Chapter 4: Carbon and the Molecule Diversity of Life
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Organic chemistry is a science based on the study of
A) functional groups.
B) vital forces interacting with matter.
C) carbon compounds.
D) water and its interaction with other kinds of molecules.
E) inorganic compounds.
C
Early 19th-century scientists believed that living organisms differed from nonliving things as a result of possessing a "life force" that could create organic molecules from inorganic matter. The term given to this belief is
A) organic synthesis.
B) vitalism.
C) mechanism.
D) organic evolution.
E) inorganic synthesis.
B
The concept of vitalism is based on a belief in a life force outside the jurisdiction of physical and chemical laws. According to this belief, organic compounds can arise only within living organisms. Which of the following did the most to refute the concept of vitalism?
A) Wohler's synthesis of urea
B) Berzelius's distinction between organic and inorganic compounds
C) Miller's experiments with ancient atmospheres
D) Rodriguez's studies of phytochemicals
E) Kolbe's synthesis of acetic acid
C
The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations presumes that
A) simple organic compounds can be synthesized in the laboratory from inorganic precursors, but complex organic compounds like carbohydrates and proteins can only be synthesized by living organisms.
B) a life force ultimately controls the activities of living organisms and this life force cannot be studied by physical or chemical methods.
C) although a life force, or vitalism, exists in living organisms, this life force cannot be studied by physical or chemical methods.
D) living organisms are composed of the same elements present in nonliving things, plus a few special trace elements found in only living organisms or their products.
E) living organisms can be understood in terms of the same physical and chemical laws that can be used to explain all natural phenomena.
E
Which property of the carbon atom gives it compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type of atom?
A) Carbon has 6 to 8 neutrons.
B) Carbon has a valence of 4.
D) A and C only
C) Carbon forms ionic bonds.
E) A, B, and C
B
How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its valence shell?
A)1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
D
What type(s) of bond(s) does carbon have a tendency to form?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) covalent
D) A and B only
E) A,B, and C
C
Which of the following is (are) true about the carbon atoms present in all organic molecules?
A) They were incorporated into organic molecules by plants.
B) They were processed into sugars through photosynthesis.
C) They are ultimately derived from carbon dioxide.
D) Only A and C are correct.
E) A, B, and C are correct.
E
What is the reason why hydrocarbons are not soluble in water?
A) The majority of their bonds are polar covalent carbon to hydrogen linkages.
B) The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
C) They are hydrophilic.
D) They exhibit considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
E) They are lighter than water.
B
How many structural isomers are possible for a substance having the molecular formula C4H10?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 3
E) 11
B
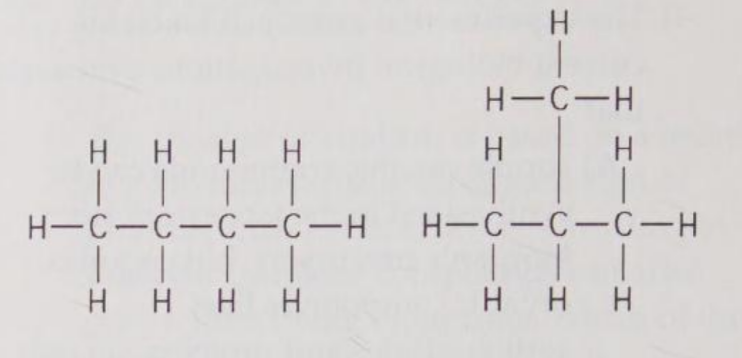
The two molecules shown in Figure 4.1 are best described as
A) optical isomers.
B) radioactive isotopes.
C) structural isomers.
D) nonradioactive isotopes.
E) geometric isomers.
C
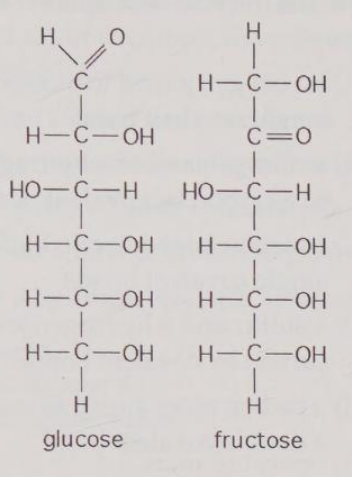
Observe the structures of glucose and fructose in Figure 4.2. These two molecules differ in the
A) number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
B) types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
C) arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
D) number of oxygen atoms joined to carbon atoms by double covalent bonds.
