muscular system (chapters 10-11)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
skeletal muscle
band like appearance and dark and light stripes
long fibers
separate cells (hard to see)
many cell nucleus present
voluntary muscle
moves bones
multi nucleated
striated
cylindrical
found in arms and legs
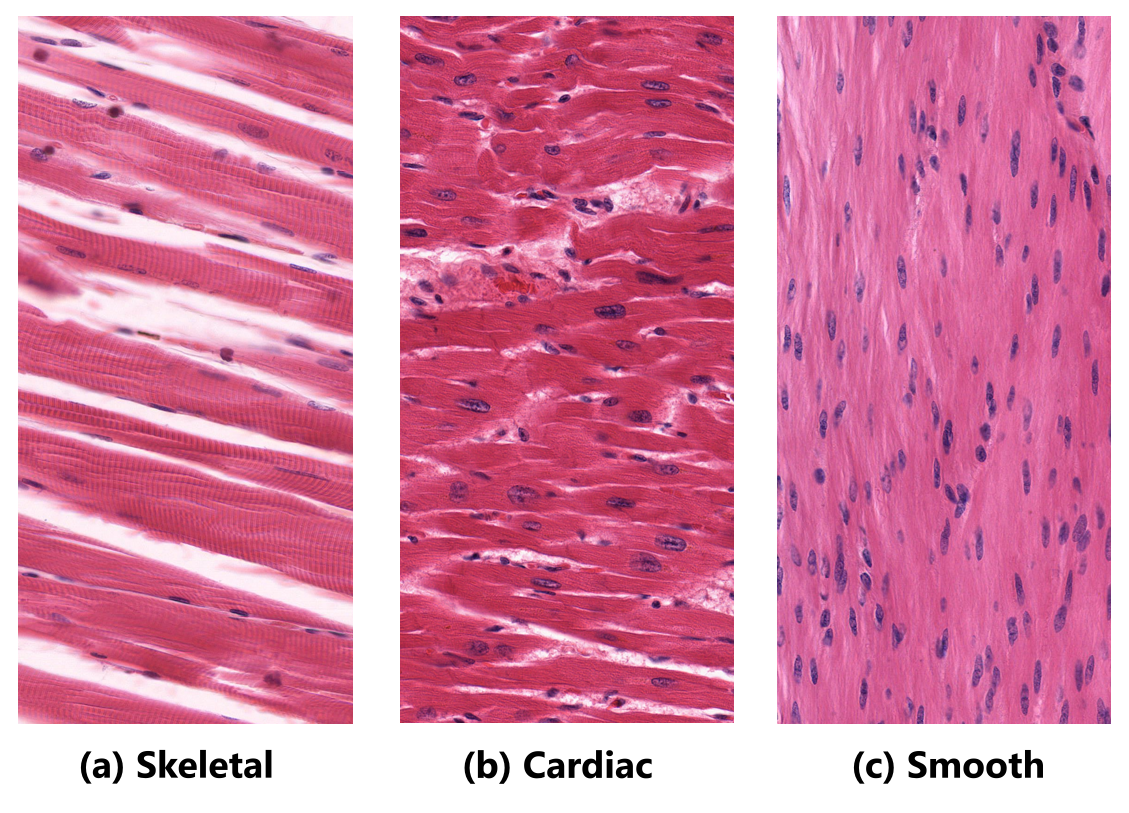
smooth muscle
not connected to bones
easier to see individual cells
involuntary muscle
single nucleated
nonstriated (because of tapered ends)
non cylindrical
found in digestive system and arteries
cardiac muscle
long fibers form a weave by joining together
involuntary
connected to bone
single nucleated
striated
cylindrical
only found in heart
properties of muscular tissue
electrical excitability
contractibility
extensibility
elasticity
electrical excitability
the signal an action potential originates in the nervous system and is transferred to neuro-muscular junction allowing contraction of the muscle
contractability
the ability of muscle to contract forcefully when stimulate by an action potential
extensibility
the ability to stretch (within limits) without damage
elasticity
the ability of muscle tissue to return to its original length and strength after each contraction or extension
fascia
dense sheet of irregular connective tissue that lines the body wall and limbs and supports and surrounds other organs and muscles
epimysium
encircles the entire muscle with dense irregular connective tissue
perimysium
surrounds group of 10-100 muscle fibers separating them into bundles called fascicles
fascicles
bundles made by perimysyium, meat tears along these lines
endomysium
separates individual muscle fibers
capillaries
microscopic blood vessels
brings in oxygen and nutrients
removes heat and waste products of muscle metabolism
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of muscle cell
contains transverse tubules
transverse tubes
t tubes
fill with interstitial fluid
helps action potential pass easily along the muscle fiber
sarcolemma
specialized plasma membrane of a muscle fiber (cell) that surrounds the sarcoplasm and acts as a barrier between the intracellular and extracellular compartments
myofibrils
have striations that make the muscle look striped
stemocleidomastoid
name is derived from its three points of attachment: the sternum (sterno), clavicle (cleido), and the mastoid process of the skull

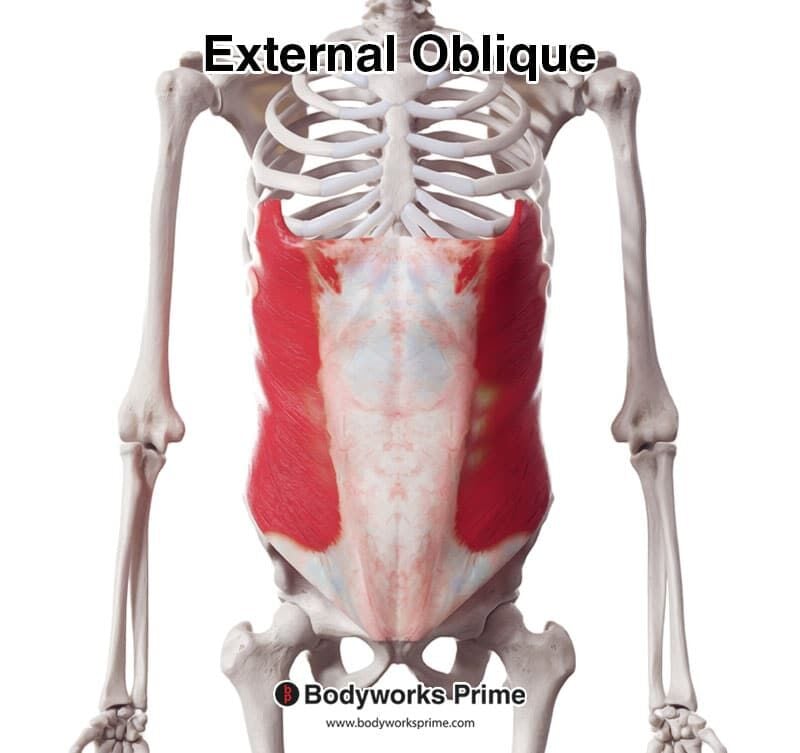
external oblique
the largest and most superficial of the three flat muscles in the lateral abdominal wall. It plays a critical role in trunk movement, core stability, and the protection of internal organs.
transversal abdominus
provides structural support to adjacent abdominal structures
compresses abdomen and increases intrabdominal pressure

rectus abdominus
flexes the trunk
tenses the anterior abdominal wall

gluteous
hip hip extension
hip lateral rotation
helps with hip abduction
