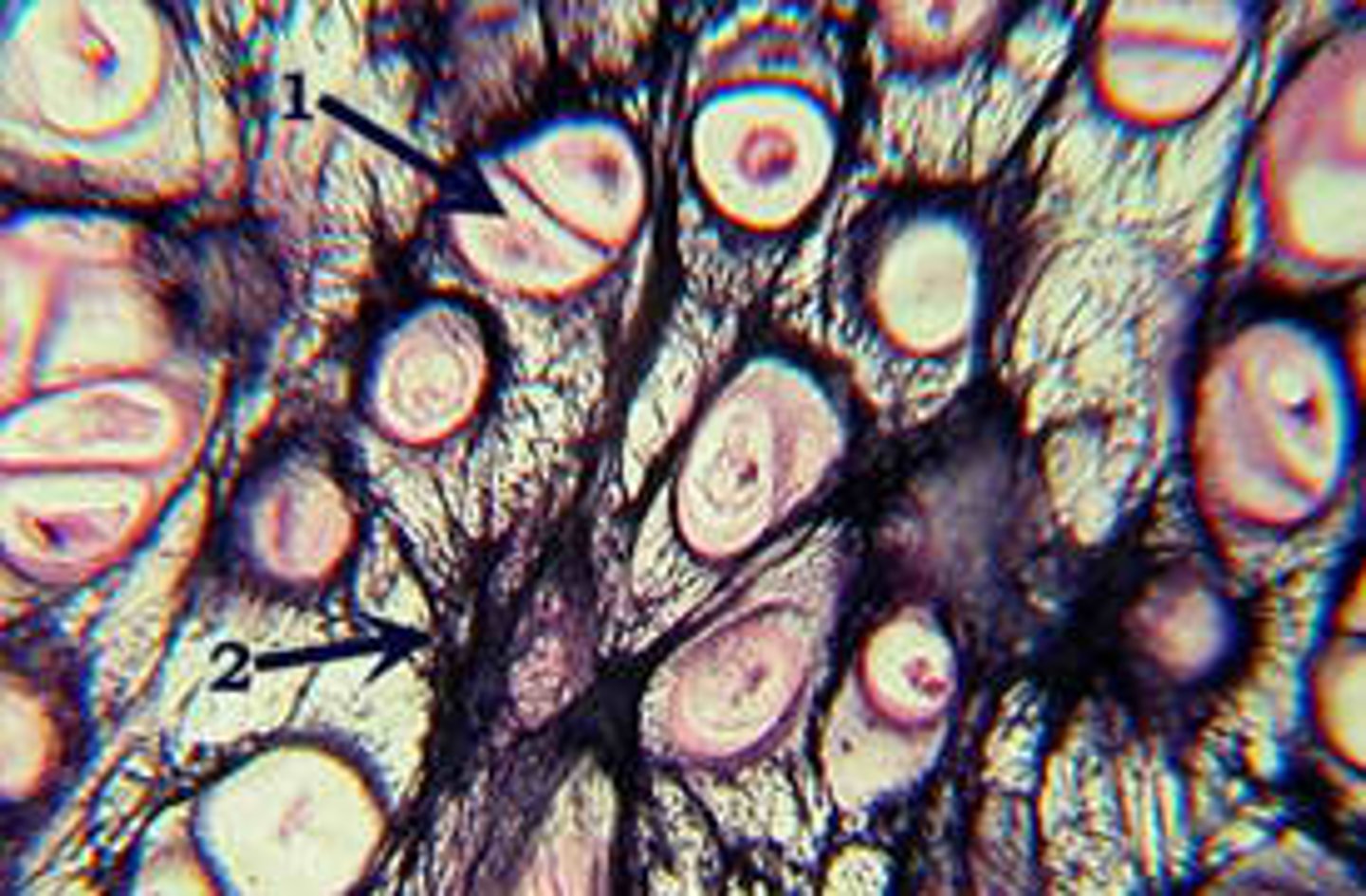
Fibrocartilage
- Has little ground substance and the matrix has thick, dense collagen fibers
- Resists strong compression
Found: in intervertebral disks, knee joint, public symphysis
Irregular bone
- Elaborate/complex shapes
- Compact bone covers internal spongy bone
- Vertebrae, ossa coxae (hip bones), and several bones in the skull (ethmoid and sphenoid bones)
Long bone
- Greater length than width
- Most common bone shape
- Upper/lower limbs
Short bone
- length nearly equal to their width
- covered by compact bone, interior is spongy bone
