lab brain
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
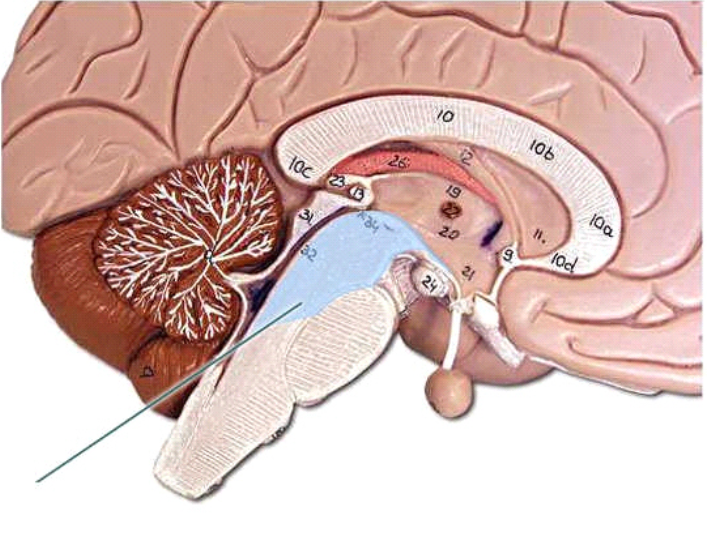
cerebral peduncle is a stalk-like structure that connects the cerebrum to the brainstem, playing a crucial role in motor control and coordination.
superior colliculus is a paired structure in the midbrain that integrates sensory information, particularly visual stimuli, and coordinates eye movements.
hypothalamus is a small but crucial brain region located below the thalamus responsible for regulating various autonomic functions, including temperature control, appetite, and sleep cycles.
