Cambridge International A-Level Geography - Coastal Environments
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Abrasion
A type of erosion in which rock fragments carried by waves grind away a surface such as a cliff face.
Attrition
The process by which particles of rock being transported by the sea are rounded and become smaller in size due to hitting one another. Particles near the shoreline become smaller and more rounded due to more frequent attrition.

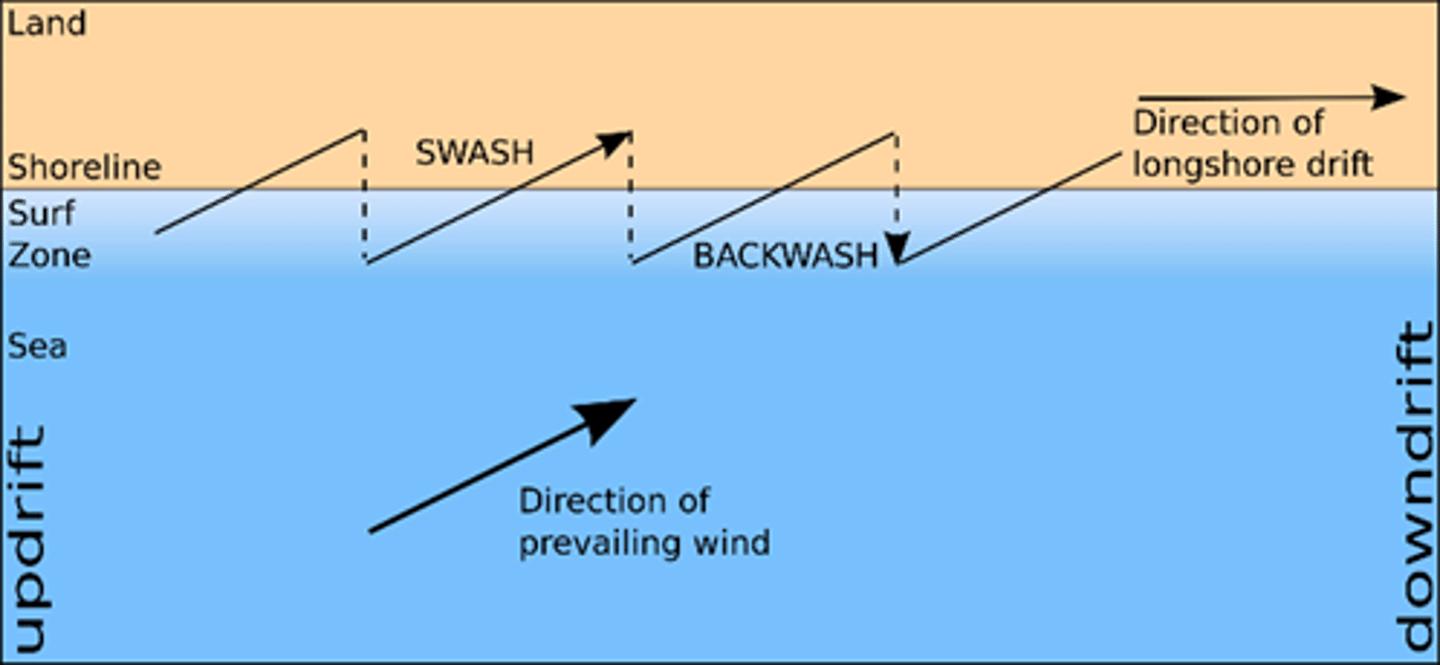
Backwash
The movement of water back down the beach due to the effect of gravity.

Constructive wave
A wave with a long wavelength and a low height, which helps to build up beaches by deposition

Corrosion
The process by which the minerals in a rock, notably calcium ions, are dissolved in acid water. It is also referred to as corrosion.
Solution
The process by which the minerals in a rock, notably calcium ions, are dissolved in acid water. It is also referred to as corrosion.
Deposition
The laying-down of material carried by the sea because of a loss of energy, often caused by increased friction with vegetation of coarse particles.

Destructive wave
a wave where the backwash is greater than the swash

Fetch
The distance of open water over which wind can blow to create waves. The greater the fetch the more potential power waves have when they hit the coast. In the south and west of England the fetch stretches for nearly 6000 km, to South America.

Hydraulic action
The force of the river against the banks can cause air to be trapped in cracks and crevices. The pressure weakens the banks and gradually wears it away.

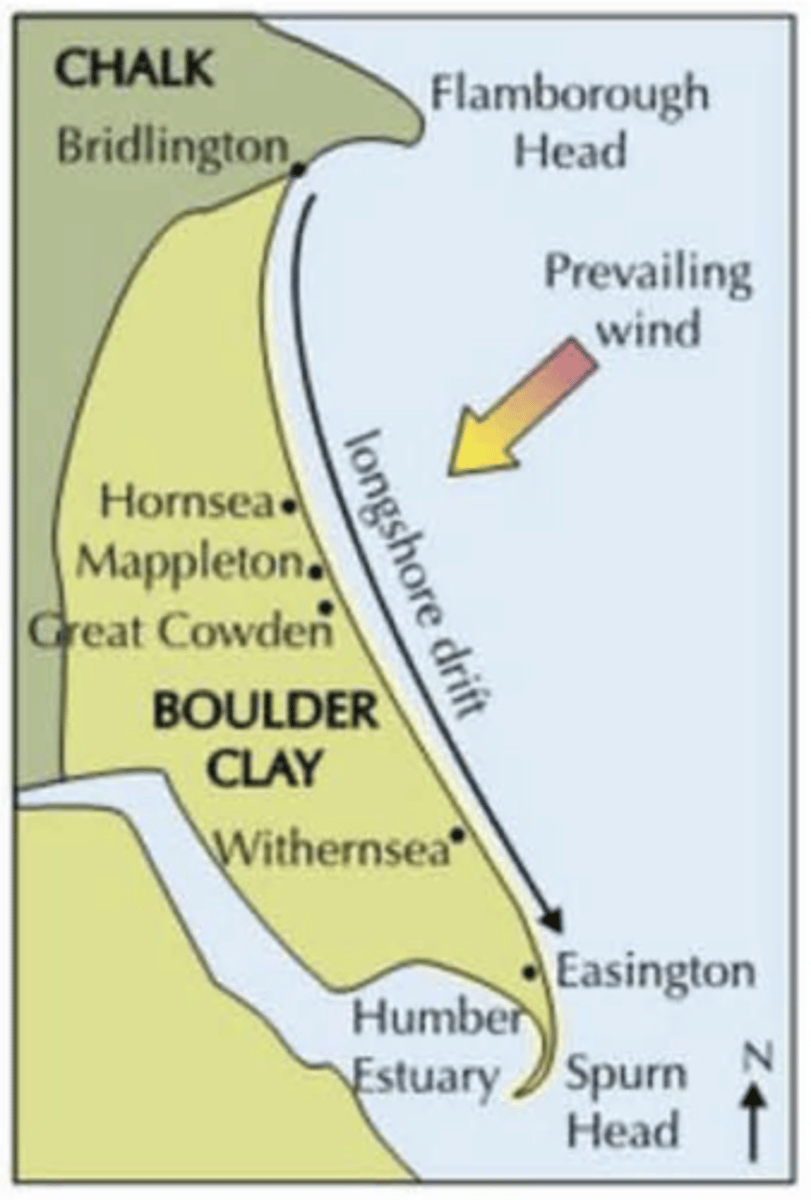
Longshore drift
the movement of material along a coast by waves that approach at an angle to the shore but recede directly away from it.

Prevailing wind
The direction from which the wind most commonly blows in a region. In the British Isles, for example, the prevailing wind is southwesterly, blowing from the Atlantic Ocean and bringing moist and mild conditions.

Swash
The movement of material up the beach in the direction of the prevailing wind.

Wave
A circular or elliptical movement of water near the surface of the sea.

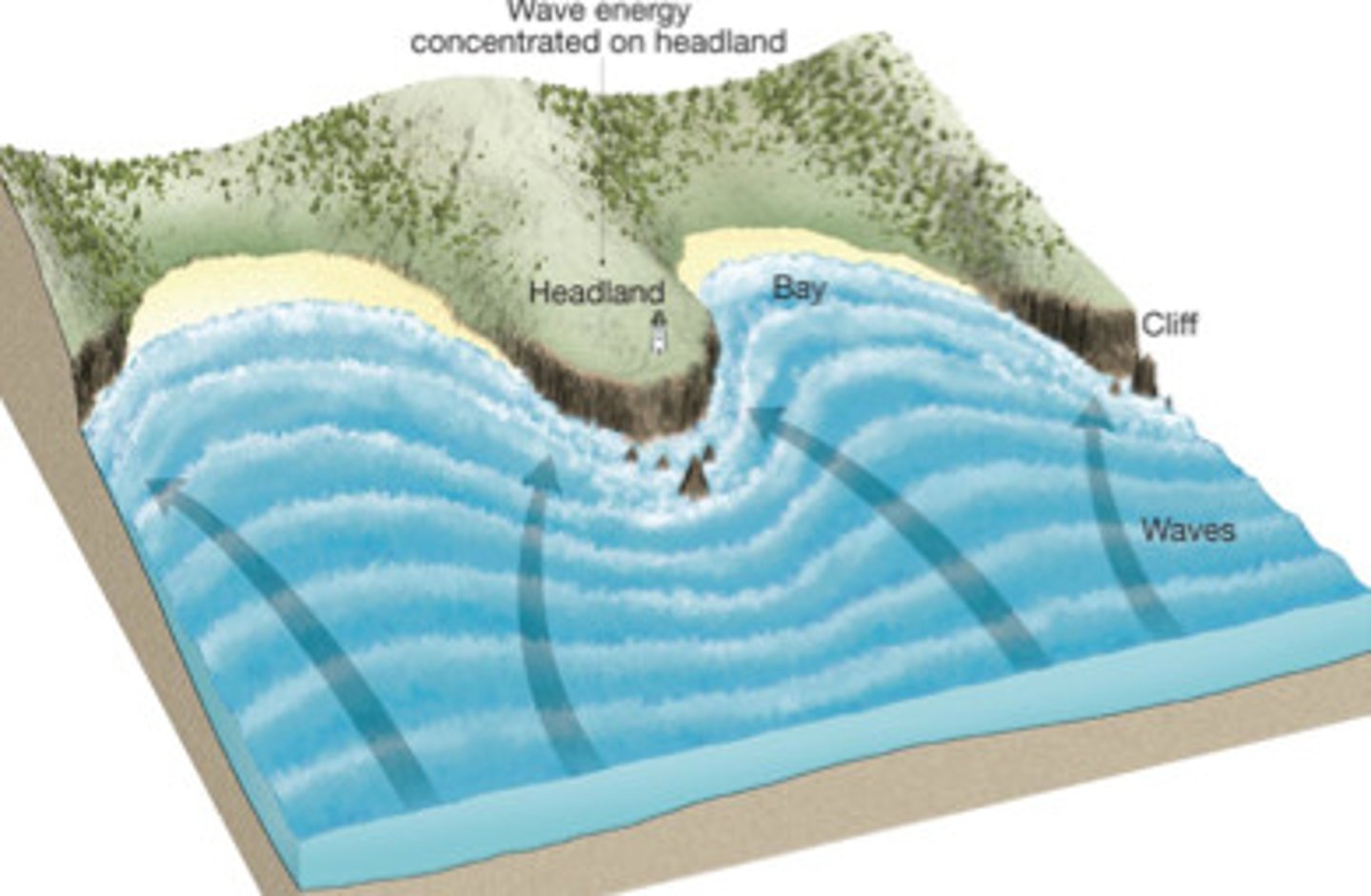
Wave refraction
The way in which a wave changes shape and loses speed as it comes in contact with the seabed. If refraction is complete, waves break parallel to the coastline. If refraction is not complete, longshore drift occurs.
Arch
A natural bridge-like feature formed by erosion. Arches are formed from the erosion of a headland where two caves meet and break through the headland.

Bar
A depositional feature: a long sandy ridge running parallel to a coastline that is submerged at high tide. Some bars develop as offshore bars whilst others form from the development of a spit across the whole of a small bay.
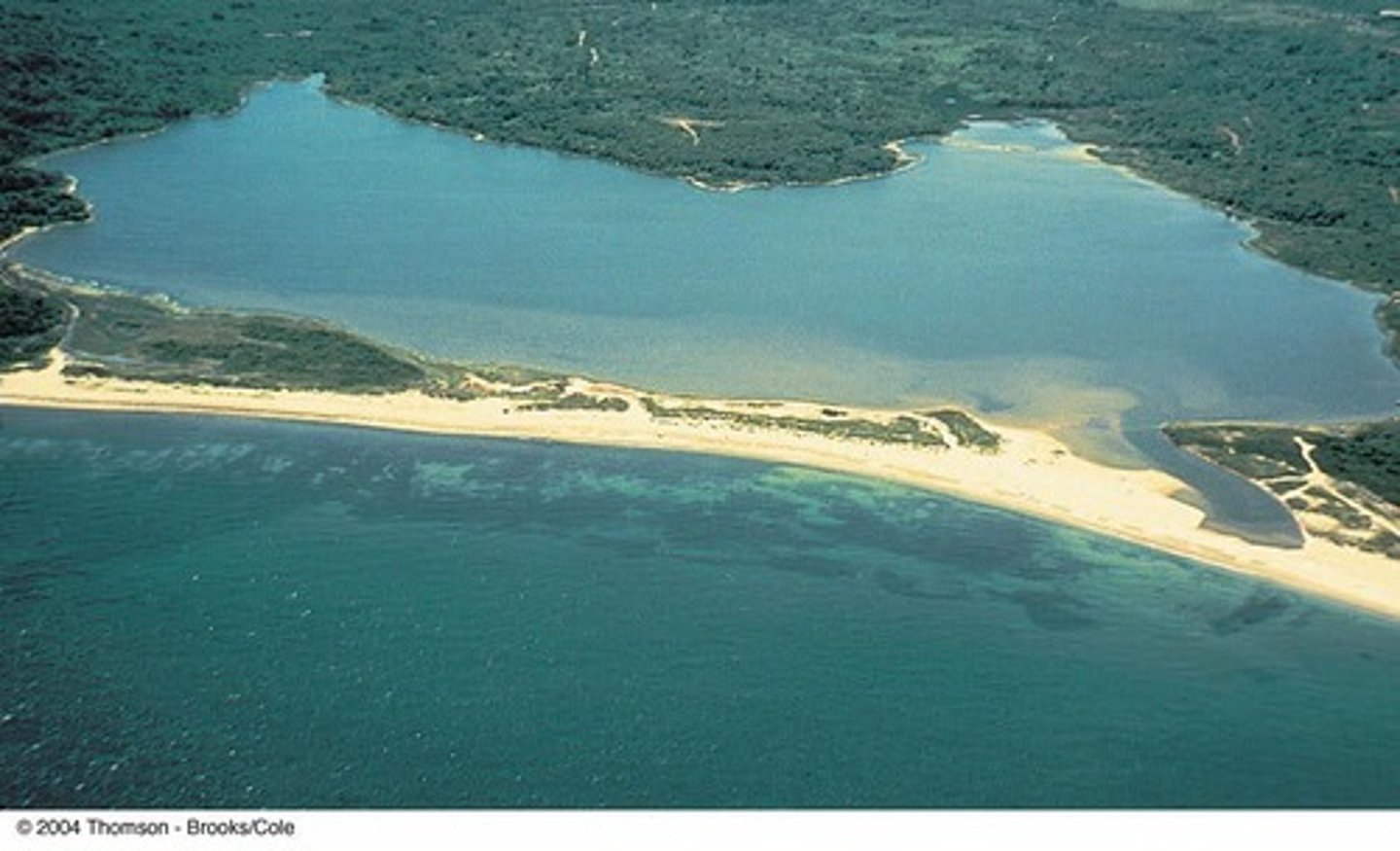

Bay
A wide, open, curving indentation of the sea.
Beach
A feature of coastal deposition, consisting of pebbles on exposed coasts or sand on sheltered coasts. It is usually defined by the high- and low-water marks.
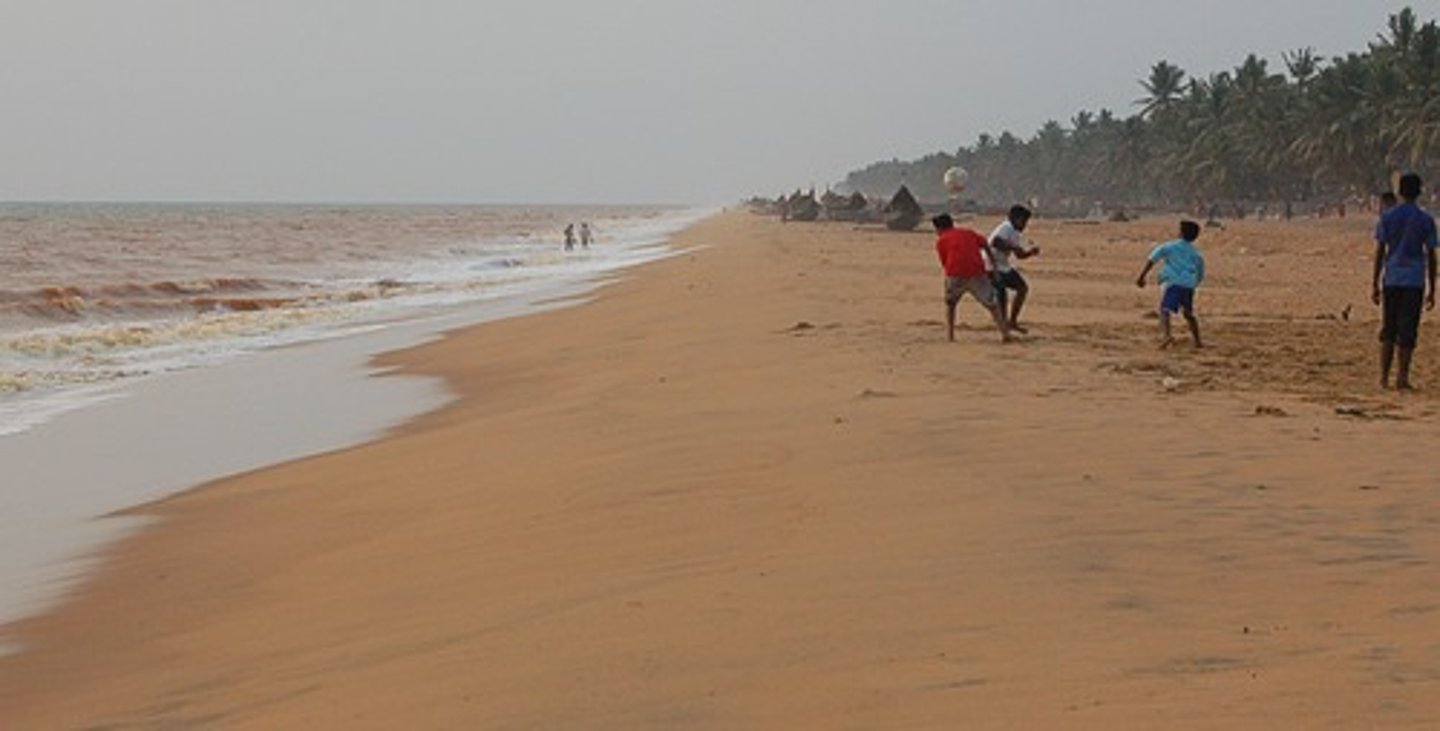

Coastal cave
Formed where relatively hard rock containing lines of weakness is exposed to severe wave action.

