unit 5 peds respiratory
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
When preparing the room for an infant with bronchiolitis, which equipment is most important?
oxygen tubing and facemask due to the high demand for supplemental oxygen (airway)
____ is an acute inflammatory process in the bronchioles and small bronchi. The treatment is supportive oxygen therapy, suctioning, and hydration.
Bronchiolitis
A child is brought to the emergency department by his parents because he suddenly developed a barking cough. Further assessment leads the nurse to suspect that the child is experiencing croup. What would the nurse have most likely assessed?
Inspiratory stridor
A child with croup typically develops a _____ This may be accompanied by inspiratory stridor and suprasternal retractions.
bark-like cough often at night.
A high fever, dysphagia, and toxic appearance are associated with ____.
epiglottitis
What is a definitive test for cystic fibrosis?
sweat chloride
How is a sweat chloride test performed to diagnose cystic fibrosis?
by stimulating a small patch of sweat glands on the inner aspect of the forearm
The caregivers of an 8-year-old bring their child to the pediatrician and report that the child has not had breathing problems before, but since taking up lacrosse the child has been coughing and wheezing at the end of every practice and game. Their friend's child has often been hospitalized for asthma; they are concerned that their child has a similar illness. The nurse knows that because the problems seem to be directly related to exercise, it is likely that the child will be able to be treated with:
a bronchodilator (opens airway) and mast cell stabilizers (decrease wheezing & exercise induced asthma)
____ are anti-inflammatory drugs used to control severe or chronic cases of asthma.
Systemic corticosteroids
_____ are given by mouth along with other asthma medications for long-term control and prevention of mild, persistent asthma.
Leukotriene inhibitors
A hospitalized toddler being treated for pneumonia requires supplemental oxygen. The respiratory rate is 44 breaths/min and the oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Which oxygen delivery device would be best for this toddler?
nasal cannula (delivers up to 4L) since it is the most comfortable and the most likely to stay in place.
Symptoms of ____ include runny nose, cough, and sneezing attacks that occur slowly over a few days.
bronchiolitis
A child requires supplemental oxygen therapy at 8 liters per minute. Which delivery device would the nurse most likely expect to be used?
A simple mask would be used to deliver a flow rate of 8 liters per minute.
A child’s parent asks the nurse how likely it is the child will develop asthma because the child's father has asthma. Which response by the nurse is appropriate?
“Immune responses can be genetic and run in the family.”
A young child is prescribed pancreatic enzymes as part of the treatment plan for cystic fibrosis. The child has difficulty swallowing medications. After teaching the parents of a young child with cystic fibrosis about how to administer pancreatic enzymes, the parents demonstrate understanding by stating:
"We can open the capsule and sprinkle it on his cereal or applesauce,"
The nurse is trying to pick a method to teach a 4-year-old with cystic fibrosis a good way to exercise her lungs. Which would be the developmentally correct strategy to help this client?
Teach the client to blow bubbles, a horn, or a pinwheel to exercise the lungs— it is age-appropriate for early childhood,
When performing the physical examination of a child with cystic fibrosis, what would the nurse expect to assess?
decreased tactile fremitus
A 2-year-old toddler is seen for acute laryngotracheobronchitis. What observation would lead the nurse to suspect airway occlusion?
The respiratory rate is gradually increasing.
Acute laryngotracheobronchitis is also know as ____. It produces edema of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
croup (barking cough/seal cough)
An increasing respiratory rate, retractions, and nasal flaring are signs of ?
major respiratory distress and occlusion.
The nurse is caring for a 10-year-old girl with cystic fibrosis who receives pancreatic enzymes. Which comment by a parent demonstrates understanding of the instructions regarding the medication?
"I should give the enzymes before each meal or snack."
Which measure would be most effective in aiding bronchodilation in a child with laryngotracheobronchitis?
Assisting with racemic epinephrine nebulizer therapy
One form of treatment for laryngotracheobronchitis is the use of nebulized racemic epinephrine. Racemic epinephrine is an alpha adrenergic agent. It works on the mucosal vasoconstriction to reduce the edema. What is the therapeutic use of this agent?
it increases the lumen of airways, allowing for better intake of air
After assessing a 6-year-old child, the nurse suspects that the child is experiencing respiratory distress due to swelling of the epiglottis and surrounding structures. Which assessment finding would help support the nurse’s suspicion? Select all that apply.
use of the tripod position
excessive drooling
muffled voice
Accessory muscle use would be more commonly associated with what respiratory condition?
asthma
A 4-year-old with bronchiolitis has been admitted to the hospital with respiratory compromise. The father asks the nurse why the physician won't prescribe an antibiotic, "My child just keeps getting worse." What is the best response by the nurse?