- carpals (wrist bones) and tarsals (bones in the foot). Sesamoid bones, which are tiny, seed-shaped bones along the tendons of some muscles, are also classified as short bones. The patella (kneecap) is the largest sesamoid bone
Flat bone
- flat, thin surfaces
- roughly parallel surfaces of compact bone with a layer of internally placed spongy bone
- provide extensive surfaces for muscle attachment and protect underlying soft tissues
- form the roof of the skull, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs
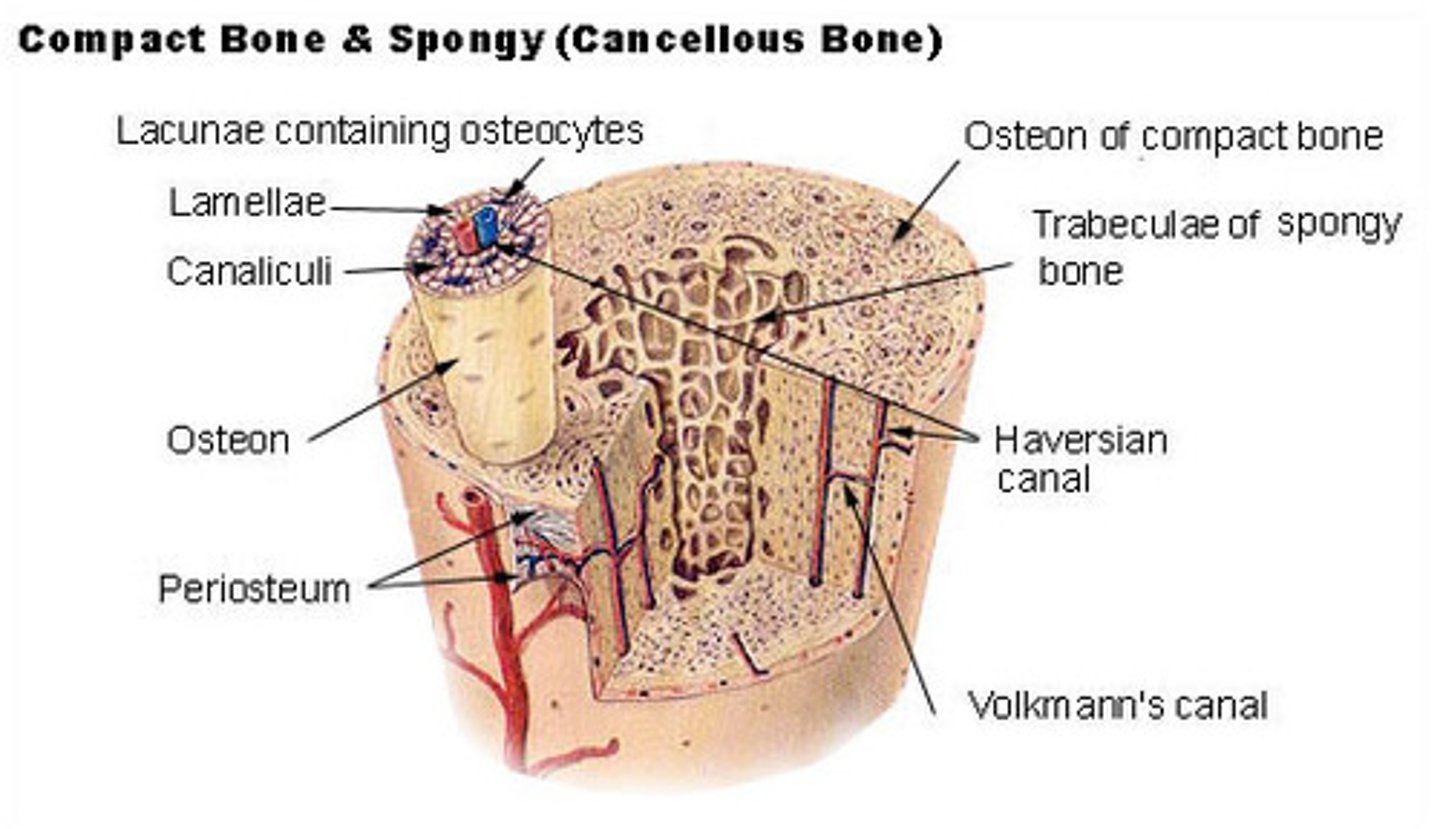
