IMSE 311: Immunity
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Immunology
Study of host’s reactions when foreign substances are introduced into the body
Immunity
Condition of being resistant to infection
Antigens (Ag)
Foreign substances that induce a host response
Chinese and Turkish People
Inhalation of powders from smallpox scabs
1500’s
Edward Jenner
Immunity from smallpox through cowpox injection
Late 1700’s
Louis Pasteur
Developed the first attenuated vaccine
“Father of Immunology”
1800’s
Attenuation
It means to make a pathogen less virulent
Elie Metchnikoff
Discovered phagocytosis by injecting foreign Ag into a transparent starfish
"Cellular Immunity”
Emil von Behring
Noncellular portion of the blood (serum) from previously infected animals could neutralize toxins
“Humoral Immunity”
Robert Koch
Tuberculosis
1900’s
Jules Bordet
Complement Pathway
1900’s
Karl Landsteiner
Blood Groups
1900’s
Kohler and Milstein
Principle of monoclonal Ab production
1900’s
Suzumu Tonegawa
Ab Diversity
1900’s
Ian Frazer
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine
2000’s
Ipilimumab
Stage IV Melanoma
2000’s
Active Immunity
Immunity that occurs when Ag is introduced into the body to produce Ab and memory cells
Pros: Long-lasting
Cons: Takes time to develop
2
How many weeks does it takes for the body to produce Ab in response to Foreign Ag?
Passive Immunity
Immunity that occurs when pre-formed Ab are introduced into an individual
Pros: Immediate protection
Cons: Short-lived and no memory cells
2 Years Old
Age wherein Ab in the body are fully developed
Natural Active Immunity
Type of immunity where foreign Ag is introduced through infection
Natural Passive Immunity
Type of Immunity where Ab is transferred from one organism to another
Artificial Active Immunity
Type of immunity you get from vaccine shots
(note: vaccines contain attenuated pathogens)
Artificial Passive Immunity
Type of immunity through injection of Ab into the body
(like booster shots)
Innate Immunity
“Natural Immunity”
Defenses against infection that are ready for immediate action when a host is attacked by a pathogen
Nonadaptive / nonspecific
No prior exposure required
Influenced by:
nutrition
age
fatigue
stress
genes
External Defense System
Physical, chemical, and biological barriers that prevent most pathogens from entering the body
Skin
Several layers of tightly packed epithelial cells that contain a protein called “keratin”, making it impermeable to most pathogens
Lactic Acid (in sweat)
Skin secretion that discourages growth of microorganisms
Fatty Acid (in sebaceous glands)
Skin secretion that maintains skin pH of approx. 5.6
Surfactants
Small proteins in mucus secretions that bind to microorganisms to help move pathogens out
Flushing of Urine
Removes many potential pathogens from the genitourinary tract
Lactic Acid
Keeps the vagina at a pH of about 5
Hydrochloric Acid
Keeps the stomach acid at the pH as low as 1
Lysozyme
Enzyme found in many bodily secretions that attacks the cell walls of microorganisms, especially those that are gram-positive
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Microbiota that is responsible for the acidity of the vagina
Hematopoietic Stem Cell
All blood cells arise from this type of cell
Heterophile Antibody
Ab which can work on other diseases
Edward Jenner’s discovery of smallpox immunity through cowpox
Pelger-Huet Anomaly
An abnormality in neutrophils wherein it only contains 2 lobes
Diapedesis
Movement of WBCs outside of blood vessels
Chemotaxis
Movement of free WBCs to the site of inflammation (towards a chemical signal, “chemotaxins”)
“Chemo na taxi”
Selectins
A cell-surface adhesion molecule that helps WBCs to hold onto the blood vessel walls
They weaken during trauma or blood vessel injury, causing an increase in circulating WBCs in the blood
Red Bone Marrow
Bone marrow that produces blood cells and contains hematopoietic stem cells
Yellow Bone Marrow
Bone marrow that is primarily composed of adipose tissue
Internal Defense System
The cellular and humoral factors that destroy foreign Ag
Neutrophils (NEUT)
50 - 75% (most abundant) (50 - 70% in the book)
10 - 15 μm
“Segmented Neutrophil”, 3 - 5 lobes
Function: Phagocytosis, kills bacteria
Granules:
Primary / Azurophilic: for anti-bacterial activity
Secondary / Specific: for oxidative burst
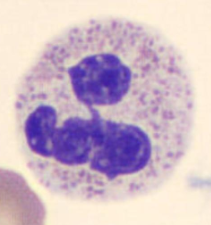
Lymphocytes (LYMPH)
20 - 40%
7 - 10 μm
Function: Adaptive immunity
Differentiates further into: (bone marrow and thymus)
B cells
T cells
NK cells
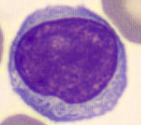
Monocytes (MONO)
4 - 10% (2 - 10% in the book)
12 - 22 μm (largest cell in the blood) (12 - 20μm in the book)
Function: Precursors of macrophage
“Scavenger cells”
Irregularly folded or horseshoe-shaped nucleus that occupies almost half of entire cell volume
Digestive vacuoles may also be observed in the cytoplasm