E) answers A, B, and C
C
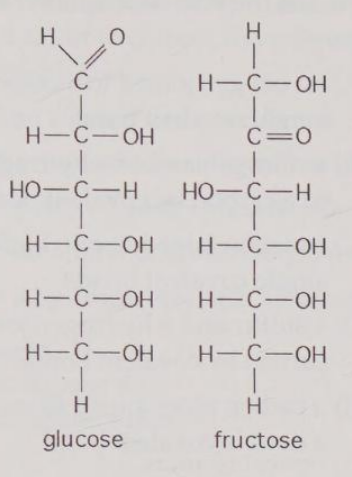
Observe the structures of glucose and fructose in Figure 4.2. These two molecules are
A) geometric isotopes.
B) enantiomers.
C) geometric isomers.
D) structural isomers.
E) nonisotopic isomers.
D
Which of the following is true of geometric isomers?
A) They have variations in arrangement around a double bond.
B) They have an asymmetric carbon that makes them mirror images.
C) They have the same chemical properties.
D) They have different molecular formulas.
E) Their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences.
A
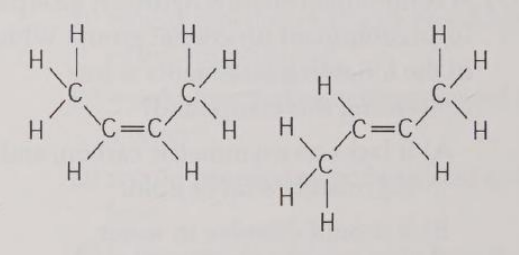
The two molecules shown in Figure 4.3 are best described as
A) enantiomers.
B) radioactive isotopes.
C) structural isomers.
D) nonisotopic isomers.
E) geometric isomers.
E
Research suggests that side effects from Ritalin, the drug used to treat attention deficit disorder, may be caused by contamination of enantiomers, or molecules that
A) have identical three-dimensional shapes.
B) are mirror images of one another.
C) lack an asymmetric carbon.
D) differ in the location of their double bonds.
E) differ in their electrical charge.
B
A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional group. Which of the following statements is true concerning this compound?
A) It lacks an asymmetric carbon, and it is probably a fat or lipid.
B) It should dissolve in water.
C) It should dissolve in a nonpolar solvent.
D) It won't form hydrogen bonds with water.
E) It is hydrophobic.
B
Which is the best description of a carbonyl group?
A) an oxygen joined to a carbon by a single covalent bond
B) a nitrogen and two hydrogens joined to a carbon by covalent bonds
C) a carbon joined to two hydrogens by single covalent bonds
D) a sulfur and a hydrogen joined to a carbon by covalent bonds
E) a carbon atom joined to an oxygen by a double covalent bond
E
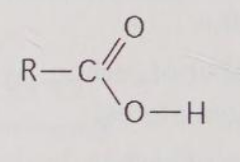
What is the name of the functional group shown in Figure 4.4?
A) carbonyl
B) ketone
C) aldehyde
D) carboxyl
E) hydroxyl
D
Which of the following contains nitrogen in addition to carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen?
A) an alcohol such as ethanol
B) a monosaccharide such as glucose
C) a steroid such as testosterone
D) an amino acid such as glycine
E) a hydrocarbon such as benzene
D
Which of the following is a false statement concerning amino groups?
A) They are basic in pH.
B) They are found in amino acids.
C) They contain nitrogen.
D) They are nonpolar.
E) They are components of urea.
D
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A) ketone and aldehyde
B) carbonyl and carboxyl
C) carboxyl and amino
D) phosphate and sulfhydryl
E) hydroxyl and aldehyde
C
Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group?
A) amino
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D) sulfhydryl
E) aldehyde
C
A carbon skeleton is covalently bonded to both an amino group and a carboxyl group. When placed in water it
A) would function only as an acid because of the carboxyl group.
B) would function only as a base because of the amino group.
C) would function as neither an acid nor a base.
D) would function as both an acid and a base.
E) is impossible to determine how it would function.
D
A chemist wishes to make an organic molecule less acidic. Which of the following functional groups should be added to the molecule in order to do so?
A) carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C) hydroxyl
D) amino
E) phosphate
D
Which functional groups can act as acids?
A) amine and sulfhydryl
B) carbonyl and carboxyl
C) carboxyl and phosphate
D) hydroxyl and aldehyde
E) ketone and amino
C
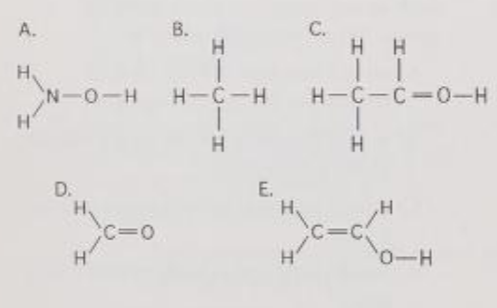
Which of the structures is an impossible covalently bonded molecule?
C
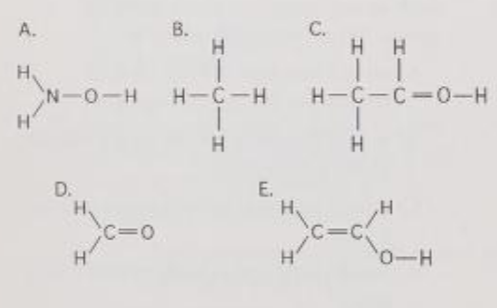
Which of the structures contain(s) a carboxyl functional group?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) C and E
E) none of the structures
E
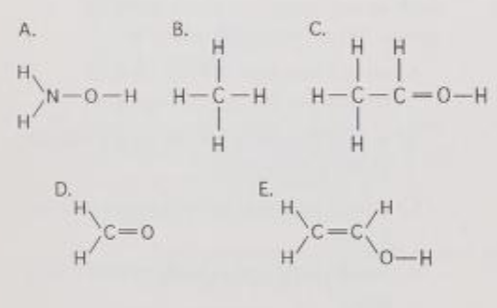
In which of the structures are the atoms bonded by ionic bonds?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) C, D, and E only
E) none of the structures
E
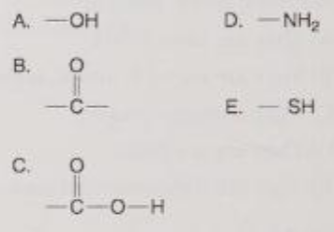
Which is a hydroxyl functional group?
A
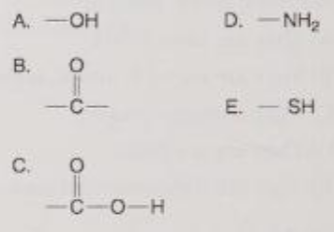
Which is an amino functional group?
D
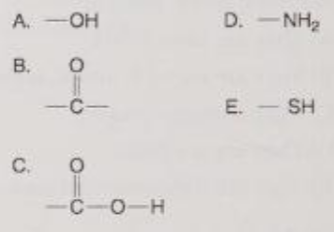
Which is a carbonyl functional group?
B
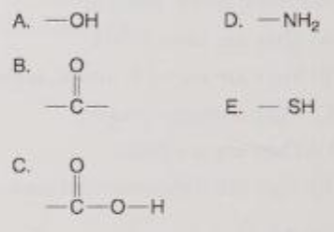
Which is a functional group that helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
E
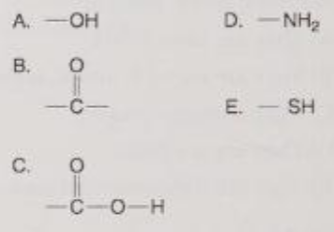
Which is a carboxyl functional group?
C
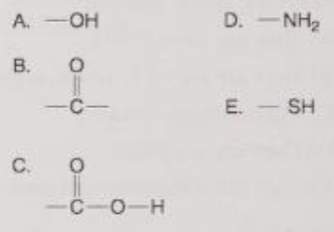
Which is an acidic functional group that can dissociate and release H+ into a solution?
C
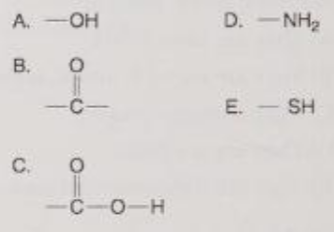
Which is a basic functional group that can accept H+ and become positively charged?
