marketing management (unit 3)✅
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Marketing objective
Goals set by a business when promoting its products or services to potential customers that should be achieved within a given time frame
What should marketing objectives include
Market size
Market share
Sales and market growth
Sales volume and value
Brand loyalty
Value of marketing objectives
Provides focus and direction for the marketing activities and strategy of the business
Ensures that the resources are used effectively
Motivates and aligns the people working within marketing
Primary research
Data collected first hand for a specific research purpose
Secondary research
Data that already exists and has been collected for a different purpose by someone else
Quantitative data
Based on numbers, easy to analyse, however there is no in-depth information
Qualitative data
Based on opinions, more in depth but harder to analyse
Measures of marketing
Market size
Market growth
Market share
Market size
Number of potential customers that could buy from your business
Market growth
Increase in the sales volume of a product over time
Market share
The proportion of total sales in an industry controlled by a particular business
Sampling
Gathering data from a sample of respondents, the results of which should be representative
Methods of sampling
Random
Quota
Stratified
Correlation
Looks at the strength of a relationship between two variables, usually on a scatter diagram
3 types of correlation
Positive
Negative
No correlation
Confidence interval
Gives the percentage probability that an estimated range of possible values in fact includes the actual value being estimated
Extrapolation
Uses trends established from historical data to forecast the future
Price elasticity of demand
Measures the extent to which the quantity demanded is affected by a change in price
Income elasticity of demand
Measures the extent to which quantity demanded is affected by a change in income
2 types of goods in YED
Normal +
Inferior -
2 types of Normal + goods
Luxury (elastic)
Necessity (inelastic)
Value proposition
A statement that clearly identifies the benefits of a company’s products and services will deliver to its customers
Market segmentation
Dividing up a market into parts that reflect different customer wants and needs
Methods of market segmentation
Demographic
Geographic
Income
Behavioural
Target market
Set of customers sharing common wants and needs that a business decides to target
Mass marketing
Where a business sells into the largest part of the market, where there are similar products from competitors
Niche marketing
Where a business targets a small segment of a larger market where customers have specific wants and needs
Market Positioning map
Illustrates the range of ‘positions’ that a product can take in a market based on two dimensions that are important to customers
7P’s of marketing mix
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
People
Physical Environment
Process
2 types of products
Consumer products (convenience, shopping and speciality products)
Industrial products (material and parts, capital items, supplies and services
