Learning: Topic 14: Convergent Boundaries: Origin of Mountains
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Which term refers specifically to geologic mountain building?
Orthorhombic
Ontogeny
Origami
Orogeny
Orogeny
Which one of the following is an example of an isostatic movement?
Numerous aftershocks associated with deep-focus earthquakes
Stream downcutting following a drop in sea level
Arching of strata at the center of a dome
Uplift of areas recently covered by thick continental ice sheets
Uplift of areas recently covered by thick continental ice sheets
What North American mountains are a geologically old mountain range that was folded and deformed during the Paleozoic?
The Appalachians in the eastern United States
The Rockies in the western United States
The Cascades in the northwestern United States
The Alps in Europe
The Appalachians in the eastern United States
Of the following, which have a crust about twice as thick as normal?
The Basin and Range Province in Arizona and Nevada
The Coast Ranges and the Sierra Nevada in California
The Himalayan Range and the Tibetan Plateau in northern India and southwestern China
The Blue Ridge Mountains in the southeastern United States
The Himalayan Range and the Tibetan Plateau in northern India and southwestern China
Which of the following best characterize the tectonic development of fault-block mountains?
Reverse faults; crustal shortening and plastic flowage of the lower crust
Reverse faults; crustal stretching and brittle failure of the lower crust
Normal faults; crustal shortening and plastic flowage of the upper crust
Normal faults; crustal stretching and brittle failure of the upper crust
Normal faults; crustal stretching and brittle failure of the upper crust
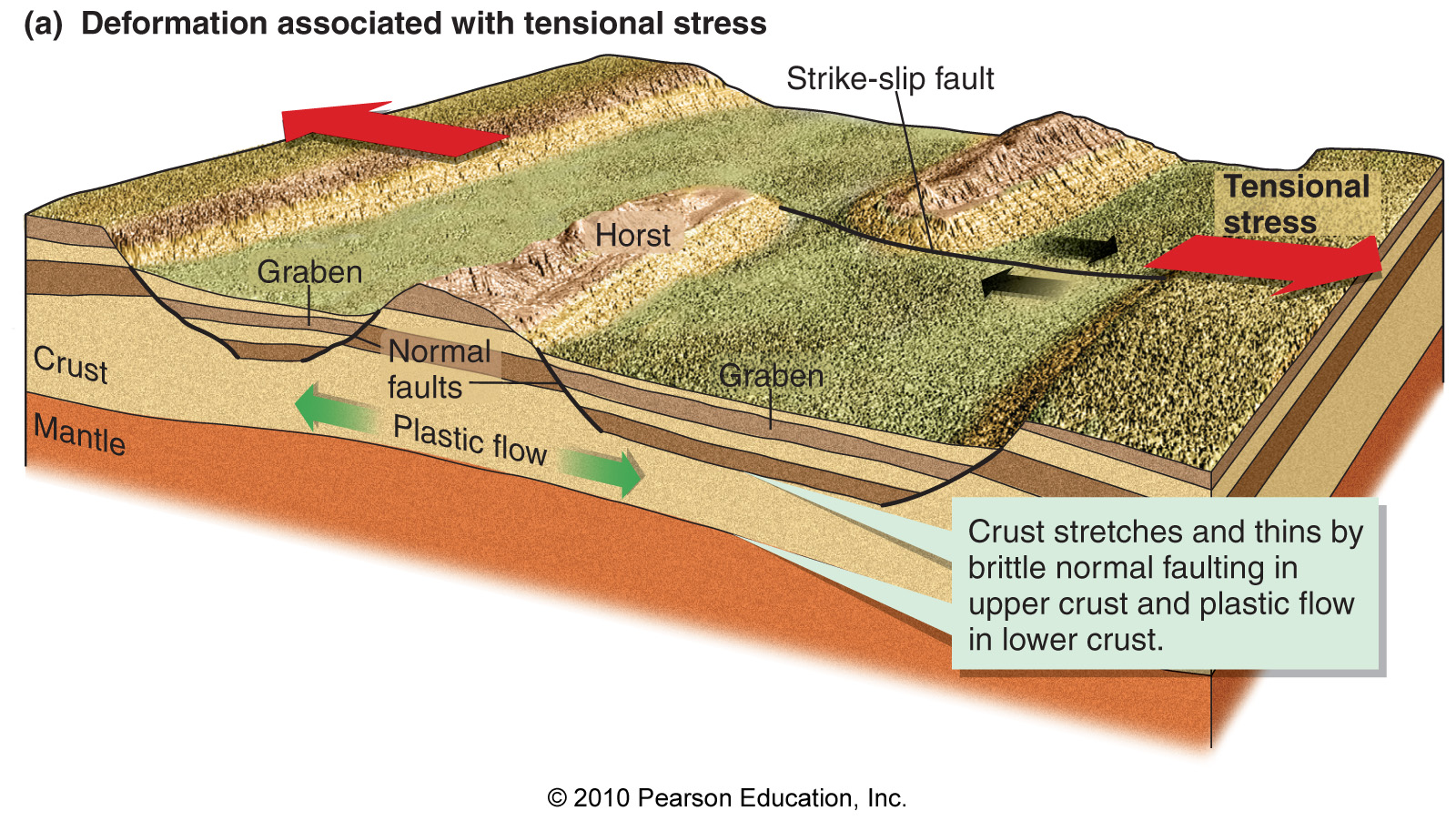
Which of the following statements best describes topographically high-standing mountainous areas?
They are generally underlain by greater-than-average thicknesses of lower-density crustal rocks.
They experience rapid erosion that thins the crust and causes the area to subside.