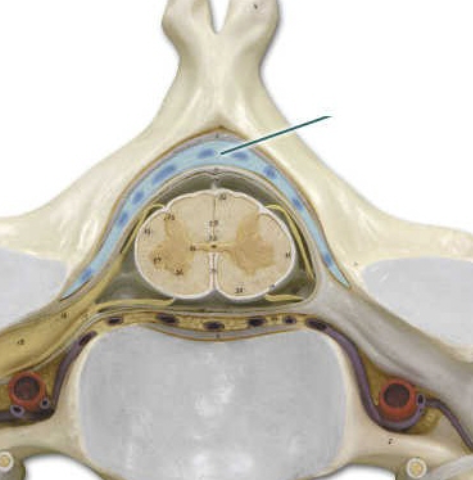
epidural space is the area between the dura mater and the skull or spinal column that contains fat and blood vessels.
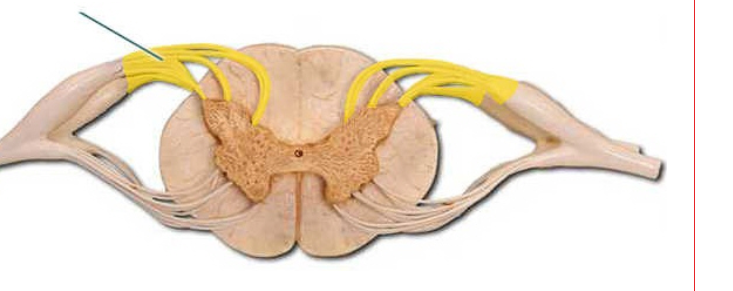
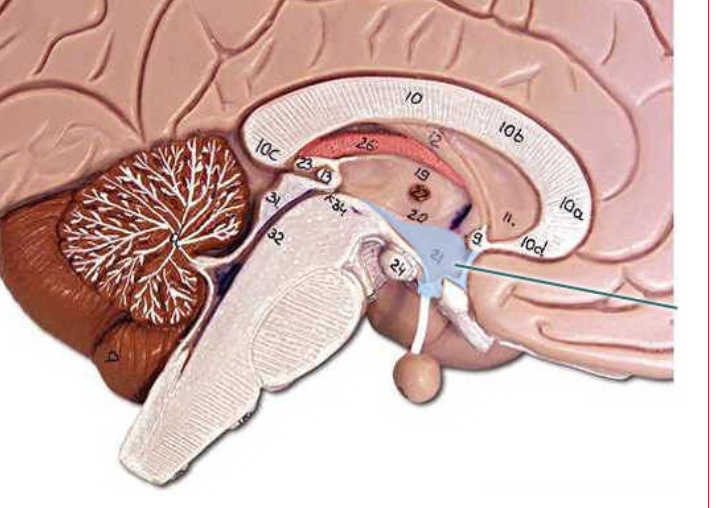
dorsal root is a bundle of nerve fibers that carry sensory information from the body to the spinal cord.
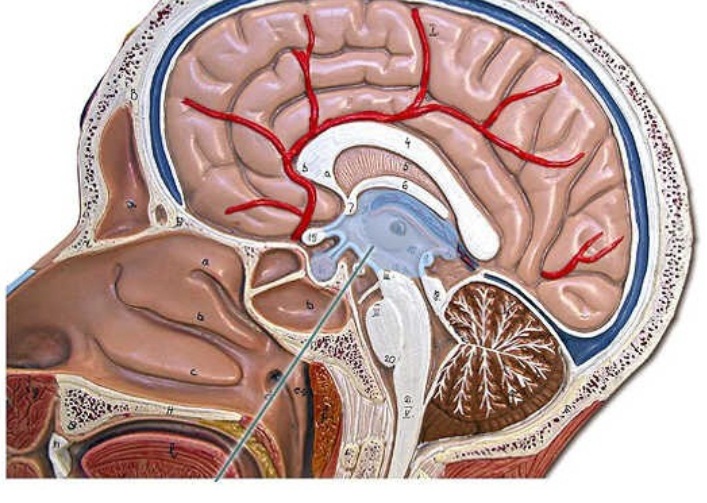
diencephalon is a region of the brain that includes structures such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus, playing key roles in sensory and autonomic functions.
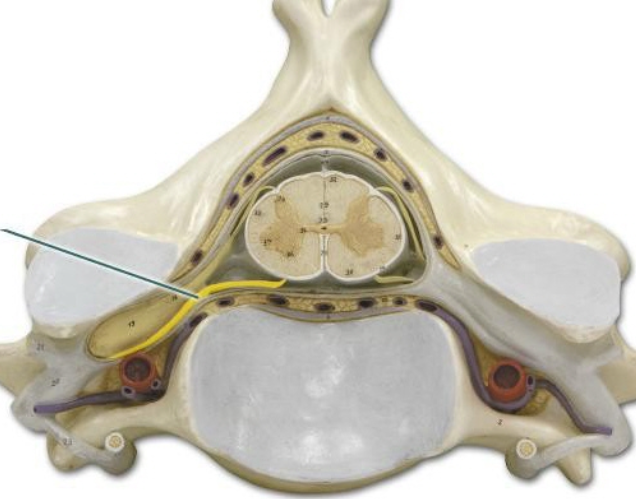
