AP Biology - Q3 Final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/244
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
1
New cards
pancrine signaling
cells that communicate to each other through nuerons at a closer distance
2
New cards
Endocrine signaling
uses hormones to talk to other cells across far distances
3
New cards
stages of cell signaling
1. Reception
2. Transduction
3. Response
2. Transduction
3. Response
4
New cards
Types of cell signaling
chemical, electromagnetic, mechanical
5
New cards
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to another molecule, usually a larger one AKA the receptor
6
New cards
what type of type of ligand will pass through the cell membrane
small nonpolar
7
New cards
G proein linked system
ligand attaches to a protein which adds a phosphate group that activates 1 enzyme
8
New cards
g protien analogy
1 ligand \= 1 enzyme reaction
9
New cards
tyrosine kinase system
is a 2 part system, when a ligand finds each of them they can activate multiple things to happen after releasing 1 hormone
10
New cards
tyrosine kinase example
insulin and puberty
11
New cards
ion channel
protein pre that opens or cloese in response to a chemical signal
12
New cards
ion channel is similar to...
...sodium potassium pump
13
New cards
intracellular receptor is found here
cytoplasm not the membrane becuase their recptor floats
14
New cards
transcription factor
acticate the cytoplasmic receptor proteins
15
New cards
Kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphate ions from one molecule to another
16
New cards
Phospatase
a protein that undoes phosphorylation by removing a phosphate group
17
New cards
secondary messengers
many signaling pathways that involve small, nonprotein, water-soluble ions,
18
New cards
cyclic AMP
acts like ATP and is the middle man/step 2 in signal transduction (form of energy that relays messages from the reveptor to somewhere else)
19
New cards
apoptosis pathway examples
viruses, mutations, fetal cell development
20
New cards
Homeostasis
a balanced state of the cell (happy place)
21
New cards
homeostatic control system
receptor, control center, effector
22
New cards
example of positive feedback
pregnancy, it ends and does not cycle
23
New cards
exmaple of negative feedback
homeostasis cycle, contiuous
24
New cards
cell division
essential to the development of a multicellular organism that begins as a fertilized egg or zygote
25
New cards
prokaryotic genome
single circular chromosome
26
New cards
Eukaryotic genome
consists of several DNA molecules that are long and linear
27
New cards
genome
a cells genetic information, packaged as DNA
28
New cards
somatic cells
(nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes
29
New cards
Gametes
reproductive cells (diploid)
30
New cards
chromatin def
The complex of DNA and proteins that condenses during cell division
31
New cards
chromatin formation
large rope of histones with DNA wrapped around them
32
New cards
plasmids
bonus DNA
33
New cards
46 chromosomes
body cells
34
New cards
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a Chromosome
35
New cards
centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
36
New cards
Mitosis
division of the nucleus
37
New cards
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
38
New cards
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
39
New cards
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
40
New cards
G1 checkpoint
checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors and DNA damage
41
New cards
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, cells make organells, make more cytoplasm, cell does its thing
42
New cards
S phase
DNA replication
43
New cards
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, cells make proteins and organelles needed for mitosis and cytikinesis
44
New cards
Prophase
cells chromatin tightens into desly packed chromosomes
45
New cards
Prophase picture

46
New cards
metaphase
sister chromatids are pulled along the spindle appartatus toward the cent of the cell and they line up in the middle.