"Bronchiolitis is almost always caused by the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Unfortunately, antibiotics don't work on viruses."
A 6-month-old infant who was born premature is being seen for a follow-up examination. The child is to receive an intramuscular injection monthly through the winter and spring season. Which drug would the nurse expect to be ordered?
Palivizumab (SYNAGIS)
Palivizumab is a monoclonal antibody used for prevention of serious lower ____; it often occurs most often in infants and toddlers, with a peak incidence around 6 months of age. Infants born prematurely are more at risk. The peak occurrence of bronchiolitis is in the winter and spring.
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease
A 9-year-old female child was brought to the emergency department after experiencing wheezing and shortness of breath while playing soccer. Vital signs upon arrival at the emergency room: temperature, 98.8°F (37.1°C); heart rate, 125 beats/min; blood pressure, 88/50 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 32 breaths/min; oxygen saturation, 92% on a simple face mask. The child appears anxious. What are the nurse’s priority interventions?
The nurse should assess the child's airway first.
Intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone should be administered promptly to decrease inflammation in the lungs, which will improve air flow
Metered-dose inhalers would not be used in status asthmaticus. (true/false)
true; MDI inhalers are for long-term control of symptoms (LABA)
After teaching the parents of an 8-year-old girl with asthma about common allergens their child should avoid, the nurse determines that the parents need additional teaching when they identify what as a common allergen for asthma?
shellfish
___, ___, and ____ are common asthma triggers.
Indoor molds, pet dander, and dust mites
The nurse is speaking with a client with cystic fibrosis. The client's partner has tested negative for carrying the cystic fibrosis mutation. The client asks if they were to have children, how many would potentially have cystic fibrosis. What is the best response by the nurse?
"If your partner does not have the cystic fibrosis gene mutation, none of your children will have the disease."
For a person to have cystic fibrosis, the person must inherit two copies of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene that contains the mutation. (true/false)
true; cystic fibrosis is genetic
The nurse is examining an 8-year-old boy with tachycardia and tachypnea. The nurse anticipates which test as most helpful in determining the extent of the child's hypoxia?
Pulse oximetry
The nurse is administering medications to a 10-year-old child who takes medications at home for a chronic condition. The child's parent is at the bedside. What are appropriate guidelines for medication administration to this client? Select all that apply.
The nurse compares the child's ID band with the medication record. (right patient)
The nurse carefully reads the label on the side of the medication bottle. (right drug)
The nurse documents the medication administration after giving the medication. (right documentation)
right route
right time
The student nurse is collecting data on a child diagnosed with cystic fibrosis and notes the child has a barrel chest and clubbing of the fingers. In explaining this manifestation of the disease, the staff nurse explains the cause of this symptom to be:
chronic lack of oxygen
A group of nurses is reviewing the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. With regard to the effect of this disease on the body, which parts of the body (besides the lungs) are most affected by this disease?
Pancreas and liver
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic (inherited) disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in organs, including the lungs and the pancreas. In people who have CF, thick mucus _______.
clogs the airways and makes it difficult to breathe
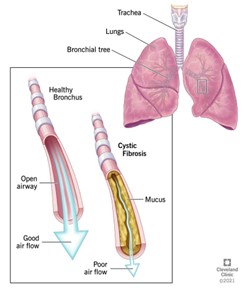
_____ is the most common lethal genetic illness of Caucasian children
cystic fibrosis
Babies and children who have CF might not be able to absorb enough nutrients from food. CF, which is chronic (long-lasting) and progressive (getting worse over time), also affects your ___, ___, ___, and ___.
liver, sinus, intestines, and sex organs.
The icky, sticky, thick mucus in CF gathers bacteria in the lungs, which leads to frequent URIs. What color mucus would indicate an infection?
green or brown
What lungs sound does the nurse anticipate in a CF patient?
crackles (due to excess mucus) so the patient will be wheezing (trying to expedite air)
What symptoms occur with a chronic respiratory condition (CF)?
clubbed nails (hypoxia) & barrel chest (overinflation/emphysema)
People with cystic fibrosis have nutritional needs that aren’t the same as the needs of people without CF. People with CF may need 1.5 to 2 times the number of calories as people without CF. What types of food would the nurse include in this patient’s diet?
high calorie, high protein, salty & fatty foods
A CF will be deficient in fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK). Low vitamin K increases a patient’s risk for?
bleeding (anemia)
A CF patient deficient in the fat-soluble vitamin D increases their risk for?
osteoporosis
What complications can occur in CF?
hemoptysis (blood in cough)
pneumothorax
respiratory failure
Hemoptysis is a common complication, almost expected. What orders does the nurse expect the physician to order?
Assess how much blood the child is coughing up throughout the shift. Administer vitamin K if blood is more than 5-10 mL per hemoptysis.