ventral root is a bundle of nerve fibers that carry motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles.
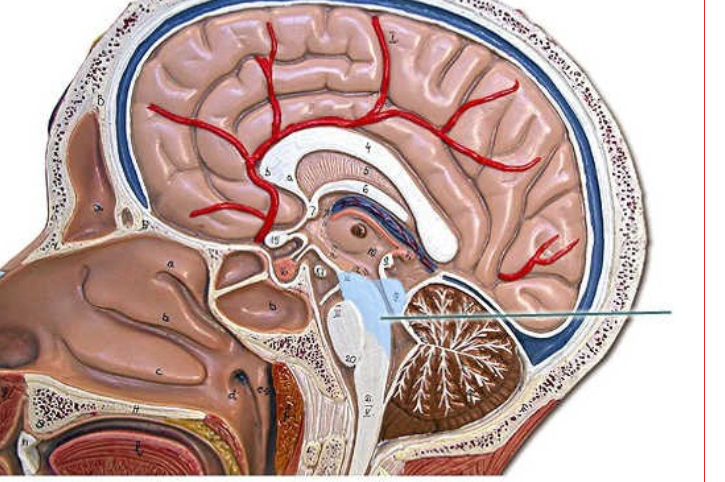
midbrain is the upper part of the brainstem, involved in motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
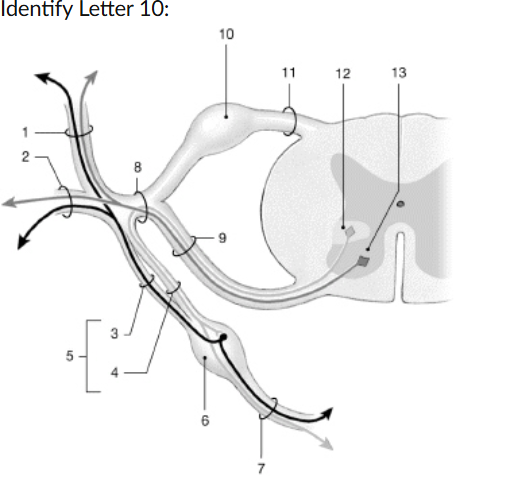
dorsal root ganglion
cerebral aqueduct
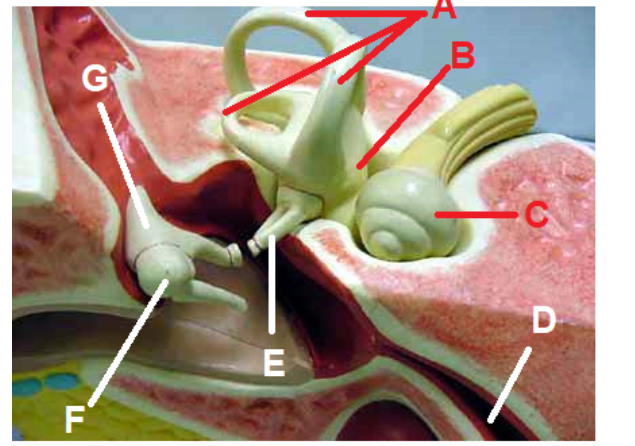
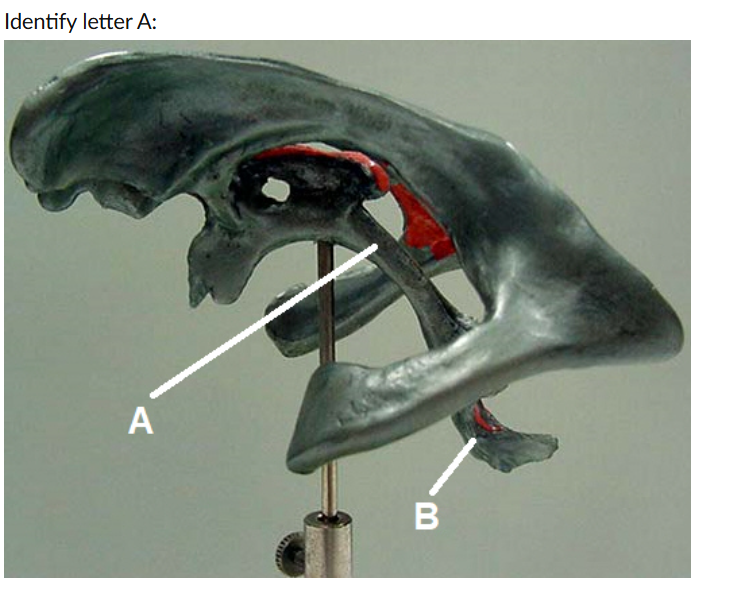
incus ( letter G)
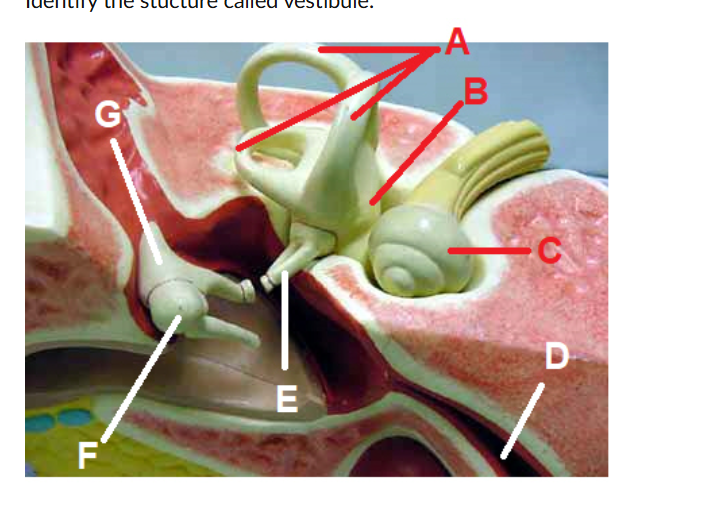
vestibule ( letter b)
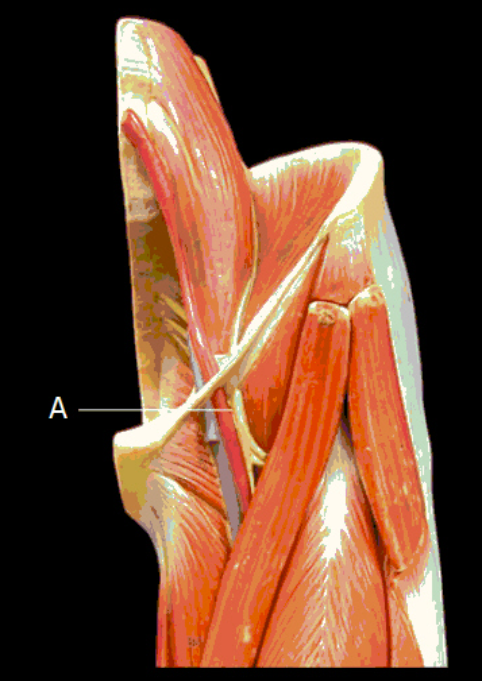
femoral nerve
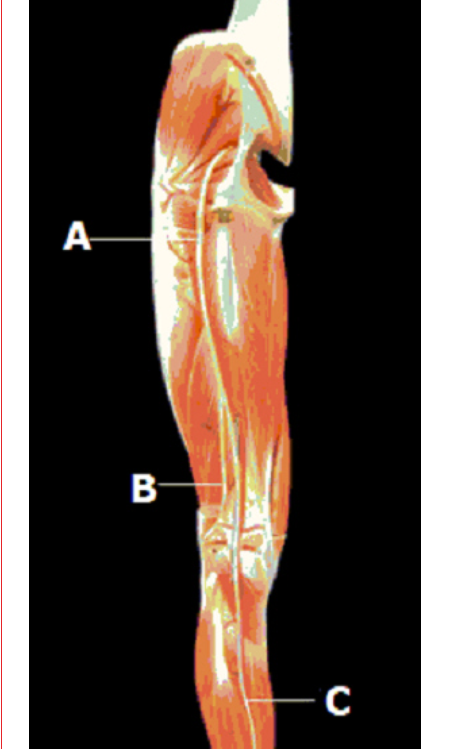
tibial nerve