47
New cards
Metaphase (picture)
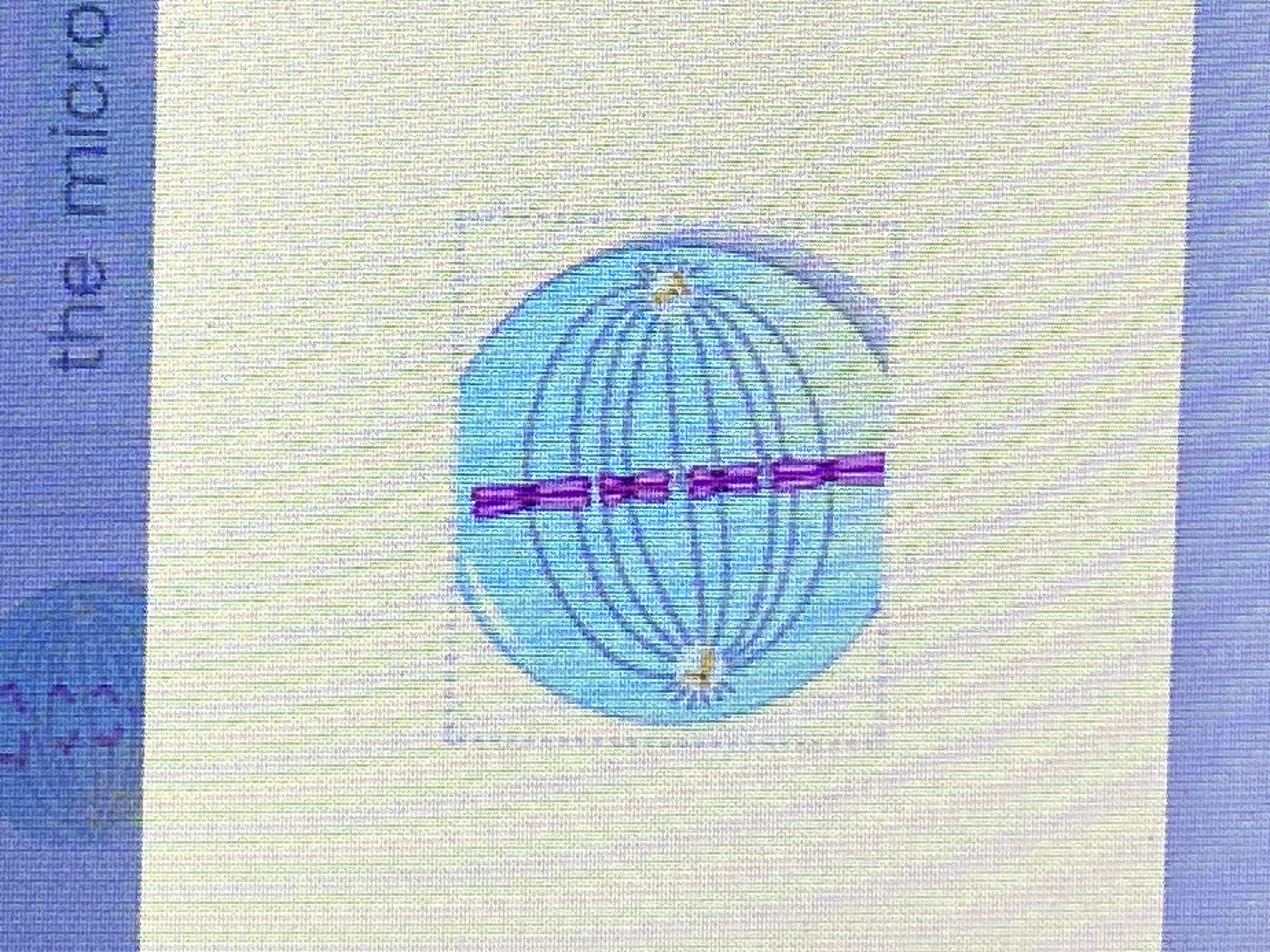
48
New cards
Anaphase
the microtubules of the spindle apparatus begin to shorten, the sister chormatids separate, the chomosomes move toward the poles of the cell
49
New cards
Anaphase (picture)
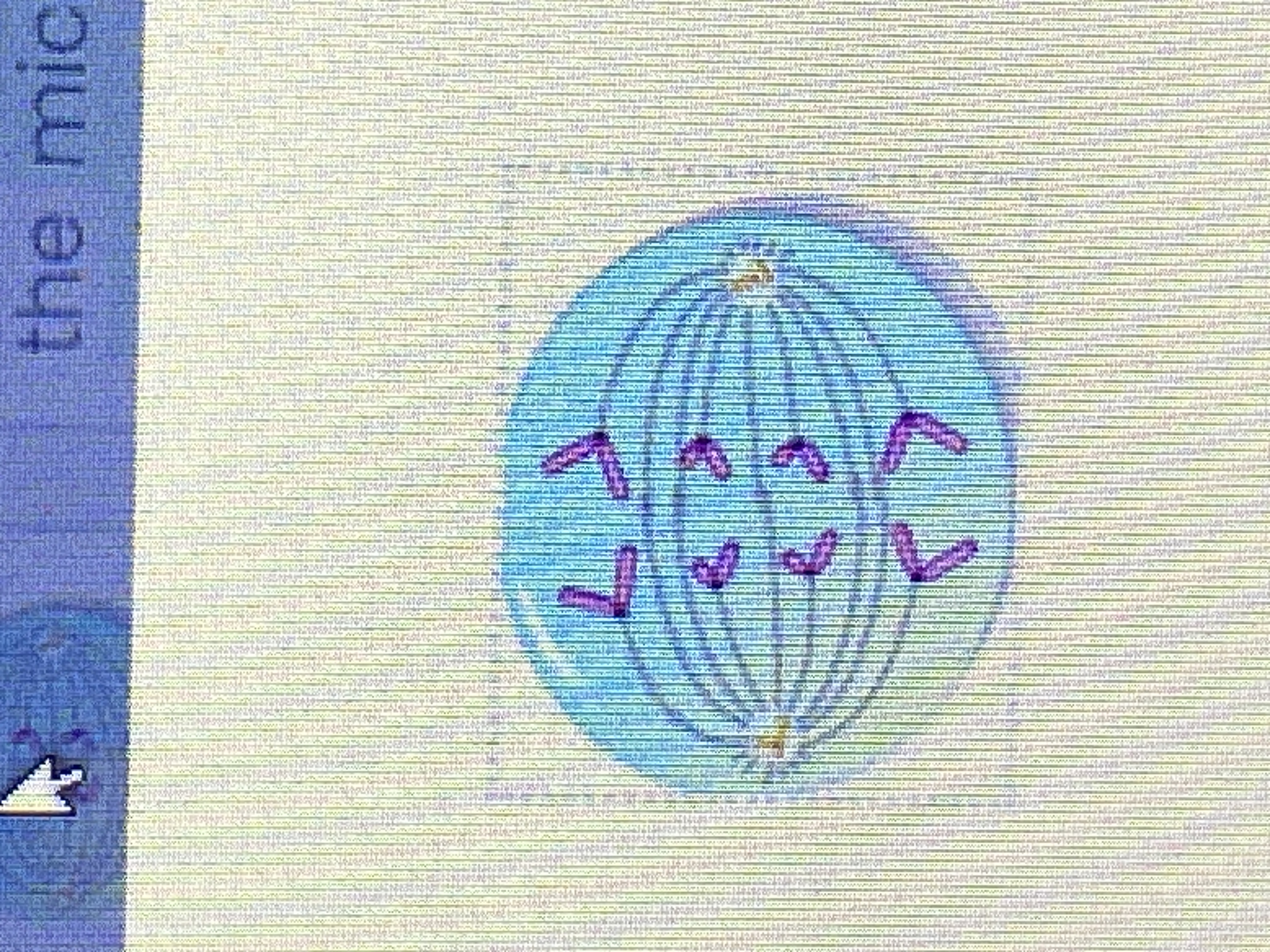
50
New cards
telophase
the chromosomes arrive at the piles and begin to relax ( DNA into chromatin form), nucleous reform at each end of the cell, spindle apparatus disassembles
51
New cards
Telophase (picture)

52
New cards
Cytokinesis in animal cells
micorfilaments constrict, or pinch the cytoplasm
53
New cards
Cytokinesis in plants
a new structure is called a cell plate forms
54
New cards
density-dependant inhibition
Growth factors that appear to be a key in cell division, normal cells do this when they bump into neighboring cells , cancer does this
55
New cards
anchorage dependence
most animal cells also exhibit thsi for cell division, dependent on being anchored
56
New cards
cancer
cells that divide to much and get in the way, takes about 8x of cell death to get a mutation, happens in the S phase
57
New cards
tumor
a mass of cells that have grown too much
58
New cards
benign tumor
An abnormal mass of cells that remains at its original site in the body, relies on anchorage
59
New cards
malignant
lost anchorage dependents and reanchores in a new place and affects surrounding areas
60
New cards
metastasis
the cells unanchore themselves, reanchore, and spread throughout the body
61
New cards
tumor suppresor genes
a normal gene that resuls in a preoten that stops cell division, brake pedal
62
New cards
p53 gene
type of tumor supressed gene that is the main starter for most cancers due to mutation.