Cliff
A rock-face along the coast, where coastal erosion, weathering and mass movements are active and the slope rises steeply (over 45 º) and for some distance. The nature of the cliff depends on the nature of the rocks and their hardness and jointing pattern.
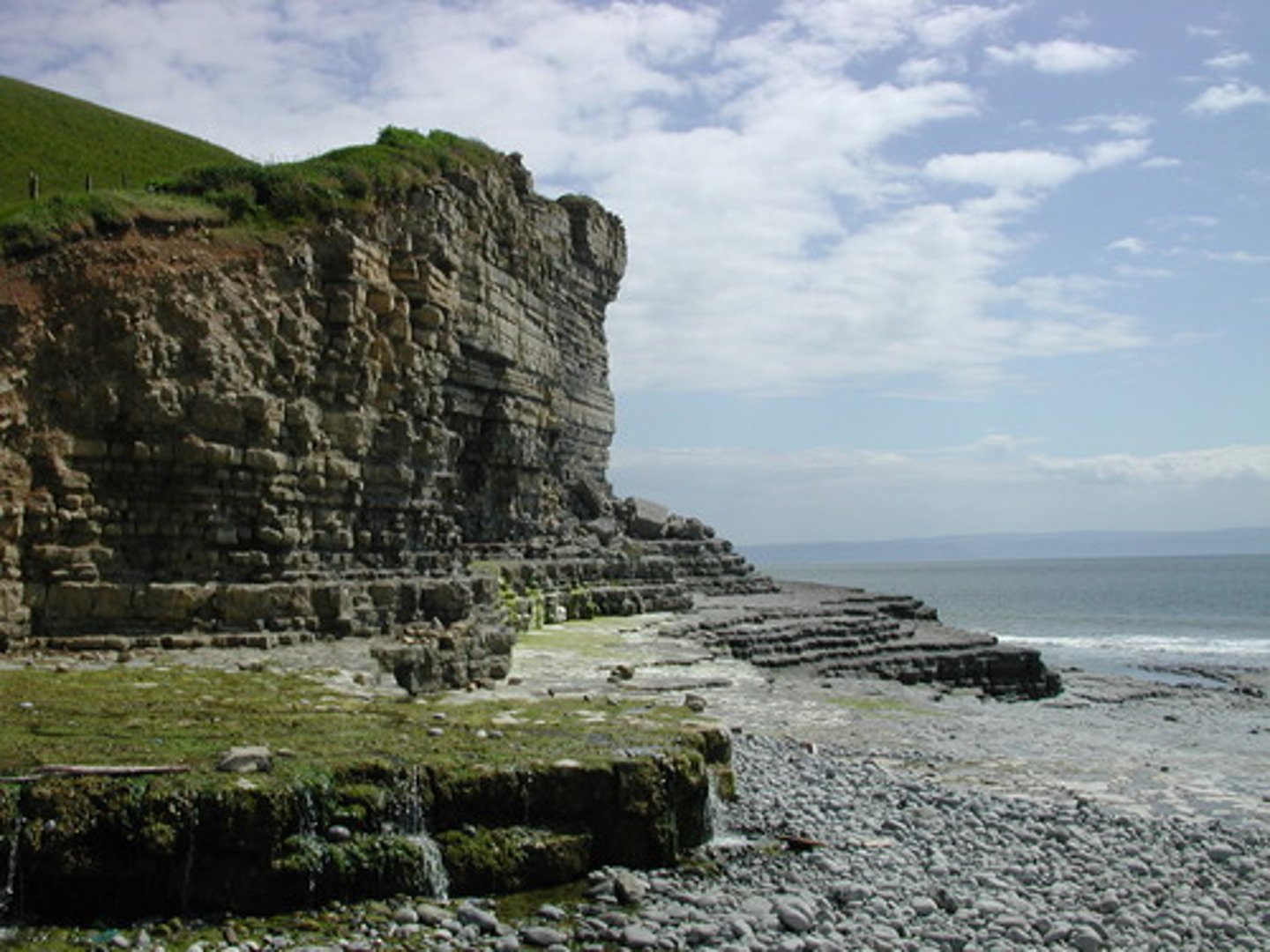

Headland
A point of land projecting into the sea, also known as a cape or promontory.
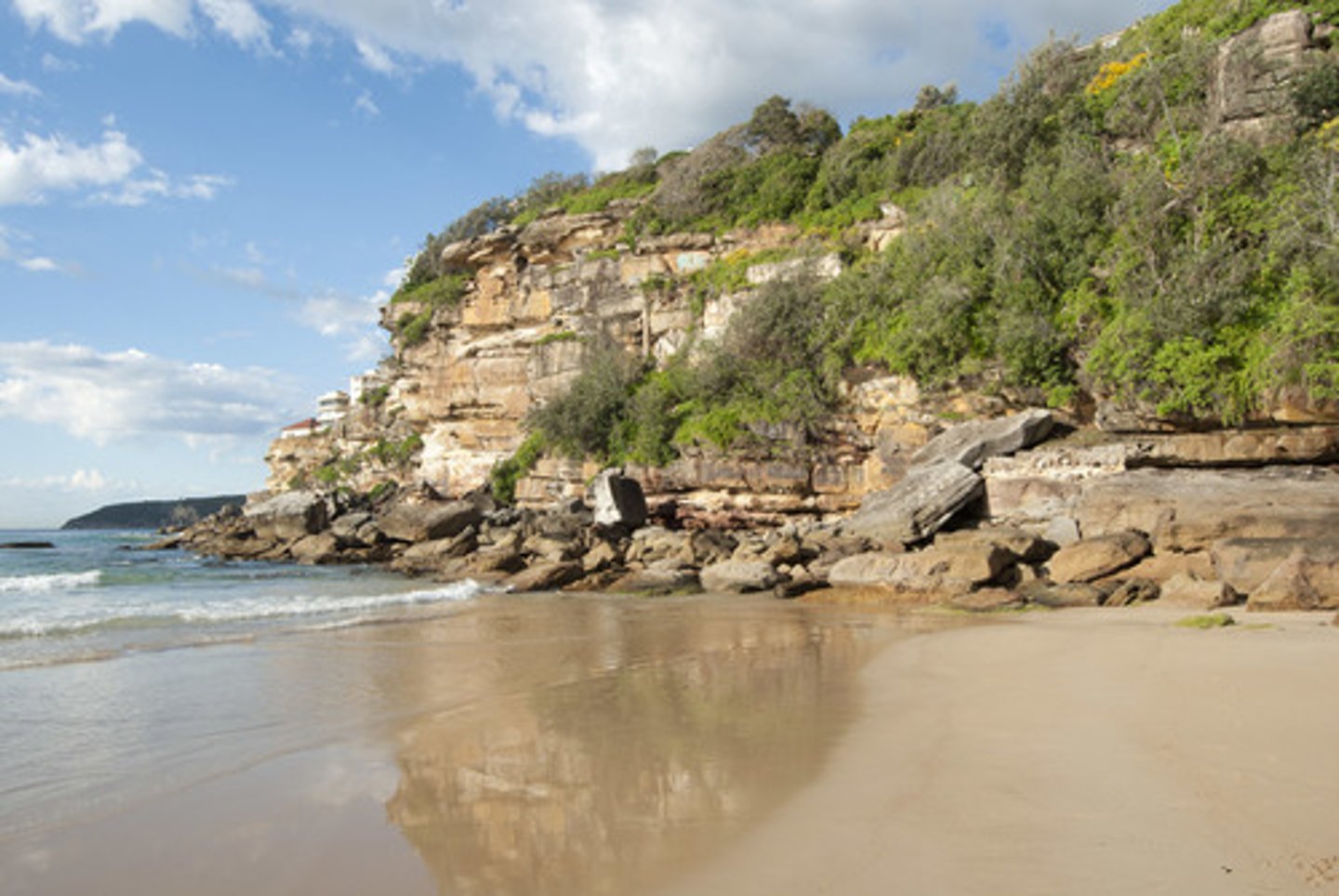

Offshore bar
A linear ridge of sand or pebbles parallel to the shoreline. Offshore bars are formed when waves disturb sediments on the seabed and form them into a submarine ridge or bar.
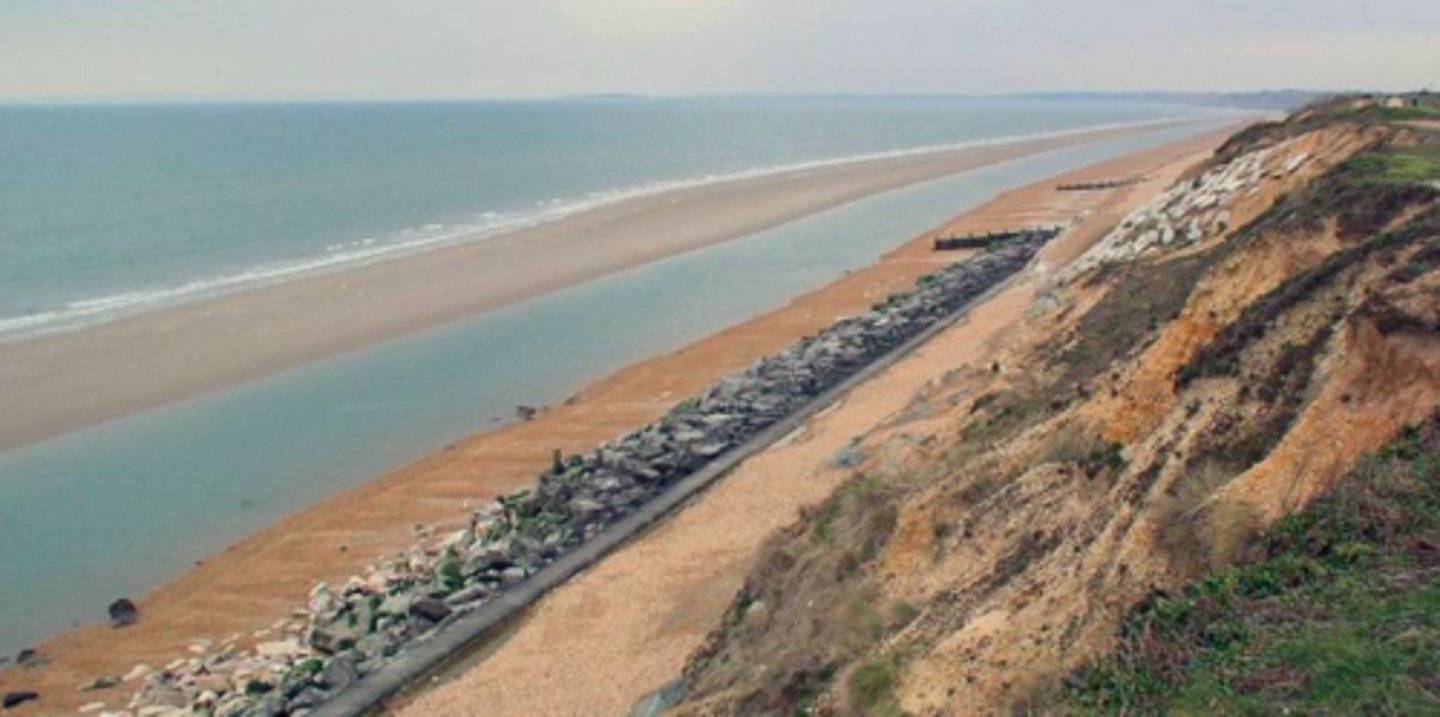

Salt marshes
Marshland with salt-tolerant vegetation. Salt marshes develop around estuaries and on the sheltered side of spits. Salt marshes usually have a network of creeks and channels by which sea water enters and leaves the marsh.

Sand dune
A mound or ridge of wind-drifted sand common on coasts and in deserts. In coastal areas, sand is trapped by vegetation, notably sea couch grass and marram grass, to form stable dunes.