constricts pupils ( parasympathetic)
inhibit salivation
sympathetic
stimulate saliva
parasympathetic
slow heartbeat
parasympathetic
relax airways
sympathetic
inhibit activity of stomach
sympathetic
secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
sympathetic
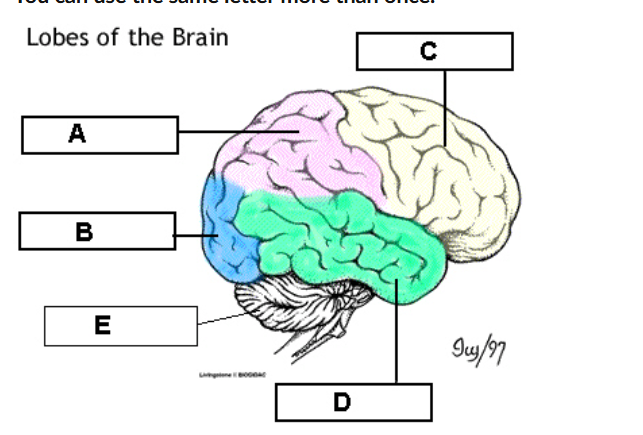
occipital ( B)_ handles vision
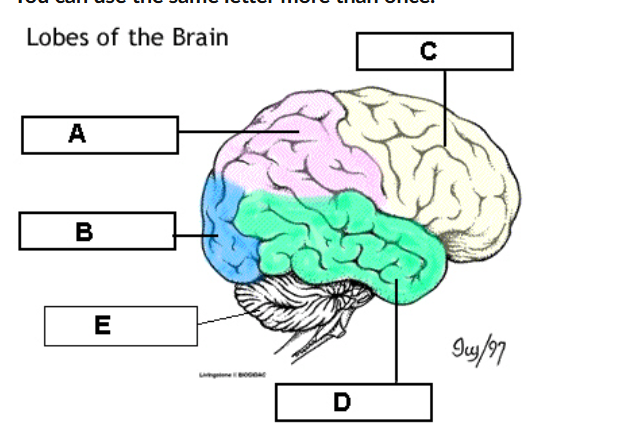
Temporal ( D) _ handless hearing
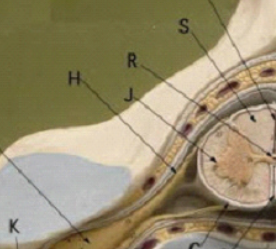
dorsal root
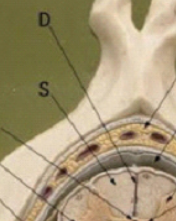
posterior medium sulcus

gray commissure

ventral horn

dorsal funiculus

subarachnoid space

spinal nerve
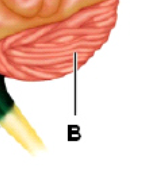
cerebellum

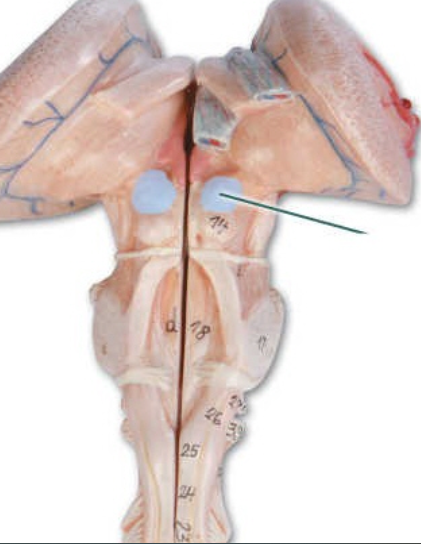
thalamus

medulla oblongata
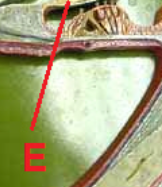
tectorial membrane
Scala tympani

cochlear duct

Scala Vestibule

Vestibular membrane