63
New cards
roles of P53
repairs DNA, stops cell division, does apoptosis, and gaurdian angel genome
64
New cards
Proto-oncogene
a normal gene that results in aprotein that starts cell division, healthy gene, responsible for normal growth
65
New cards
oncongenes
cancer causing genes, they are mutated cells
66
New cards
apoptosis
programmed cell death
67
New cards
telomerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells.
68
New cards
what genes cause cancer?
oncongenes, proto-oncongene, telomerase, anchorage dependence, density dependent inhibition, apoptosis
69
New cards
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
70
New cards
genetics
the scientific study of heredity and vatiation
71
New cards
Gametes
genes that are passed to the nxt generation through reproductive cells
72
New cards
Locus
specific location of the gene
73
New cards
karyotype
micrograph in whcih the pairs of homologous chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size
74
New cards
autosomes
the non-sex paired chromosomes
75
New cards
homologous chromosomes
pairs that carry genes that control the same inherited characters
76
New cards
zygote
the fertilized egg now has 2 haploid sets of chormosomes bearing genes from the maternal and paternal family lines
77
New cards
syngamy
these cells fuse resulting fertilization
78
New cards
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms creating 4 simalar chromosomes
79
New cards
mitosis
produces 2 identical daughter cells
80
New cards
chiasmata
the chromatieds are crossed and segments of the chromosmes are traded
81
New cards
synapsis
special proteins attach homologous tighly together
82
New cards
mutautions
original source of genetic diversity
83
New cards
3 sources of gentic variability
1. independent assortment
2. crossing over
3. randomfertilization
2. crossing over
3. randomfertilization
84
New cards
independent assortment
random orientation of tetrads at the metaphase plate
85
New cards
crossing over
produces recombinant chromosomes which combine genes inherited from each parent
86
New cards
random fertilization
any sperm can fertilize any egg
87
New cards
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
88
New cards
law of independent assortment
Each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation
89
New cards
alleles
alternative versions of henes that account for variations in inherited characteristics
90
New cards
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
91
New cards
metabolic pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
92
New cards
catabolic process
release of energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds
93
New cards
Anabolic process
consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds
94
New cards
Kinetic energy
energy of motion
95
New cards
potential energy
the energy that matter possess because of its location or structure
96
New cards
Thermodynamics 1st law
energy can be trasferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed
97
New cards
Thermodynamics 2nd law
every energy transformation must make the universe more disordered
98
New cards
Entropy
a quantity used as a measure of disorder or randomness
99
New cards
how do cells make macromolecules without violating the laws of thermodynamics
organisms are open systems and take in organized energy like light and replace tghem with less oredered forms, especially heat
100
New cards
Free energy
the portions of a systems energy that is able to perform work