Parts of a long bone
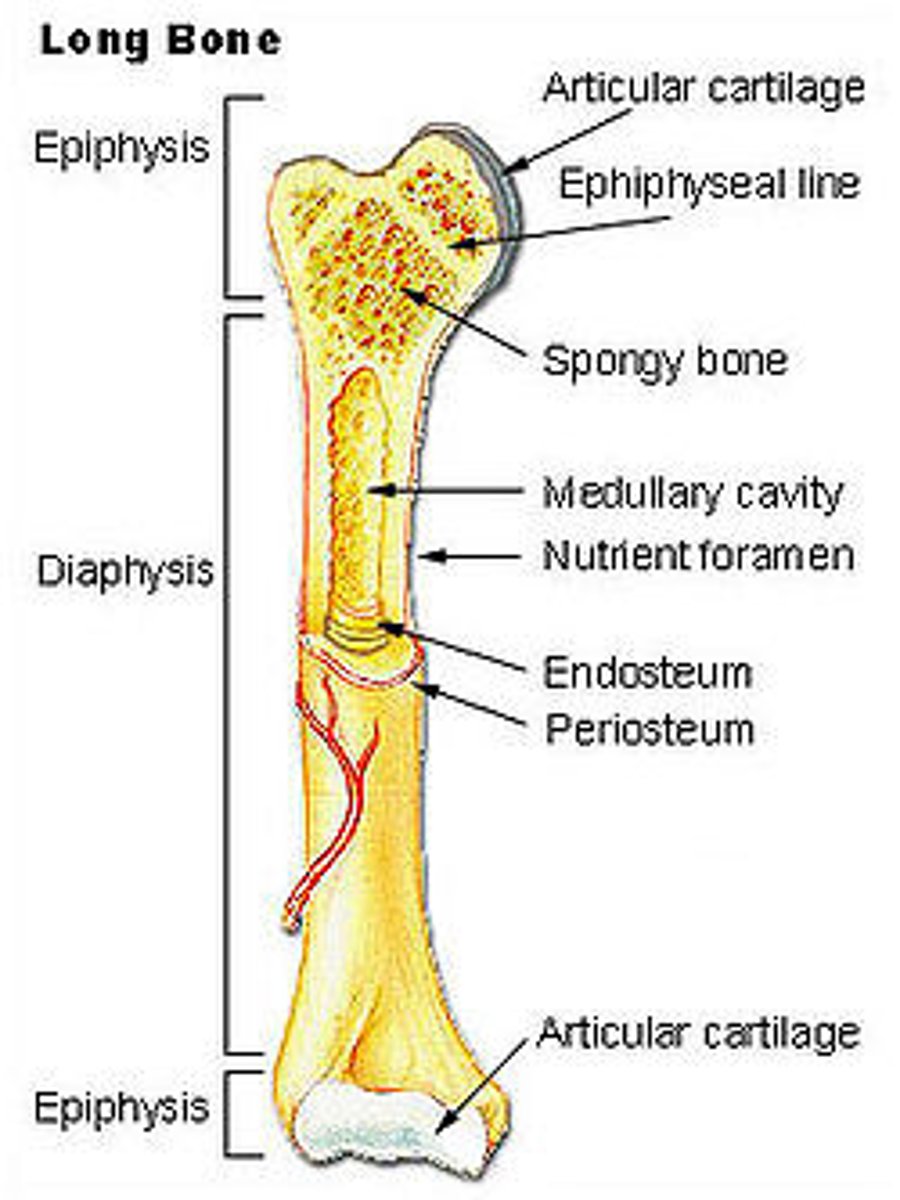
Cross-section of bone
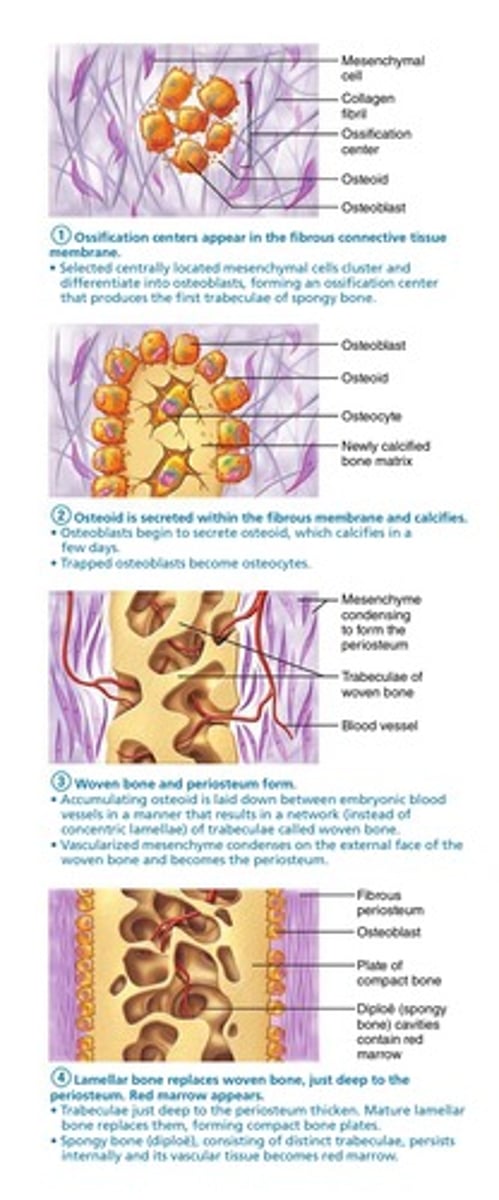
Intramembranous ossification
-bone growth within a membrane
-produces the flat bones of the skull, some of the facial bones (zygomatic bone, maxilla), the mandible (lower jaw), and the central part of the clavicle (collarbone)
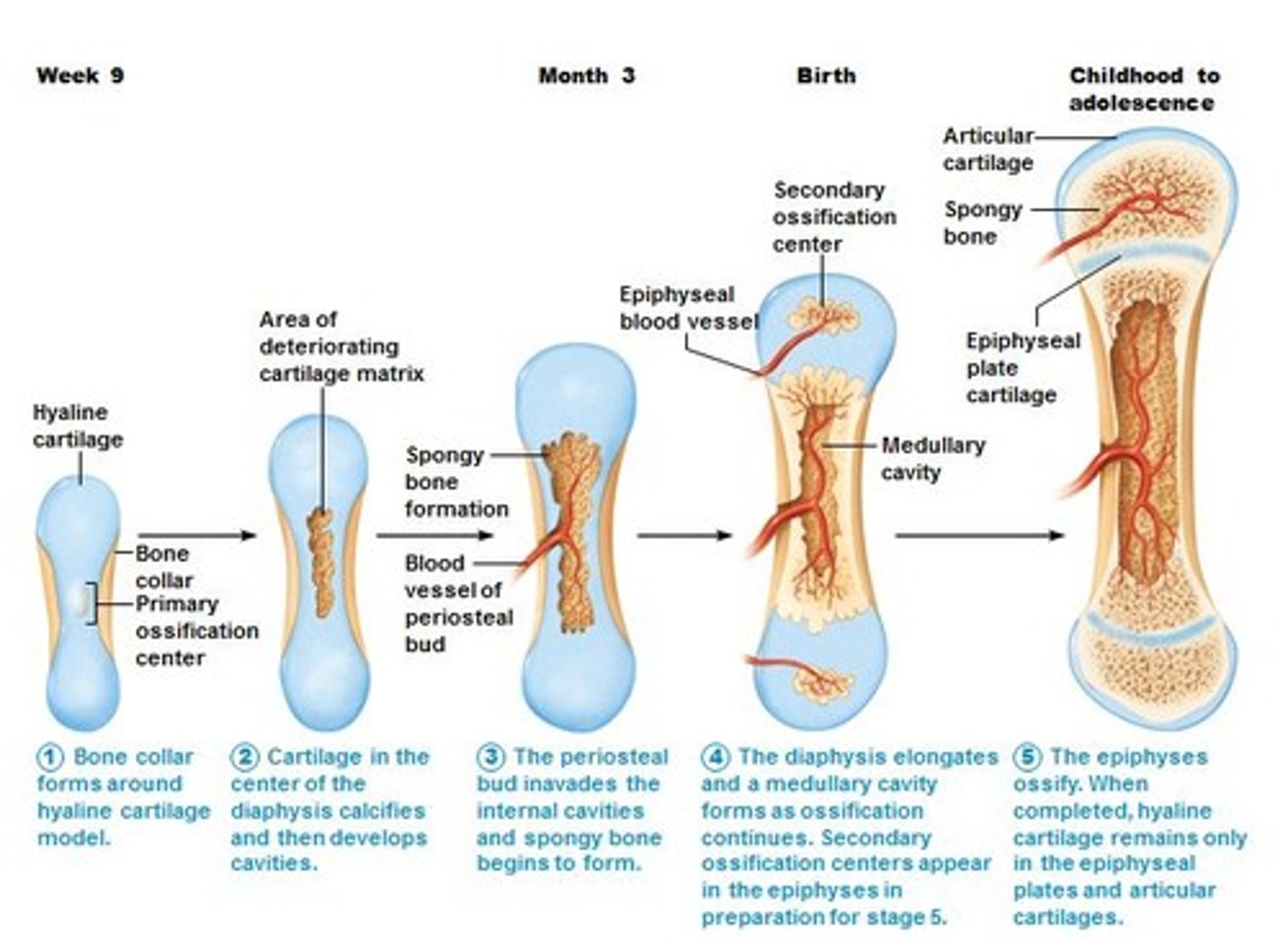
Endochondral ossification
-begins with a hyaline cartilage model and produces most of the other bones of the skeleton, including those of the upper and lower limbs, the pelvis, the vertebrae, and the ends of the clavicle
Foramen
A hole in the bone (typically for nerves/blood vessels)
Fossa
A depression in a bone ex: mandibular fossa, lacrimal fossa
Process
projection from bone, narrow or wide, protrudes from surrounding bone ex:styloid or mastoid process
Meatus
a hole or tube-like structure ex:auditory meatus
Canal
A groove or tube-like structure ex:optic canal
Osteoblast
Build new bone
Osteoclast
Break down (consume) bone
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
Which has more cartilage, an adult or a juvenile?