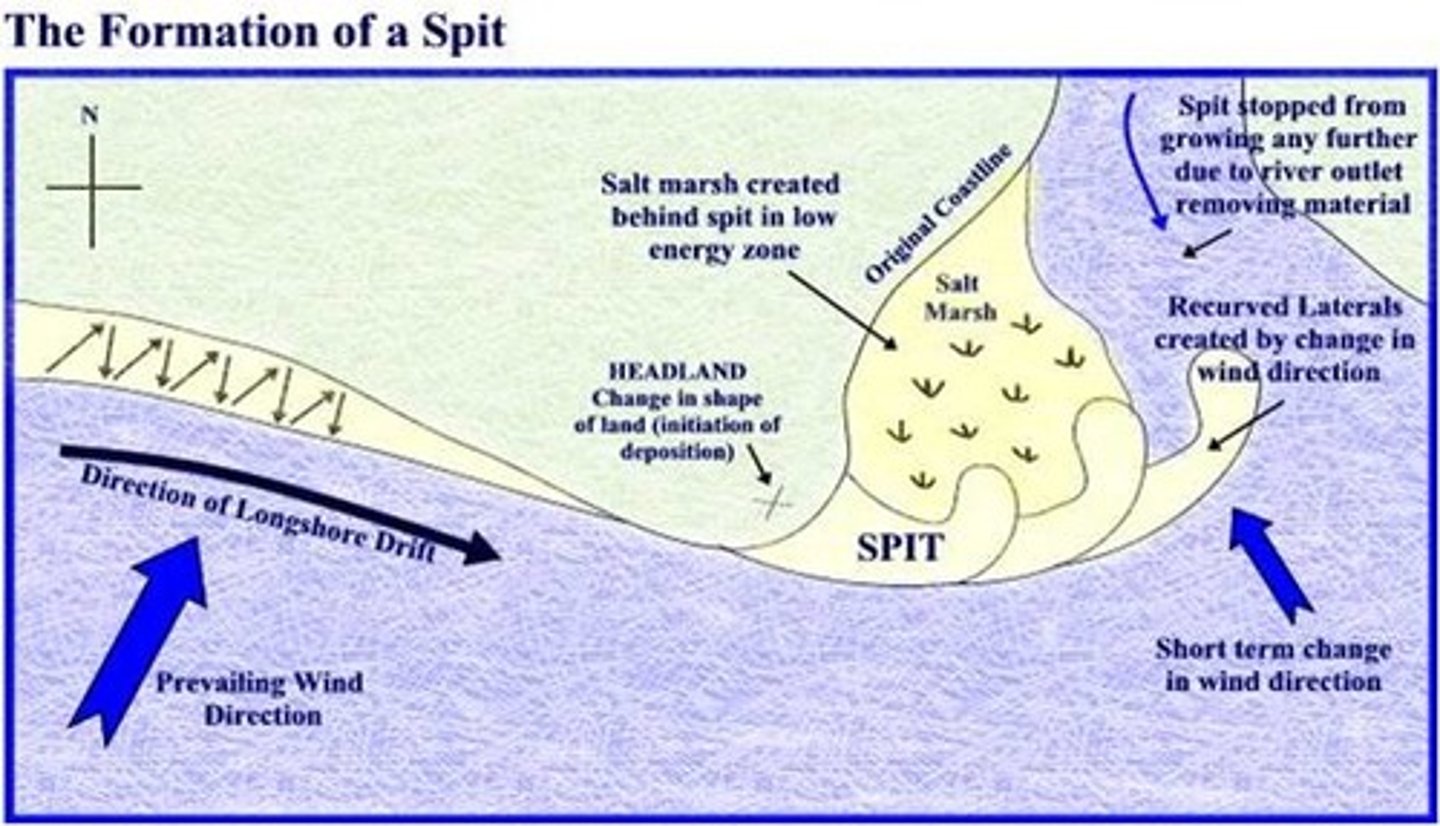
Spit
A ridge of sand or shingle connected to the land at one end and in the open sea at the other end. It is formed by the interruption of longshore drift due to wave refraction, river currents, secondary winds and/or changes in the shape of the coastline.
Stack
An isolated upstanding pillar of rock that has become separated from a headland by coastal erosion. It is usually formed by the collapse of an arch.
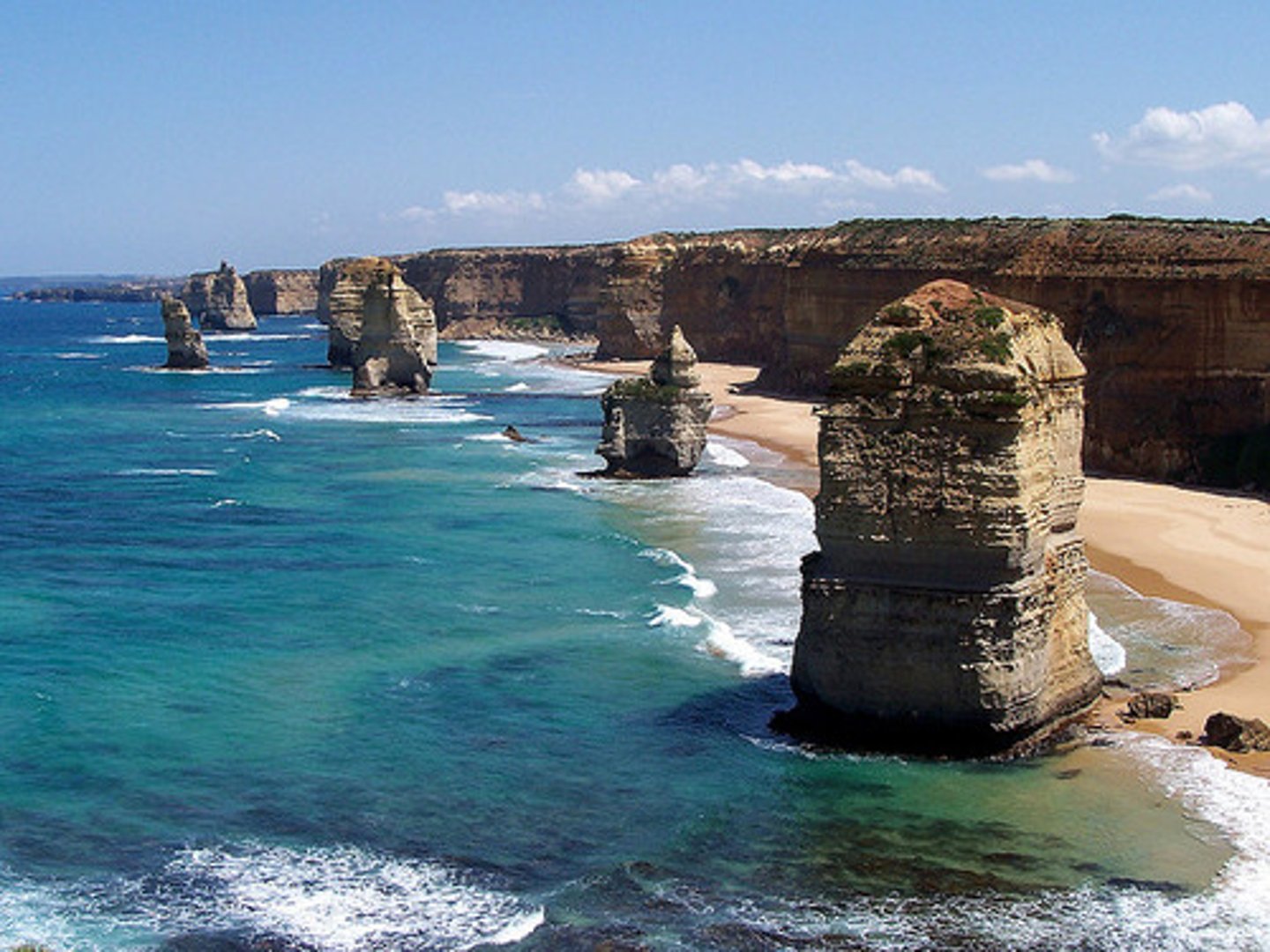

Stump
An eroded stack, which is exposed only at low tide.
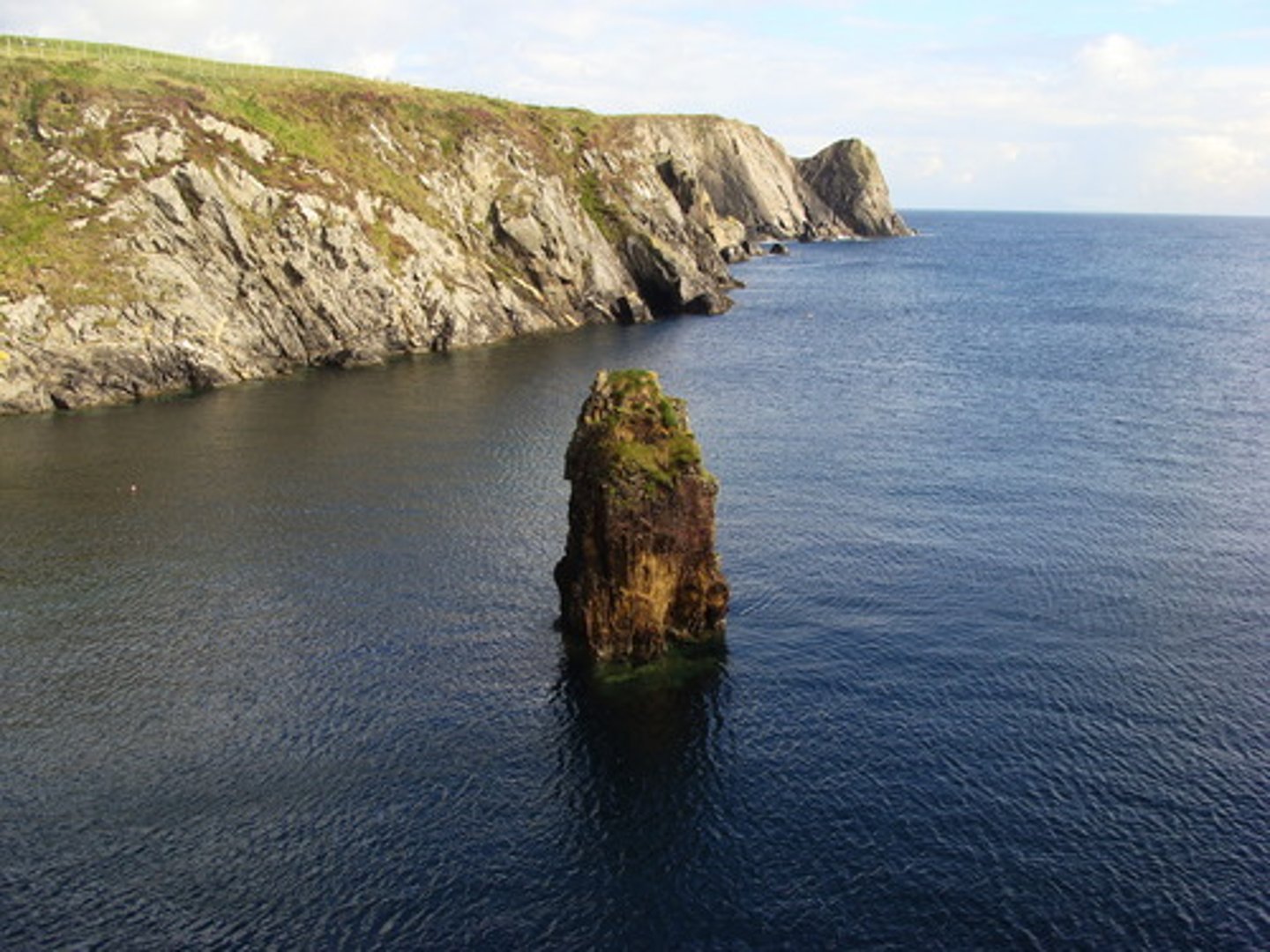

Wave-cut platform
A gently sloping rock surface found at the base of a coastal cliff. It is covered by water at high tide but exposed at low tide. It is formed by the erosion (by waves) of a former cliff face.

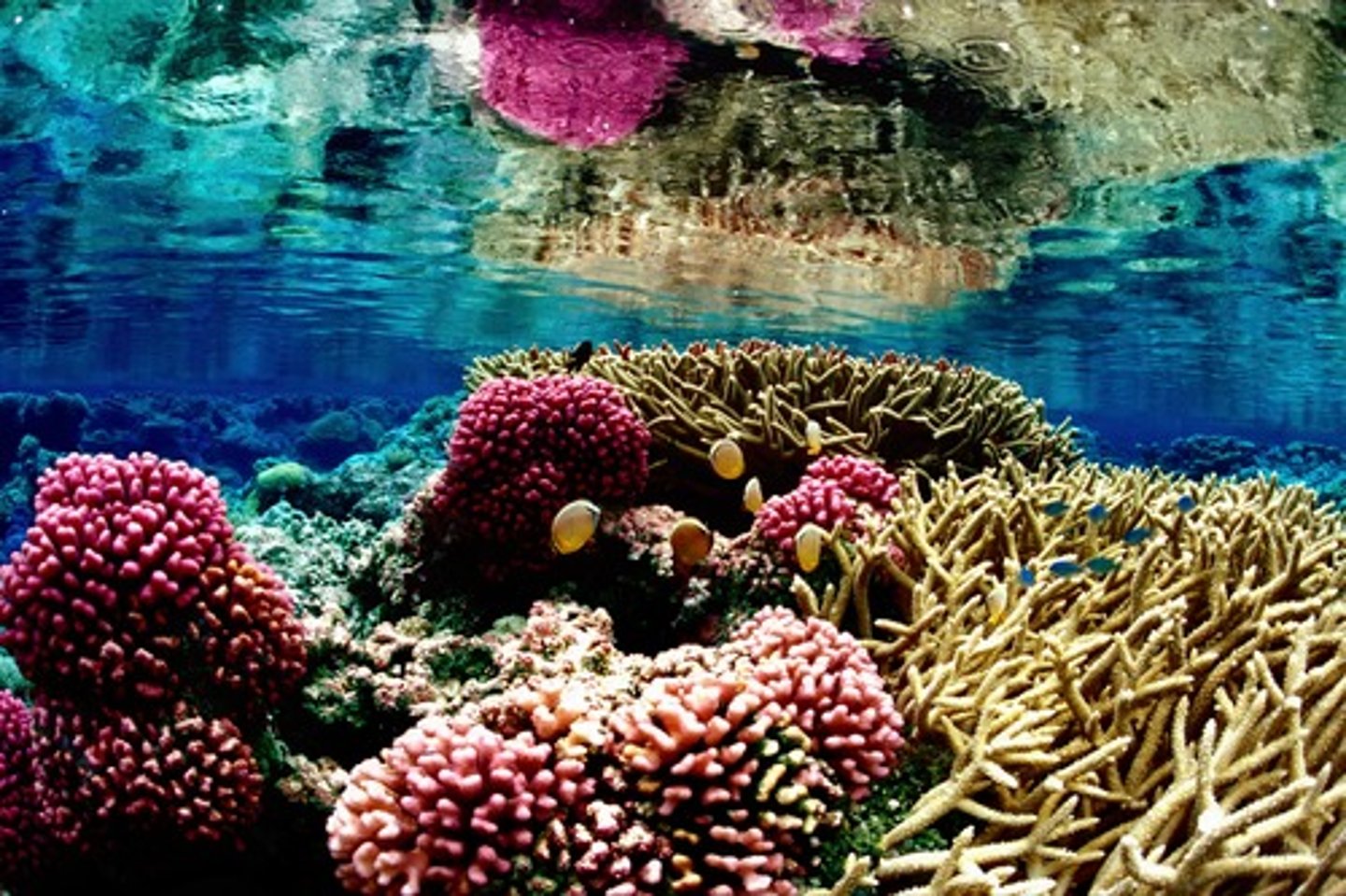
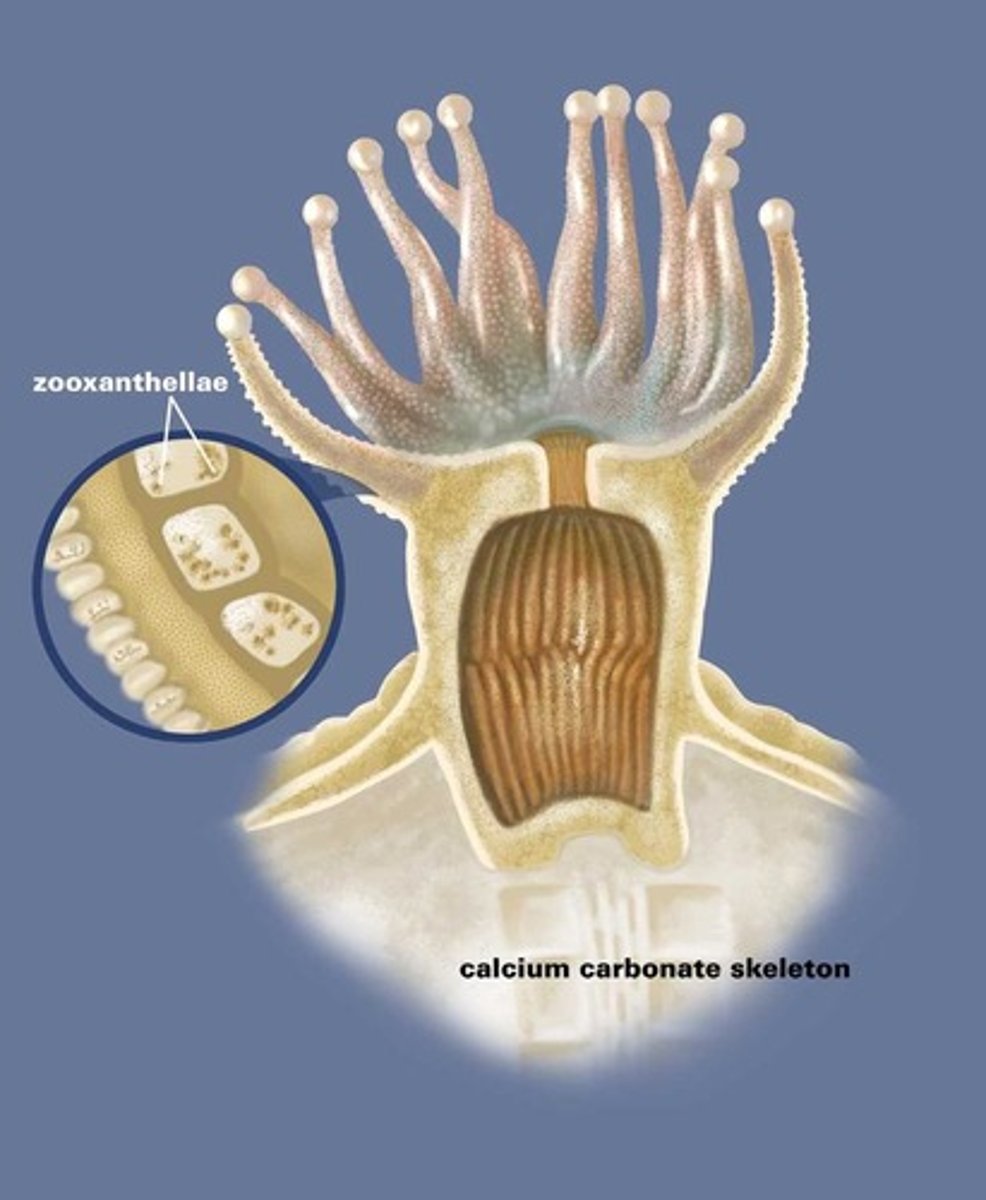
Coral
A living organism (polyp) living in clear, tropical waters. Corals live in communities known as reefs. They secrete lime and build a skeleton.