D
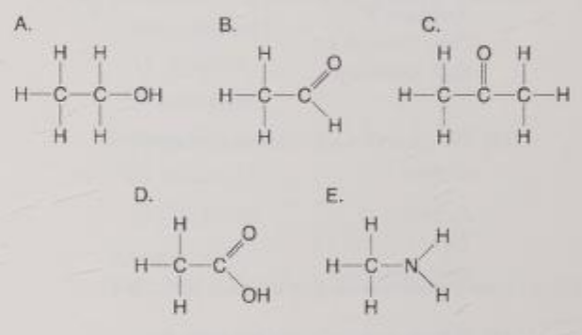
Which molecule is water-soluble because it has a hydroxyl functional group?
A
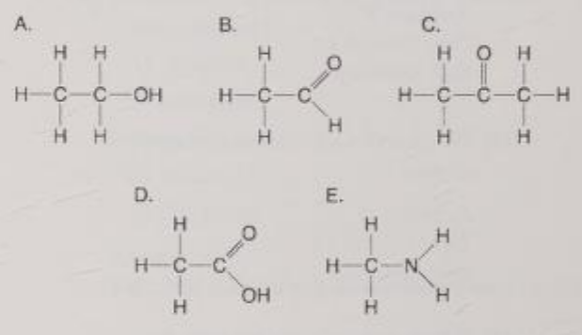
Which molecule is an alcohol?
A
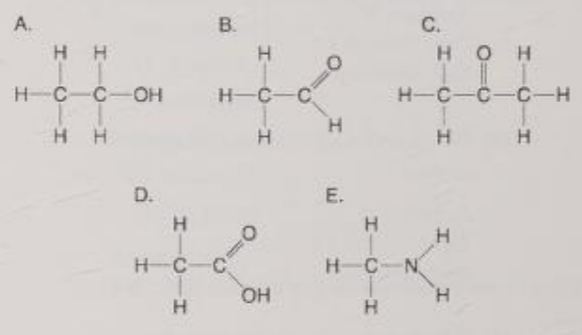
Which molecules contain a carbonyl group?
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) C and D
D) D and E
E) E and A
B
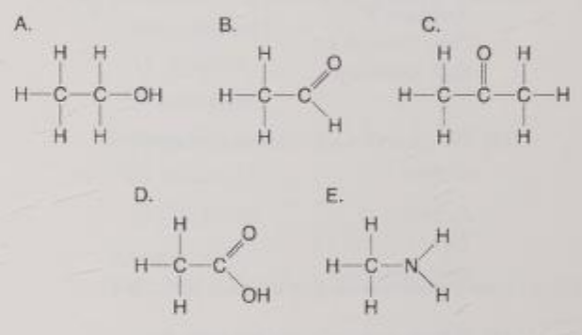
Which molecule has a carbonyl functional group in the form of a ketone?
C
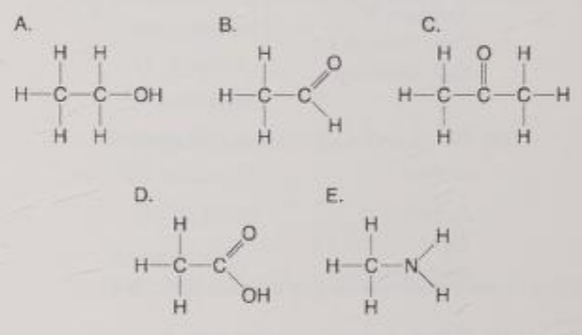
Which molecule has a carbonyl functional group in the form of an aldehyde?
B
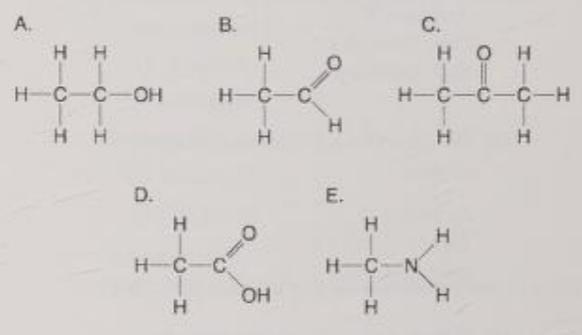
Which molecule contains a carboxyl group?