Adult
Osteogenesis
New bone formation
What happens when epiphyseal plates have closed?
Becomes an epiphyseal line
What are the cells involved in producing new bone tissue?
Osteoblasts
What is the periosteum? Where is it located? How is this different from endosteum?
- outer layer (covers compact bone)
- endosteum is the inner layer and lines the medullary cavity
What is an osteon? What are the concentric tubes that make up an osteon?
- a structural unit of compact bone
- made of lamellae
Components of the axial skeleton
Skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
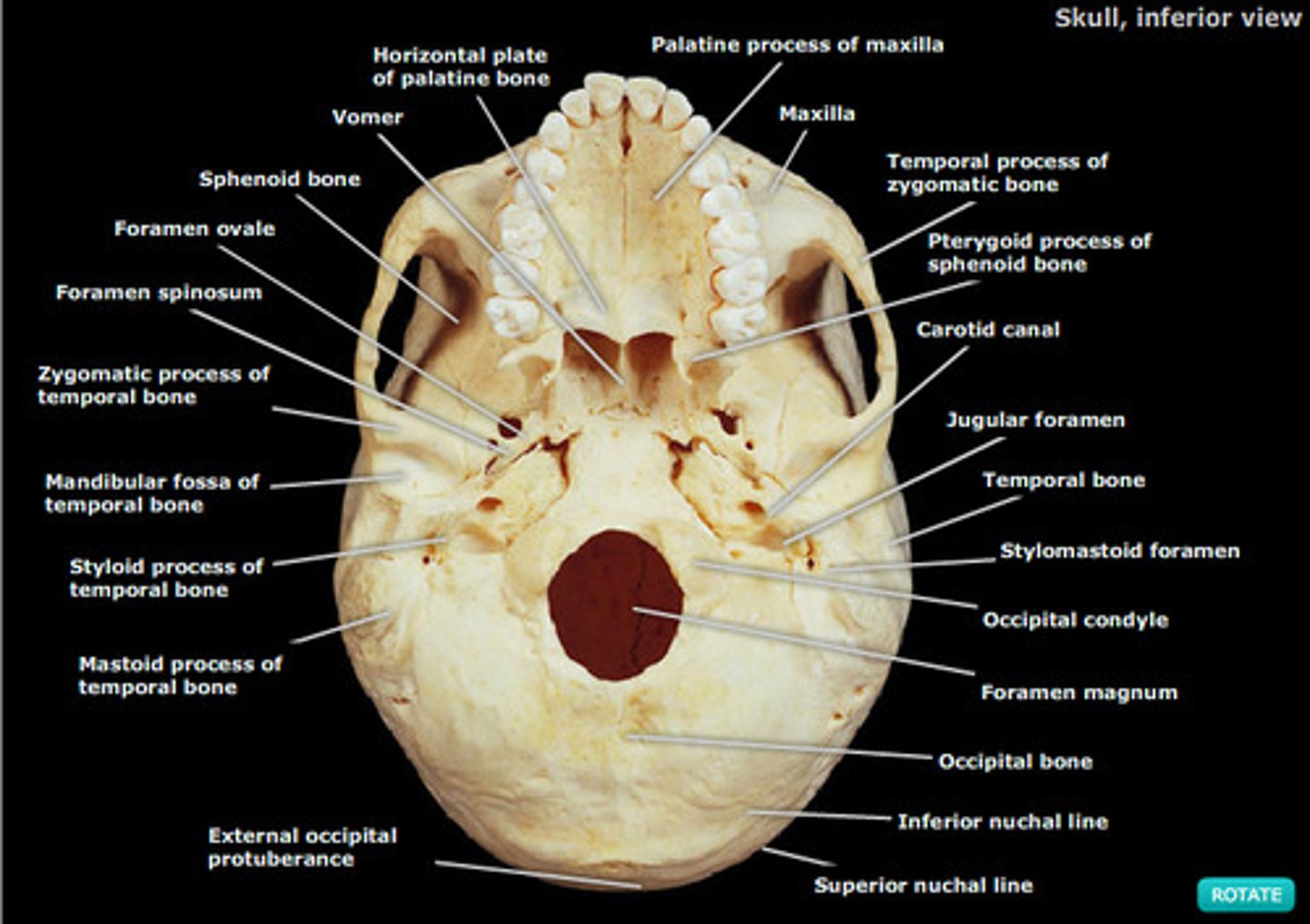
Skull bones
https://html1-cluster-e.mheducation.com/smartbook2/data/150203/highlighted_epubmhe/OPS/img/chapter007/mck85278_0704l.png
Coronal suture
between the anterior frontal bone and the more posterior parietal bones
Sagittal suture
in the midline of the cranium (along the midsagittal plane) and is the articulation between the right and left parietal bones
Squamous suture
articulates the temporal bone and the parietal bone of that side
What forms the bones of the neck?