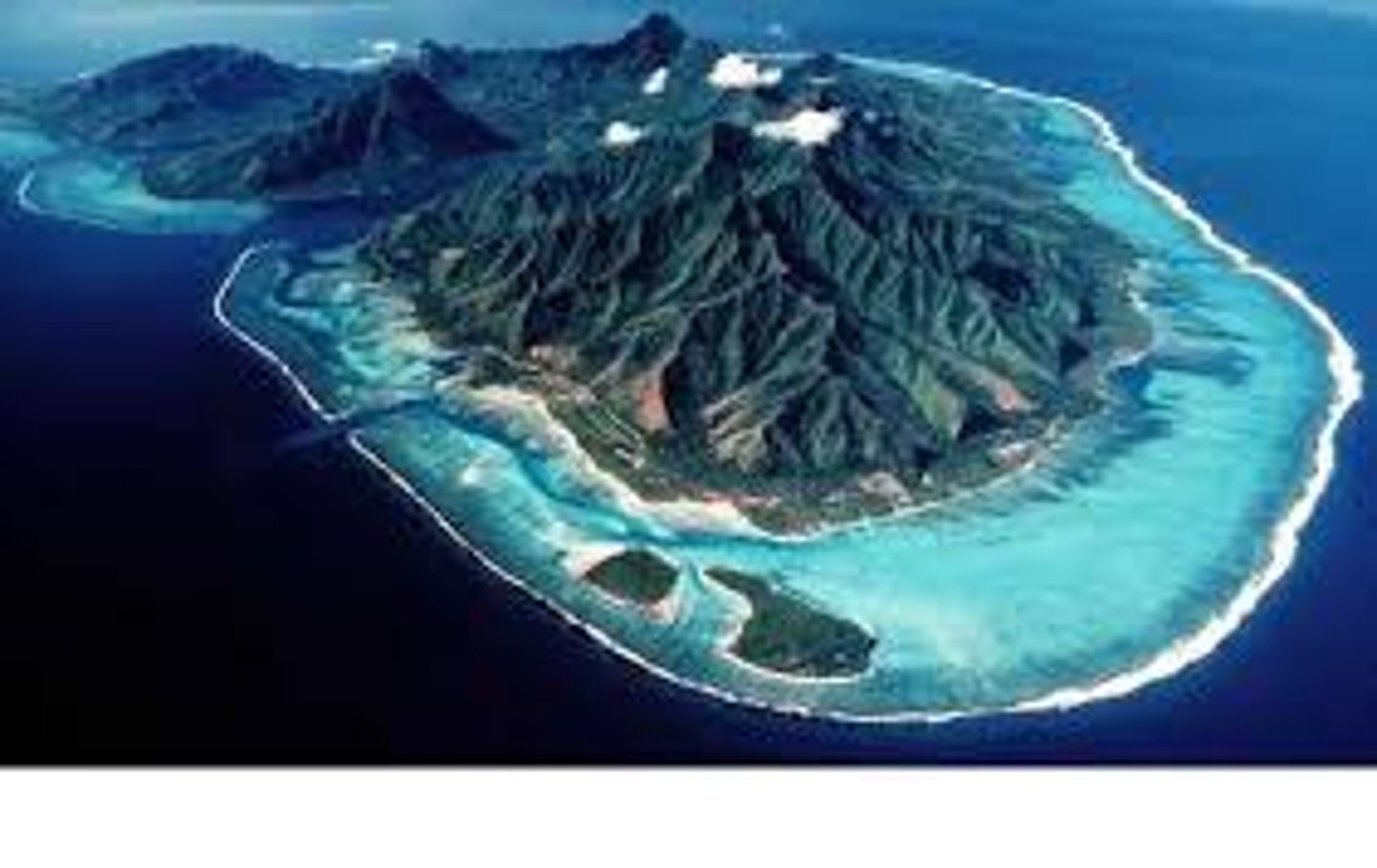
Atoll
A coral reef surrounding a central lagoon, which may have developed around volcanic islands that have submerged or may have developed upwards as sea levels have risen.
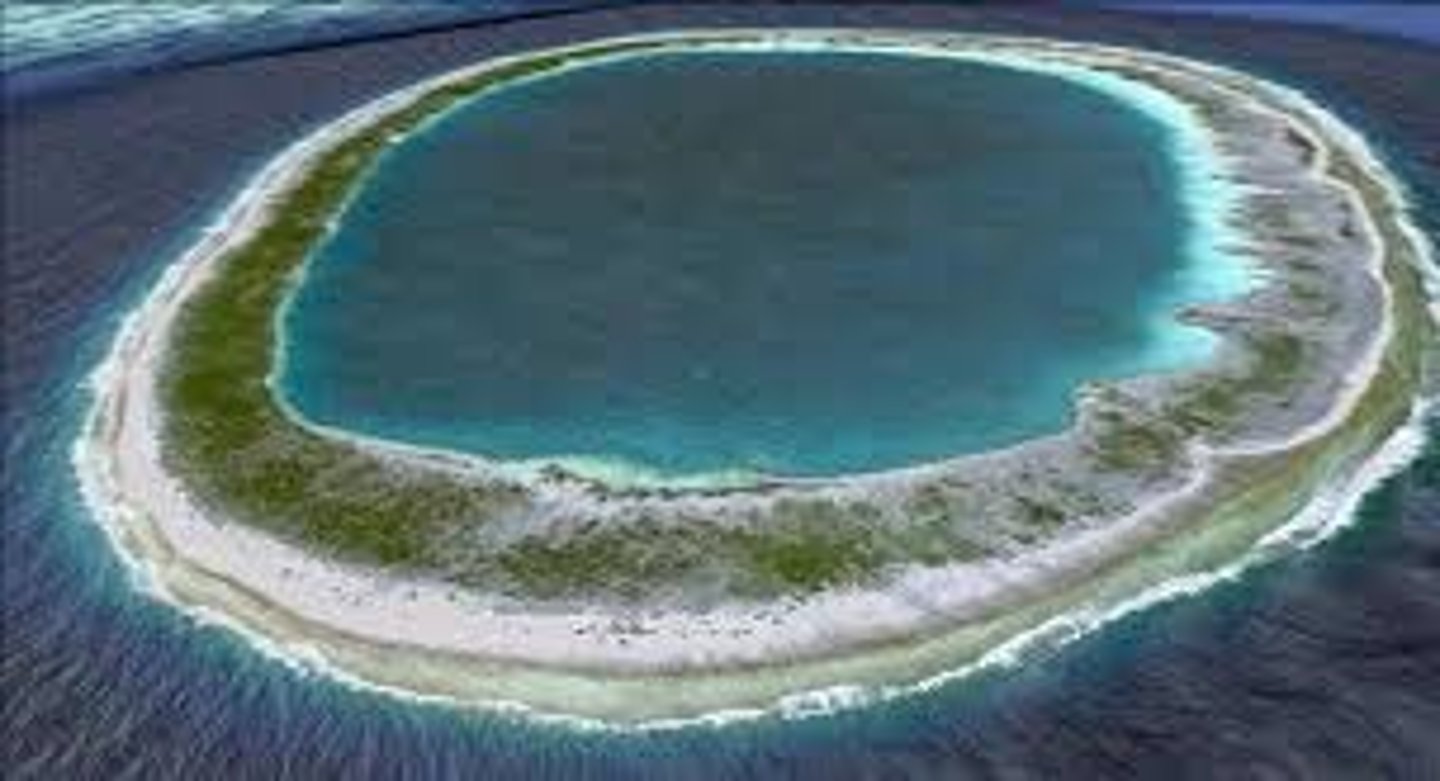

Barrier reef
A coral reef running parallel to the coastline and separated from the shoreline by an extensive lagoon system.
Fringing reef
a coral reef attached to the coastline.

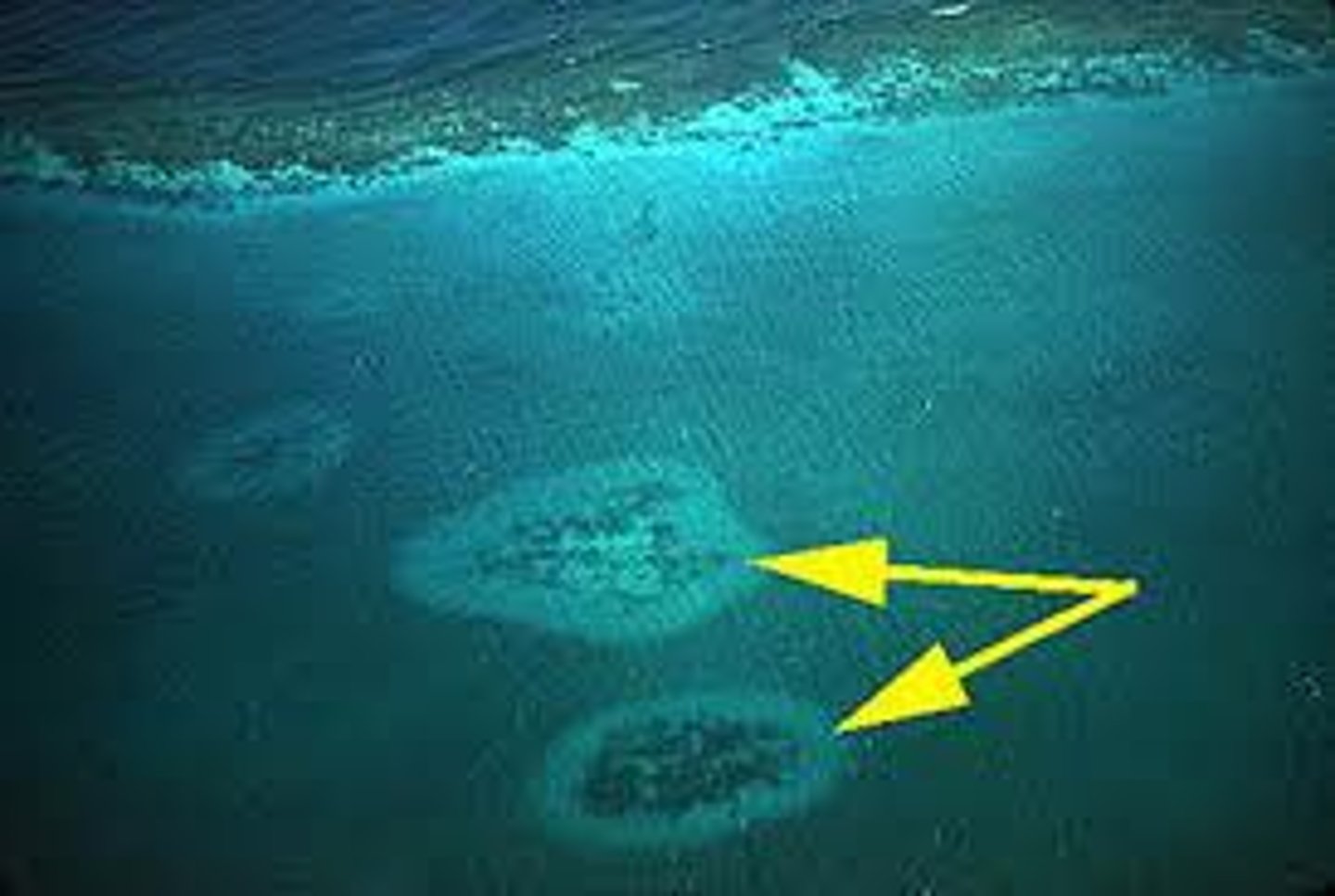
Patch reef
A small circular or irregular reef that rises from the sea floor of lagoons behind barrier reefs or within atolls.

Coral bleaching
The expulsion of the algae from coral causing it to lose colour.
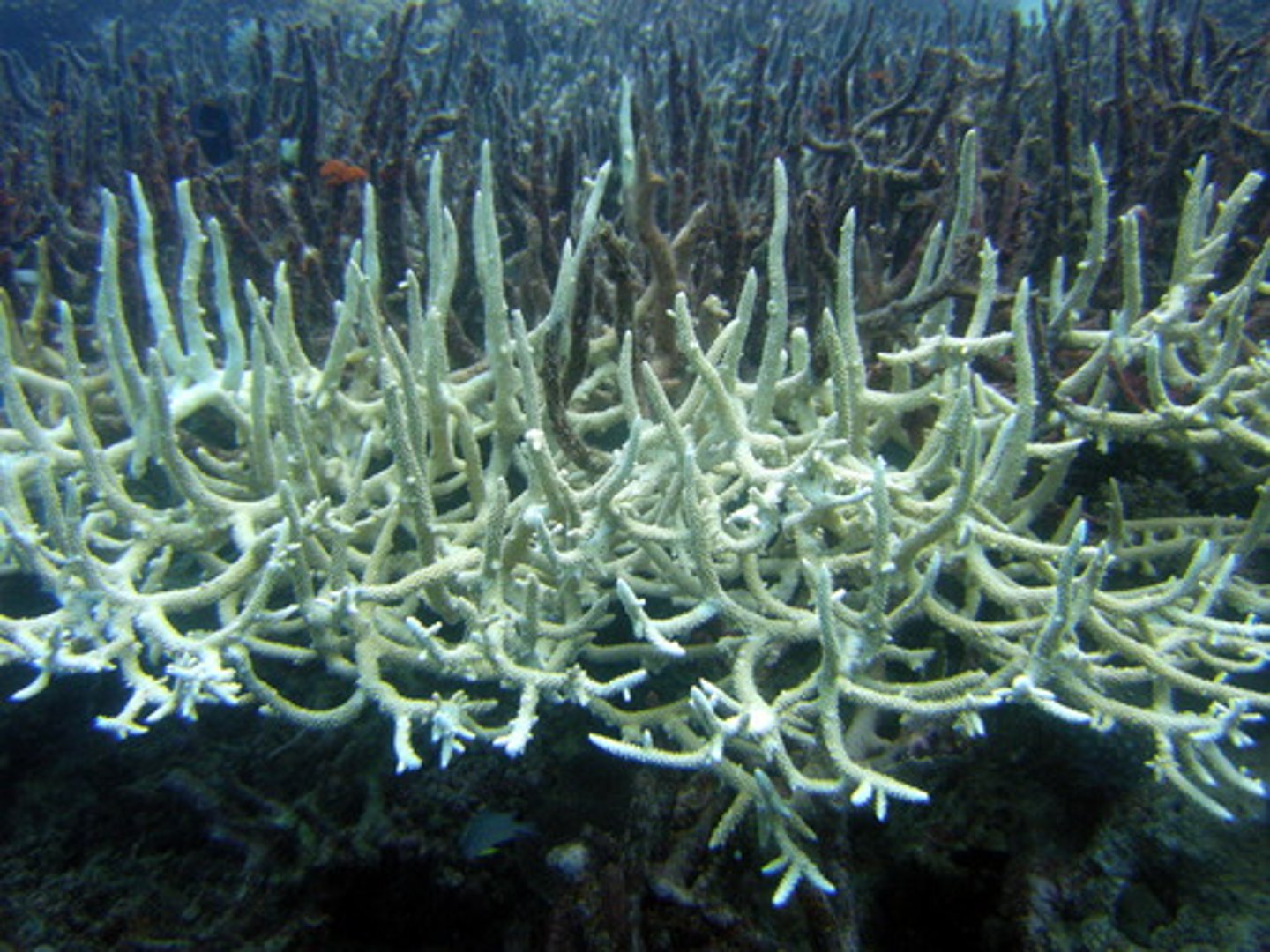

Zooxanthellae
Algae that live in a symbiotic relationship with coral and give it its colour.
Coastal protection
Refers to measures taken to prevent coastal erosion and/or flooding. To reduce erosion, several different forms of coastal protection are used. These can be divided into soft engineering and hard engineering.

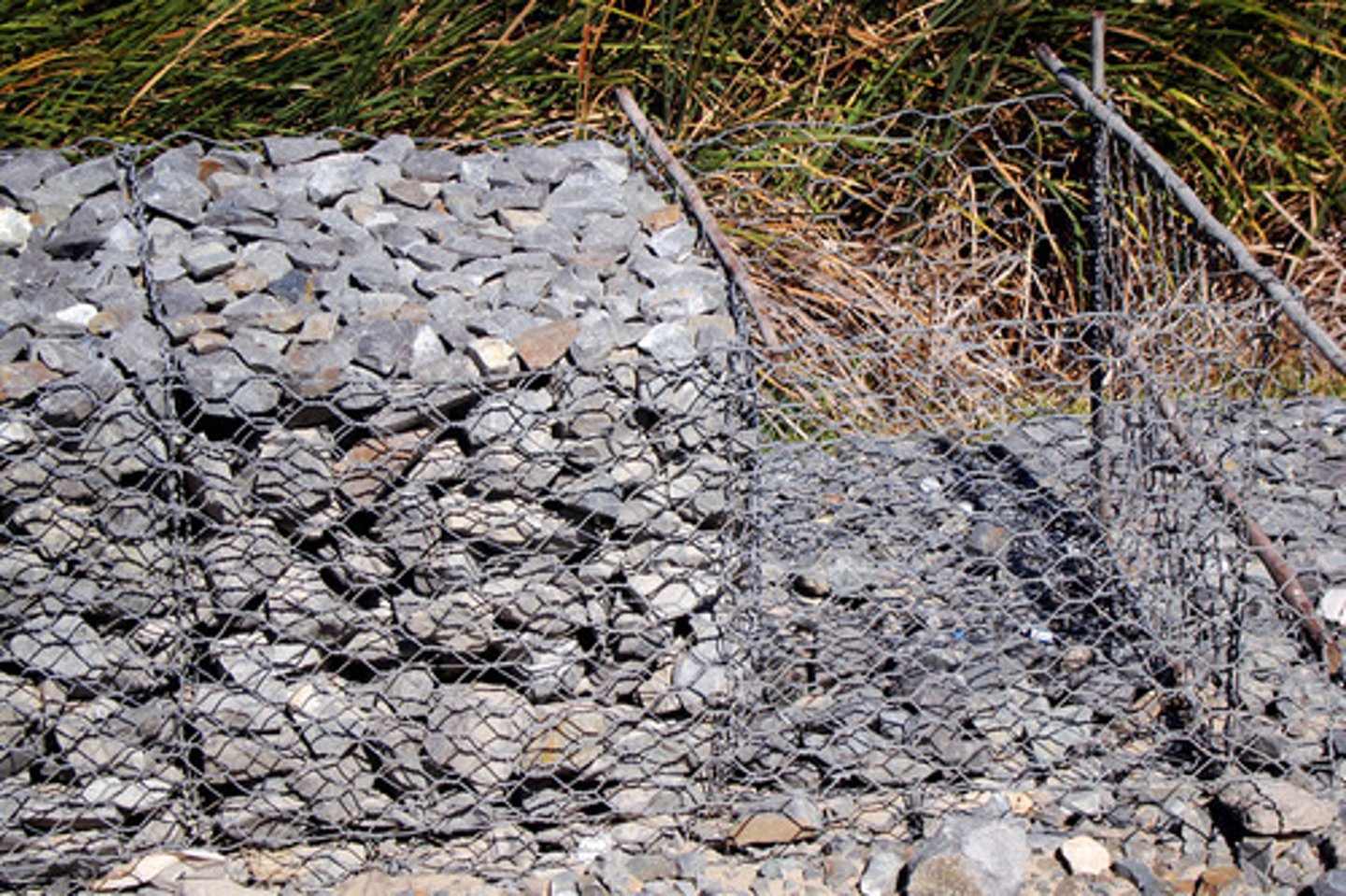
Gabion
A wire basket filled with rocks or stones used for stabilising slopes and protecting the base of cliffs in areas of coastal erosion.