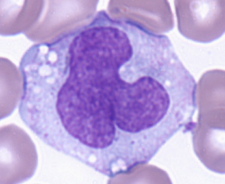
Eosinophils (EO)
1 - 3% (1 - 4% in the book)
12 - 15 μm (10 - 15μm in the book)
Function: kills large parasites
Bi-lobed, eccentric nucleus (away from the center)
Granules: reddish-orange in color (takes up acid eosin dye)
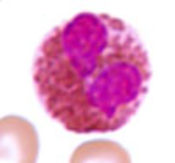
Basophils (BASO)
< 1% (least numerous)
10 - 15 μm (smallest of the granulocytes)
Function: Inducing and maintaining allergic reactions
Obscured nucleus
Granules: densely staining deep-bluish-purple granules that contains:
Histamine
Heparin
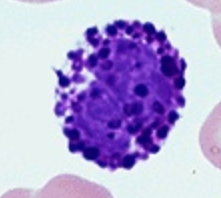
Macrophages
25 - 80 μm
Function:
Presents phagocytosed antigens to T lymphocytes (initiates specific immunity)
Anti-tumor
Slow mobility / immobile
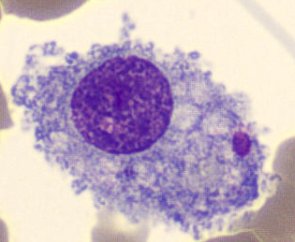
Kupffer Cell
Macrophage in the liver
Microglial Cell
Macrophage in the brain
Osteoclast
Macrophage in the bones
Alveolar Macrophage / Dust Cell
Macrophage in the lungs
Histiocyte
Macrophage in the connective tissues
Hofbauer Cell
Macrophage in the placenta
Littoral Cell
Macrophage in the spleen
Mesangial Cell
Macrophage in the kidneys
Type A Lining Cell
Macrophage in the synovial
Mast Cells
20 μm (larger than BASOs)
Function: (versatility)
Major conduit between innate and adaptive immunity
Allergic reactions
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
Resembles basophil (also contains histamine and heparin)
Life Span: 9 - 18 months
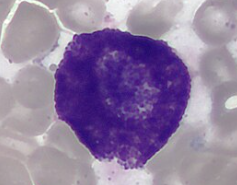
Dendritic Cells
Covered with long, membranous extensions that resemble nerve cell dendrites
Most potent phagocytic cell
Most effective APC in the body

Acute Phase Reactants
Normal serum constituents that rapidly increase or decrease in concentration because of infection, injury, or trauma to the tissues
positive acute-phase reactants (increases)
negative acute-phase reactants (decreases)
Liver Parenchymal Cells / Hepatocytes
Which cell primarily produces acute-phase reactants in response to an increase in cytokines?
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
Acute-Phase Reactant
Most widely used indicator of acute inflammation but not preferred because it doesn’t say where the inflammation is located
Capable of:
Opsonization (coating of foreign particles to trap)
Agglutination
Precipitation
Activation of complement by classical pathway
Serum Amyloid A (SAA)
Acute-Phase Reactant
Acts as a chemical messenger, similar to a cytokine
Found to increase significantly more in bacterial infections than in viral infections
Contributes to cleaning up remnants of pathogens (waste) because of high affinity for high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
SAA deficient > lipid buildup > “plaque” > “Arteriosclerosis”
Cytokines
“Messenger cells”
Intercellular signaling polypeptides
Mannose-Binding Protein (MBP)
Acute-Phase Reactant
Also known as “Mannose-Binding Lectin”
Acts as an “opsonin”
Widely distributed on mucosal surfaces
Lack of MBP has been associated w/ recurrent yeast/fungal infections
Mannose
Main carbohydrate component of fungi
Alpha 1 - Antitrypsin (AAT)
Acute-Phase Reactant
General plasma inhibitor of proteases released from leukocytes
Limits the harmful side effects of inflammation
AAT deficient > uninhibited proteases > “Premature Emphysema”
Haptoglobin
Acute-Phase Reactant
Binds irreversibly to free hemoglobin released by intravascular hemolysis
Antioxidant
Helps in protecting the kidneys from damage
Haptoglobin deficiency > unregulated free HGB > oxidative damage > masks protein behavior > “Chronic Kidney Disease” (CKD)
Fibrinogen (Factor I)
Acute-Phase Reactant
Most abundant coagulation factor in plasma
Cleaved by thrombin (Factor IIa) to form fibrils that make up a fibrin clot
Formation of a clot creates a barrier that helps prevent the spread of microorganisms further into the body
Ceruloplasmin
Acute-Phase Reactant
Principal copper-transporting protein in human plasma
“Wilson’s disease” > copper buildup > Ceruloplasmin depletion > “Kayser Fleischer Ring” (blindness, symptom of Wilson’s disease)
Adaptive Immunity
“Specific Immunity”
Has the ability to memorize an antigen
T Cell / T Lymphocytes
61 - 80% of LYMPH
Differentiate in Thymus
Function:
Cytokine production
Cell-mediated Immunity (tumor + virus-infected cells)
CD3 (found in all T Cells), CD4, and CD8
B Cell / B Lymphocytes
10 - 20% of LYMPH
Differentiate in Bone Marrow
Function: Produces highly specific Ab
CD19, CD20, and CD21
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
10 - 15% of LYMPH
Differentiate in Bone Marrow
Function: Kill target cells without prior exposure to them (like cancer cells)
CD16 and CD56
Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Marker
Helps to identify LYMPH subtypes because they are difficult to distinguish visually
Ficoll-Hypaque
Liquid solution used in CD marking to isolate specific WBCs
400 x g for 30 minutes
Centrifugation parameter for CD marking