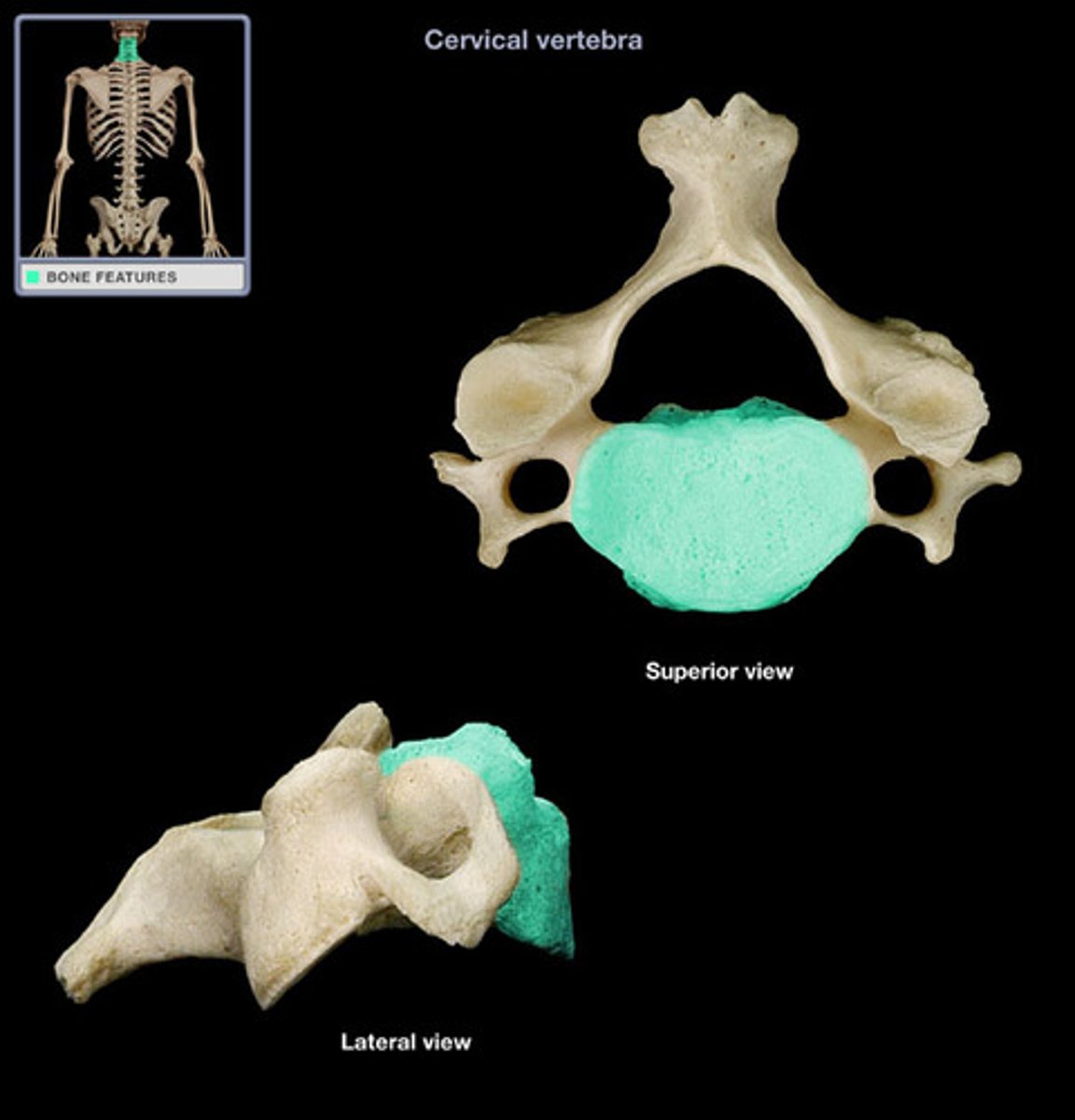
Seven cervical vertebrae C1-C7
What bones form the superior region of the back?