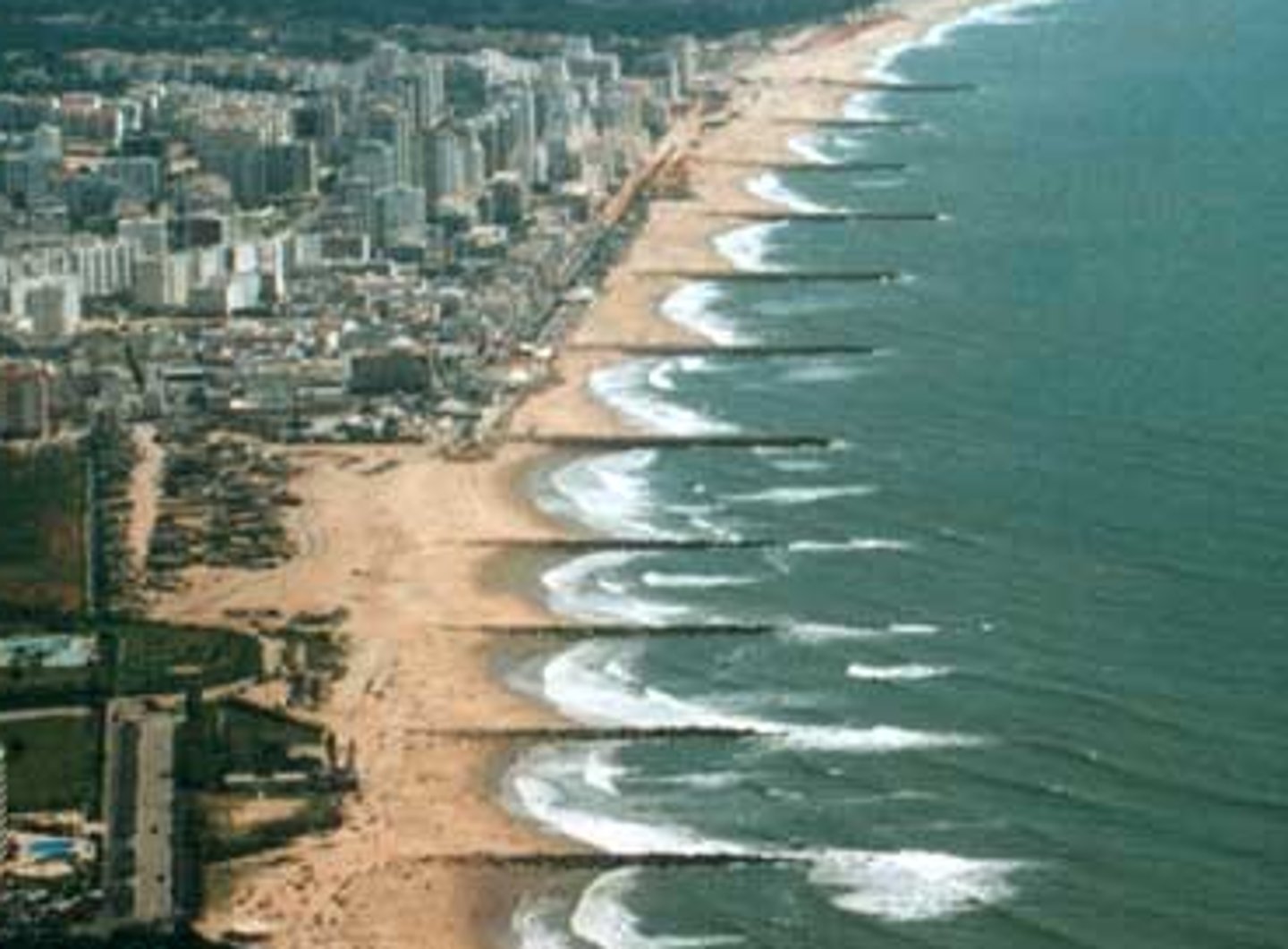
Groyne
A wooden or concrete barrier built at right-angles to a beach in order to block the movement of material along the beach by longshore drift. Groynes are usually successful in protecting individual beaches. However, as they prevent beach material from being transported along the coast they can starve beaches further down the coast of sand and shingle; hence these beaches may be at increased risk of wave erosion.
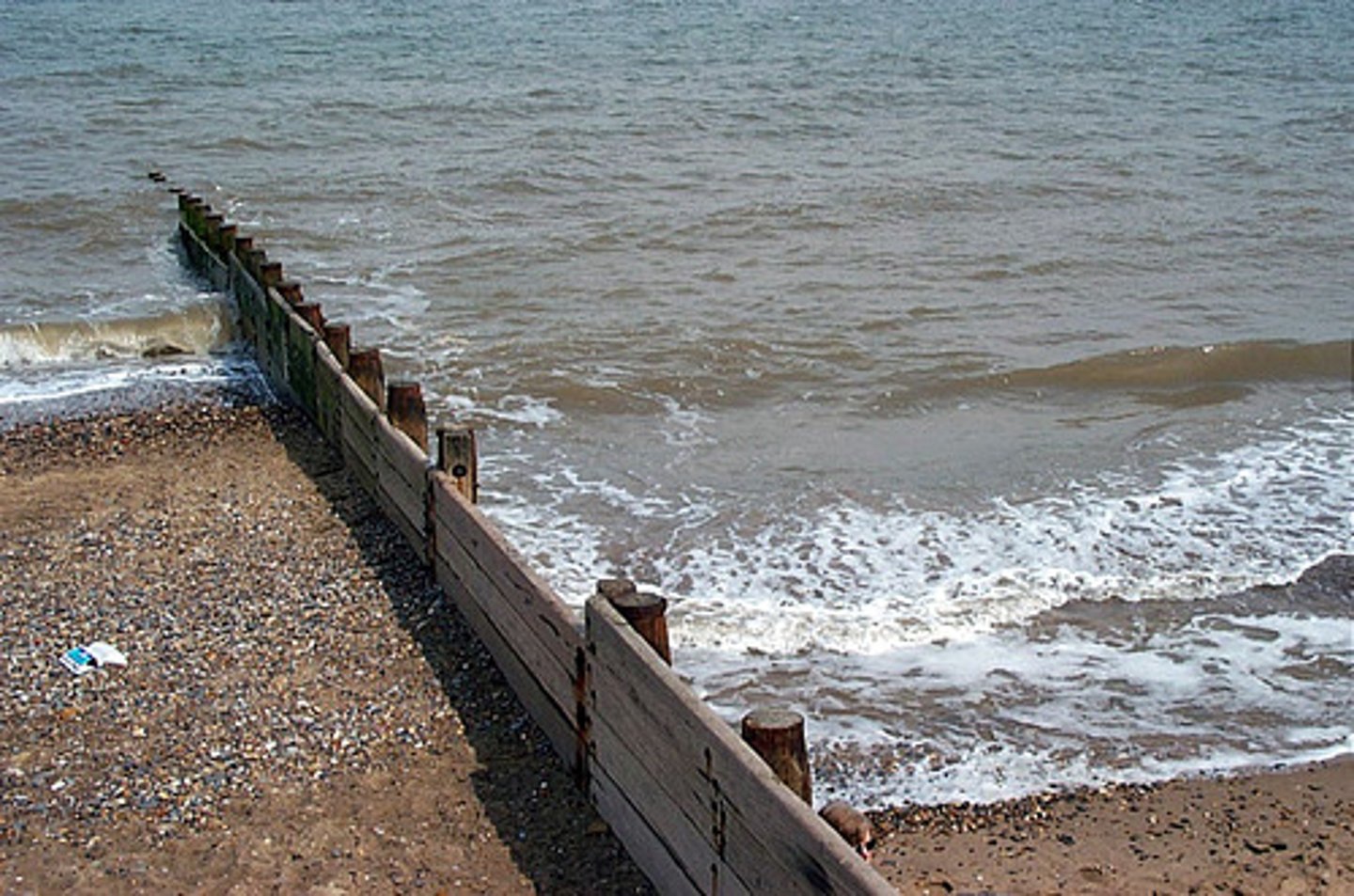

Hard engineering
any form of coastal (or river) protection scheme that involves altering the natural environment with concrete, stone, steel, metal, etc; e.g. the use of seawalls, gabions, groynes or revetments. Artifi cial structures are built in order to protect the natural environment from erosion.
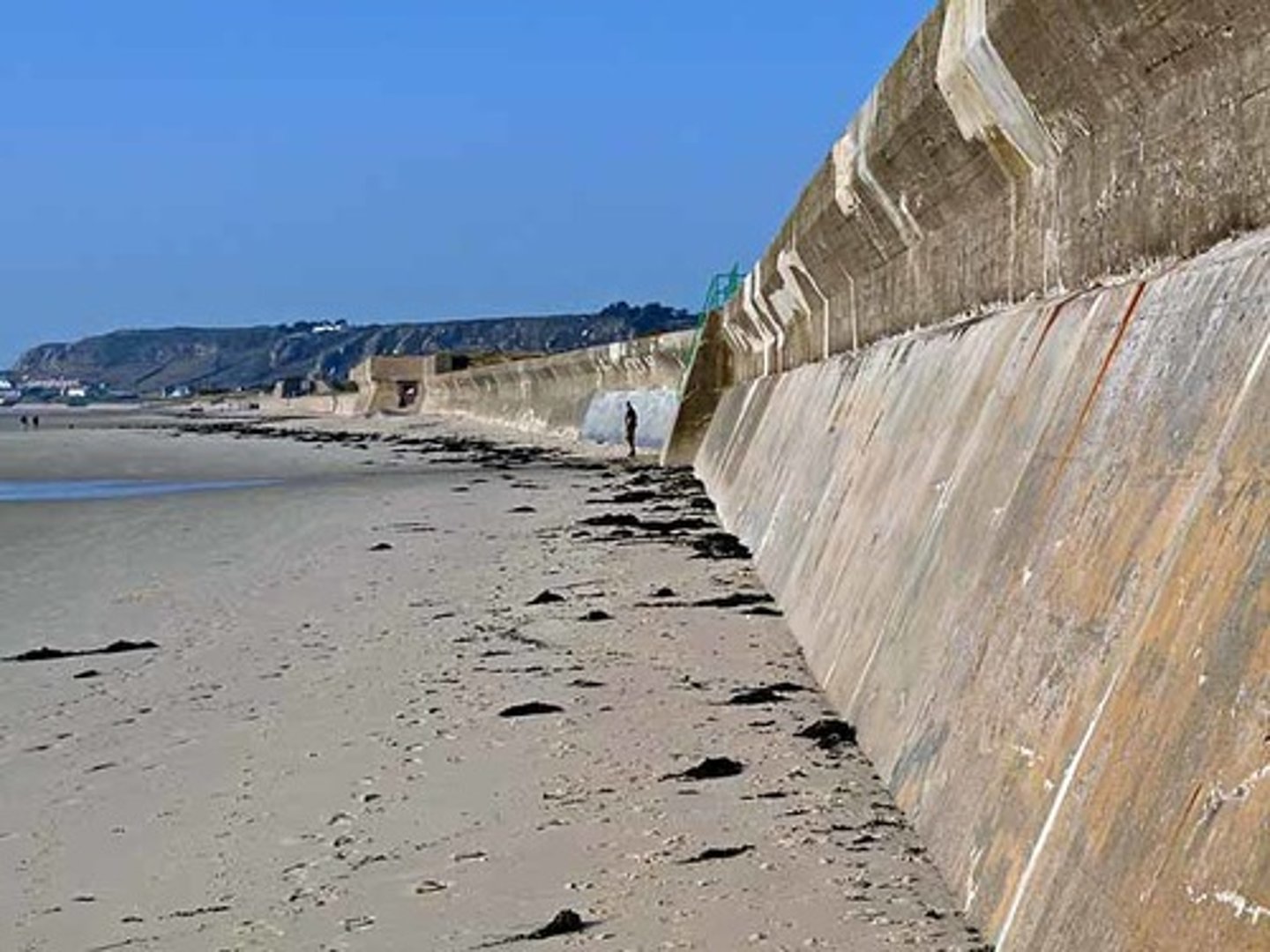

Managed retreat
Allowing the coastline to retreat (erode) in certain areas, i.e. letting nature take its course in areas where the population density or the value of land is low.
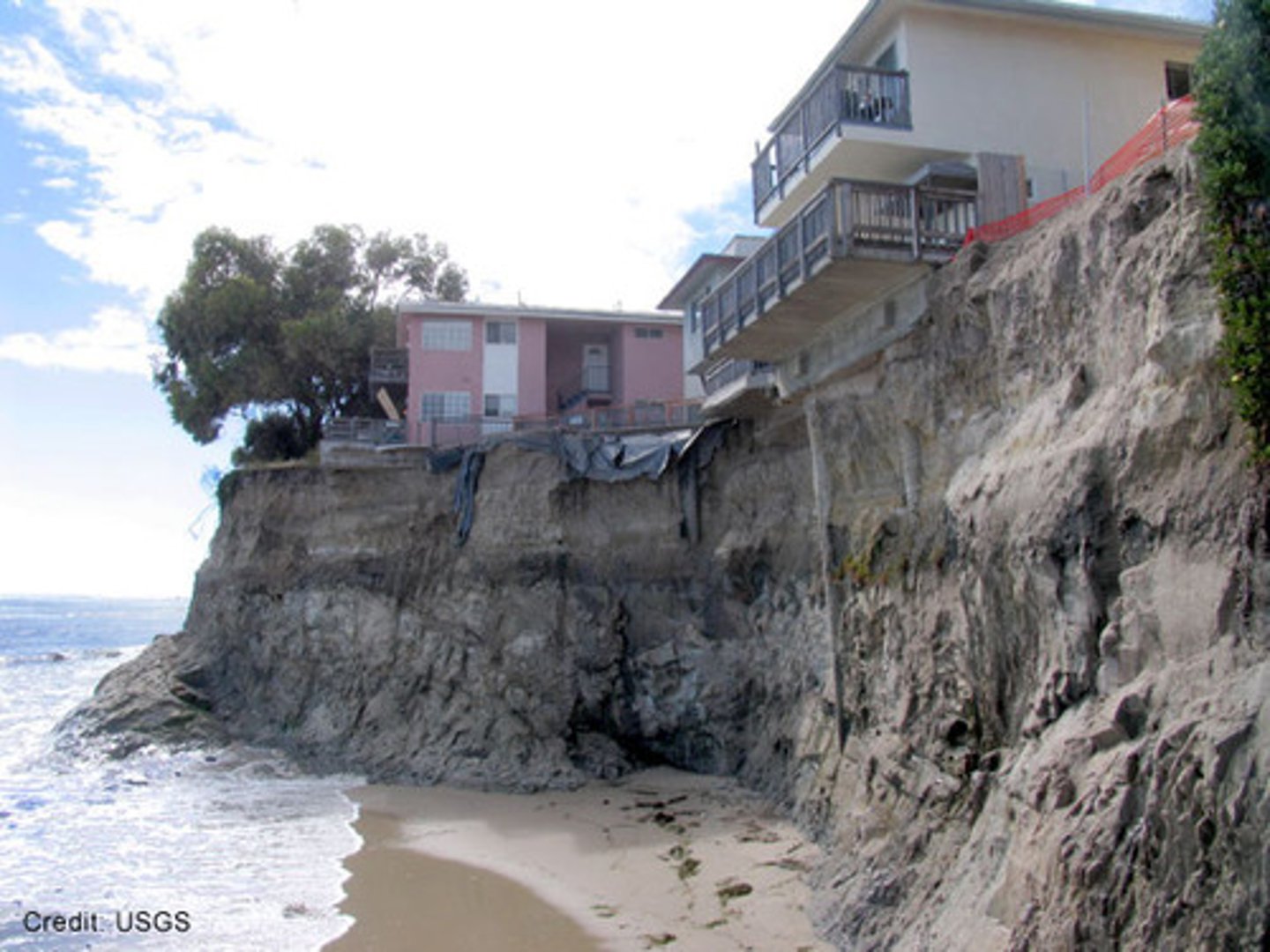