D
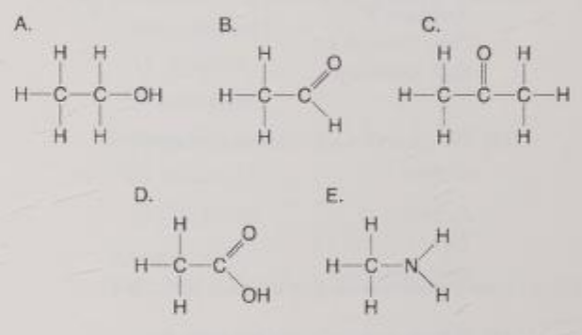
Which molecule can increase the concentration of a hydrogen ions in a solution and is therefore an organic acid?
D
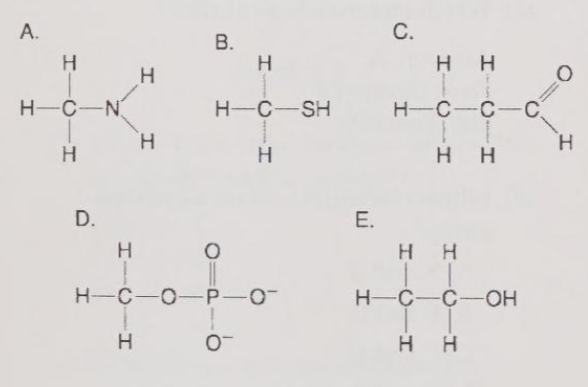
Which molecule contains an amino functional group, but is not an amino acid?
A
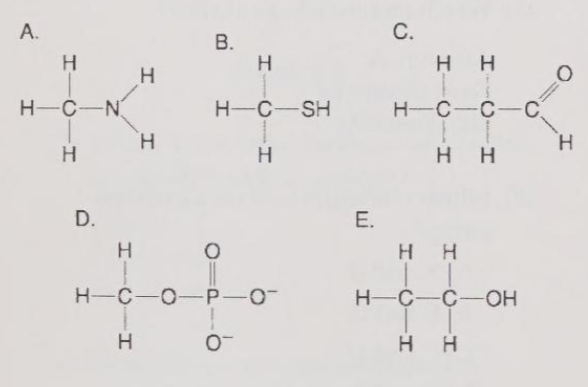
Which molecule is a thiol?
B
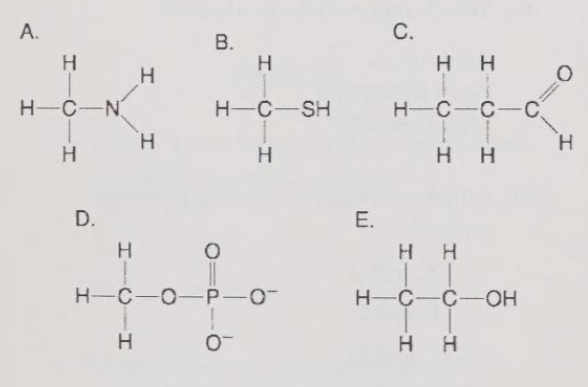
Which molecule is an organic phosphate?
D
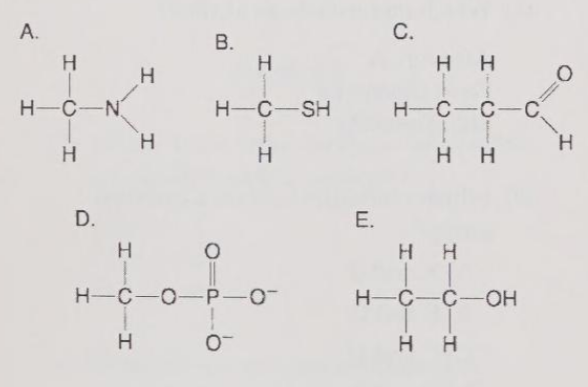
Which molecule can function as a base?