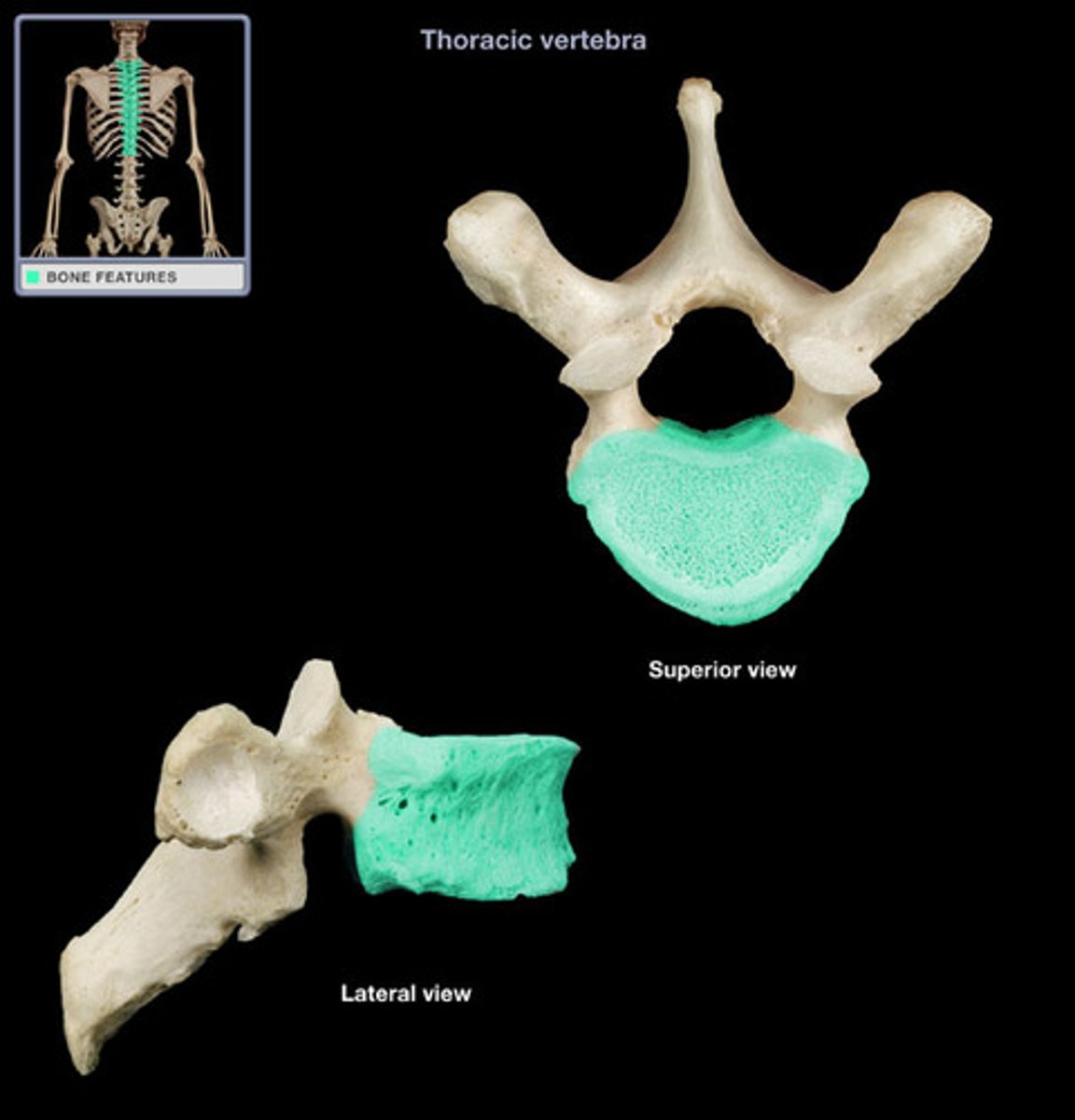
Twelve thoracic vertebrae T1-T12
What bones form the inferior concave region ("small") of the back?