If a child is coughing up hemoptysis that is 60 mL, what interventions does the nurse need to HOLD?
Hold chest PT (physiotherapy) because it will make them cough up more blood.
What nursing intervention can the nurse do that patient’s parents do at home to help to cough up secretions?
chest PT (cupping the front of back to move secretions out of the body)
What treatment is done before chest physiotherapy?
administer aerosol first to move mucus/secretions more effectively
What are examples of pancreatic enzymes that are given to CF patients?
Pancrease, Creon, Ultrase
People with CF lose a lot of salt in their sweat. Although there’s not a set standard, healthcare providers generally tell people with CF to eat salty foods. This is true especially during hot, humid weather and exercise. The nurse can recommend what during meals/snacks?
add salt as desired because they have hypoalbuminea
____ is used to decrease viscosity of the mucus, thin out secretions in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Pulmozyme
Pulmozyme (DNase) is a genetically engineered enzyme given by aerosol that does what?
alters the mucus in the airways; This is given before performing chest PT.
A child has just finished eating a hot dog. The child begins to cough but it progressively starts to gag. The coughing stops so you suspected the child is now choking. What other findings would the nurse assess to confirm this findings?
the child is turning blue and is wheezing with visible sternal retractions
How does the nurse perform Heimlich maneuver on a child that is 1 year and under?
back blows on the child
First-time parents are getting ready to feed their child. The child has been breathing faster than normal (60-88). What is the nurse’s priority patient education?
Parent must call nurse first prior to feedings since the child is at high risk for aspiration.
Infants must be how old to qualify for the synagis vaccine (RSV prevention)?
at least 32 weeks unless they have a CLD then its given early
What physical findings would be indicative that the patient has frequent allergies?
crease on nose
Crying is more likely to cause the airways to swell and close off for which diagnosis?
epiglottitis
Why is stridor a medical emergency?
stridor is caused by the narrowing of the airway, which is indicative of an obstruction that can lead to respiratory failure/distress
Bronchiolitis is what type of infection?
viral so it cannot be treated with antibiotics meaning it has to run its course and treat the symptoms
What respiratory virus causes bronchiolitis in 80% of cases?
RSV most commonly does but adenoviruses/parainfluenza viruses (common cold) can cause it too
_____ increases mucus and edema in the bronchioles. This causes narrowing, which makes breathing difficult.
Bronchiolitis
Since RSV causes bronchiolitis, what type of precautions/isolation does the nurse need to implement for this patient?
droplet (bc of respiratory secretions) and contact (gloves)
_____ is given to prevent RSV (which is what causes bronchiolitis), and it is given IM in the vastus lateralis.
Synagis
A mother calls the clinic and states her child has shown signs and symptoms of a cold/flu. The mother is worried because the child has been coughing and wheezing with “grunting noises” in the past 30 minutes. What does the nurse suggest this mother to do?
seek medical attention (ER)
A cold/flue has to run its course so it can be treated at home. The nurse educates the parent to receive medical attention by HCP when the child does what?
when the child is showing signs of breathing problems such as nostrils flaring, retractions, and rapid breathing >60 bpm as well as signs of dehydration.
What is important patient education to a parent taking care of a child at home with cold like symptoms?
to encourage fluids because the child is at high risk for dehydration (children goes down fast)
A child experiencing _____ will need IV fluids and not PO feedings because they will not be able to eat and breathe at the same time.
more than 60 bpm
What lung assessment (or respiratory) findings will a nurse find in a patient with bronchiolitis?
the child will have crackles due to excess secretions, wheezing or diminished lung sounds
A nurse assess a child and the parent states “the baby cried early with no tears and has not had any wet diapers since last night” The nurse notices the child’s oral mucosa and it is extremely dry. What nursing intervention is needed?
IV fluids if respirations are abnormal or PO fluids if RR is normal
If a nurse is preparing to feed a child less than 1 year old that has bronchiolitis (bc they are usually the ones that get this), they must ________. These patients are at an increased risk for choking/aspiration since they will have high respirations due to RSV.
suction the child before feeding via bottle.
The parents need to note respirations and call the nurse to come in to verify respirations if high before feeding. The nurse explains to the parents that the baby can choke and aspirate while high RR and feedings. What can the nurse recommend the parents do instead?
non-nutritive pacifier to soothe child
Even though synagis is an immunization used to prevent RSV, the nurse must educate the parent that:
Children treated with this medicine may still get RSV but will not get as sick as if they were not treated at all. It is also given 1 month before and end of RSV season (monthly).
Who Qualifies to receive the synagis vaccine?