Polder
Land reclaimed from the sea, especially common in the Netherlands.
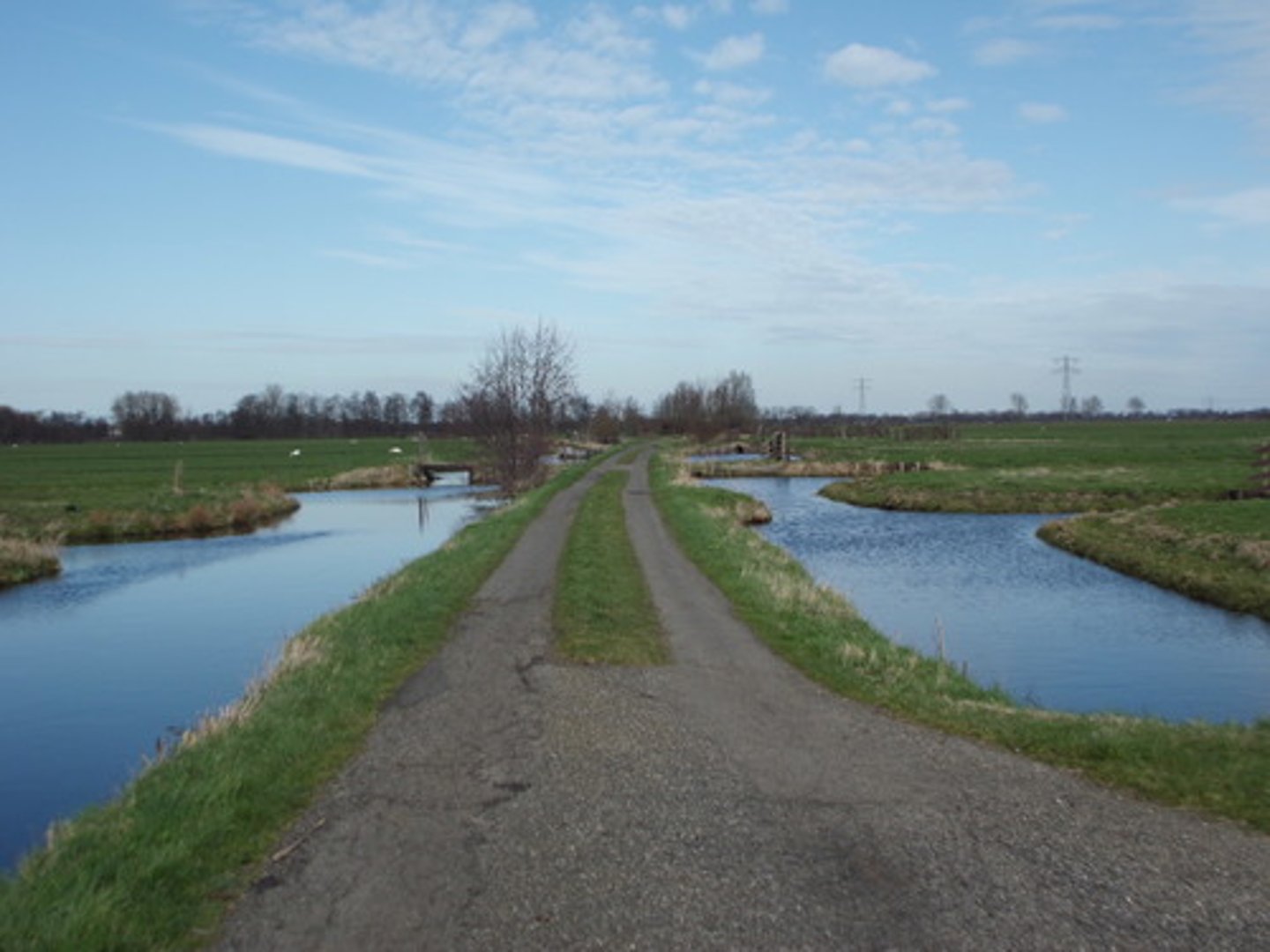

Revetment
A form of hard engineering in which the energy of the waves is absorbed by wooden planks or reflected by concrete structures.
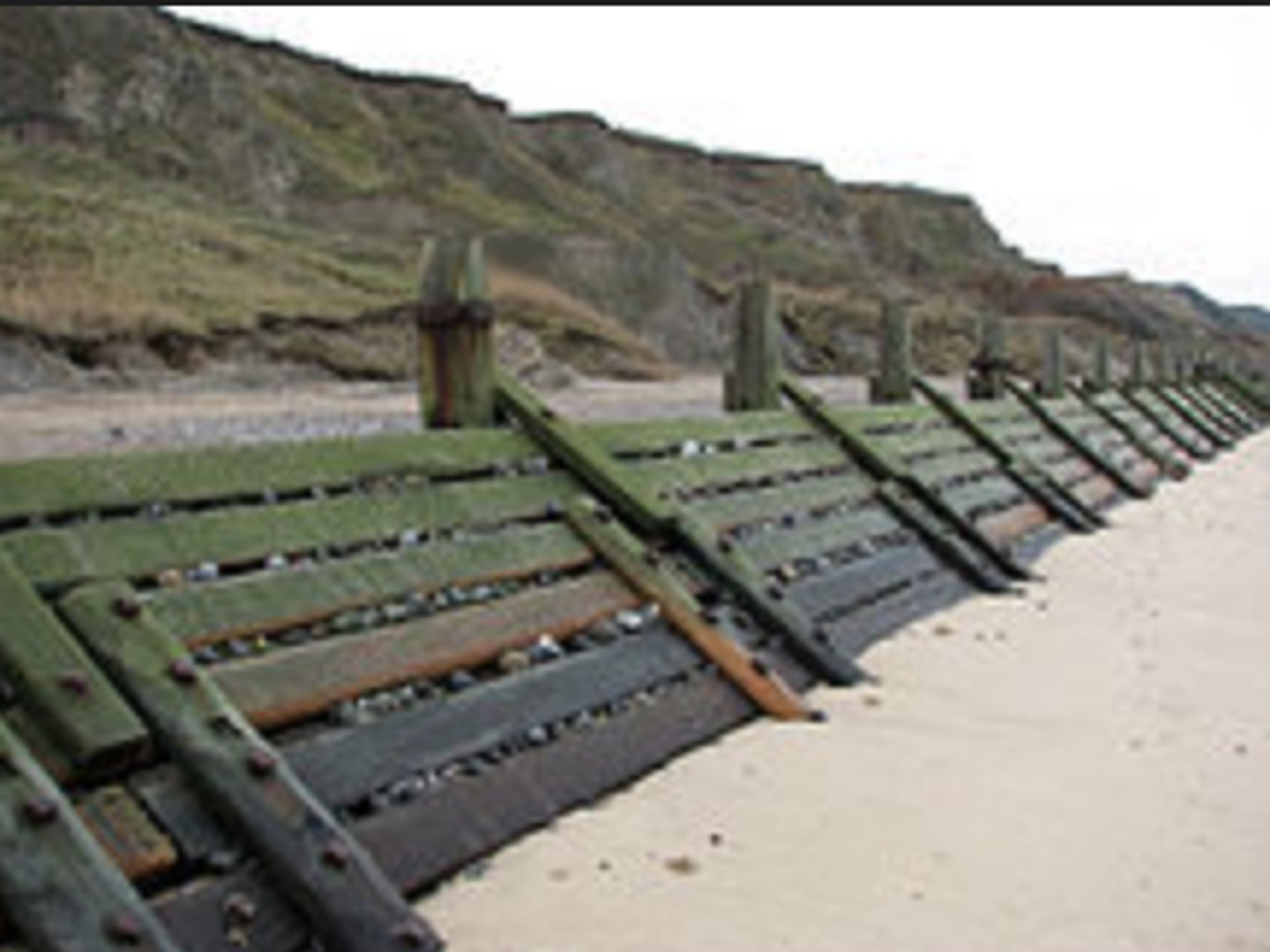

Sea defences
Any form of measure, e.g. seawalls, rock armour, gabions and revetments, which help control coastal erosion and/ or flooding.
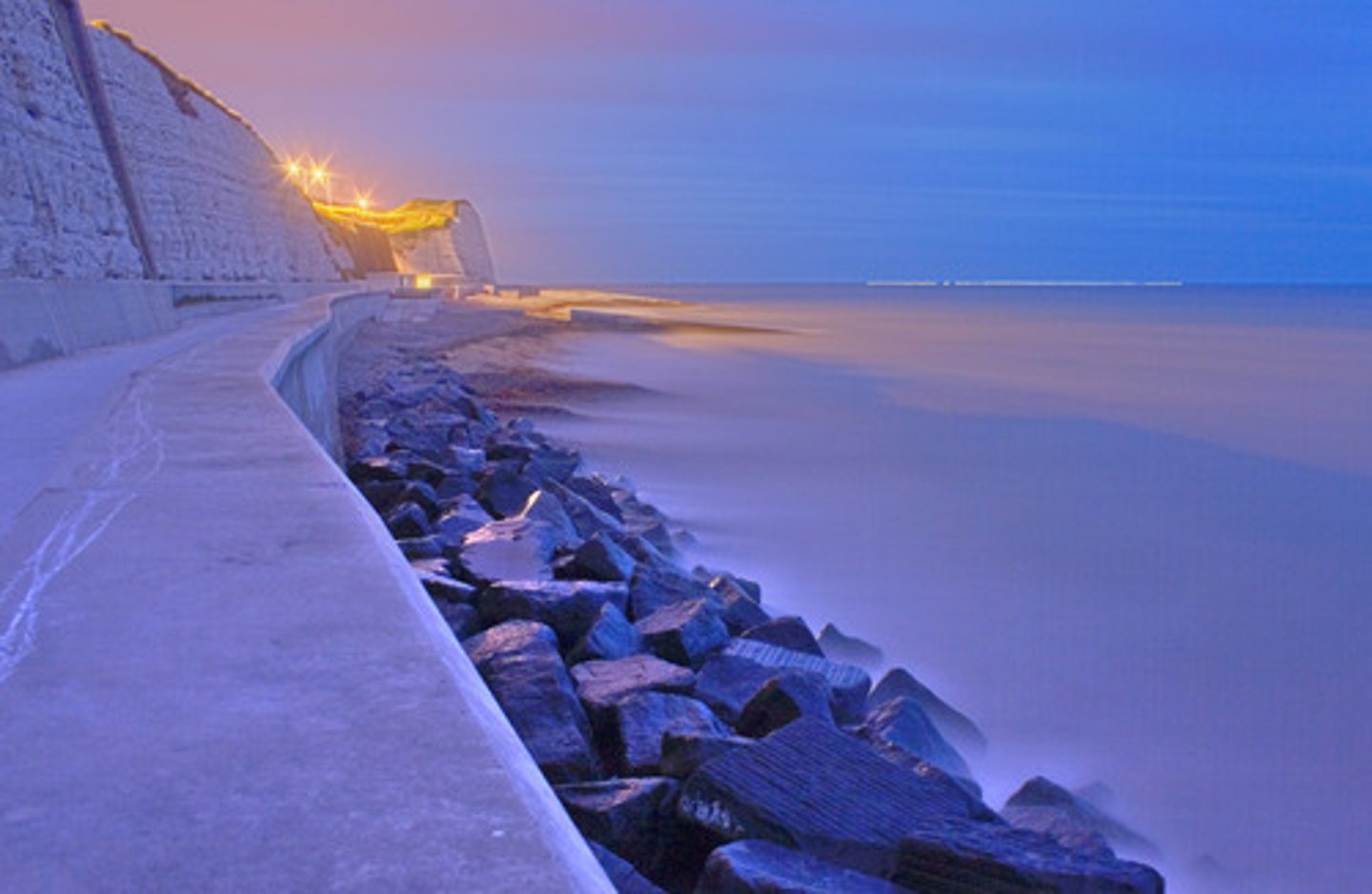

Soft engineering
Any form of coastal (or river) protection that involves the use of natural means, e.g. sand dunes, salt marshes, tree planting and/or beach replenishment.

spilling breakers
-gently sloping sea floor
-wave energy expended over longer distance
-water slides down front slope of wave

plunging breakers
waves which occur on a beach with a moderately steep slope, curl over and form tunnel until they break

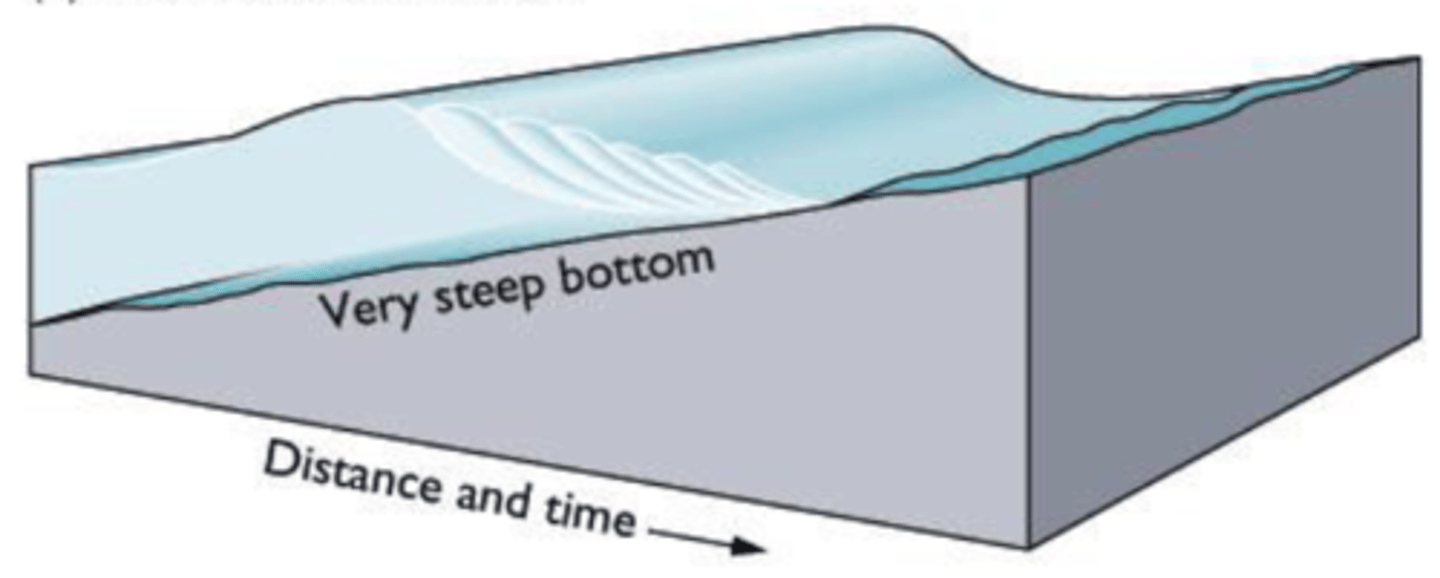
surging breaker
when the ocean bottom has an abrupt slope, the wave energy is compressed into a shorter distance, and the wave will surge forward
storm surge
a rising of the sea as a result of atmospheric pressure changes and wind associated with a storm.

Freeze-thaw weathering
Water enters a crack in a rock, the water freezes and expands the crack and repetition the pressure releases and the rock cracks creating sharp jagged scree.
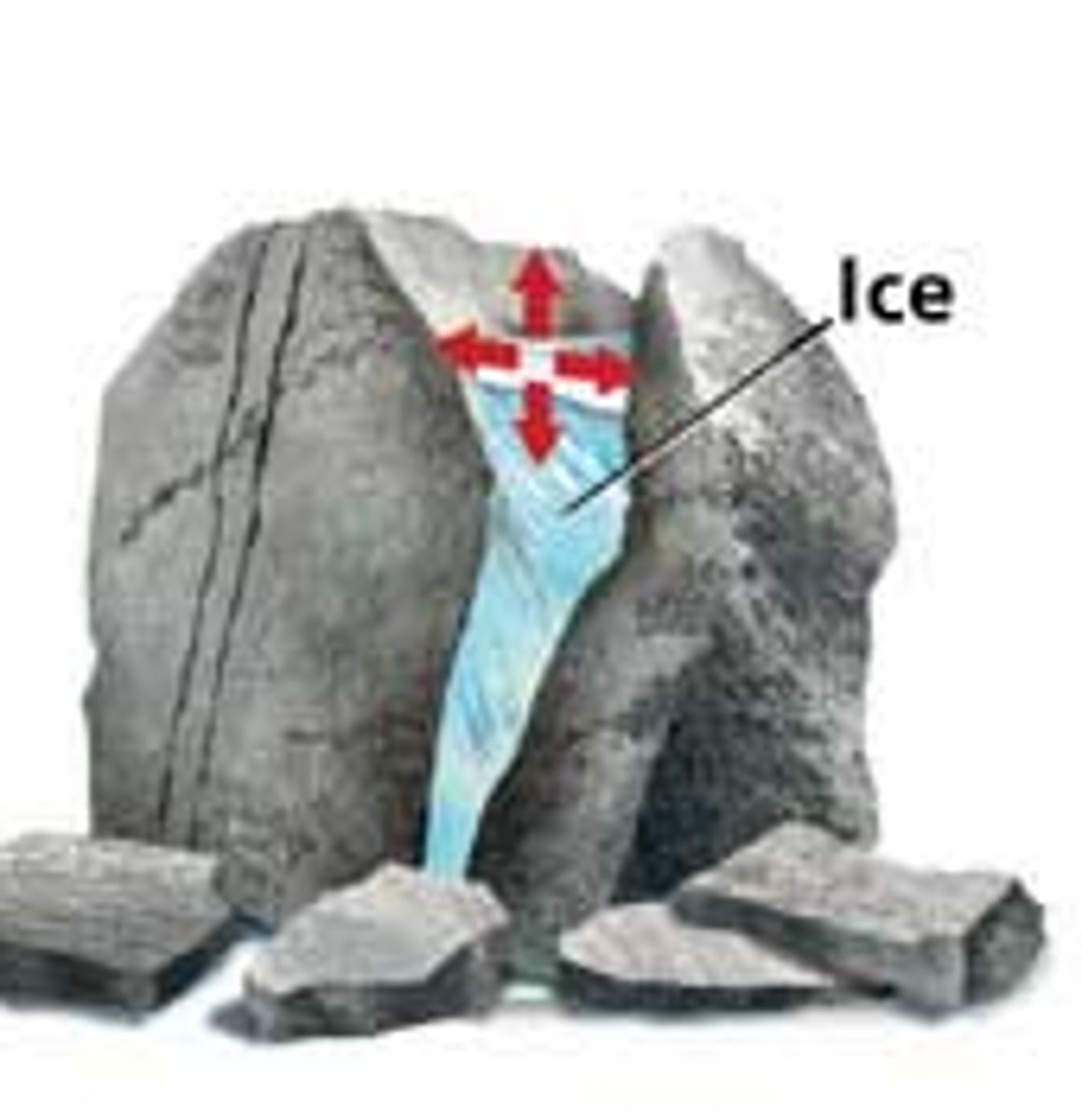