A
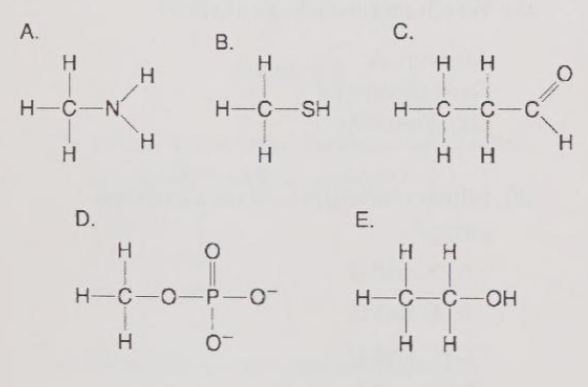
Which of the following statements is (are) true about the phosphate ion?
A) It is negatively charged.
B) It has acid properties.
C) It is hydrophobic.
D) Only A and B are true.
E) A, B, and C are true.
D
Hydrocarbons
A) are polar.
B) are held together by ionic bonds.
C) contain nitrogen.
D) contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
E) are held together by hydrogen bonds.
D
What kind of effect does R-dopa have on Parkinson’s disease?
A) It alleviates the symptoms
B) It makes the symptoms worse
C) At first it makes the symptoms worse but over the long term it alleviates the symptoms
D) At first it alleviates the symptoms but over the long term it makes the symptoms worse
E) R-dopa has no effect on Parkinson’s disease
E
Structural isomers are molecules that
A) are enantiomers.
B) are hydrocarbons.
C) have a ring structure.
D) are mirror images.
E) differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms.
E
Which of the functional groups does not contain oxygen?
A) carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C) hydroxyl
D) carbonyl
E) phosphate
B
If this functional group is at the end of a carbon skeleton, the molecule is called an aldehyde.
A) amino
B) sulfhydryl
C) carbonyl
D) carboxyl
E) hydroxyl
C
Organic chemistry is currently defined as
A) the study of compounds that can be made only by living cells.
B) the study of carbon compounds.
C) the study of vital forces.
D) the study of natural (as opposed to synthetic) compounds.
E) the study of hydrocarbons.
B
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Hydroxyl is to as is to aldehyde.
A) carbonyl; ketone
B) oxygen; carbon
C) alcohol; carbonyl
D) amine; carboxyl
E) alcohol; ketone
C
Which of the following hydrocarbons has a double bond in its carbon skeleton?
A) C3H8
B) C2H6
C) CH4
D) C2H4
E) C2H2
D
The gasoline consumed by an automobile is a fossil fuel consisting mostly of
A) aldehydes.
B) amino acids.
C) alcohols.
D) hydrocarbons.
E) thiols.
D
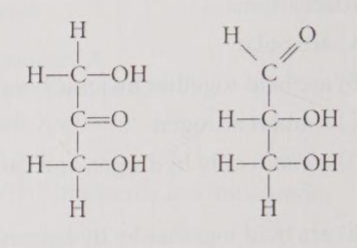
Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between the two sugar molecules shown in Figure 4.9.
A) structural isomers
B) geometric isomers
C) enantiomers
D) isotopes
A
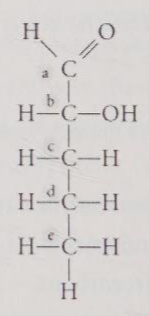
Identify the asymmetric carbon in the molecule shown in Figure 4.10.
B
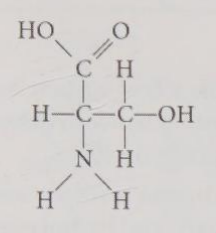
Which functional group is not present in the molecule shown in Figure 4.11?
A) carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C) hydroxyl
D) amino
B
Which action could produce a carbonyl group?
A) the replacement of the hydroxyl of a carboxyl group with hydrogen
B) the addition of a thiol to a hydroxyl
C) the addition of a hydroxyl to a phosphate
D) the replacement of the nitrogen of an
amine with oxygen
E) the addition of a sulfhydryl to a carboxyl
A
Which functional group is most likely to be responsible for an organic molecule behaving as a base?
A) hydroxyl
B) carbonyl
C) carboxyl
D) amino
E) phosphate
D
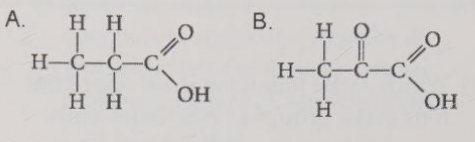
Given what you know about the electronegativity of oxygen, predict which of the molecules shown in Figure 4.12 would be the stronger acid.
B