Less than 2 years with chronic lung disease (CLD) who have received medical therapy for CLD within 6 months before RSV season
32 weeks or earlier w/o CLD
Severe immunodeficiencies- lack of immune system
A patient receiving supplemental oxygen via a nasal cannula has an O2 sat of 90%. The patient is already on 6L of oxygen. What does the nurse do?
the nurse must change the oxygen delivery method by switching to a simple face mask bc it can go up to 10L, then NOTIFY HCP of change
When is a non-rebreather used and how is it used?
when a child has a chronic lung disease such as cystic fibrosis; the bag always need to be inflated
Croup is what kind of infection?
viral (due to parainfluenza, influenza, RSV, measles, and adenovirus)
Croup is a general term used to describe a group of symptoms described by a ____, ____, and _____.
barky or brassy cough, degrees of inspiratory stridor and varying.
The condition causes swelling of the child’s voice box (larynx) and windpipe (trachea), which leads to symptoms including a distinctive barking cough and raspy breathing. The child will display a:
“seal like” cough due to the child’s airway is narrowed from the inflammation of the mucosa larynx and trachea.
The mother reports her child has had a runny nose/stuffy nose that does not go away and has been progressively getting worse. She later mentions the child went to bed with a low-grade fever and later awoken at night with a bark, brassy cough. What does the nurse suspect?
a viral infection called croup (ACUTE LARYNGOTRACHEOBRONCHITIS); the fever needs to be treated with antipyretics
When a child has acute spasmodic croup (mild croup that happens abruptly or suddnely), how can this be treated at home?
o Parents are taught the signs of respiratory distress.
o Patient education: Stridor (labored breathing) is indicative that the child needs medical attention ASAP.
o Parents need to provide humidified air/cool mist .
o Vaporizer nebulized mist.
o Supplemental oxygen (as ordered)
A child has developed stridor after several days of having a barky, seal-like cough with rhinitis. What does the nurse suspect and how is it going to be treated?
LTB(Laryngotracheobronchitis) since it slowly progressed; Racemic (or nebulized) epinephrine treatment for longer croup
What patient teaching does the nurse need to give to parent who has child with croup?
Avoid enforcing discipline and making the child cry because it can further cause narrowing of the airway.
Educate parent to decrease anxiety so the child can feed off of positive, calm energy instead on negative, anxious energy.
Decrease environmental stimulation, including taking vital signs such as BP.
What are the side effects of the medication Racemic (or nebulized) epinephrine (treatment for longer croup)?
increased heart rate and increased agitation since it speeds things up
What medications are part of the treatment plan for child with croup?
racemic (if stridor or difficulty breathing is present)
corticosteroids to decrease inflammation
albuterol
antibiotics if it is caused from a bacteria infection
intubation may be needed to have an airway- Last resort.
Acute croup can be treated with_____.
cool mist air
Epiglottitis is caused by what type of infection and how is it treated?
bacterial ( Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcal); antibiotics
The epiglottis is a thin flap of cartilage near the base of your tongue. It keeps food and liquids from going down your windpipe (trachea) when you swallow. Epiglottitis symptoms include pain when swallowing, severe sore throat and difficulty breathing. Epiglottitis is a _____.
medical emergency.
What can prevent an epiglottitis bacterial infection?
immunization such as the HIB vaccine that is given at 2 months of age
What are the predictive symptoms that a child is developing epiglottitis and needs medical attention immediately?
absence of spontaneous cough (child is sicker than he actually looks)
presence of drooling (excess saliva)
agitation (resp. distress)
If epiglottitis is suspected, the nurse should not attempt to visualize the throat directly or try to obtain a throat culture but instead:
report to HCP or refer the child for medical evaluation immediately because examination of the throat with a tongue depressor is contraindicated since it can completely close off the airway
The nurse is doing her hourly rounds during her 12-hour shift. What patient does the nurse need to see first?
a patient that is in his room that is sitting upright and lean forward with the chin thrust, mouth open, and protruding tongue (tripod position)
What nursing interventions are key when a nurse has a patient with epiglottis?
Keep Calm
Keep patient Close to nurse’s station
Noninvasive interventions are applying oxygen such as nasal cannula and is done when the patient is not in an emergency. (supplemental oxygen)
Intubation equipment must be readily available.
X-ray is needed to diagnose if epiglottitis is suspected.
Throat inspection should only be attempted by experienced personnel when:
emergency equipment is available to proceed with immediate intubation or tracheostomy.
What are the 4 Ds of epiglottitis?
Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing.
Dysphonia: Hoarseness or an abnormal voice(muffled)
Drooling: When saliva flows out of your mouth involuntarily.
Distress: Difficulty breathing or lack of oxygen.
A child develops epiglottis due to pneumonia. What medications does the nurse anticipate the HCP ordering?
IV antibiotics such Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, or Cephalosporins for 3 days then PO along with corticosteroids to reduce swelling in the airways