salt weathering
a weathering process where salt crystals grow and expand in the cracks and holes of rock, creating pressure which eventually causes fragments of rock to break away
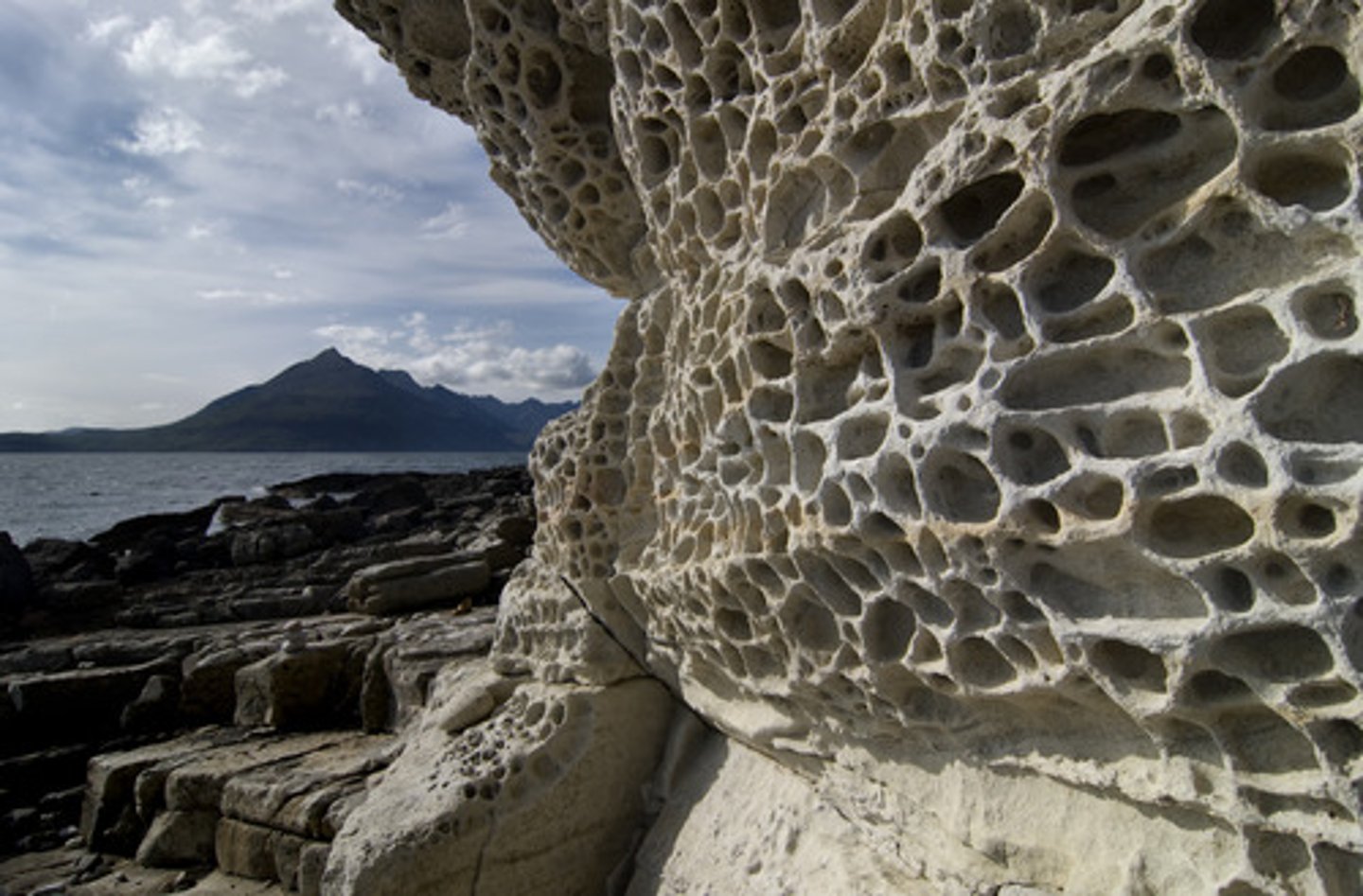

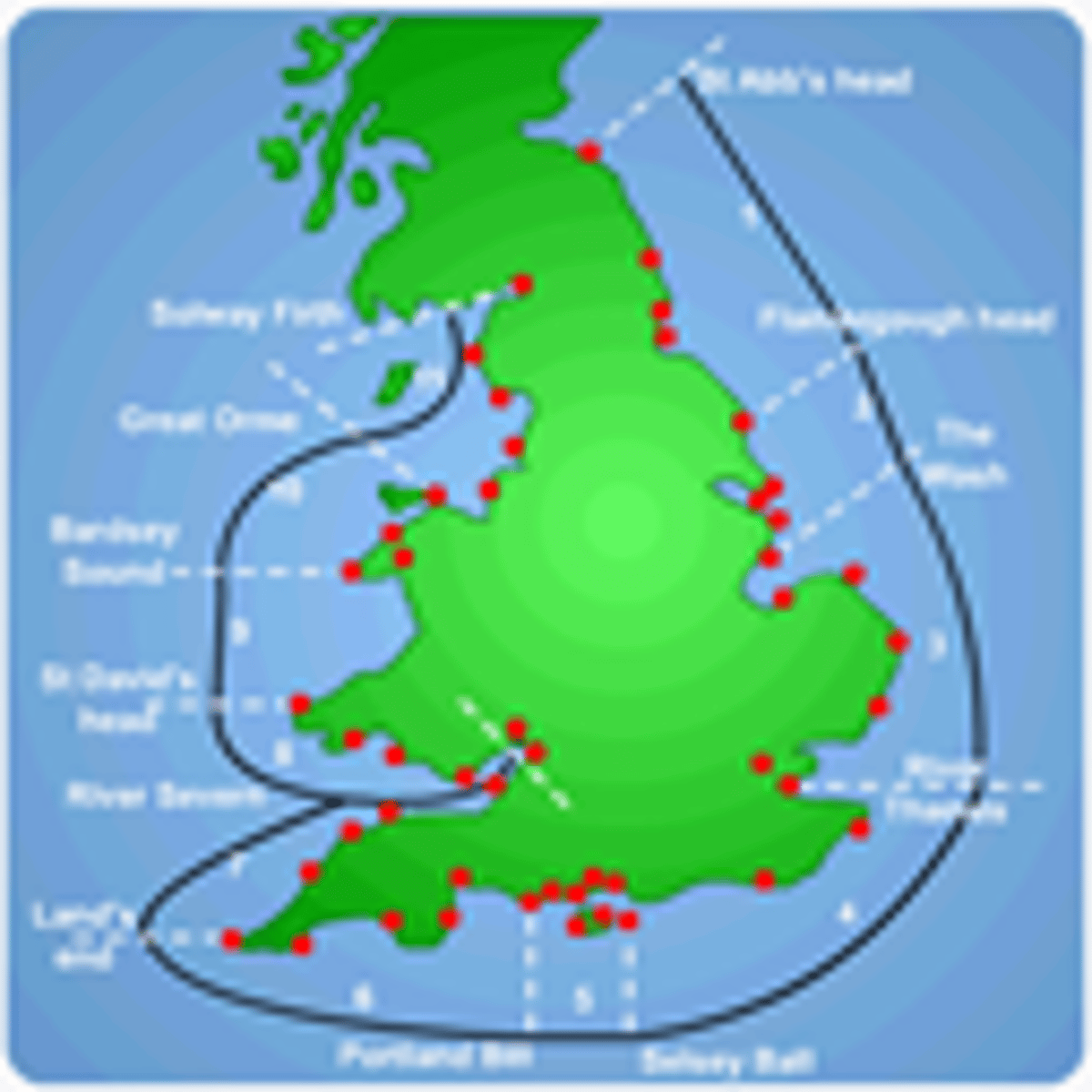
Littoral cells
All coastlines divide up into distinct sediment littoral cells containing sediment sources, transport paths and sinks. Each littoral cell is isolated from adjacent cells and can be managed as a holistic unit.
Swash-aligned coasts
are produced where the waves break in line with the coast. The swash and backwash move material up and down the beach. They are smoothly curved, concave beaches
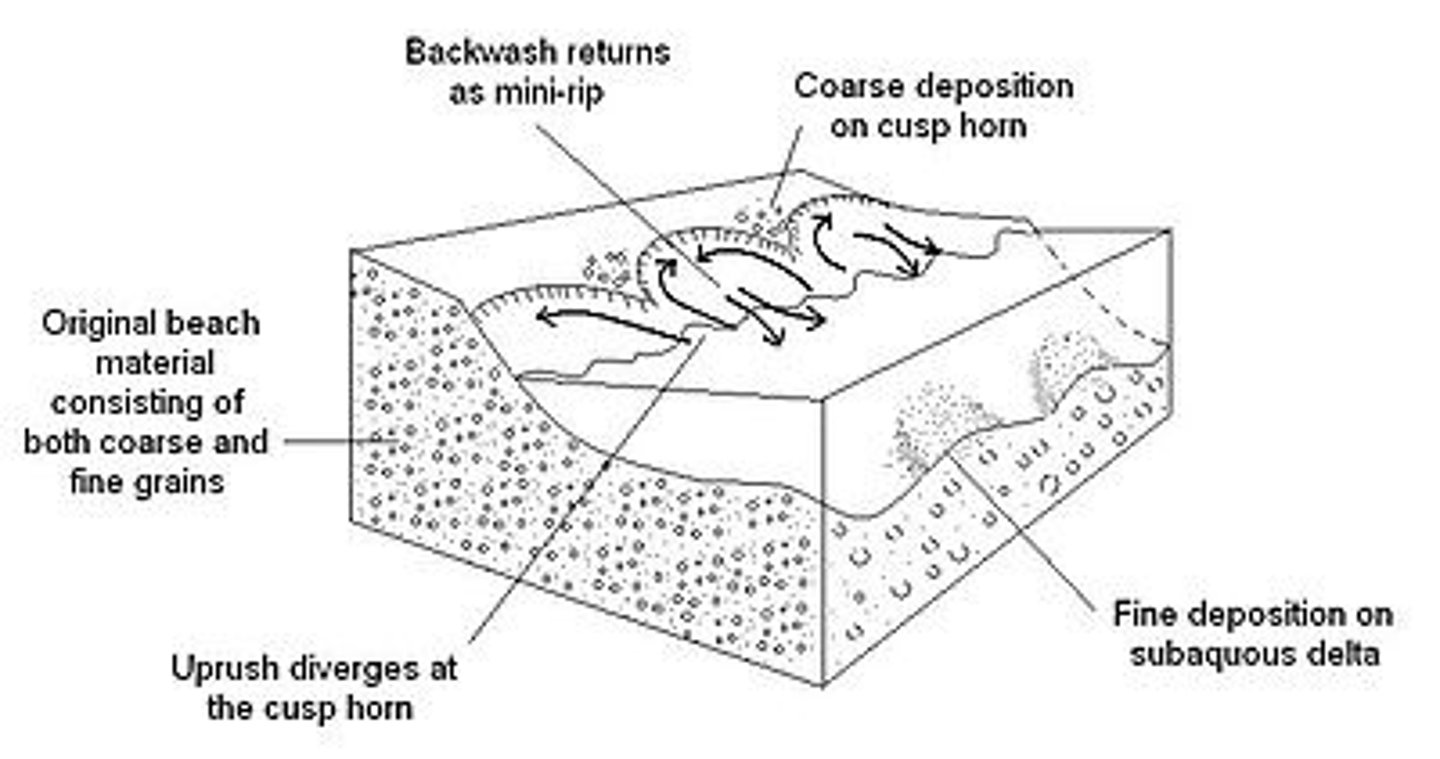
Drift-aligned coasts
are produced where waves break at an angle to the coast. Material is transported along the beach via longshore drift as the swash is at an angle so the backwash is perpendicular.
Compound spit
Depositional feature where the previous forms can be seen as different endings.

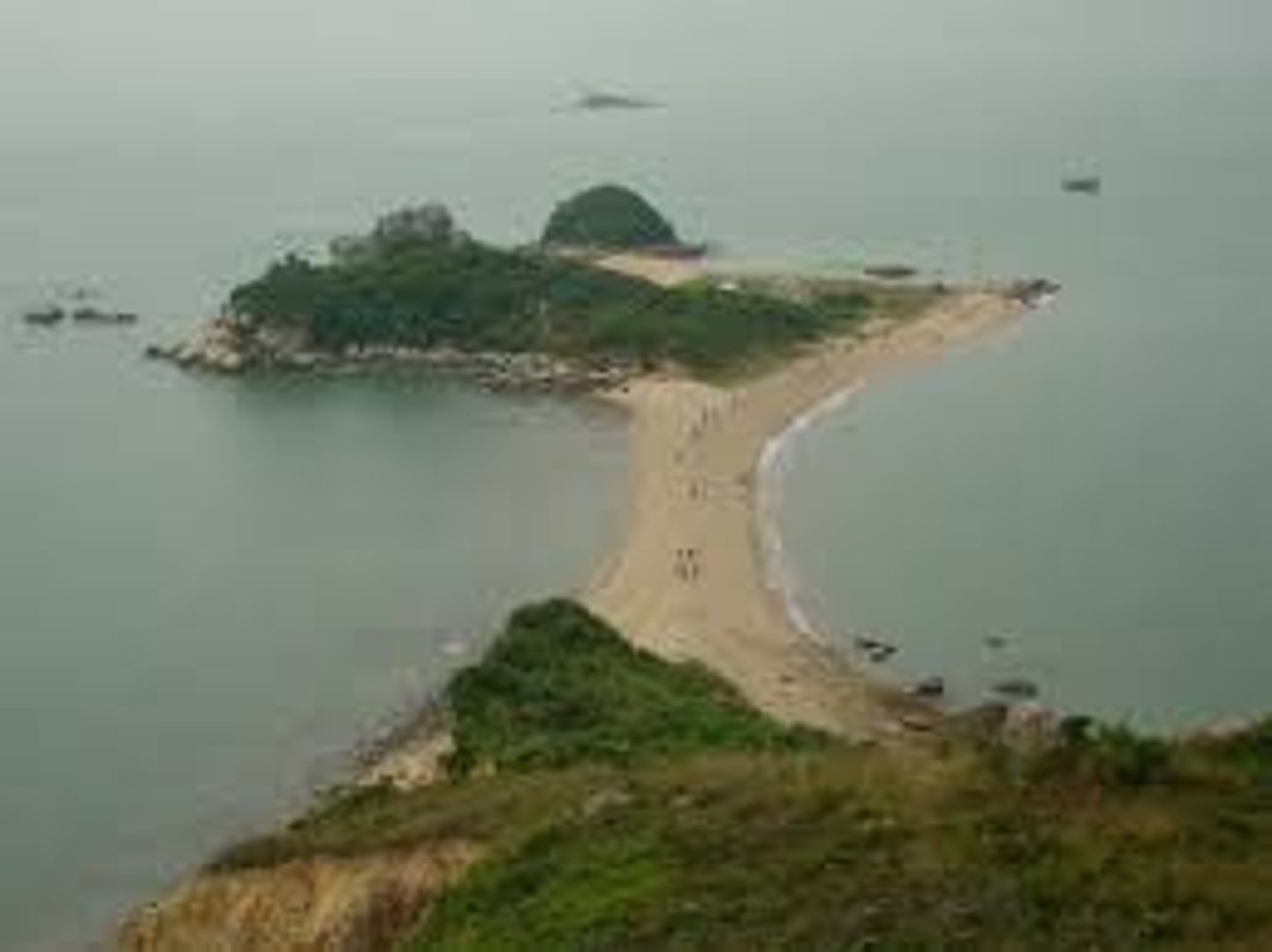
Tombolo
A ridge of sand that connects an island to the mainland or to another island

