Lab 7 (Nerve + Muscle Tissues, NJM, Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, Somatic Reflexes) Review
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Neuron
specialized cells that transmit nerve impulses.
Soma (Cell Body)
neuron cell body, containing the nucleus and perikaryon (cytoplasm)
Dendrites
receive impulses toward the soma.
Axon
carries impulses away from the soma received from other neurons/cells.
Oligodendrocytes
myelinate central nervous system (CNS) axons.
Schwann Cells
myelinate peripheral nervous system (PNS) axons.
Afferent (Sensory) Neurons
carry impulses towards the CNS.
Efferent (Motor) Neurons
carry impulses away from CNS.
Interneurons
entirely within CNS (brain + spinal cord); receives, processes, and decides how the body responds to stimuli.
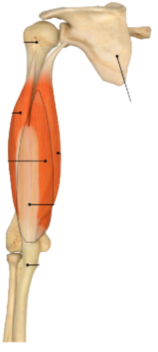
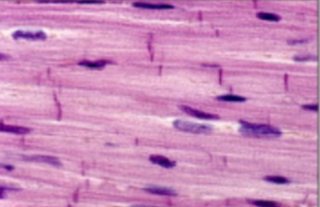
Skeletal Muscle
fibers attached to skeleton; striated, voluntary.
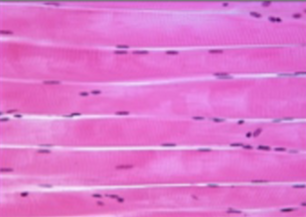
Cardiac Muscle
only cover walls of the heart; branched, intercalated discs.
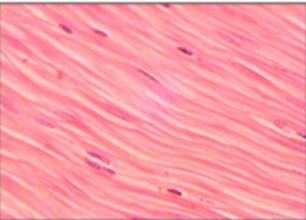
Smooth Muscle
covering wall of internal organs; no striations, involuntary.
Neuromuscular Junction
how a nerve signal becomes a muscle contraction.
Steps of Muscle Contraction
The nerve signal reaches the axon terminal.
Calcium enters the terminal. (MUST KNOW)
Causes vesicles to release ACh into the synaptic cleft. (MUST KNOW)
ACh binds to receptors on the muscle. (MUST KNOW)
Immediately after, muscle creates its own action potential. (MUST KNOW)
Signal travels down sarcolemma + T-tubules.
Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
Calcium binds to troponin directly, causing the muscle to contract. (MUST KNOW)
Patellar Reflex
L2- L4, function of leg extension.
Biceps Reflex
C5-C6, forearm flexion.
Triceps Reflex
C7-C8, forearm extension.