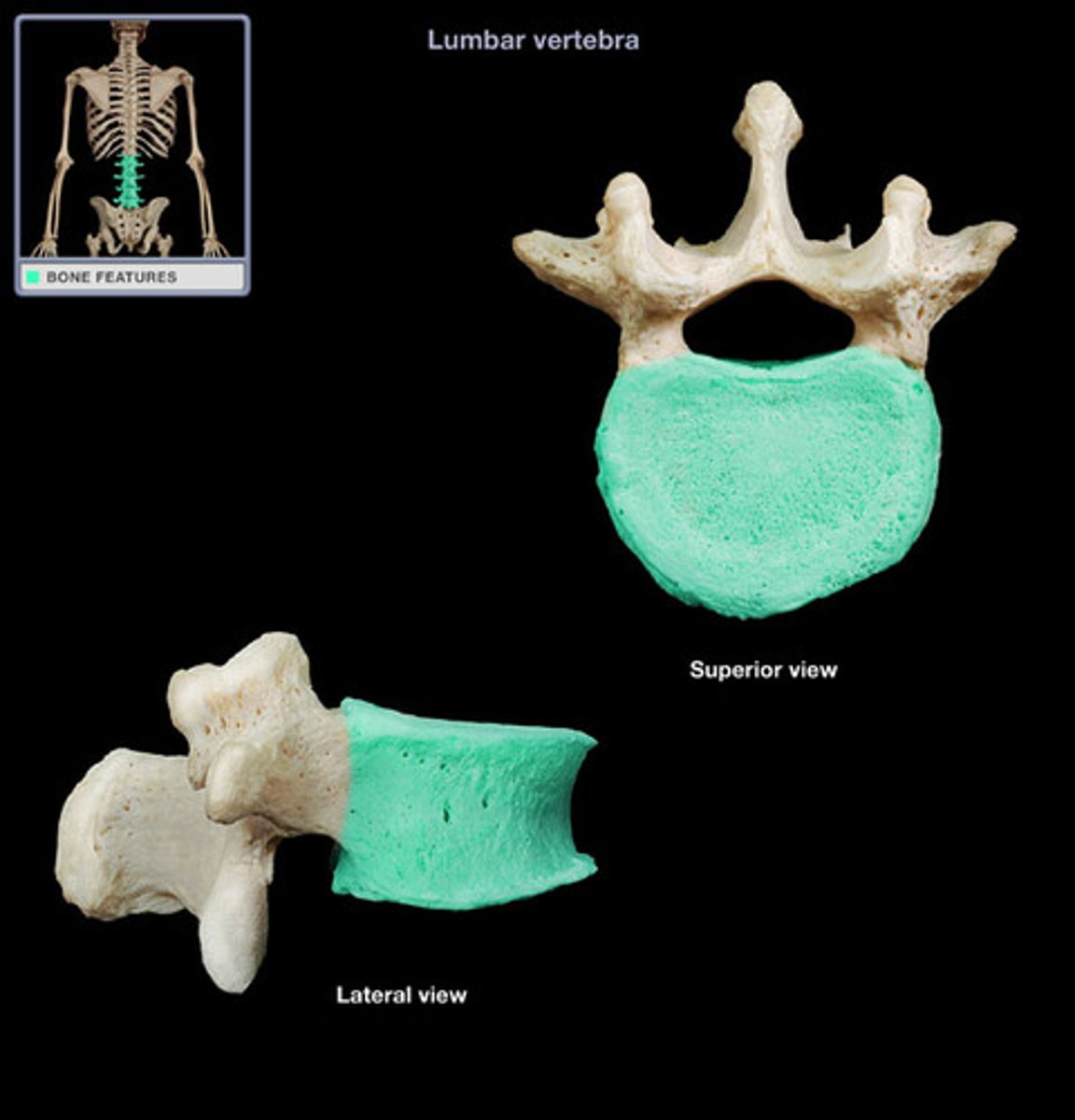
Lumbar vertebrae L1-L5
Sacrum
formed from five sacral vertebrae (S1-S5), which fuse into a single bony structure by the mid to late 20s
Coccyx
commonly called the "tailbone," is formed from four coccygeal vertebrae (Co1-Co4) that start to unite during puberty
Cervical vertebrae
Thoracic vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae
Spinal curvatures
These spinal curvatures better support the weight of the body when standing than a straight spine could.
Thoracic Cage
acts as a protective framework around vital organs, including the heart, lungs, trachea, and esophagus. It also provides attachment points for many muscles supporting the pectoral girdles
What is the function of the axial skeleton?
To form a framework that supports and protects the organs. The axial skeleton also houses special sense organs (the organs for hearing, balance, taste, smell, and vision) and provides areas for the attachment of skeletal muscles
Are most of the bones of the skull formed by endochondral or intramembranous ossification?
Intramembranous
What is the term for joints in the skull?
Sutures
What is a fontanelle? Why are these present in the fetus and infant?
A fibrous membrane remnants that are not yet ossified. To ease the babies passage.
What are the functions of the cranial bones?
Surround and enclose the brain
What are the functions of the facial bones?
protect the entrances to the digestive and respiratory systems as well as providing attachment sites for facial muscles
What does the external acoustic meatus protect/surround?