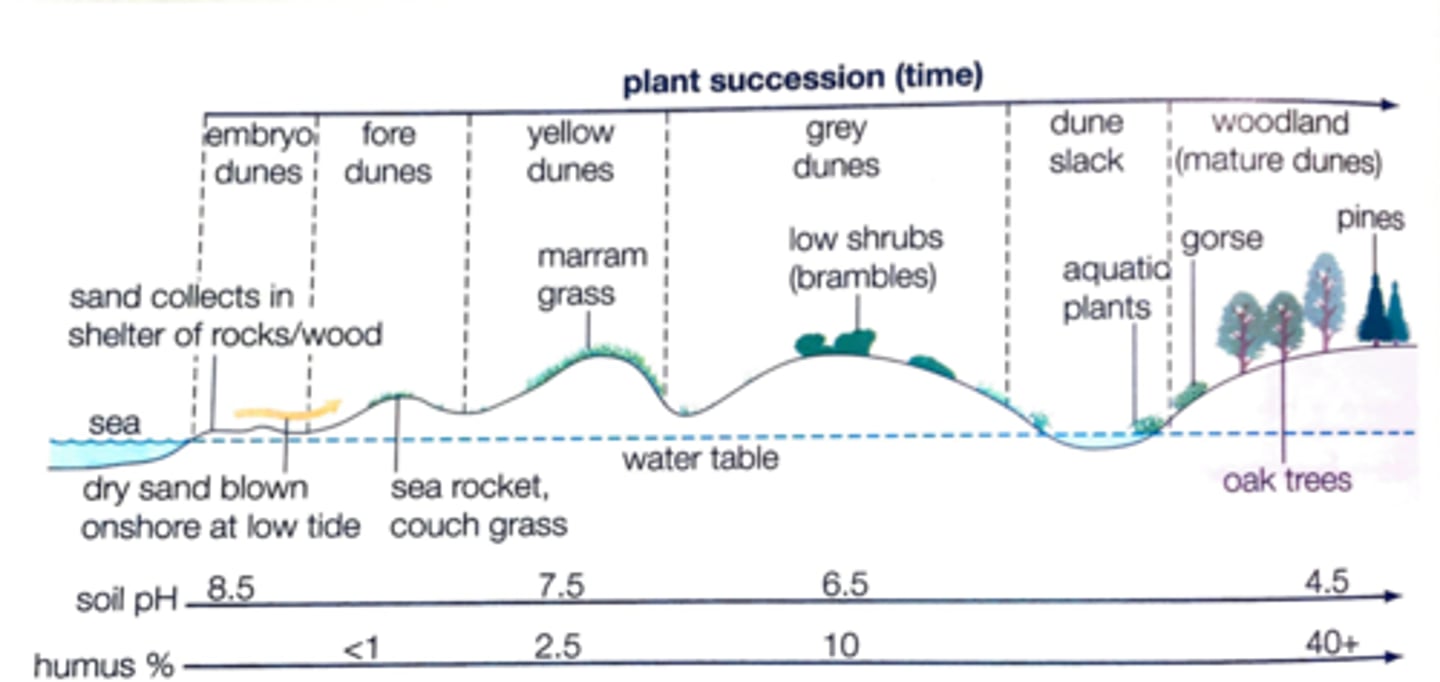
Sand dune succession
Embryo dune - fore dune - yellow dune - grey dune
Ebryo - as sand deposited, development of pioneer species, high sanity, high pH (alkaline), halophyte plants
Fore - plants trap sediment, aids growth of dune
Grey - as matter dies - humus layer is developed, decreases pH
Climax - humus decreases pH, more acidic
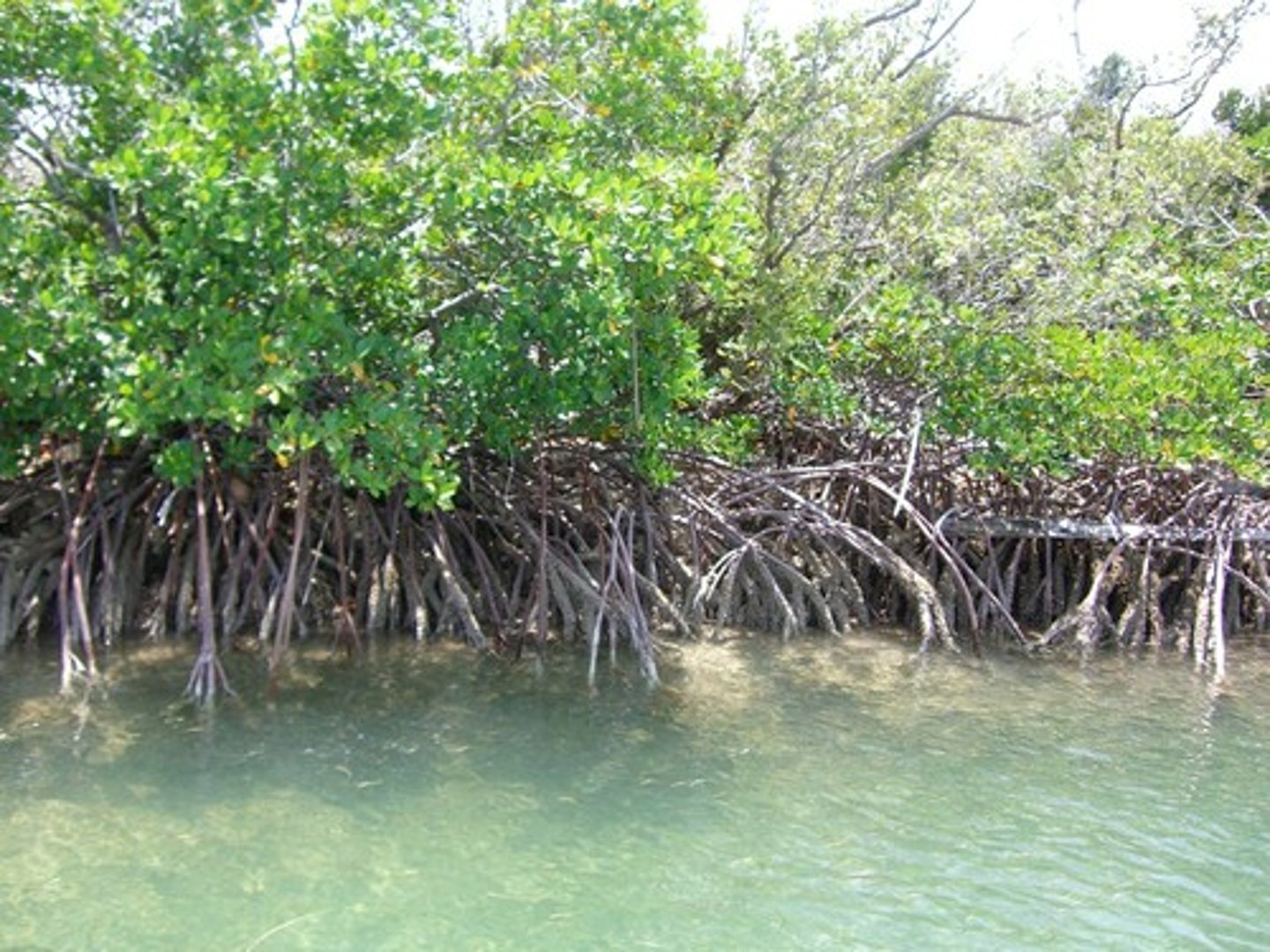
Mangroves
coastal ecosystems inhabited by salt-tolerant trees and shrubs

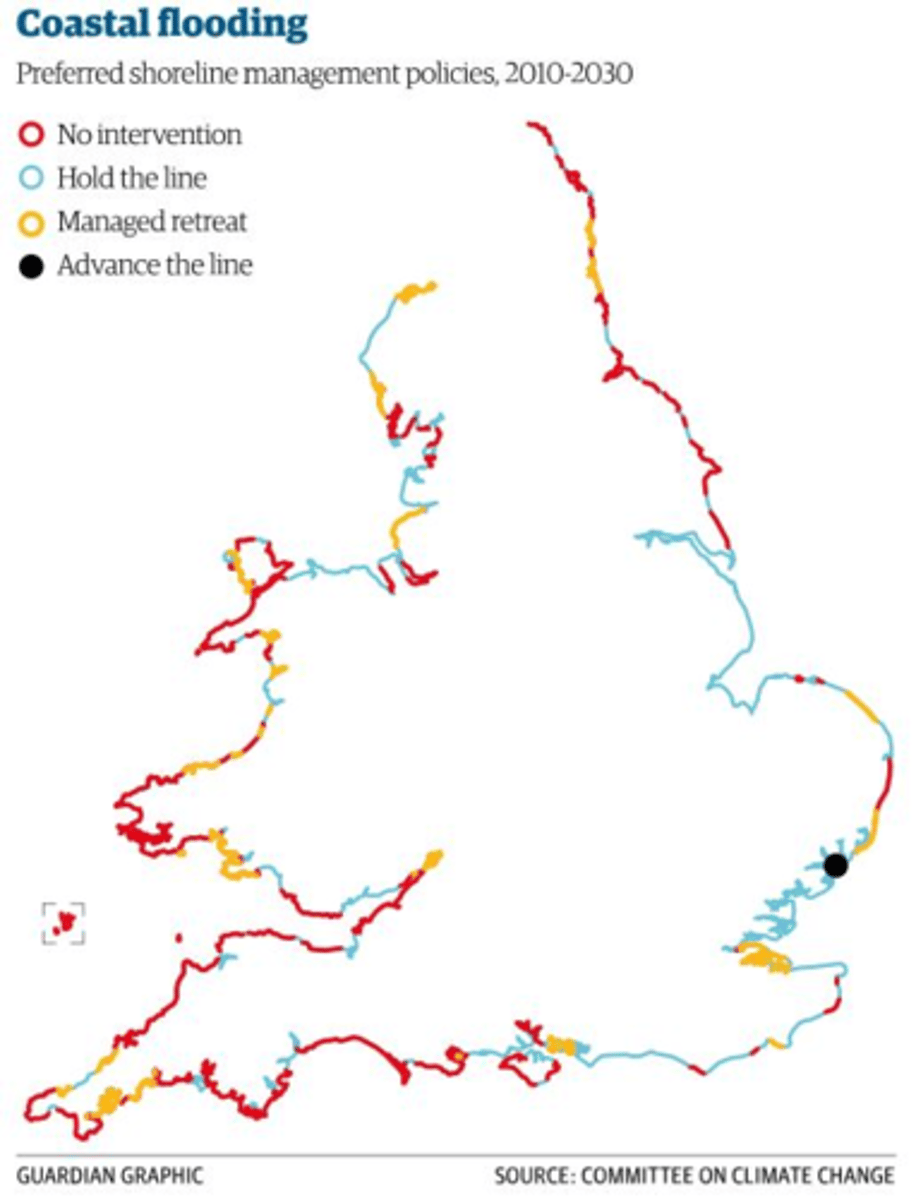
SMPS
Shoreline Management Plans- they are sectored into four options: do nothing, hold the line, strategic realignment and advance the line.
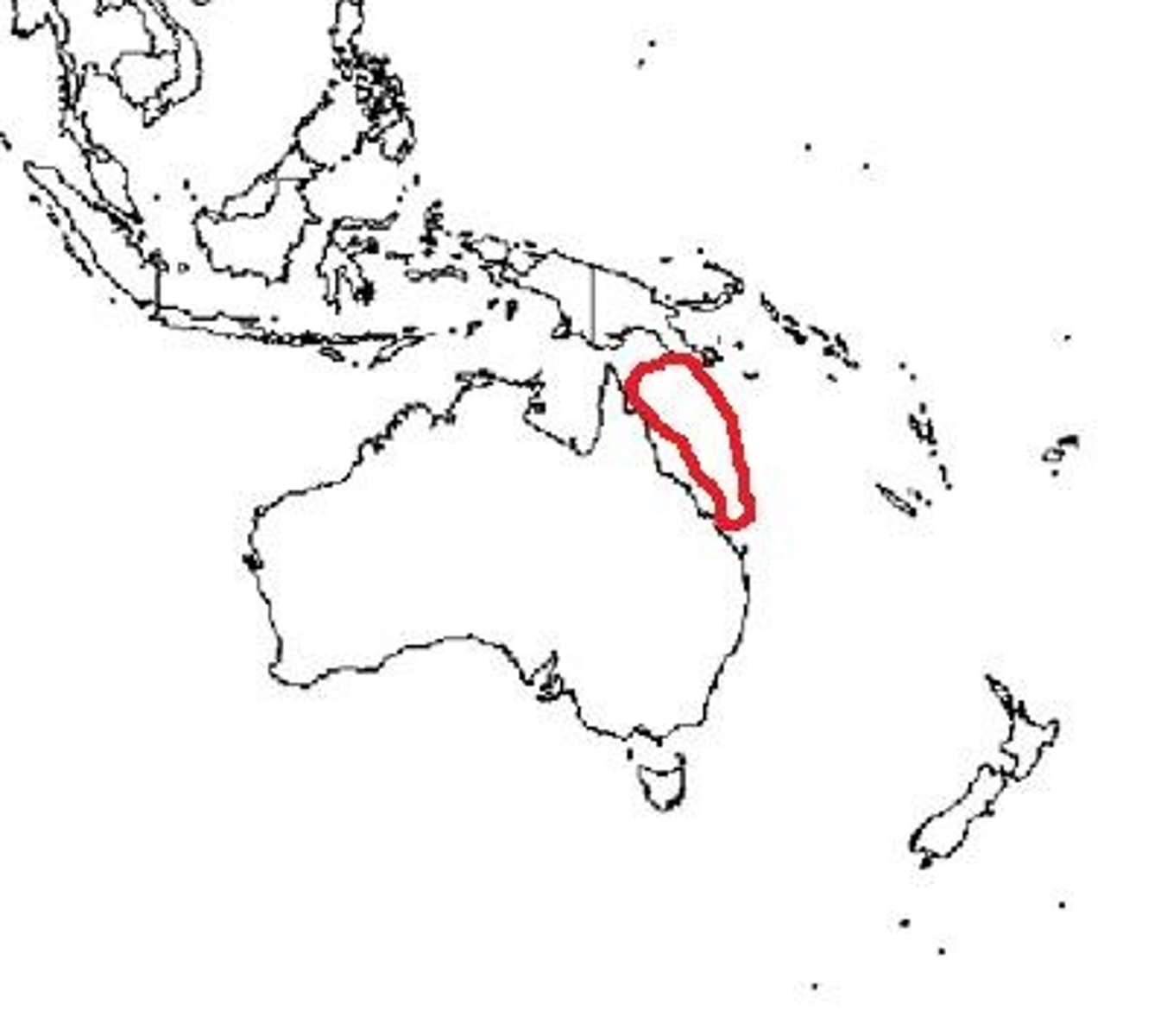
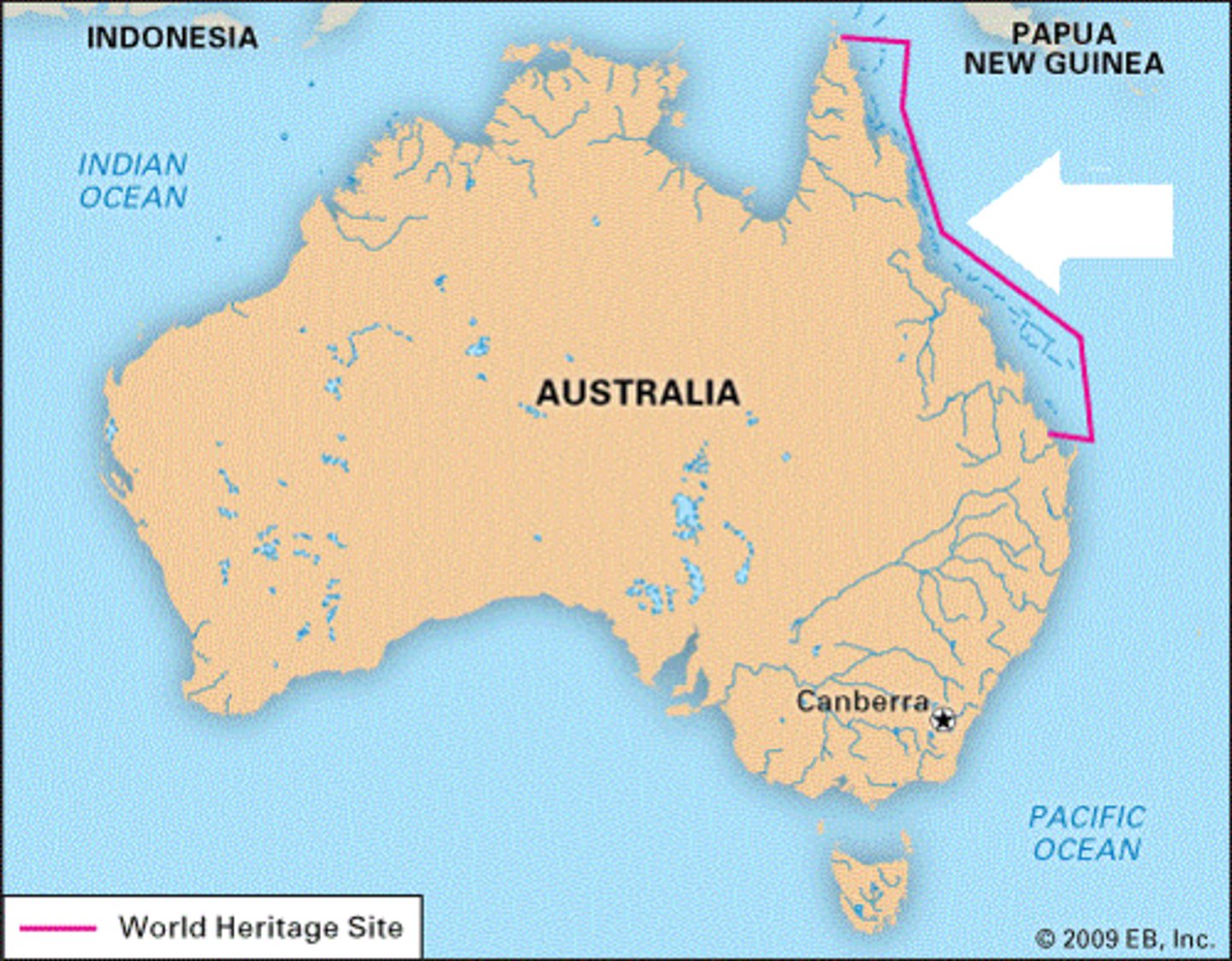
Great Barrier Reef
a 1,250-mile chain of more than 2,500 reefs and islands along Australia's northeast coast, containing some 400 species of coral
Holderness Coast
soft boulder clay, cliffs eroding quickly, Spurn Head Spit