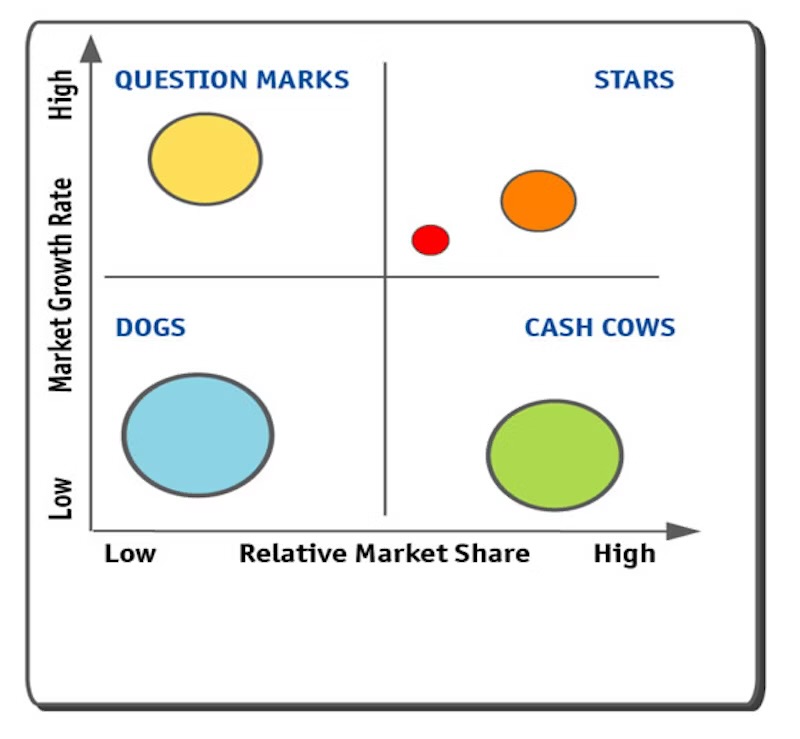
Product portfolio analysis
Assesses the position of each product or brand in a firms portfolio to help determine the right marketing strategy for each
2 dimensions in the Boston Matrix
Relative Market share
Rate of Market growth
4 categories of the Boston matrix
Question marks (low market share, high market growth)
Cash cows (high market share, low market growth)
Stars (high market share, high market growth)
Dogs (low market share, low market growth)
Boston matrix
A business tool for product portfolio analysis
Product life cycle
A theoretical model which describes the stages a product goes through over its life
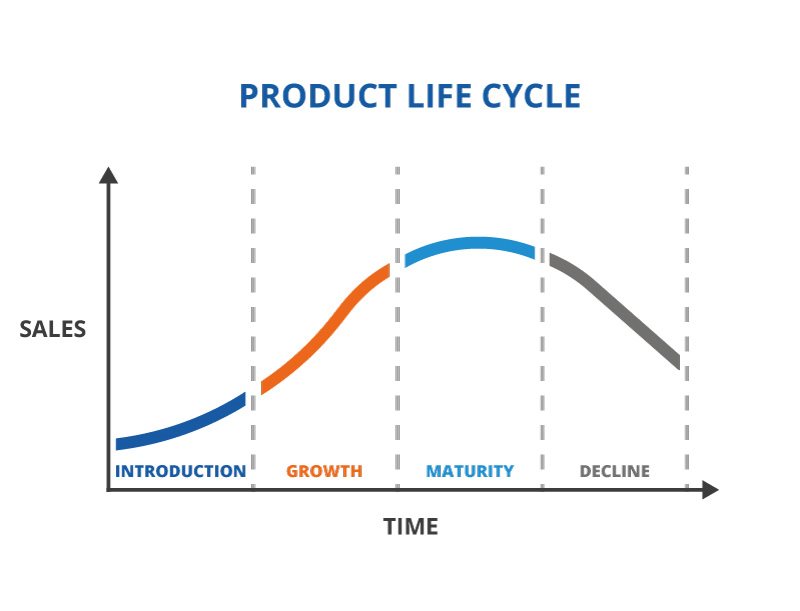
Stages in the product life cycle
Development
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
Extension strategies
Methods used to lengthen the life cycle of a product, usually introduced at the maturity stage
Price
The money charged for a product or service, everything that a customer has to give up in order to acquire a product or service
Main factors influencing pricing
Costs
Product life cycle
Elasticity of demand
Market share
Competitions
Marketing objectives
Types of pricing
Penetration pricing
Prime skimming
Dynamic pricing
Cost-plus pricing
Competitive pricing
Psychological pricing
Aim of promotion
To ensure that customers are aware of the existence and positioning of products
Branding
The process of developing a product with a unique character that is consistent and well recognised
Brand extension
Using an existing brand name to introduce a new product or service
Brand stretching
Where the brand is used for a diverse range or products, not necessarily connected
Logo
Symbol or picture that represents the business, easy to recognise, establishes brand loyalty and can create a favourable image
Types of promotional methods
Advertising
Personal selling
Sales promotion
Public relations
Sponsorship
Direct marketing
Aim of distribution
To make products available in the right place, at the right time, in the right quantities
Distribution channels
The stages a product moves through from production to final consumption
Intermediary
A third-party entity that facilitates transactions between a seller and a buyer, typically acting as a middleman in the distribution chain
Parties in a distribution channel
Wholesalers
Retailers
Distributors
Agents
Direct channels
Indirect channels
Involves the use of intermediaries between the producer and consumer
Multi-channel distribution
Involves a business using more than one type of distribution channel
People
The employees of a business who interact with customers and potential customers
Process
The procedures involved in a transaction; how easy or difficult it is for a customer to make a purchase
Physical environment
Aesthetics of the place where the customer makes the purchase
Integrated marketing mix
Elements of the mix should work together to achieve the desired effect, there must be internal consistency
Digital marketing
Interacting with customers using digital communications
E-commerce
The buying and selling of goods and services using an electronic network like the internet