They subside rapidly to compensate for erosion.
They have thicker, higher-density mantle rocks beneath them at shallow depths.
They are generally underlain by greater-than-average thicknesses of lower-density crustal rocks.
What happens to create an accretionary wedge?
The edge of the overriding plate faces a subduction zone.
The base of a passive continental margin meets the seafloor.
Oceanic plate volcanoes are fed by long-lived hot spots in the mantle.
An oceanic plate moves along a transform fault.
The edge of the overriding plate faces a subduction zone.
What term describes the zone where two continents collide, often preserving slivers of oceanic lithosphere between the colliding plates?
Terrane
Ophiolite
Passive margin
Suture
Suture
What types of materials are characteristic of volcanism along a continental arc?
Rhyolitic pyroclastic materials and lavas
All of the listed options
Andesitic lavas and pyroclastic materials
Basaltic lava flows
Andesitic lavas and pyroclastic materials
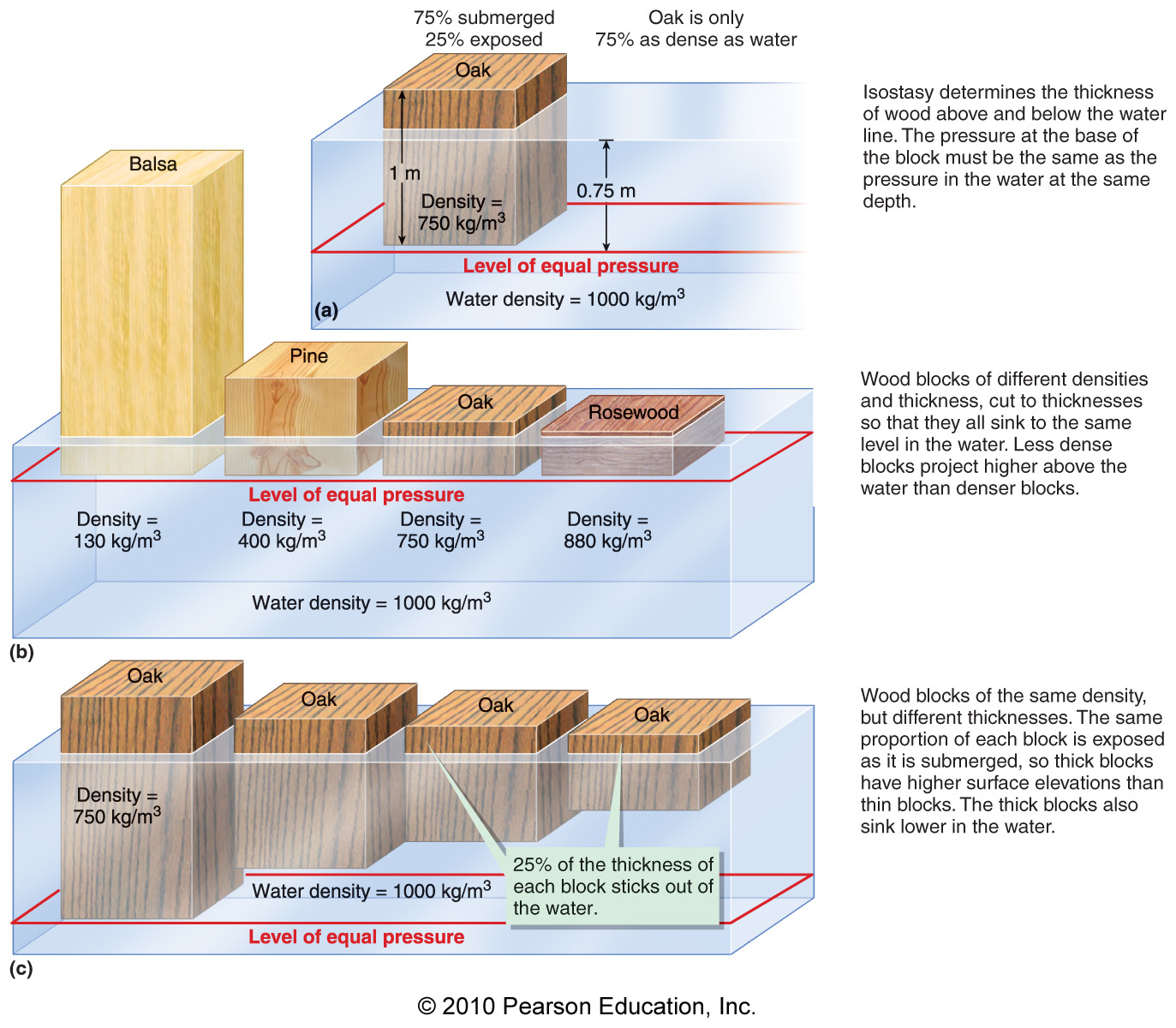
What concept shows that rocks of the crust and upper mantle are floating in gravitational balance?
Isotropy
Ecstasy
Isometrics
Isostasy
Isostasy
Which of the following is not a feature found in subduction zones?
Suture zones
Deep-ocean trenches
Forearc basins
Volcanic arcs
Suture zones
What is the name of a thick accumulation of sediments and small, tectonic blocks formed of material scraped off a descending lithospheric plate?
Subterranean-accumulation complex
Mass-movement complex
Continental shelf terrain complex
Accretionary-wedge complex
Accretionary-wedge complex
Which of the following forces create backarc regions?
Compression
Extension
Shearing
Uplift
Extension
What type of basin is characterized by thick sequences of relatively undeformed sedimentary rocks?
Transform fault
Evaporite
Backarc
Forearc
Forearc